How does the greenhouse effect work
How does the greenhouse effect work
Why the Greenhouse Effect Is Important: How It Works and Causes Global Warming
Oct. 21 2019, Updated 4:51 p.m. ET
The more I research the climate crisis as an adult, the more I wish I had paid better attention in science class as a child. Case in point: My teachers definitely taught me about the greenhouse effect, but I don’t remember what we learned at all. (I mostly just remember making dioramas out of shoeboxes.)
Back then, I had no idea just how important the science we were learning about the environment really was — not only in terms of my grades (don’t worry, I still did well in science class thanks to those dioramas), but also in terms of the future of humanity. Luckily, I’ve since woken up to that fact and started paying attention to science — and I’ve learned that one of the most important concepts to understand in this fight to protect the climate is the greenhouse effect.
Read on for all the basics you need to know about the greenhouse effect, how it causes global warming, and what we can do to reduce our impact in terms of emitting greenhouse gases.
How Does the Greenhouse Effect Work?
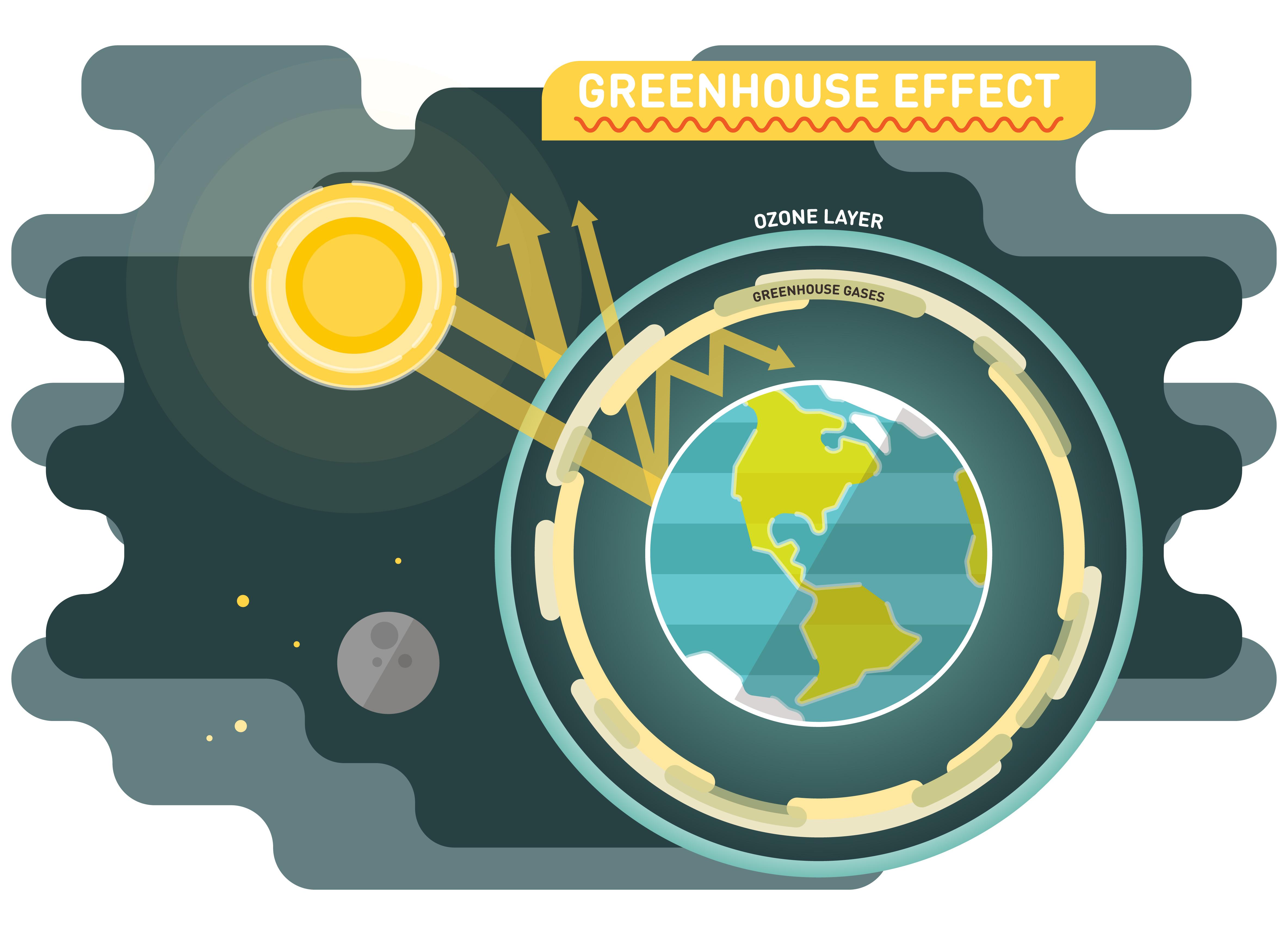
The greenhouse effect is the natural process of the sun warming the Earth’s surface. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere (primarily carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and water vapor) trap the sun’s heat and cause the global temperature to rise, otherwise known as global warming.
Why Is It Called the Greenhouse Effect?
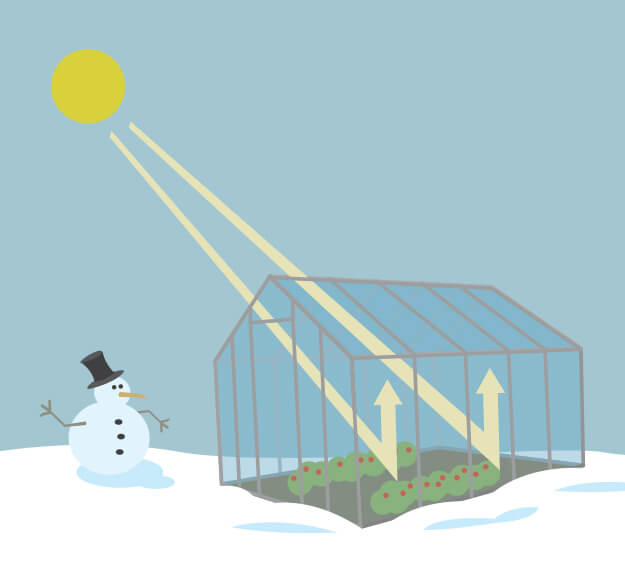
This process is called the greenhouse effect because it echoes what happens in a greenhouse used to grow plants in the winter. The sun enters the greenhouse during the day, and the glass walls trap the sun’s heat, which warms up the air inside the greenhouse, even keeping the greenhouse warm overnight when the sun is down and outside temperatures are low.
Why Is the Greenhouse Effect Important?
The greenhouse effect is the reason our global temperature is rising — and global warming is a significant part of the climate crisis. The more greenhouse gases we emit, the more heat we trap in the atmosphere, the more the globe warms up. As global temperatures rise, we witness changes in ecosystems all over the Earth. For example, ice caps are melting, sea levels are rising, and oceans are warming — all of these changes affect animal habitats and put various species at risk of becoming endangered or extinct.
Why Is the Greenhouse Effect Harmful?
As you can gather from the above information, the greenhouse effect is harmful to so many different ecosystems on our planet. As humans continue doing activities that put greenhouse gases into the atmosphere — such as burning fossil fuels, producing trash, and raising livestock — the greenhouse effect continues to make our Earth a little less inhabitable for us.
What Greenhouse Gases Are Produced by Humans?
According to the U.S. Congress’ ACS, the greenhouse gases in our atmosphere that occur both naturally and due to human activity include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and water vapor. Then, there are the fluorinated gases (such as chlorofluorocarbons or CFCs), which are greenhouse gases that do not occur naturally and are only caused by human activity, as per ACS.
Greenhouse gases do occur on their own from a few natural processes on Earth that we cannot help — for example, natural matter decaying and respiration. But if those were the only things causing greenhouse gases to enter our atmosphere, we wouldn’t be in a climate crisis.
That said, most greenhouse gas emissions come from human activities — and the sharp increase in these activities is what has gotten us into the climate emergency we are currently in. The activities we do that are responsible for the most significant greenhouse gas emissions include burning fossil fuels, animal agriculture (which is responsible for at least 14.5 percent of human-caused greenhouse gas emissions, according to the New York Times), clearing land for agriculture, and more, as per the EPA.
Which Greenhouse Gas Is the Worst?
According to the IPCC via the EPA, in 2014, the global breakdown of greenhouse gas emissions was as follows: carbon dioxide from fossil fuels, 65 percent; carbon dioxide from forestry and agriculture, 11 percent; methane, 16 percent; nitrous oxide, 6 percent; fluorinated gases, 2 percent.
While methane is notably a smaller percentage than carbon dioxide, methane is still of immense concern because it is more potent than CO2 — according to a study published on ScienceDaily, methane is actually about 30 times more potent at trapping heat in the atmosphere than CO2 is.
How Does Earth’s Greenhouse Effect Work?
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect.
The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear. French mathematician Joseph Fourier is sometimes given credit as the first person to coin the term greenhouse effect based on his conclusion in 1824 that Earth’s atmosphere functioned similarly to a “hotbox”—that is, a heliothermometer (an insulated wooden box whose lid was made of transparent glass) developed by Swiss physicist Horace Bénédict de Saussure, which prevented cool air from mixing with warm air. Fourier, however, neither used the term greenhouse effect nor credited atmospheric gases with keeping Earth warm. Swedish physicist and physical chemist Svante Arrhenius is credited with the origins of the term in 1896, with the publication of the first plausible climate model that explained how gases in Earth’s atmosphere trap heat. Arrhenius first refers to this “hot-house theory” of the atmosphere—which would be known later as the greenhouse effect—in his work Worlds in the Making (1903).
Despite its name, the greenhouse effect is different from the warming in a greenhouse.
The atmosphere allows most of the visible light from the Sun to pass through and reach Earth’s surface. As Earth’s surface is heated by sunlight, it radiates part of this energy back toward space as infrared radiation. This radiation, unlike visible light, tends to be absorbed by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, raising its temperature. The heated atmosphere in turn radiates infrared radiation back toward Earth’s surface. (Despite its name, the greenhouse effect is different from the warming in a greenhouse, where panes of glass transmit visible sunlight but hold heat inside the building by trapping warmed air.)
Without the heating caused by the greenhouse effect, Earth’s average surface temperature would be only about −18 °C (0 °F). On Venus the very high concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causes an extreme greenhouse effect resulting in surface temperatures as high as 450 °C (840 °F).
Without the heating caused by the greenhouse effect, Earth’s average surface temperature would be only about −18 °C (0 °F).
Although the greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon, it is possible that the effect could be intensified by the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere as the result of human activity. From the beginning of the Industrial Revolution through the end of the 20th century, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increased by roughly 30 percent and the amount of methane more than doubled. A number of scientists have predicted that human-related increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases could lead by the end of the 21st century to an increase in the global average temperature of 0.3 to 4.8 °C (0.5 to 8.6 °F) relative to the 1986–2005 average. This global warming could alter Earth’s climates and thereby produce new patterns and extremes of drought and rainfall and possibly disrupt food production in certain regions.
Greenhouse Effect: Advantages and Disadvantages
With the increasing buzz around climate change and global warming, the whole idea of the greenhouse effect is being increasingly discussed. While some experts illustrate how greenhouse gases are important for sustainable growth, others highlight the detrimental effect it has on the human existence. Invariably, there are both negative and positive effects of greenhouse effect. Before we jump to say if the greenhouse effect is good or bad, it will be a good idea to understand what is the greenhouse effect and what are the advantages and disadvantages of the greenhouse effect. This article will draw a comparison between the pros and cons of the greenhouse effect by delving deep into the whole phenomenon-
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
Greenhouse effect refers to a process where thermal radiation from the earth’s surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and then radiated in all directions. The main greenhouse gases include Carbon Dioxide, Methane, Nitrous Oxide and Ozone. However, the first three are more worrying when it comes to the greenhouse effect as Ozone’s detrimental role kicks in more with respect to global warming. How the greenhouse effect functions is a two way process. Firstly, being poor absorbers, these gases are unable to prevent the solar radiation that enter the earth’s surface. This in turn raises the earth’s temperature. However, these gases effectively absorb outgoing radiation and redirect it to the earth’s surface. This further adds to the earth’s temperature. This in a nutshell is the greenhouse effect. For centuries, this process has been in play to maintain the earth’s temperature. In fact, some countries which have lower temperatures artificially replicate this mechanism to construct greenhouse buildings to create pleasant temperate conditions.
So what’s the Problem?
If we say that the greenhouse effect has been in play for centuries and is in fact a necessity for human existence, then the question remains, why is it a cause for concern over the past few years. Well, the answer is not too difficult to guess. The rise in the burning of fossil fuels and an increase in the carbon footprint across the globe is leading to an excess of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This exponential increase in atmospheric CO2 is creating a temperature imbalance. The logic is simple. As the amount of CO2 is increasing so is its power to entrap solar radiation and direct it to the earth’s surface. This is contributing to an incremental rise in the earth’s temperature, which is now touching dangerous levels. Additionally, the greenhouse effect is causing rapid climate change with global warming, melting glaciers, erratic temperate conditions, etc. Thus, it is not the greenhouse effect essentially which is the cause of the problem. In fact, it is the human interference that has ruined the balance between the incoming and outgoing radiation, due to increased CO2 which is problematic.
Greenhouse Effect Advantages
To discount the contribution of the greenhouse effect by labelling it as an evil is an overstatement. As mentioned above, the greenhouse effect is an important element for sustainable living. There are several greenhouse effect benefits. Some of the top benefits of greenhouse gases are as follows-
Greenhouse effect supports and promotes life
It is no surprise that human existence and life is only possible at a certain temperature. While the earth’s atmosphere also faces variations, they are within a set limit and not too erratic. The greenhouse effect helps earth maintain a decent temperature that makes this planet habitable. The entire credit for this inhabiting temperature goes to the greenhouse gases. Owing to the presence of these greenhouse gases, the earth is warm enough. Simply because the greenhouse gases are able to entrap the solar radiation and bounce it back to the earth’s surface, is the reason the earth hasn’t frozen yet. Additionally, the greenhouse gases also ensure that we are not fried by the sun’s heat by absorbing some percentage of the radiation. Therefore, on the one hand, benefits of greenhouse gases turn to their ability to prevent the heat from escaping the earth’s surface help human life have a warm enough climate. On the other hand, their ability to bounce of a fair share of the radiation, help the human life avoid an unpleasantly hot and unbearable atmosphere. Additionally, they have been of vital importance in maintaining our planet’s water level. In the absence of greenhouse gases, the polar caps would rapidly melt, raising water levels beyond alarming marks.
Protection from Danger
Imagine a sieve that you use at home to filter milk and dispose off the impurities. Well, the greenhouse gases play the exact same role in protecting earthlings from dangerous solar radiation. They block those parts of the solar radiation which are harmful to our existence and bounce them back into the atmosphere. The greatest example is that of the UV or Ultra- Violet radiation. Ozone, which is one of the main greenhouse gases, acts as a shield against the UV rays entering the earth. In the absence of the ozone layer, there will be no resistance to the UV rays and they would reach us directly. They carry immense potential to harm the earth’s surface and its inhabitants.
Benefits of Greenhouse Gases for Photosynthesis
Greenhouse Effect Disadvantages
It is true that the greenhouse effect is a boon to maintaining the earth’s habitable temperature and has multiple other benefits. However, it comes with a few disadvantages as well-
Global Warming
While the greenhouse effect maintain the temperature, its increase directly translates to rising temperatures. As the volume of greenhouse gases is increasing with more burning of fossil fuels, etc, its is contributing to an increase in the planet’s average temperature and climate. In fact, the past few years have seen much warmer summers in comparison to the decadal average trend. As the gases increase, their ability and power to trap the heat and radiate it back to the earth also increases. This invariably increases the earth’s temperature.
Increasing Water Levels
Next in line comes the increase in water levels above the safe marks. The logic is quite simple. As the average temperature of the earth is steadily increasing, the polar ice caps are rapidly undergoing a melt down. This is resulting in massive rise in water levels, well beyond the safe levels. This rapid increase in the ocean water levels can invariably lead to flooding of low lying areas and demand evacuation. The increase in water levels will accentuate displacement and cost human lives along with destruction of flora and fauna. Additionally, the existence on the polar caps of penguins and polar bears is under deep threat,
Destruction of Marine Life
It is a well known fact that oceans absorb CO2 and maintain the alkalinity. However, the rate at which carbon dioxide is increasing is bad for marine life. As more and more carbon dioxide gets absorbed by the oceans, their alkalinity levels will touch dangerous marks. This is increasingly posing a serious threat to the marine life that stands at a danger of extinction if the rise in alkalinity continues.
Why is Greenhouse Effect a Concern for Students
The pros and cons of greenhouse effect is one of the most popular topics given to students for assignment and essay writing. Most students wonder the reason behind the same. Academic institutions have two reasons for encouraging students to work on this topic. Firstly, being topical in nature, it is important for students to be aware about what is happening at the environmental level. They need to be aware about how the greenhouse effect works and its impact. The logic is simple, to be update to date about the current happenings. Secondly, assignments on advantages and disadvantages of greenhouse effect can sensitize students about the need of the hour and help them realize how small steps they take can go a long way to preventing the increase in the greenhouse effect.
If you have recently been given an assignment on the advantages and disadvantages of greenhouse effect and wish to get grades in it, consider getting help from experts at TutorBin. The panel of global subject matter experts can help you submit well written and informative assignments and essays on the pros and cons of greenhouse effect and other science topics too.
The Greenhouse Effect
Energy from the Sun that makes its way to Earth can have trouble finding its way back out to space. The greenhouse effect causes some of this energy to be waylaid in the atmosphere, absorbed and released by greenhouse gases.
Without the greenhouse effect, Earth’s temperature would be below freezing. It is, in part, a natural process. However, Earth’s greenhouse effect is getting stronger as we add greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. That is warming the climate of our planet.
How Does the Greenhouse Effect Work?
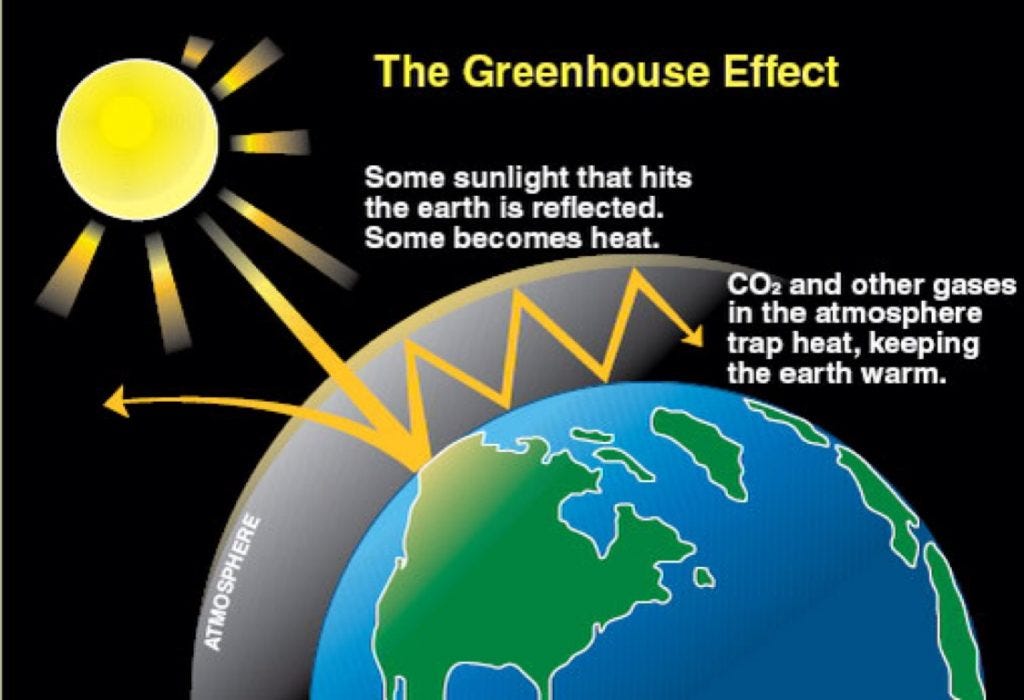
Solar energy absorbed at Earth’s surface is radiated back into the atmosphere as heat. As the heat makes its way through the atmosphere and back out to space, greenhouse gases absorb much of it. Why do greenhouse gases absorb heat? Greenhouse gases are more complex than other gas molecules in the atmosphere, with a structure that can absorb heat. They radiate the heat back to the Earth’s surface, to another greenhouse gas molecule, or out to space.
There are several different types of greenhouse gases. The major ones are carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and nitrous oxide. These gas molecules all are made of three or more atoms. The atoms are held together loosely enough that they vibrate when they absorb heat. Eventually, the vibrating molecules release the radiation, which will likely be absorbed by another greenhouse gas molecule. This process keeps heat near the Earth’s surface. Most of the gas in the atmosphere is nitrogen and oxygen, which cannot absorb heat and contribute to the greenhouse effect.
A Couple of Common Greenhouse Gases
Above: (Left) The Earth’s surface, warmed by the Sun, radiates heat into the atmosphere. Some heat is absorbed by greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and then radiated to space (A). Some heat makes its way to space directly (B). Some heat is absorbed by greenhouse gases and then radiated back towards the Earth’s surface (C). (Right) With more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere later this Century, more heat will be stopped by greenhouse gases, warming the planet. (Image: L.S.Gardiner/UCAR)
More Greenhouse Gases = A Warmer Earth
Even though only a tiny amount of the gases in Earth’s atmosphere are greenhouse gases, they have a huge effect on climate. Sometime during this century, the amount of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is expected to double. Other greenhouse gases like methane and nitrous oxide are increasing as well. The quantity of greenhouse gases is increasing as fossil fuels are burned, releasing the gases and other air pollutants into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases also make their way to the atmosphere from other sources. Farm animals, for example, release methane gas as they digest food. As cement is made from limestone, it releases carbon dioxide.
With more greenhouse gases in the air, heat passing through on its way out of the atmosphere is more likely to be stopped. The added greenhouse gases absorb the heat. They then radiate this heat. Some of the heat will head away from the Earth, some of it will be absorbed by another greenhouse gas molecule, and some of it will wind up back at the planet’s surface again. With more greenhouse gases, heat will stick around, warming the planet.
What Is the Greenhouse Effect?
Watch this video to learn about the greenhouse effect!
How does the greenhouse effect work?
As you might expect from the name, the greenhouse effect works … like a greenhouse! A greenhouse is a building with glass walls and a glass roof. Greenhouses are used to grow plants, such as tomatoes and tropical flowers.
A greenhouse stays warm inside, even during the winter. In the daytime, sunlight shines into the greenhouse and warms the plants and air inside. At nighttime, it’s colder outside, but the greenhouse stays pretty warm inside. That’s because the glass walls of the greenhouse trap the Sun’s heat.
A greenhouse captures heat from the Sun during the day. Its glass walls trap the Sun’s heat, which keeps plants inside the greenhouse warm — even on cold nights. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth. Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases.
During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere. Earth’s surface warms up in the sunlight. At night, Earth’s surface cools, releasing heat back into the air. But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. That’s what keeps our Earth a warm and cozy 58 degrees Fahrenheit (14 degrees Celsius), on average.
Earth’s atmosphere traps some of the Sun’s heat, preventing it from escaping back into space at night. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
How are humans impacting the greenhouse effect?
Human activities are changing Earth’s natural greenhouse effect. Burning fossil fuels like coal and oil puts more carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
NASA has observed increases in the amount of carbon dioxide and some other greenhouse gases in our atmosphere. Too much of these greenhouse gases can cause Earth’s atmosphere to trap more and more heat. This causes Earth to warm up.
What reduces the greenhouse effect on Earth?
Just like a glass greenhouse, Earth’s greenhouse is also full of plants! Plants can help to balance the greenhouse effect on Earth. All plants — from giant trees to tiny phytoplankton in the ocean — take in carbon dioxide and give off oxygen.
The ocean also absorbs a lot of excess carbon dioxide in the air. Unfortunately, the increased carbon dioxide in the ocean changes the water, making it more acidic. This is called ocean acidification.
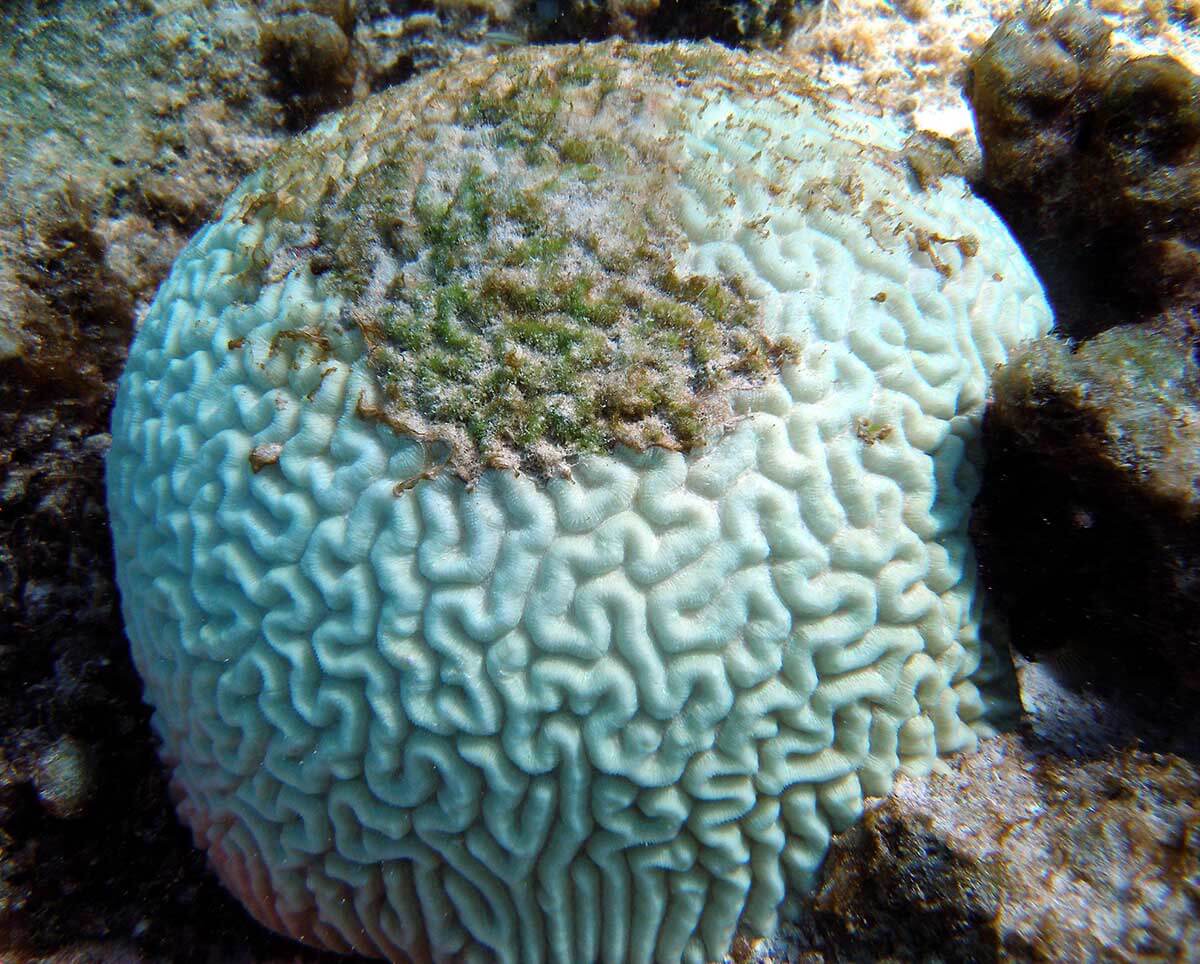
More acidic water can be harmful to many ocean creatures, such as certain shellfish and coral. Warming oceans — from too many greenhouse gases in the atmosphere — can also be harmful to these organisms. Warmer waters are a main cause of coral bleaching.
This photograph shows a bleached brain coral. A main cause of coral bleaching is warming oceans. Ocean acidification also stresses coral reef communities. Credit: NOAA