How does virtualization help with disaster recovery within a data center
How does virtualization help with disaster recovery within a data center
Data Center Disaster Recovery: A Complete Guide
Data center disaster recovery can be considered a success if your organization manages to easily recover and rapidly resume operations without causing major disruption to your business. Creating a comprehensive data center disaster recovery plan can help you mitigate potential risks and threats, prepare for possible disasters, and minimize their impact on business performance and productivity.
An effective data center disaster recovery plan generally includes the following steps:
Unlike other disaster recovery plans, the data center disaster recovery plan focuses solely on how to recover your data center facility and restore critical data and IT infrastructure to normal operating mode after a disaster.
Today’s blog post intends to answer the following question: how does virtualization help with disaster recovery within a data center? Moreover, you will learn about Site Recovery functionality as well as what data center disaster recovery best practices it can provide you with.
What Is a Data Center?
A data center is a physical facility used for housing computer systems and infrastructure components, conducting business operations, and storing critical data and applications. Data center infrastructure generally includes routers, switches, security devices, storage systems, servers, application delivery controller, etc. Each of these components needs to be securely protected in order to ensure the high availability of data centers and continuous performance of critical operations.
Why Do You Need Data Center Disaster Recovery?
In order to stay competitive in their respective markets, organizations need to provide on-demand services to their customers and minimize the risk of data loss. This explains the increase in demand for virtualization technology because business owners are interested in simplifying data center management, optimizing resource utilization, cutting costs, and ensuring on-demand scalability and flexibility.
As a result, data center facilities have dramatically transformed in the last decade. Traditional on-premises data centers have in many cases been replaced with large-scale virtual environments. However, data centers are still extremely fragile and can be exposed to various dangers and threats such as security breach, data theft, ransomware attacks, viruses and worms, etc.
Modern data centers are constantly evolving and their capabilities are growing exponentially. The same goes for attacks on these centers, as they become ever more sophisticated and hard to predict and avoid. Thus, it is critical that you prepare for potential disasters in advance and stay aware of their possible consequences.
In order to ensure reliable data protection and efficient system recovery, a responsible business owner needs to consider which data center disaster recovery strategies work best for their particular data center facility. On the basis of the chosen DR strategies, you can create a comprehensive data center disaster recovery plan which can guide you through the entire DR process.
How Does Virtualization Help With Disaster Recovery Within a Data Center?
As mentioned above, traditional on-premises data centers are now being replaced with virtualization platforms on mass scale. The main reason for this is the multiple benefits that virtualization can provide you with, no matter the size of the organization or amount of expected workload. Let’s discuss how virtualization can help with data center disaster recovery in detail below.
Improving resource utilization
Traditional data centers are highly dependent on physical servers, with each being dedicated to conducting a specific operation or running a single application. Due to this, most hardware resources are left unused and wasted. With virtualization, you can abstract away the underlying physical hardware and replace it with virtual hardware. Thus, you can consolidate multiple virtual machines (VMs) on top of a single physical server and effectively share computing resources among those VMs.
Eliminating compatibility issues
Traditional data centers house computer systems which run on a variety of models of servers, which may lead to hardware compatibility issues during data center disaster recovery. In such case, you need to install similar hardware on both the production center and DR site to prevent disaster recovery from failing. However, building a DR site with hardware equipment similar to that used in the primary site can be a costly option.
With virtualization, on the other hand, a VM can be easily recovered to any hardware. Physical hardware does not have to be compatible on both sites to efficiently perform data center disaster recovery. All you need is a remote location with a few physical servers which are properly set up and ready to take on the production workload, should there be any need.
Conducting successful data center disaster recovery
Virtualization makes it easier to protect your critical data and applications by creating VM backups and replicas and storing them at a remote location. Virtualization also allows you to easily move VMs from one server to another, without affecting your VM performance or data integrity. As a result, if a disaster affects your data center, you can rapidly move the production workload to a DR site and resume your operations there.
Currently, the virtualization market provides many different backup and recovery solutions which allow you to schedule backup and replication jobs, conduct failover and failback testing, and completely automate the DR process.
Non-disruptive testing
Even once you have built a DR site and designed a comprehensive DR plan, there is still a high risk of failing at data center disaster recovery. Thus, you need to conduct DR plan testing in order to verify that the data center disaster recovery plan is functional, identify any issues and inconsistencies in your DR plan, and later update it accordingly. Third-party data protection solutions allow for testing DR strategies even during working hours without affecting your production environment.
Ensuring cost-efficiency
With virtualization, organizations can reduce the expenses of purchasing and maintaining physical hardware in data centers. Due to the efficient use of available physical resources, you can build a DR site which requires less equipment, takes up less physical space, and is easy to maintain.
Moreover, virtualization can considerably reduce the data center footprint, meaning that to support DR activities, you now need a smaller number of physical servers, less networking hardware, and fewer server racks. Essentially, the smaller your data center footprint, the higher your ability to successfully recover will be during data center disaster recovery.
Minimized downtime
If a disaster strikes a traditional on-premises data center, it generally takes weeks or even months, depending on the exact nature of the damage caused, to resume operations and restore the production center to its original state. In contrast, the time spent on recovery of a virtualized data center is significantly shorter because you can easily back up critical data and applications, store them in a remote location, and rapidly fail over to a DR site, should disaster strike. Many data protection solutions can even enable you to automate the DR process from start to finish, thus reducing downtime and minimizing its impact on your productivity.
How to Create a Data Center Disaster Recovery Plan
Creating a data center disaster recovery plan is extremely important as it may affect the outcome of your disaster recovery. In order to design a comprehensive data center disaster recovery plan, you first need to conduct operational risk assessment and business impact analysis. As a result, you will be able to identify the risks that your data center is most exposed to, measure their possible impact on your productivity, and evaluate the preparedness of your infrastructure for data center disaster recovery.
Thanks to this plan, you can determine which recovery objectives are most appropriate for your business, which DR strategies work best for a specific DR scenario, and which data and applications should be considered most critical for your virtual environment and, thus, be recovered first.
Keep in mind that a data center disaster recovery plan doesn’t simply provide you with guidelines on how to respond to a disaster. A comprehensive data center disaster recovery plan should include the measures and procedures required for preventing a DR event from occurring, detecting potential threats and risks, and mitigating vulnerabilities of your data center.
In order to present such control measures, you need to periodically test your data center disaster recovery plan and check the preparedness of your data center facility for an actual DR event. This way, you will be able to identify inconsistencies in your plan and improve the DR preparedness of your data center and IT infrastructure.
Due to the growing demand for data center services, it’s no wonder that some organizations decide to choose third-party vendors for backing up their data center facilities and performing DR activities during an actual disaster.
Previously, data center disaster recovery was only in the budget of a few large enterprises because it is a challenging task which requires a substantial amount of investment and resources. However, the growth of virtualization technology has made disaster recovery affordable to organizations of any size and budget. With multiple data protection options, a rich feature set, and affordable pricing, NAKIVO Backup & Replication has become one of the most competitive players in the market.
NAKIVO Backup & Replication allows you to protect VMware, Hyper-V, and AWS EC2 environments using the following data protection options: backup, backup copy, backup to cloud, and replication. Each of them is used for specific purposes and can radically transform your approach to data protection management.
With regard to data center disaster recovery, the built-in Site Recovery functionality is definitely worthy of your attention. You can create multiple site recovery workflows by combining various actions and conditions (start or stop VMs/instances; failover or failback VMs/instances; run, stop, enable, or disable jobs; send notifications, etc.) into an automated algorithm, which can be run as soon as disaster hits your data center. Site recovery workflows can be of any level of complexity depending on your current needs and DR expectations. With the help of the workflows, you can automate and orchestrate the entire DR process, perform non-disruptive testing of DR workflows, run emergency or planned failover and failback, and simplify data center migration.
Creating a workflow is a simple five-step process which can be configured even without any technical expertise. This functionality is built into NAKIVO Backup & Replication and doesn’t require any additional licensing. Thus, you can receive a full-fledged DR solution capable of protecting and recovering your data center facility for a fraction of the price of the competition.
To find out more about this feature, read our series of blog posts on Site Recovery in NAKIVO Backup & Replication. Alternatively, you can download Free Trial and test the product in your VMware, Hyper-V, AWS EC2, or mixed environment today.
virtual disaster recovery
Virtual disaster recovery is a type of DR that typically involves replication and allows a user to fail over to virtualized workloads.
For the most efficient virtual disaster recovery, an organization should copy virtual machine (VM) workloads off-site on a regular basis. Replication can essentially make a real-time copy of VMs in a separate location, thus strengthening DR.
Virtualization provides flexibility in disaster recovery. When servers are virtualized, they are containerized into VMs, independent from the underlying hardware. Therefore, an organization does not need the same physical servers at the primary site as at its secondary disaster recovery site.
Other benefits of virtual disaster recovery include ease, efficiency and speed. Virtualized platforms typically provide high availability in the event of a failure. Virtualization helps meet recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs), as replication is done as frequently as needed, especially for critical systems. DR planning and failover testing is also simpler with virtualized workloads than with a physical setup, making disaster recovery a more attainable process for organizations that may not have the funds or resources for physical DR.
In addition, consolidating physical servers with virtualization saves money because the virtualized workloads require less power, floor space and maintenance. However, replication can get expensive, depending on how frequently it’s done.
Adding VMs is an easy task, so organizations need to watch out for VM sprawl. VMs operating without the knowledge of DR staff may fall through the cracks when it comes time for recovery. Sprawl is particularly dangerous at larger companies where communication may not be as strong as at a smaller organization with fewer employees. All organizations should have strict protocols for deploying virtual machines.
Virtual infrastructures can be complex. In a recovery situation, that complexity can be an issue, so it’s important to have a comprehensive DR plan.
A virtual disaster recovery plan has many similarities to a traditional DR plan. An organization should:
As with a traditional DR setup, you should clearly define who is involved in planning and testing, and the role of each staff member. That extends to an actual recovery event, as staff should be ready for their tasks during an unplanned incident.
The organization should review and test its virtual disaster recovery plan on a regular basis, especially after any changes have been made to the production environment. Any physical systems should also be tested. While it may be complicated to test virtual and physical systems at the same time, it’s important for the sake of business continuity.
Virtual disaster recovery, though simpler than traditional DR, should retain the same standard goals of meeting RTOs and RPOs, and ensuring a business can continue to function in the event of an unplanned incident.
The traditional disaster recovery process of duplicating a data center in another location is often expensive, complicated and time-consuming. While a physical disaster recovery process typically involves multiple steps, virtual disaster recovery can be as simple as a click of a button for failover.
Rebuilding systems in the virtual world is not necessary because they already exist in another location, thanks to replication. However, it’s important to monitor backup systems. It’s easy to «set it and forget it» in the virtual world, which is not advised and is not as much of a problem with physical systems.
This Zerto video explains some best practices for
disaster recovery in a virtual world.
Like with physical disaster recovery, the virtual disaster recovery plan should be tested. Virtual disaster recovery, however, provides testing capabilities not available in a physical setup. It is easier to do a DR test in the virtual world without affecting production systems, as virtualization enables an organization to bring up servers in an isolated network for testing. In addition, deleting and recreating DR servers is much simpler than in the physical world.
Virtual disaster recovery is possible with physical servers through physical-to-virtual backup. This process creates virtual backups of physical systems for recovery purposes.
For the most comprehensive data protection, experts advise having an offline copy of data. While virtual disaster recovery vendors provide capabilities to protect against cyberattacks such as ransomware, physical tape storage is the one true offline option that guarantees data is safe during an attack.
With ransomware now a constant threat to business, virtual disaster recovery vendors are including capabilities specific to recovering from an attack. Through point-in-time copies, an organization can roll back its data recovery to just before the attack hit.
Hyper-convergence, which combines storage, compute and virtualization, is another major trend. As a result, hyper-converged backup and recovery has taken off, with newer vendors such as Cohesity and Rubrik leading the charge. Their cloud-based hyper-converged backup and recovery systems are accessible to smaller organizations, thanks to lower cost and complexity.
These newer vendors are pushing the more established players to do more with their storage and recovery capabilities.
There are several data protection vendors that offer comprehensive virtual backup and disaster recovery. Some key players include:
Related Terms
Maximize the benefits of virtual disaster recovery
disaster recovery (DR)
Disaster recovery failover choices: Synchronous mirrors, P2V and the cloud
Cloud DR: Key choices in cloud disaster recovery
Researchers with Palo Alto Networks took the stage at Black Hat to explain how configurations and system privileges in Kubernetes.
Companies preparing to send employees to tech conferences should have a COVID-19 safety plan and prepare for the possibility that.
CCNA 3 v7.0 Modules 13 – 14 Exam Answers
1. A company uses a cloud-based payroll system. Which cloud computing technology is this company using?
browser as a service (BaaS)
infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
software as a service (SaaS)*
wireless as a service (WaaS)
2. For a data center, what is the difference in the server virtualization data traffic compared with the traditional client-server model?
Data traffic from clients will be routed to multiple virtual servers.
There are significant data exchanges between virtual servers.*
There is more data traffic flowing from virtual servers to clients.
More network control traffic is generated between virtual servers and clients.
3. Which component in a traditional infrastructure device provides Layer 2 and Layer 3 functions to create data paths within a network?
data plane
control plane*
adjacency table
forwarding information base
4. Which network traffic management technology is a basic element in SDN implementations?
OpenFlow*
OpenStack
IEEE 802.1aq
Interface to the Routing System
5. Which type of hypervisor would most likely be used in a data center?
Type 2
Type 1*
Nexus
Hadoop
Explanation: The two type of hypervisors are Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 hypervisors are usually used on enterprise servers. Enterprise servers rather than virtualized PCs are more likely to be in a data center.
6. Which is a characteristic of a Type 1 hypervisor?
installed directly on a server*
best suited for consumers and not for an enterprise environment
does not require management console software
installed on an existing operating system
Explanation: Type 1 hypervisors are installed directly on a server and are known as “bare metal” solutions giving direct access to hardware resources. They also require a management console and are best suited for enterprise environments.
7. Which two layers of the OSI model are associated with SDN network control plane functions that make forwarding decisions? (Choose two.)
Layer 1
Layer 2*
Layer 3*
Layer 4
Layer 5
Explanation: The SDN control plane uses the Layer 2 ARP table and the Layer 3 routing table to make decisions about forwarding traffic.
8. What pre-populates the FIB on Cisco devices that use CEF to process packets?
the routing table*
the adjacency table
the ARP table
the DSP
Explanation: CEF uses the FIB and adjacency table to make fast forwarding decisions without control plane processing. The adjacency table is pre-populated by the ARP table and the FIB is pre-populated by the routing table.
9. What is a function of the data plane of a network device?
sending information to the CPU for processing
building the routing table
resolving MAC addresses
forwarding traffic flows*
Explanation: Networking devices operate in two planes; the data plane and the control plane. The control plane maintains Layer 2 and Layer 3 forwarding mechanisms using the CPU. The data plane forwards traffic flows.
10. Which statement describes the concept of cloud computing?
separation of application from hardware*
separation of management plane from control plane
separation of operating system from hardware
separation of control plane from data plane
Explanation: Cloud computing is used to separate the application or service from hardware. Virtualization separates the operating system from the hardware.
11. Which cloud model provides services for a specific organization or entity?
a public cloud
a hybrid cloud
a private cloud*
a community cloud
Explanation: Private clouds are used to provide services and applications to a specific organization and may be set up within the private network of the organization or managed by an outside organization.
12. What two benefits are gained when an organization adopts cloud computing and virtualization? (Choose two.)
provides a “pay-as-you-go” model, allowing organizations to treat computing and storage expenses as a utility*
enables rapid responses to increasing data volume requirements*
distributed processing of large data sets in the size of terabytes
elimination of vulnerabilities to cyber attacks
increases the dependance on onsite IT resources
Explanation: Organizations can use virtualization to consolidate the number of required servers by running many virtual servers on a single physical server. Cloud computing allows organizations to scale their solutions as required and to pay only for the resources they require.
13. Which type of Hypervisor is implemented when a user with a laptop running the Mac OS installs a Windows virtual OS instance?
type 2*
virtual machine
type 1
bare metal
Explanation: Type 2 hypervisors, also know as hosted hypervisors, are installed on top of an existing operating system, such as Mac OS, Windows, or Linux.
14. A small company is considering moving many of its data center functions to the cloud. What are three advantages of this plan? (Choose three.)
The company only needs to pay for the amount of processing and storage capacity that it uses.*
Cloud services are billed at a fixed fee no matter how much processing and storage are used by the company.
The company does not need to be concerned about how to handle increasing data storage and processing demands with in-house data center equipment.*
The company can increase processing and storage capacity as needed and then decrease capacity when it is no longer needed.*
Single-tenant data centers can easily grow to accommodate increasing data storage requirements.
Cloud services enable the company to own and administer its own servers and storage devices.
Explanation: Cloud computing offers many advantages to the company. Since the cloud data storage and processing facilities are owned by third-parties, the company does not need to be concerned about how it will handle increasing data storage and processing demands with its own data center equipment. The company can easily increase or decrease processing power and storage capacity based on need. Also, cloud services are billed by usage, so the company does not have the costs of supporting its own expensive data center that is not always used to maximum capacity.
15. How does virtualization help with disaster recovery within a data center?
support of live migration*
guarantee of power
improvement of business practices
supply of consistent air flow
Explanation: Live migration allows moving of one virtual server to another virtual server that could be in a different location that is some distance from the original data center.
16. What technology allows users to access data anywhere and at any time?
Cloud computing*
virtualization
micromarketing
data analytics
Explanation: Cloud computing allows organizations to eliminate the need for on-site IT equipment, maintenance, and management. Cloud computing allows organizations to expand their services or capabilities while avoiding the increased costs of energy and space.
17. Which action takes place in the assurance element of the IBN model?
verification and corrective action*
configuring systems
translation of policies
integrity checks
Explanation: The assurance element of the IBN model is concerned with end-to-end verification of network-wide behavior.
18. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 3 v7.0 Modules 13 – 14 Exam Answers p18
Which data format is used to represent the data for network automation applications?
XML
YAML
HTML
JSON*
Explanation: The common data formats that are used in many applications including network automation and programmability are as follows:
JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) – In JSON, the data known as an object is one or more key/value pairs enclosed in braces < >. Keys must be strings within double quotation marks ” “. Keys and values are separated by a colon.
eXtensible Markup Language (XML) – In XML, the data is enclosed within a related set of tags data.
YAML Ain’t Markup Language (YAML) – In YAML, the data known as an object is one or more key value pairs. Key value pairs are separated by a colon without the use of quotation marks. YAML uses indentation to define its structure, without the use of brackets or commas.
19. What is the function of the key contained in most RESTful APIs?
It is the top-level object of the API query.
It is used to authenticate the requesting source.*
It represents the main query components in the API request.
It is used in the encryption of the message by an API request.
Explanation: Many RESTful APIs, including public APIs, require a key. The key is used to identify the source of the request through authentication.
20. Which two configuration management tools are developed using Ruby? (Choose two.)
Puppet*
Ansible
SaltStack
Chef*
RESTCONF
Explanation: Chef and Puppet are configuration management tools developed using Ruby. Ansible and SaltStack are configuration management tools developed using Python. Ruby is typically considered a more difficult language to learn than Python. RESTCONF is a network management protocol.
21. Which term is used to describe a set of instructions for execution by the configuration management tool Puppet?
Playbook
Cookbook
Manifest*
Pillar
Explanation: The configuration management tool Puppet uses the name Manifest to describe the set of instructions to be executed.
22. Which term is used to describe a set of instructions for execution by the configuration management tool SaltStack?
Cookbook
Manifest
Pillar*
Playbook
Explanation: The configuration management tool SaltStack uses the name Pillar to describe the set of instructions to be executed.
23. Which scenario describes the use of a public API?
It requires a license.
It can be used with no restrictions.*
It is used between a company and its business partners.
It is used only within an organization.
Explanation: Public, or open, APIs have no restrictions and are available to the public. Some API providers do require a user to obtain a free key or token prior to using the API in order to control the volume of API requests received and processed.
24. What is YAML?
It is a scripting language.
It is a data format and superset of JSON.*
It is a compiled programming language.
It is a web application.
Explanation: Like JSON, YAML Ain’t Markup Language (YAML) is a data format used by applications to store and transport data. YAML is considered a superset of JSON.
25. Which RESTFul operation corresponds to the HTTP GET method?
post
patch
update
read*
Explanation: RESTful operations correspond to the following HTTP methods (shown to the left with the RESTful operation on the right):
POST > Create
GET > Read
PUT/PATCH > Update
DELETE > Delete
26. Which technology virtualizes the network control plane and moves it to a centralized controller?
SDN*
fog computing
cloud computing
IaaS
Explanation: Networking devices operate in two planes: the data plane and the control plane. The control plane maintains Layer 2 and Layer 3 forwarding mechanisms using the CPU. The data plane forwards traffic flows. SDN virtualizes the control plane and moves it to a centralized network controller.
27. What are two functions of hypervisors? (Choose two.)
to partition the hard drive to run virtual machines
to manage virtual machines*
to protect the host from malware infection from the virtual machines
to share the antivirus software across the virtual machines
to allocate physical system resources to virtual machines*
Explanation: The hypervisor does not protect the hosting OS from malware. Neither does it allow sharing software across virtual machines. The hard drive of the supporting computer does not need to be partitioned to run virtual machines. The hypervisor creates and manages virtual machines on a host computer and allocates physical system resources to them.
28. What is a difference between the functions of Cloud computing and virtualization?
Cloud computing requires hypervisor technology whereas virtualization is a fault tolerance technology.
Cloud computing separates the application from the hardware whereas virtualization separates the OS from the underlying hardware.*
Cloud computing provides services on web-based access whereas virtualization provides services on data access through virtualized Internet connections.
Cloud computing utilizes data center technology whereas virtualization is not used in data centers.
Explanation: Cloud computing separates the application from the hardware. Virtualization separates the OS from the underlying hardware. Virtualization is a typical component within cloud computing. Virtualization is also widely used in data centers. Although the implementation of virtualization facilitates an easy server fault tolerance setup, it is not a fault tolerance technology by design. The Internet connection from a data center or service provider needs redundant physical WAN connections to ISPs.
29. How is the YAML data format structure different from JSON?
It uses indentations.*
It uses end tags.
It uses hierarchical levels of nesting.
It uses brackets and commas.
Explanation: The structure in YAML is defined by indentations rather than brackets and commas.
30. What is the most widely used API for web services?
XML-RPC
SOAP
JSON-RPC
REST*
Explanation: REST accounts for more than 80% of all API types used for web services, making it the most widely used web service API.
31. What is REST?
It is a way to store and interchange data in a structured format.
It is an architecture style for designing web service applications.*
It is a human readable data structure that is used by applications for storing, transforming, and reading data.
It is a protocol that allows administrators to manage nodes on an IP network.
Explanation: REST is not a protocol or service, but rather a style of software architecture for designing web service applications.
32. What is a difference between the XML and HTML data formats?
XML does not use predefined tags whereas HTML does use predefined tags.*
XML encloses data within a pair of tags whereas HTML uses a pair of quotation makes to enclose data.
XML formats data in binary whereas HTML formats data in plain text.
XML does not require indentation for each key/value pair but HTML does require indentation.
Explanation: XML is a human readable data structure used to store, transfer, and read data by applications. Like HTML, XML uses a related set of tags to enclose data. However, unlike HTML, XML uses no predefined tags or document structure.
33. To avoid purchasing new hardware, a company wants to take advantage of idle system resources and consolidate the number of servers while allowing for multiple operating systems on a single hardware platform. What service or technology would support this requirement?
dedicated servers
Cisco ACI
Virtualization*
software defined networking
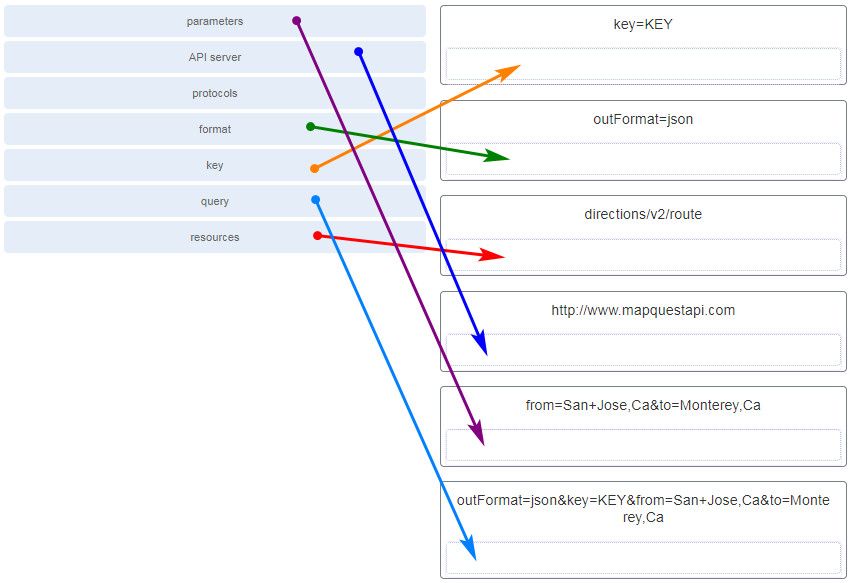
34. Match the term to the RESTful API request http://www.mapquestapi.com/directions/v2/route?outFormat=json&key=KEY&from=San+Jose,Ca&to=Monterey,Ca component. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA 3 v7.0 Modules 13 – 14 Exam Answers p34
35. Which cloud computing opportunity would provide the use of network hardware such as routers and switches for a particular company?
software as a service (SaaS)
wireless as a service (WaaS)
infrastructure as a service (IaaS)*
browser as a service (BaaS)
Explanation: This item is based on information contained in the presentation.
Routers, switches, and firewalls are infrastructure devices that can be provided in the cloud.
36. What component is considered the brains of the ACI architecture and translates application policies?
the Application Network Profile endpoints
the Nexus 9000 switch
the hypervisor
the Application Policy Infrastructure Controller*
Explanation: The ACI architecture consists of three core components: the Application Network Profile, the Application Policy Infrastructure Controller, which serves as the brains of the ACI architecture, and the Cisco Nexus 9000 switch.
37. Which statement describes the concept of cloud computing?
separation of management plane from control plane
separation of control plane from data plane
separation of application from hardware*
separation of operating system from hardware
Explanation:Cloud computing is used to separate the application or service from hardware. Virtualization separates the operating system from the hardware.
38. In which situation would a partner API be appropriate?
an internet search engine allowing developers to integrate the search engine into their own software applications
company sales staff accessing internal sales data from their mobile devices
someone creating an account on an external app or website by using his or her social media credentials
a vacation service site interacting with hotel databases to display information from all the hotels on its web site*
Explanation: Partner API programs incorporate collaboration with other business. They facilitate communication and integration of software between a company and its business partners.
39. Because of enormous growth in web traffic, a company has planned to purchase additional servers to help handle the web traffic. What service or technology would support this requirement?
virtualization
data center
cloud services
dedicated servers*
Disaster Recovery и миграция c помощью VMware vCloud Availability. Часть 2
Привет! В прошлом посте я рассказал о возможностях VMware vCloud Availability (vCAV) и показал, как организовать Disaster Recovery (DR) и миграцию в рамках нескольких площадок облачного провайдера. Сегодня посмотрим, как с помощью vCAV восстановиться или просто смигрировать в облако сервис-провайдера с on-premise-площадки. В нашем примере будем настраивать DR с локальной площадки заказчика в облако в СПб.
На этапе подготовки нужно решить, как обеспечить доступ к серверам после их восстановления в облаке. Для этого нужно организовать сетевую связность между локальной площадкой и облаком. Об основных способах подключения к облаку я писал здесь.
Для удобства сделал быструю навигацию по инструкции:
Настраиваем vCloud Availability Appliance for Tenants на локальной площадке
Чтобы подготовить on-premise-площадку к переезду или восстановлению, необходимо развернуть и настроить виртуальную машину с vCloud Availability Appliance for Tenants.
Дальше идем по стандартному алгоритму загрузки шаблона:
Здесь же активируем опцию Allow access from cloud, чтобы администратор vCloud Director мог обращаться к локальной площадке из облака.
Указываем место размещения для восстановленной ВМ: папку и ресурсный пул.
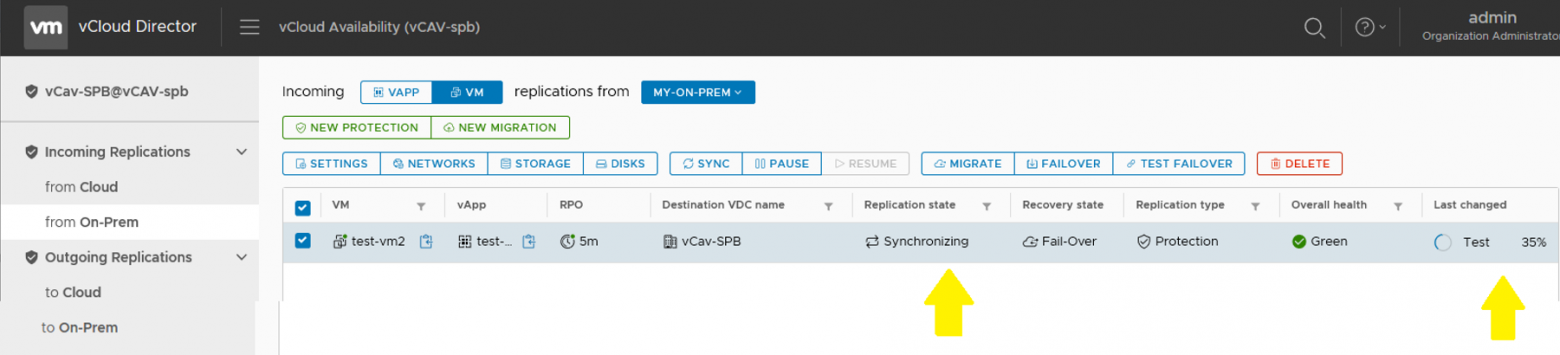
Настраиваем DR из on-premise в облако провайдера
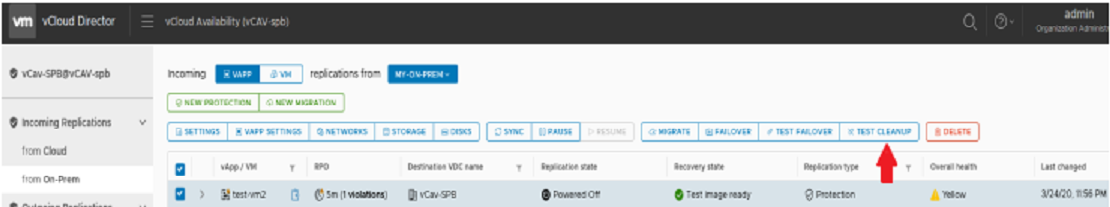
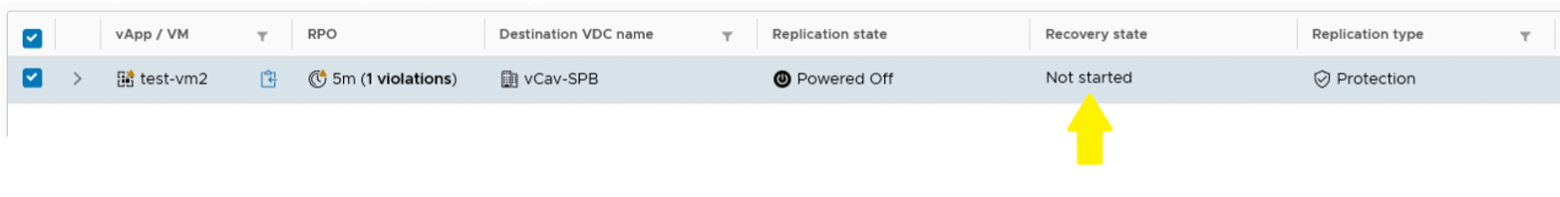
Тестируем восстановление
Ждем, когда она завершится.
И нажимаем кнопку Cleanup.
Переключаемся из on-premise в облако
При необходимости можно сделать обратное переключение из облака на локальную площадку.
В этих статьях мы рассмотрели основные сценарии использования vCAV и показали, как легко защитить свою инфраструктуру или выполнить миграцию.
Инструмент несложен в настройке, и главное — можно самостоятельно управлять процессом репликации.
What is Disaster Recovery?
Disaster recovery is an organization’s method of regaining access and functionality to its IT infrastructure after events like a natural disaster, cyber attack, or even business disruptions related to the COVID-19 pandemic. A variety of disaster recovery (DR) methods can be part of a disaster recovery plan. DR is one aspect of business continuity.
Address and Overcome the Top Challenges of Deploying a Disaster Recovery Solution
Disaster Recovery as-aService using VMware Site Recovery with VMware Cloud on AWS
How does disaster recovery work?
Disaster recovery relies upon the replication of data and computer processing in an off-premises location not affected by the disaster. When servers go down because of a natural disaster, equipment failure or cyber attack, a business needs to recover lost data from a second location where the data is backed up. Ideally, an organization can transfer its computer processing to that remote location as well in order to continue operations.
5 top elements of an effective disaster recovery plan
How to build a disaster recovery team?
Whether creating a disaster recovery strategy from scratch or improving an existing plan, assembling the right collaborative team of experts is a critical first step. It starts with tapping IT specialists and other key individuals to provide leadership over the following key areas in the event of a disaster:
While not necessarily part of the IT department, the following roles should also be assigned to any disaster recovery plan:
What are the types of disaster recovery?
Businesses can choose from a variety of disaster recovery methods, or combine several:
How to plan for COVID-19 disaster recovery & business continuity
COVID-19 and the resulting global crisis have pushed many companies to support employees working remotely and forced organizations to rethink their disaster recovery and business continuity strategies. With the pandemic in play, even just a network outage can have a significant effect on the business.
Here are a few things to consider:
What are the benefits of disaster recovery software?
No organization can afford to ignore disaster recovery. The two most important benefits of having a disaster plan in place, including effective DR software, are: