How many consonant sounds are there in english
How many consonant sounds are there in english
How many consonant sound?
Asked by: Ms. Elyssa Konopelski IV
There are 24 consonant sounds in most English accents, conveyed by 21 letters of the regular English alphabet (sometimes in combination, e.g., ch and th).
What are the 24 consonant sounds?
English has 24 consonant sounds. Some consonants have voice from the voicebox and some don’t. These consonants are voiced and voiceless pairs /p/ /b/, /t/ /d/, /k/ /g/, /f/ /v/, /s/ /z/, /θ/ /ð/, /ʃ/ /ʒ/, /ʈʃ/ /dʒ/. These consonants are voiced /h/, /w/, /n/, /m/, /r/, /j/, /ŋ/, /l/.
What are the 21 consonant sounds?
(The pronunciation of vowels, on the other hand, can differ drastically depending on dialect). There are 21 consonants: B, C, D, F, G, H, J, K, L, M, N, P, Q, R, S, T, V, W, X, Y, and Z.
What are the 18 consonant sounds?
How many vowels and consonant sounds are there?
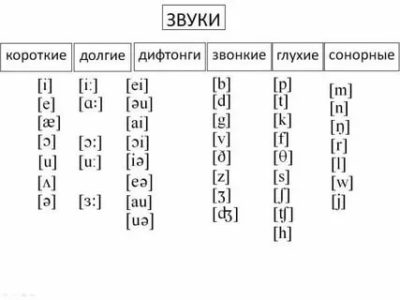
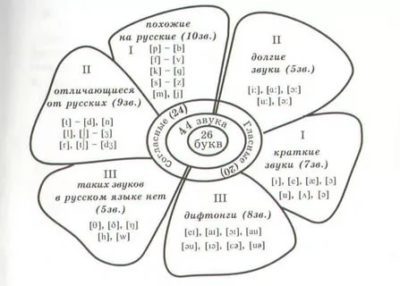
The English Language is created through the different combinations of 44 sounds (phonemes), 20 vowels and 24 consonants.
24 Consonant Sounds in American English with the IPA
44 related questions found
What are the 20 vowels sounds?
English has 20 vowel sounds. Short vowels in the IPA are /ɪ/-pit, /e/-pet, /æ/-pat, /ʌ/-cut, /ʊ/-put, /ɒ/-dog, /ə/-about. Long vowels in the IPA are /i:/-week, /ɑ:/-hard,/ɔ:/-fork,/ɜ:/-heard, /u:/-boot.
What are the 7 vowels?
In writing systems based on the Latin alphabet, the letters A, E, I, O, U, Y, W and sometimes others can all be used to represent vowels.
What are the 44 phonemes?
What are the 42 phonic sounds?
Learning the letter sounds: Children are taught 42 letter sounds, which is a mix of alphabet sounds (1 sound – 1 letter) and digraphs (1 sound – 2 letters) such as sh, th, ai and ue. Using a multi-sensory approach each letter sound is introduced with fun actions, stories and songs.
What are the 44 sounds?
How many consonant words are there?
There are 21 consonant letters in English, for 24 consonant sounds in most English accents. Because of the history of the English language, there is no neat one-to-one relationship between letter and sound. th and ch each stand for a single sound, and x in fox stands for two sounds (ks).
What are consonants examples?
A consonant is a speech sound that is not a vowel. It also refers to letters of the alphabet that represent those sounds: Z, B, T, G, and H are all consonants. Consonants are all the non-vowel sounds, or their corresponding letters: A, E, I, O, U and sometimes Y are not consonants. In hat, H and T are consonants.
What are the 26 consonant sounds?
Consonant sounds and consonant letters
The word consonant may be used ambiguously for both speech sounds and the letters of the alphabet used to write them. In English, these letters are B, C, D, F, G, J, K, L, M, N, P, Q, S, T, V, X, Z and often H, R, W, Y.
What are 2 consonants together called?
Clusters are made of two or more consonant sounds, while a digraph is a group of two consonant letters standing for a single sound. For example, in the word ship, the two letters of the digraph ⟨sh⟩ together represent the single consonant [ʃ].
What are the 12 pure vowel sounds?
There are 12 pure vowels or monophthongs in English – /i:/, /ɪ/, /ʊ/, /u:/, /e/, /ə/, /ɜ:/, /ɔ:/, /æ/, /ʌ/, /ɑ:/ and /ɒ/. The monophthongs can be really contrasted along with diphthongs in which the vowel quality changes. It will have the same syllables and hiatus with two vowels.
What letter sounds should be taught first?
As soon as the learner acquires one letter sound correspondence, introduce a new one. Letters that occur frequently in simple words (e.g., a, m, t) are taught first. Letters that look similar and have similar sounds (b and d) are separated in the instructional sequence to avoid confusion.
What is tricky word?
What are tricky words? Tricky words are those words which cannot be sounded out easily. Emergent readers may find them difficult to read as they have not yet learned some of the Graphemes in those words.
Which phonics should I teach first?
What is the year 1 phonics test?
Officially named the Phonics Screening Check, the year 1 phonics test occurs in the month of June when all year 1 pupils, and some year 2 pupils, will take a test to assess their phonics abilities. The test is designed to see if pupils have learnt phonic decoding and blending skills to an appropriate standard.
How many phoneme sounds are there?
There are 44* phonemes in the English language, that is, there are 44 different sounds that make up all English words. Many phonemes have more than one grapheme, that is, they can be written using different spellings, for example, f, ff, and ph are all graphemes for the phoneme /f/.
What are the 8 vowel sounds?
Which word has all 5 vowels?
Eunoia is the shortest English word that contains all the main five vowels.
Do any words have no vowels?
Words with no vowels
How many sounds in English
Phonetics of the English language: how to pronounce sounds and letters
How to read sounds correctly
Pronunciation table of English sounds
It is worth noting that digraphs and diphthongs are read differently depending on which part the words are in.
For example, gh is not pronounced in the middle of a word: light [laıt] (light), and sometimes it sounds like “f” at the end: enough [ı’nʌf] (enough); oo can be pronounced as a long [ʋ:], “y” in Russian: moon [mʋ: n] (moon), short [ʋ]: good [gʋd] (good), like a short [ʌ], similar to “a «In Russian: blood [blʌd] (blood), but together with» r «it is quite different, like [ʋə]: poor [pʋə] (poor).
Syllables in English
Let’s define what a syllable is. A syllable is the minimum spoken unit of speech, consisting of a sound (one vowel or in combination with a consonant sound), pronounced, one might say, in one breath. Considering that vowels are read differently depending on the type of syllable, consider what the same syllables are. In English, syllables are:
1.Open: the end of a syllable is a vowel sound: go, toy, my.
2. Conditionally open: the end of a syllable is a dumb «e» after a consonant: take, smoke, lime.
3.Closed: the end of a syllable is a consonant sound: get, sun, red.
Basic rules for dividing words into syllables:
1. If there is one consonant letter on the border of syllables, then it moves to the right: stu-dent (student), pu-pil (student).
2. If there is only one consonant in a word, but there are sonorant (nasal) sounds [m], [n], [l], [w], [r], [j], there can be several syllables: mi-ld (soft ), fi-nd (find).
3. If there are two consonant letters on the border of a word, one of which is a consonant l, it is part of the next syllable along with the consonant letter in front of it: ta-ble (table), sta-ble (stable).
4. If there are more than two consonants on the border of syllables, then one of them closes the syllable, and the second opens the next one: lit-tle (small), sim-ple (simple).
The article provides only the basic rules for reading letters and sounds in English. The phonetics of the English language is a broad and interesting subject of study. Want to know more? Sign up for an English course at Native English School or, to get started, take advantage of our free trial lesson, which you can sign up for simply by filling out the form.
Read more, listen to audio, practice speaking! Come to lessons at the NES and improve your knowledge. See you in class!
Lesson 14. Pronunciation of English sounds [w] and [r]. Reading letter combinations wr, wh, rh, er / or
We continue our lessons on teaching reading in English. On the left plate, green arrows indicate the sounds that we have already passed. Since we have studied almost all consonants, in this lesson we will repeat 8 learned vowel sounds to consolidate their pronunciation. There are only 4 consonants left. Sounds [r] и [w] we go through in this lesson, and the sounds [j] and [ŋ] in the next. So, let’s begin!
From lesson number 14 you will learn:
Let’s start with the pronunciation of sounds, and then move on to reading letter combinations.
So the letter Ww denotes a sound in writing [w]. Letter Rr denotes a sound in writing [r]. Both sounds are quite complex, because there are no similar sounds in Russian.
How to pronounce the English sound [w] correctly?
Pronunciation of the English sound [w]. Now that your mouth is ready, let’s start pronouncing the sound. Pull your lips into a tube for a moment, as if you want to utter the sound «y», and when you start saying «u», immediately smile sharply. The result is a sound a bit like «v».
Actually sound [w] very often the letters «y» and «v» are conveyed in Russian. Even in official sources, the name William is spelled either William or William. Because in Russian there is NO such sound.
If you have not yet fully understood how to pronounce the English sound [w] correctly, then pronounce it like a short «y», but in no case, like «in».
Note again that when you say “w” your lips are rounded and NOT touching your teeth, the same lip position must be observed when pronouncing the sound [w].
When pronouncing the sound «in», the upper teeth touch the lower lip. This shouldn’t be!
How to pronounce English [r] sound correctly?
I will say right away that this is a very complex sound. At least it was like that for me.
What you need to do to make an English sound [r] right and how does English [r] differ from Russian “r”?
Reading letter combinations with the sound R: wr, rh, er / or
1. Letter r and combination of letters re at the end of a word not readable: car, care and are used to designate type III of a syllable (as in the word car) and type IV of a syllable (as in the word care). You can read more about the types of syllables in English.
2. Letter combinations er, or at the end, words are read like [ə]: sister, doctor, etc.
Reading letter combinations with the sound W: wh
An exception.Wh before o read how [H]: who (who), whose (whose)
2. At the end of a word wnot readable: slow
Phonetic exercises for practicing the sounds [w] and [r] with audio recording (closed content)
Paid content is hidden. Registered users who have paid for access have the right to view paid content.
Title: Teaching to read in English. Subscription code 19
Description: Access to a course of lessons on teaching reading in English and pronunciation at the same time. 50% discount until 01.01.2020/XNUMX/XNUMX. Author T.V. Nabeeva
Phrases with the sounds [w] and [r] for practicing during the week:
Let’s sum up Lesson 14, from which you learned:
See you at the next English lesson. Learn to read English on your own and learn English on your own friends! The author of the lessons, Tatiana Nabeeva.
Table and rules for the pronunciation of consonants and vowels of English letters
By Natalia Mar 6, 2019
The sounds that English letters represent are 44 English phonemes, which are divided into two categories: consonants and vowels. Since sounds cannot be recorded, graphemes (letters or combinations of letters) are used to convey sounds in writing.
English alphabet
There are 26 letters in English. The standard English alphabet starts with a and ends with z.
When classifying alphabetic characters, the following are distinguished:
Learning the English alphabet requires knowledge of both the symbol representing each letter and the phonetic sounds associated with that letter. Learning English phonetics is difficult. Only a small number of letters have no exceptions in the basic sound.
In most cases, each letter has multiple phonemes. The letter B sometimes sounds like bat (bat) or does not sound, for example, in the words crumb (kram), dumb (dam). The letter C sounds like «k» for cat (cat) or «c» for ceiling (si: ling), or «pm» for church (tch: pm). And the list of exceptions is endless.
Vowel sounds
Vowels represent the main category of phonemes in English speech. There are 20 vowel sounds in spoken English. This discrepancy (in relation to alphabetic characters) underlies the difficulty of writing in English.
| Short | Long | Diphthongs |
| a [æ] | A (ā) [eı] | [eɪ] |
| e [ɛ] | E (ē) [i:] | [aɪ] |
| i [ɪ] | I (ī) [aı] | [ɔɪ] |
| o [ɒ] | O (ō) [ou] | [ɪə] |
| u [ʌ] | U (ū) [ju:] | [eə] |
| [ʊə] | ||
| [əʊ] | ||
| [aʊ] |
Consonant Sounds
| Deaf | Voiced | Others |
| p | b | c |
| t | d | h |
| k | g | j |
| f | v | l |
| s | z | m |
| n | ||
| q | ||
| r | ||
| w | ||
| x | ||
| y |
Transcription and stress
Phonetic transcriptions tell about the pronunciation of words. In English dictionaries, this is a necessary condition, since the spelling does not say how the word is pronounced.
| Vowels | Consonants |
| ʌ | b |
| ɑ: | d |
| æ | f |
| e | g |
| ə | h |
| ɜ: ʳ | j |
| ɪ | k |
| i: | l |
| ɒ | m |
| ɔ: | n |
| ʊ | ŋ |
| u: | p |
| aɪ | r |
| aʊ | s |
| eɪ | ʃ |
| oʊ | t |
| ɔɪ | tʃ |
| eəʳ | θ |
| ɪəʳ | ð |
| ʊəʳ | v |
| w | |
| z | |
| ʒ | |
| dʒ |
The rules do not fully cover aspects of stress in English words. The language is characterized by the presence of exceptions, and the English themselves are mistaken, especially in polysyllabic words.
But, obviously, some basic rules still apply:
Prefixes in two-syllable words are not stressed, except in some nouns or adjectives. Two-syllable nouns starting with a prefix are studied individually.
English consonants
There are fewer consonants in the English alphabet than consonants. Therefore, to expand the alphabet, digraphs are used like «Ch», «sh», «th» and «zh», and some letters and digraphs represent more than just one consonant. For example, the sound written “th” in this is transcribed as / ð /, and “th” in thin is / θ /.
English consonants are classified according to their combination of functions:
In addition, there is a function «Dull alveolar stop», / t / when the airflow mechanism is down.
According to the method of formation, consonants are divided into:
Our readers recommend trying 5 free lessons of the «ENGLISH BEFORE AUTOMATION» course with Anastasia Bozhok.
Those who attend even 1 lesson will learn more in more than a few years!
Get 5 Free Lessons Here
No homework. No cramming. No textbooks
From the «ENGLISH TO AUTOMATION» course you:
You can get 5 lessons for free here
Features of English consonants
A consonant combination is a set of two or three consonant letters that, when pronounced, retain the original sound. Such sets occur either at the beginning or at the end of a word. For example, the word brave, where both «b» and «r» are pronounced, is an initial combination. In the word bank «-nk» is the final combination.
Classification:
Digraphs
Examples of digraphs:
| Ch- | — ch |
| Kn- | — ck |
| Ph- | -sh |
| Sh- | -ss |
| Th- | -th |
| wh- | -tch |
| Wr- |
Features of digraphs:
Vowel letters of the English alphabet
›Grammar and rules› Alphabet ›Vowel letters of the English alphabet with transcription and Russian pronunciation
English is becoming more widespread every day. Today it is spoken by most of the world’s population, which automatically makes it an international language of communication. In addition to the American continents, it is being studied in Europe and Asia. Australia, as part of the former British Empire, has long recognized English as the official language.
If in Western Europe, American and British English are studied by children from a very early age, in Russia, Ukraine and other CIS countries, they are treated very mediocre. The school curriculum skims through the most frequent words, while the children are not really explained the rules for their use. All this forces people to learn on their own, which is much more difficult.
Today we will analyze how the vowels of the English alphabet are used in words. They influence the quality of pronunciation and language perception.
Constructing words in American
The consonants of the English alphabet are the basis of all words. The total number of letters is 26, of which consonants are 20, and there are only 6 vowels in English. Despite such a meager number, they can take various forms of pronunciation, as a result, from 6 letters, about 20-24 sounds are obtained. All vowels and consonants are listed in the table below:
As you can see in the picture, the vowels in the English alphabet are highlighted in yellow. A transcription is written next to each letter, thanks to which you can learn how to pronounce this or that letter correctly.
The need for transcription was always due to the fact that it is simply impossible to explain the correct pronunciation using the example of the Russian language.
If in Russian one letter is equated to one sound, then most of the vowels in the English alphabet are pronounced using a combination of two phonemes.
| Letter | Transcription | transcript |
| Aa | [ei] | Hey |
| Her | [I:] | Long «and» |
| Ii | [ai] | Ай |
| Oo | [Where] | Oh oh |
| Uu | [ju:] | Long «yu» |
| Yy | [wai] | wye |
The last letter «Yy» can be a vowel or a consonant depending on the type of syllable. This should be taken into account when reading and parsing words morpheme. What sound will determine this or that letter depends on its position in the word and syllable.
Types of syllables of the English alphabet
How to quickly learn to read English from scratch on your own. Tips for English learners
You don’t have to burn books to destroy a culture. You can just get people to stop reading them.
But, if at school or university you studied German or French, or your school base turned out to be smaller than you would like, and now you have decided to learn English, then let’s start with the very primary and basic and learn a few methods of where to start in order to master reading rules.
English alphabet
I think you know that English is different from Russian and German, in which we basically read and write. In English, the system is a little more complicated. The very first thing we need to do is learn the alphabet.
The English alphabet has 26 letters, including 21 consonants and 5 vowels. Knowledge of letters and the ability to pronounce them correctly is the key to successful and competent reading in English.
English alphabet with transcription of the names of letters.
A very easy way to memorize letters visually and by ear is with the help of a song. Watch the video and sing the song until you memorize the letters of the alphabet.
You can use the same method to teach the alphabet to your children and sing along with your little ones.
After studying the alphabet, let’s start learning the combination of letters and reading short words. There are a number of rules in English that you need to learn, practice and remember if you want to read English words correctly.
The same letter can be read in different ways, depending on the letters that surround it, as well as whether it is closed or open syllable.
Rules for reading English consonants
Letters such as t и d sound similar, but pronounced with aspirated. For example, the words table, teacher, dad, dirty.
Letter c has two reading options. Before letters i, e, y it reads like [s]— city, face, cyber. And before the rest of the vowels it reads like [k]— cat, cake, factory.
The vowel rule i, e, y works with the letter g. In front of them, it reads like [dʒ]— gym, George, giant. Before other consonants, the letter is read as [g].
Letter q always occurs in a combination of letters qu and reads like [kW]— quick, queen, square.
Letter j always reads like [dʒ]— jacket, jam, joy.
Table of the ratio of consonants and sounds in English.
How vowels are read in English
In English, a word can end in an open or closed syllable, which affects pronunciation. For example, the words cat, pot, sit end in a closed syllable and have vowels a, o, i give sounds [a, o, i].
Words such as name, home, five end with an open syllable, since there is a letter at the end of the word ewhich is not readable. But, thanks to her, the vowels in the middle of the word are read in the same way as they are pronounced in the alphabet, that is, the word name is read [neɪm].
Types of English vowel reading in stressed syllables.
Reading vowel combinations in English
There are certain combinations of letters that have well-established rules for reading, although English is the language of exceptions, and when reading more complex words, you should refer to the dictionary. The table below shows English vowel combinations with examples how they are read and how they sound.
Table of combinations of vowels in English.
And of course, there are exceptions to all the rules. However, do not worry and think that you will never be able to learn it. Everything can be understood, you just have to try a little and practice.
English diphthongs with transcription
When you learn the basic rules of reading, you will see that there are diphthong sounds that are quite difficult to reproduce in English, especially if you start learning the language not from childhood, but in adulthood.
Table of English diphthongs with transcription.
Transcription of sounds in English
Practice shows that when children learn a language, they must necessarily learn transcription, while adults do not want to learn it and it can be difficult for them.
If you still want to learn how to write and read the transcription, then great! And if not, then you can use online dictionaries where the word will be pronounced for you. One of the best dictionaries today is Multitran and the Lingvo online dictionary.
Remember to use dictionaries, not translators!
Here’s an example of reading short words with transcription:
English vowel table and transcription.
There are some advantages to being in the internet age. Sitting at home, you can learn a variety of knowledge online. For your attention video tutorial, which explains the basic principles of reading. Nevertheless, even having received knowledge through an online lesson, they need to be consolidated in order to form a skill.
In this section, we want to share with you the experience that was gained in practice, teaching students of different levels. These tips have proven their effectiveness and usefulness in language learning. They can be used for beginner to advanced levels. Use)
Learn English tongue twisters
Here tongue twisters, which are often aimed at practicing one sound, can help you. Here are some examples you can use.
Sounds [ɪ, i :, e, ǝ] in English and their pronunciation
It would seem that it is impossible to put the correct pronunciation without outside help. Let’s destroy this myth with our article workshop. With the help of a detailed analysis of each sound, comparison with our Russian «analogues», training videos and tongue twisters, we will bring your pronunciation of English sounds as close as possible to the ideal.
The sounds that we will analyze today can often seem to us, Russian-speaking, very similar to each other: / ɪ, i :, e, ǝ /. To “put in your head” the difference between them, go through each stage of the article sequentially and complete all the tasks
Almost all sounds of the English language differ from the sounds of the Russian language. And even at first glance, similar sounds can be articulated in different ways. Articulation in this case is the position of the organs of speech (tongue and lips in the first place) during the pronunciation of a sound. However, as many as 12 consonant sounds in English can be easily pronounced by a Russian-speaking person. These are the sounds [p, b, k, f, v, m, z, h, t, d, l, n].
Phonetics is the area of the English language that audio and video materials are best suited for learning. You can endlessly read about sounds, and you never learn how to pronounce them correctly.
Be sure to watch the video tutorial. There is an exercise for you to practice your pronunciation!
This video lesson is part of the RealStudy Starter Level Online Course.
I want try course for free
Sounds [p, b, k, f, v, m, z]
Pronunciation features
1. Z should be pronounced with less accent than we do in Russian. In general, the English pronounce muffled sounds more powerfully than voiced ones.
2. When pronouncing v, I highly recommend biting your lower lip with your upper teeth a little. This helps not to deafen the given sound in all positions. Do not forget that, unlike Russian, voiced consonants are never stunned in English. Therefore, for example, move will always be [muːv
mov], and never [muf].
3. The sounds [p], [t] and [k] at the beginning of the stressed syllable are pronounced aspirated or aspirated. After each of these sounds, we exhale a little (but so that it can be heard), and then we pronounce the next sound. Remember that if [p], [t] and [k] come after [s], for example, sport, skate, then there will be no aspiration. The whistling sound [s] seems to steal aspiration from the following [p], [t] and [k].
Sound [h]
The h sound is a simple exhalation without a voice. The easiest way to train him is with words that begin with this sound.
Enjoy learning English online with Puzzle English for free
Today there will be a small «culinary» master class. We will tell you what English speech consists of, what is the difference between letters and sounds, and how to bake and bite it all Oh, that is, read and pronounce.
We will master reading transcription in English, exercises to develop this skill. You will understand what sounds are, and how they are recorded. It will become easier to perceive written speech. Learn the rules of reading in English (exercises to help master difficult combinations are included).
But first, check out a poem that one little girl wrote:
Hanging tickut streams
And the first dosht pashol
And now the prashli of the maroza
And Visna has come
You have most likely noticed the difference between how it is written and how it SHOULD be written. From the first grade, teachers tell schoolchildren: do not finish, togeьNot visny, веsleep. But this is illogical, because it is precisely “finish».
Surprisingly, there are languages in which you do not need to learn the «correct» option. For example, in Korean or Georgian, everything is spelled and heard. Imagine how easy it is for children to live there!
Meanwhile, English-speaking students have fun in competition spelling. The conditions are as follows: the presenter speaks the word out loud, and the contestant must pronounce it letter by letter. This is not an easy task because the oral form often does not match the spelling.
Why is it so hard?
Once upon a time, English was the same as Georgian. In the sense that, as it was heard, it was written. But then changes began to occur, and the spelling rules seemed to have frozen in place, remaining a kind of monument to the past.
Now we have what we have: handkerchief, conscience и pronunciation, Knight, wheel и thorough. How to read such words? The first thing to do is
Transcription Is a written expression sounds speech, that is, how we hear the word. Many transcription characters match the usual Latin alphabet. Transcribed words are placed in square brackets:
The 44 Phonemes in English
Despite there being just 26 letters in the English language there are approximately 44 unique sounds, also known as phonemes. The 44 sounds help distinguish one word or meaning from another. Various letters and letter combinations known as graphemes are used to represent the sounds.
The 44 English sounds fall into two categories: consonants and vowels. Below is a list of the 44 phonemes along with their International Phonetic Alphabet symbols and some examples of their use. Note that there is no such thing as a definitive list of phonemes because of accents, dialects and the evolution of language itself. Therefore you may discover lists with more or less than these 44 sounds.
Consonants
What is the International Phonetic Alphabet?
How can you pronounce a word you’ve never read? It can be a bit tricky. How about a word in a foreign language? Now that must be impossible! Or is it? Imagine a set of symbols that could tell you how to pronounce any word in any language on the planet? Well that is exactly what the International Phonetic Alphabet is. Currently, the IPA consists of 107 sound symbols, 52 diacritics (accents) and 4 prosodic marks (intonations) encompassing virtually every phoneme used in every language on the earth. So for any written word, you can identify the associated phoneme symbols, and with a bit of practice, pronounce the word! Congratulations, you can speak Greek now!
The IPA was created by the International Phonetic Association. Founded in 1886 in Paris, their original mission was to help school children pronounce words in foreign languages and to aid in the teaching of reading. Today their mission is to promote the scientific study of phonetics.
Vowels
| Phoneme | IPA Symbol | Graphemes | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | Г¦ | a, ai, au | cat, plaid, laugh |
| 26 | eЙЄ | a, ai, eigh, aigh, ay, er, et, ei, au, a_e, ea, ey | bay, maid, weigh, straight, pay, foyer, filet, eight, gauge, mate, break, they |
| 27 | e | e, ea, u, ie, ai, a, eo, ei, ae | end, bread, bury, friend, said, many, leopard, heifer, aesthetic |
| 28 | i: | e, ee, ea, y, ey, oe, ie, i, ei, eo, ay | be, bee, meat, lady, key, phoenix, grief, ski, deceive, people, quay |
| 29 | ЙЄ | i, e, o, u, ui, y, ie | it, england, women, busy, guild, gym, sieve |
| 30 | aЙЄ | i, y, igh, ie, uy, ye, ai, is, eigh, i_e | spider, sky, night, pie, guy, stye, aisle, island, height, kite |
| 31 | Й’ | a, ho, au, aw, ough | swan, honest, maul, slaw, fought |
| 32 | oКЉ | o, oa, o_e, oe, ow, ough, eau, oo, ew | open, moat, bone, toe, sow, dough, beau, brooch, sew |
| 33 | КЉ | o, oo, u,ou | wolf, look, bush, would |
| 34 | КЊ | u, o, oo, ou | lug, monkey, blood, double |
| 35 | u: | o, oo, ew, ue, u_e, oe, ough, ui, oew, ou | who, loon, dew, blue, flute, shoe, through, fruit, manoeuvre, group |
| 36 | Й”ЙЄ | oi, oy, uoy | join, boy, buoy |
| 37 | aКЉ | ow, ou, ough | now, shout, bough |
| 38 | Й™ | a, er, i, ar, our, ur | about, ladder, pencil, dollar, honour, augur |
| 39 | eЙ™Кі | air, are, ear, ere, eir, ayer | chair, dare, pear, where, their, prayer |
| 40 | Й‘: | a | arm |
| 41 | Йњ:Кі | ir, er, ur, ear, or, our, yr | bird, term, burn, pearl, word, journey, myrtle |
| 42 | Й”: | aw, a, or, oor, ore, oar, our, augh, ar, ough, au | paw, ball, fork, poor, fore, board, four, taught, war, bought, sauce |
| 43 | ЙЄЙ™Кі | ear, eer, ere, ier | ear, steer, here, tier |
| 44 | КЉЙ™Кі | ure, our | cure, tourist |
Teaching phonemic awareness
Knowing that phonemic awareness is a critical skill and being able to effectively teach it are two different things. The book 50 Reading Strategies for K-8 Learners ( Sage Publications ) s uggests 5 guidelines for phonemic awareness instruction:
Begin with assessment and then use playful, individualized, multisensory instruction
Consistent with all the researched advice on teaching phonemic awareness above, educational therapist and author Dr. Erica Warren, believes that the key to successfully teaching the 44 phonemes in English is assessment, followed by individualized, multi-sensory instruction. She has developed a helpful assessment tool and a number of fun, effective instruction/remediation tools for helping young readers master the essential sounds of the English language. And she created a custom bundle of tools just for Reading Well parents and professional visitors at a special discounted price. The bundle includes an easy to administer assessment tool and over 50 fun, multisensory games and activities which children love. We suggest you check it out.
Final sounds on the 44 phonemes in English
The difficulty people with dyslexia have in distinguishing phonemes is most clearly revealed in their poor spelling. While any phoneme can be a challenge, some are more problematic than others. The vowels and digraphs generally present more difficulty than the consonants, although any sound can present difficulty depending on the particular word and phrase in which it resides.
English consonants

English consonants are categorized as to:
Labial Consonants
Depending on what mobile and fixed speech organs articulate a speech sound, consonants may be labial, lingual and glottal.
bilabial articulated with both lips – [w], [m], [p], [b]
labiodental articulated with the lower lip and upper teeth – [f], [v].
Lingual Consonants
Forelingual consonants:
interdental (predorsal dental) – [θ], [ð]
(the tongue’s front surface forms a partial occlusion with the upper teeth);
apical alveolar – [t], [d], [n], [l], [s], [z], [∫], [ʒ], [t∫], [dʒ]
(the front edge rises to the alveolar ridge);
cacuminal post-alveolar – [r]
(the front edge is raised and a little bent to the alveolar back slope).
In mediolingual consonants an occlusion is formed by raising the middle part to the hard palate. Such is articulating the only English dorsal palatal [j] sound.
Backlingual consonants are articulated by raising the back part to the soft palate – [k], [g], [ŋ]. These are dorsal velar sounds.
Glottal Consonant
The only English glottal [h] sound forms in the glottis. Exhaled air goes via the narrowed glottis with a slight friction noise, the vocal cords don’t vibrate, speech organs in super-glottal cavities shape to pronounce a vowel after the glottal consonant.
Occlusive/Constrictive Consonants
By noise-forming occlusion type, consonants may be occlusive articulated with a full occlusion in the mouth cavity and constrictive articulated with a partial occlusion in the mouth cavity.
Occlusive consonants – [p], [b], [t], [d], [k], [g], [m], [n], [ŋ], [t∫], [dʒ].
Constrictive consonants – [f], [v], [θ], [ð], [s], [z], [∫], [ʒ], [h], [w], [l], [r], [j].
Non-Sonorous Consonants
Both occlusive and constrictive consonants may be non-sonorous and sonants.
Occlusive non-sonorous consonants divide into plosives and affricates. In pronouncing plosive consonants the full occlusion opens, air leaves the mouth cavity producing plosive noise – [p], [b], [t], [d], [k], [g]. Affricates are sounds with an occlusive start closely blending with a fricative indent. Speech organ opening to form a full occlusion happens smoothly with sounds articulated by 1 effort – [t∫], [dʒ].
Fricative Consonants
In articulating constrictive non-sonorous (fricative) consonants, air blows from the narrow glottis creating friction noise. The glottis can shape flat as in [f], [v] or rounded as in [s], [z]. Fricative consonants – [f], [v], [θ], [ð], [s], [z], [∫], [ʒ], [h].
Nasal Consonants
Occlusive sonants are nasal. In the mouth cavity a full occlusion forms, the soft palate lowers and air leaves the nasal cavity. Nasal sonants – [m], [n], [ŋ].
Oral Sonants
Constrictive sonants are oral. They may be medial (the tongue’s sides rise and touch side teeth, air blows along its central part) – [w], [r], [j] and lateral (the front edge rises to the alveoli and touches them, the sides lower, air leaves via side passages – [l].
Unicentral/Bicentral Consonants
Most English consonants are unicentral as having 1 formation place, i.e. a noise-forming focus. However in some cases the main noise-forming occlusion is added with another occlusion giving the sound an extra shade. Such consonants are bicentral. A secondary/extra occlusion can form by raising the tongue’s middle part to the hard palate. Here the sound takes on a soft shade. It’s a second middle focus as in [∫], [ʒ], [t∫], [dʒ] and the so called «light» [l] sound version. If the secondary occlusion forms by raising the back part to the soft palate, it creates an acoustic effect of velarization with the sound acquiring a hard shade. It’s a second back focus as in [w], [r] and the so called «dark» [ł] sound version.
Voiced/Voiceless Consonants
By presence/absence of vocal cords vibration, consonants may be voiced accompanied with vocal cords vibrations and voiceless pronounced with passive non-vibrating vocal cords. The first are voiced non-sonorous and sonants, the second voiceless non-sonorous consonants.
Fortis/Lenis Consonants
English voiceless consonants are pronounced energetically and named fortis. Voiced consonants are accompanied with weak muscular tension and named lenis.
Do You Know Everything About Consonant Sounds and Letters in English?
This Overview Will Help You From Getting Tongue-Tied
A consonant is a speech sound that’s not a vowel. The sound of a consonant is produced by a partial or complete obstruction of the airstream by a constriction of the speech organs. In writing, a consonant is any letter of the alphabet except A, E, I, O, U, and sometimes Y. There are 24 consonant sounds in English, some voiced (made by a vibration of the vocal cords) and some voiceless (no vibration).
Consonants Versus Vowels
When spoken vowels have no obstruction in the mouth, as opposed to consonants, which do. In his book «Letter Perfect,» the author David Sacks described the difference between speaking consonants and vowels this way:
«Whereas vowels are pronounced from the vocal cords with minimal shaping of expelled breath, consonant sounds are created through obstruction or channeling of the breath by the lips, teeth, tongue, throat, or nasal passage. Some consonants, like B, involve the vocal cords; others don’t. Some, like R or W, flow the breath in a way that steers them relatively close to being vowels.»
When consonants and vowels are put together, they form syllables, which are the basic units of pronunciation. Syllables, in turn, are the foundation of words in English grammar. Phonetically, however, consonants are much more variable.
Consonant Blends and Digraphs
When two or more consonant sounds are pronounced in succession without an intervening vowel (as in the words «dream» and «bursts»), the group is called a consonant blend or consonant cluster. In a consonant blend, the sound of each individual letter can be heard.
By contrast, in a consonant digraph, two successive letters represent a single sound. Common digraphs include G and H, which together mimic the sound of F (as in the word «enough»), and the letters P and H, which also sound like an F (as in «phone»).
Silent Consonants
In a number of cases in English, consonant letters can be silent, such as the letter B following M (as in the word «dumb»), the letter K before N («know»), and the letters B and P before T («debt» and «receipt»). When a double consonant appears in a word, usually only one of the two consonants is sounded (as in «ball» or «summer»).
Stop Consonants
Consonants can also serve as a means of bracketing a vowel, stopping their sound. These are called stop consonants because the air in the vocal tract is completely stopped at some point, usually by the tongue, lips, or teeth. Then to make the consonant sound, the air is suddenly released. The letters B, D, and G are the most frequently used stops, though P, T, and K also can serve the same function. Words that contain stop consonants include «bib» and «kit.» Stop consonants are also called plosives, as their sounds are small «explosions» of air in the mouth.
Consonance
Broadly, consonance is the repetition of consonant sounds; more specifically, consonance is the repetition of the consonant sounds of accented syllables or important words. Consonance is frequently used in poetry, song lyrics, and prose when the writer wants to create a sense of rhythm. One well-known example of this literary device is the tongue twister, «She sells seashells by the seashore.»
Using ‘A’ and ‘An’
In general, words that begin with vowels should be introduced by the indefinite article «an,» while words that start with consonants are set off with an «a» instead. However, when the consonants at the beginning of the word produce a vowel sound, you would use the article «an» instead (an honor, a house).



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/close-up-of-symbol-on-keys-of-keyboards-678877045-59b857bd9abed50011d28822.jpg)