How many keys has enhanced keyboard
How many keys has enhanced keyboard
How Many Keys on a Keyboard
Have you ever wondered how many keys are on a keyboard? It depends if you mean a computer keyboard or a piano keyboard.
In this article, we will explore both types of keyboards.
Table of Contents
How Many Keys On A Keyboard?
How Many Keys on a Computer Keyboard?
Keyboards come in all shapes and sizes, but the vast majority can be divided into three broad categories: those with 74 keys or fewer, those with 101-104 keys, and those with 105 keys or more.
The most common type of keyboard is the 104-key board, which includes a full set of alphanumeric keys as well as a separate number pad, function keys, and other assorted Control and Alt keys. This type of keyboard is typically used with desktop computers.
Laptop keyboards, on the other hand, generally have fewer keys, since they must be small enough to fit within the limited space available on a laptop’s chassis. As a result, many laptop keyboards have been shrunk down to just 74 keys.
Finally, some keyboards – usually those designed for gaming – have been expanded to include additional keys beyond the standard 104. These extra keys can be used to activate special in-game commands or macros, providing a competitive advantage for gamers. No matter what type of keyboard you prefer, there’s sure to be one that fits your needs.
IBM/PC Keyboards
Apple Keyboards
Miscellaneous Keyboards
Some keyboards include additional keys beyond the standard 104, catering to specific uses such as gaming, media center control, or programming. The most common of these are Korean, Japanese, and Brazilian keyboards, which arrange keys differently to accommodate the frequency of certain characters in those languages.
Others may have programmable keys that can be customized to trigger various actions or macros, or media keys to control the playback of music and video or launch applications.
Gaming keyboards often incorporate specialized functions like backlighting, on-the-fly macro recording, and extra USB ports. While the exact number varies depending on the keyboard’s functions, most keyboards with extended functionality fall into the range of 110 to 115 keys.
How Many Keys on a Keyboard on Mac
Mac keyboards come in two versions. The most current one has a compact version with only 78 keys (as compared to the older version that has a full-size keyboard layout with 109 keys).
The smaller keyboard is designed to be as unobtrusive and portable as possible.
The larger keyboard has tools that will help you be more efficient while working at your Mac, but it also has all of the other keys that you’ll find on a regular full-size computer keyboard.
How Many Keys on a Keyboard With Numpad?
A numeric keypad, number pad, Numpad, or ten key, is the palm-sized, usually 17-key section of a standard computer keyboard, usually on the far right. It provides calculator-style efficiency for entering numbers.
Built to replicate the math functions of an adding machine or calculator, they allow efficient input using only the operator’s right hand (for those who are not ambidextrous).
Many computers have a combination of numeric keypad and keypad cursor arrow keys.
A keyboard with Numpad has a total of 104 keys.
How Many Keys on a Keyboard Without Numpad?
The term TKL stands for “Ten Key Less” and refers to keyboards without a Numpad on the side. This means that the keyboard has 87 or 88 keys, vs. a standard 104-keyset keyboard.
For most non-Numpad users, the reduction of unused keys just improves aesthetics and ergonomics. However, if you have small hands or need to use a mouse more often then you may find a TKL layout is best for you.
How Many Keys Are on a Piano Keyboard?
In piano, the kind of keyboard that is generally preferred by most teachers and players is the one with the full 88 keys.
This type of keyboard is said to be fully chromatic in contrast to other keyboards which are limited to playing a number of notes by only having a few keys.
What is the Minimum Number of Keys for a Beginner Keyboard?
The number of keys on a keyboard has an impact on the range of music that can be played. Most keyboards come in smaller and larger sizes, each with a different number of keys.
If you are a beginner, get a keyboard between 66 and 76 keys. These keyboards are easy to find, affordable, and perfect for beginners and children.
The most common size is an 88-key keyboard. 88-key keyboards are used by almost all professional pianists and offer the widest range of musical abilities.
While it is possible to play on a smaller instrument (like a 73 or 76-key), it may prove more difficult to learn certain pieces.
Many piano teachers for beginners insist that their students use an 88-key keyboard as soon as they start taking lessons.
A beginner’s guide to mechanical keyboards — how they work and how they can improve your typing
Twitter LinkedIn icon The word «in».
LinkedIn Fliboard icon A stylized letter F.
Flipboard Facebook Icon The letter F.
Email Link icon An image of a chain link. It symobilizes a website link url.
Most computer keyboards look the same — three rows of letters, a row or two of numbers, and a lot of punctuation and function keys. But although they look similar, keyboards can vary wildly when it comes to how they work on the inside.
Most people today use one of two kinds of keyboards: membrane and mechanical keyboards.
Membrane keyboards, the more common type, feature some sort of rubber dome under each key. When you press a key, the rubber is compressed, and the key makes an electrical connection with the keyboard’s wires.
Mechanical keyboards are very different — instead of rubber, they have a plastic switch under the key that makes the connection go through.
This might not sound that different, but the style of key has a huge impact on how you type.
How a mechanical keyboard works
In principle, a keyboard switch is a simple device. It’s composed of a stem that attaches to the keycap, held up by a spring. When you push down on the keycap, that forces the stem to go down, allowing two electrical contacts to touch.
But mechanical keyboards have a very different feel than membrane keyboards, because the keys make a spring-loaded switch go off, and once pressed down, you’ll feel or hear a distinctive click. This means you’ll always know when a key’s been pressed — there’s no second-guessing about whether a press actually went through.
In comparison, membrane keyboards tend to feel «mushy» because they’re applying pressure to a rubber dome, and there’s no definitive click of triggering a switch. Typing quickly on membrane keyboards means you’re more likely to make errors.
Even so, not all mechanical keyboards work alike. The switches in mechanical keyboards are generally classified as either tactile or linear. A linear switch needs to be pressed down all the way, while tactile switches activate about halfway down, which means they activate more quickly, with less typing effort.
In either case, the principal is the same: mechanical keyboards help you type faster by marking each keypress with a click that you can feel and usually hear.
Uses for mechanical keyboards
Membrane keyboards are more common in large part because they’re less expensive than mechanical keyboards — they’re also quieter than mechanical keyboards, which can be quite loud.
Still, many people prefer mechanical keyboards, particularly programmers and gamers. Both groups appreciate the precise control and feedback that mechanical keyboards provide.
Unlike most membrane keyboards, the sounds, feel, and feedback from mechanical keyboards let typists type faster and more accurately, and let gamers control their in-game movement more precisely.
Pros and cons of mechanical keyboards
In addition to precision, mechanical keyboards also have a significantly longer lifespan. Many mechanical keyboards are rated to last anywhere from 20 million to 100 million keypresses, while it’s typical for a membrane keyboard to only be rated for 5 million to 10 million.
Mechanical keyboards also offer special features that are of interest to gamers, such as «rollover.» Rollover ensures that every keypress is sensed, even if keys are pressed simultaneously. Mechanical keyboards can do this easily, while membrane keyboards aren’t especially good at it, and will often cancel simultaneous presses.
If a key or switch on your mechanical keyboard breaks, you can almost always replace them. Keycaps can be removed with a key puller, a simple tong-like tool that will likely be included with the keyboard.
Many gamers replace their keycaps as they age, or replace them with custom keycaps (such as special WASD keys). And because keycaps can be easily removed, it’s also easy to clean a mechanical keyboard.
Not everyone appreciates mechanical keyboards, though. As mentioned, they can be loud, which is distracting if you’re sharing a room with other people. In general, they’re also more expensive than membrane keyboards, though there are exceptions.
That said, if you’re looking to improve your typing speed or accuracy, you might want to check out a mechanical keyboard.
IBM Enhanced Keyboard
| This article requires additional photographic illustration — need other angles, rear labels, disassembly shots etc |
 | |
| Part number | Various (see main text) |
|---|---|
| Branding | IBM, Lexmark, Unicomp, others |
| Manufacturer | IBM, Lexmark, Maxi Switch, Unicomp |
| Layouts | 101/102/104 ANSI, 102/103/105 ISO |
| Keyswitches | Buckling spring over membrane, rubber dome |
| Interface | PS/2, AT, USB, Terminal |
| Dimensions | 492 × 210 × 58 mm (19.37 × 8.27 × 2.28 in.) with legs extended [1] |
| Weight | 2.0–2.5 kg |
| Introduced | 1985 |
| Price | $69–300 (Depending on version, year of production etc) $217 (1992) [2] |
The Enhanced Keyboard, first produced in 1985, is a 101-105-key keyboard designed for personal computers and terminals. It is commonly known by the manufacturing designation Model M, although it was not the only keyboard with this designation. It was manufactured by IBM at its plants in the US, UK and Mexico; by Lexmark and Maxi Switch; and by Unicomp, who continues to manufacture it to this day. Its key layout became the industry standard, and is still used on most desktop keyboards in an extended 104/105-key form.
Contents
History
The Enhanced Keyboard entered production in mid 1985 and first appeared with the IBM 3161 terminal. It used a new layout, seemingly inspired by the DEC LK201 keyboard, with elements of the 122-key terminal keyboard layout. The original terminal models featured a 102-key (US) or 103-key (rest of the world) layout. The first PC-compatible Enhanced Keyboard was packaged with the IBM 7531 Industrial PC, an industrial version of the PC/AT. Compared with the terminal keyboard, it featured lock lights, a detachable cable, and a 101- or 102-key layout (the numeric keypad having one less button on the former). In 1986, IBM produced variants of the Enhanced Keyboard for certain models of the IBM PC/XT, PC/AT and XT/286. The Enhanced Keyboard and its variants became standard for IBM’s PS/2 line of computers in 1987, and an option for various IBM terminals and other computers.
In 1991, IBM divested its Office Products Division, resulting in the formation of Lexmark, who took over most of IBM’s keyboard production. Lexmark produced the Enhanced Keyboard for IBM and other vendors, and under its own brand. Due to pressures on IBM to produce cheaper computers, the Enhanced Keyboard appeared only on high-end systems after IBM discontinued the PS/2 line in 1994, and as an optional accessory for other systems. Eventually Lexmark could no longer justify producing keyboards, and a staff buyout of their keyboard business resulted in the creation of Unicomp. IBM continued to offer the Enhanced Keyboard, producing them at their Greenock, Scotland plant, as well as outsourcing to Lexmark and Unicomp.
Around 1999, IBM began to discontinue both producing and offering the Enhanced Keyboard. Unicomp continued to produce them for other vendors as well as selling directly to the public. Unicomp’s designs have not differed from late IBM ones, save for the introduction of Windows keys, USB connections, and different colour options.
Design details
The Enhanced Keyboard consists of a Model M assembly mounted inside a plastic (usually ABS, or a mixture of PC and ABS) casing. The casing consists of a separate upper and lower part, which clasp together at the front of the keyboard with interlocking tabs, and are secured at the back with four 5.5 mm (7/32″) hexagonal screws. The controller card is located either under the keyboard assembly or mounted on the assembly itself, above the numeric keypad. On original examples, the cable exits the casing at the center back of the keyboard; on later ones, it exits at the top right. Older style cases have a square gap in the case which allows for either an SDL socket for a removable cable, or a non-removable cable with a square filler. On variants for the PC/XT and terminals, the lock light area above the numeric keypad is blank. The keys on most Enhanced Keyboards consist of a separate base (stem) and a detachable printed cover, but some used single-piece key. Double-piece key eventually became optional, as some customers found the single-piece design less likely to be lost or stolen. Virtually all Enhanced Keyboards have a small speaker grille on their bottom surfaces; however, only a few variants actually include a speaker (the keyboards of the RS/6000 workstations being the primary example).
Distinctive sound
The Model M’s buckling-spring key mechanism has a distinctive sound described as «clicky». Most users accepted the sound as an inherent part of using the keyboards. Some users, including present-day enthusiasts, consider it a reminder of the Model M’s sturdiness compared to other manufacturers’ quieter but cheaper and less durable rubber-dome keyboards (many of which were made to resemble the Model M).
Some customers requested quieter keyboards for situations requiring them (e.g. libraries and medical facilities). IBM responded by producing Quiet Touch Keyboards with rubber dome switches instead of buckling springs, and with a different style of key stem. While not as prized today as buckling-spring Model M’s, many Quiet Touch Keyboards are still in service and are considered among the best rubber dome keyboards made. A later initiative to provide a quieter Model M, without conceding to rubber domes, was the Soft Touch Keyboard made by Lexmark for IBM from 1995–96, whose buckling springs were greased to reduce their volume.
International Enhanced Keyboards
In contrast to IBM’s previous keyboards, the Enhanced Keyboard was produced with two different physical key arrangements: one for US English and another for Europe, the Middle East and Africa. (Far Eastern IBM keyboards, with unique designs, were manufactured by IBM Japan.) This likely mirrored tastes in typewriter layouts: Non-U.S. keyboards often included dedicated keys for accented characters in other languages; the US market preferred large shift and return keys, considered easier for typing. For the international market, IBM had a 102-key layout (later known as the ISO layout) seemingly inspired by the 5251’s key layout. These keyboards were produced in IBM’s plant in Greenock, Scotland (where they also made PCs, terminals and laptops for the non-US/non-Japanese markets). The standard Enhanced Keyboard had the necessary membrane contacts to support both ANSI and ISO layouts, so the only physical difference aside from the different keycaps was the location of the spring/hammer assemblies to accommodate the appropriate keys.
Unlike in the US, the Greenock plant remained under IBM’s control after the Lexmark divestiture. IBM continued to manufacture ISO layout Model M’s, but followed the trend of Lexmark’s keyboards and adopted the ‘blue’ logo and drainage holes. Unlike their American keyboards, IBM changed these designs without changing their part numbers, meaning that for each ISO part number there are three distinct variations. Around 1994 they switched from a 1391401-based design to a 52G9xxx-based one. By 1995 or 1996, they had changed to a 42H1292-style design. Due to more stringent regulations in the EU/UK compared to the US, many Greenock-made Model M’s also have electrically-grounded space bars made out of ABS (often easily recognisable by yellowing) to prevent static electricity (often caused by monitors, then based on cathode ray tube technology) from building up and discharging into the user. Furthermore, Greenock-made M’s with drainages holes do not have drainage channels inside.
In addition to the usual 13914xx part numbers, IBM also manufactured keyboards under a wide variety of seemingly random part numbers. They also made some rubber-dome variants, most of whose part numbers begin with 71G.
US-layout keyboards were also made in Greenock. All 42H1292s made after 1996 were produced there. Earlier variants were also produced in Greenock, sometimes with the same part number, but there were some Greenock-specific US keyboards; for example, the 1396790 was a standard 101-key variant based either on the 1391401 or 52G9658, depending on its year of manufacture. The different part number seems to have indicated a US layout keyboard for customers in Europe, the Middle East and Africa (EMEA). The 1396790 is common in the Netherlands and other countries in the EMEA regions where the US layout is popular. The 1394950 was an Industrial model made from 1996 on, and was largely identical to the earlier 1394946 with one distinguishing feature: instead of the hard plastic label with raised silvered letters, it has a simple flat sticker.
Starting in 1986, IBM also made keyboards at their Mexican PC manufacturing center in Guadalajara, Mexico. These keyboards were largely intended for the Latin American market, although there were also some for the French Canadian and US markets. Lexmark eventually took control of keyboard production there, producing a number of Mexican-made Lexmark Model M’s. Production in Guadalajara likely ceased in 1996 when Lexmark stopped making keyboards. Unlike Greenock Model M’s, Mexico-made Model M’s have no defining characteristics from IBM US/Lexmark Model M’s. Mexico-made Model M’s should not be confused with the Maxi Switch–made IBM Model M13 derivatives made in a different plant in a different part of the country.
As with US Model M’s, international layout Model M’s left production in 1999. For most Model M sub-variants (with the main exception of the M15) there were ISO versions, although they are generally rarer.
Earthed (grounded) space bar from a 1996 Greenock Model M
Практические работы для устранения академической задолженности по дисциплине «Английский язык» за VIII семестр для специальности «Технология продукции общественного питания»
Практические работы для устранения академической задолженности по дисциплине «Английский язык» за VIII семестр для специальности «Технология продукции общественного питания» для студентов группы Тп41 ГБПОУ СО ТПК
Просмотр содержимого документа
«Практические работы для устранения академической задолженности по дисциплине «Английский язык» за VIII семестр для специальности «Технология продукции общественного питания»»
для устранения академической
задолженности за VIII семестр
По дисциплине «Английский язык»
Преподаватель: Лихачева С.В.
What is а Personal Computer?
Personal computers (РС) are small, relatively inexpensive computers for an individual user. Their price can bе from а few hundred dollars to thousands of dollars. All are based on the microprocessor technology that enables manufacturers to put an entire CPU on one chip. Personal computers are used in business for word processing, accounting, desktop publishing. At home, the most popular use for personal computers is for playing games. Personal computers first appeared in the late 1970s. One of the first and most popular personal computers was the Apple 11, made in 1977 bу Apple Computer. Then, in 1981, IВМ (International Business Machines) made its first personal computer, known as the IВМ РС. The IВМ РС quickly became the most popular personal computer.
Computer programs are called software. Software is instructions for hardware (the machines) to do work. Software is often divided into two categories:
Systems software: the operating system аnd all the utilities that еnablе the computer to function.
Applications software: programs that do real work for users. For example, word processors, spreadsheet programmes, and games are applications software.
What are Peripheral Devices?
Peripheral devices are computer devices, such as а CD-ROM drive or printer. Peripheral devices саn bе external, such as а mouse, keyboard, printer, monitor, and scanner. Peripheral devices саn bе internal, such as а CD-ROM drive or internal modem.
microprocessor = chip – микрonроцессор
disk drive – дисковод
CD-R.OM drive- дисковод ми компакт-дисков
Answer the questions:
1. What is а personal computer?
2. What are personal computers used for?
3. What were the first models of РС?
4. What are computer programs called?
5. What is hardware?
Computer keyboard is the set of typewriter-like keys that enables you to enter data into а computer. Computer keyboards are similar to electric-typewriter keyboards but contain additional keys. The keys on computer keyboards are often classified as follows:
The standard layout of letters, numbers, and punctuation is called QWERТYkeyboard because the first six keys оn the top row of letters spell QWERТY. The QWERТY keyboard was designed in the 1800s for mechanical typewriters.
There is no standard computer keyboard, although many manufacturers imitate the keyboards of PCs. There are actually three different РС keyboards: the original РС keyboard, with 84 keys; the АТ keyboard, also with 84 keys; and the enhanced keyboard, with 1О 1 keys. The three differ somewhat in the placement of function keys, the Control key, the Return key, and the Shift keys.
In addition to these keys, IBM keyboards contain the following keys:
Page Up, Page Down, Ноте, End, Insert, Pause, Num Lock, Scroll Lock, Break, Caps Lock, Print Screen.
What is а Hard Disk Drive (HDD)?
Hard disk drive is the mechanism that reads and writes data on а hard disk. Hard disk drive has many inflexiblе platters (discs) coated with magnetic material. Read/write heads can record computer data on these discs. А typical hard disk rotates at 3,600 revolutions per minute, and the read/write heads ride over the surface of the disk on а cushion of air 25 micron deep. Hard disk drives (HDDs) for PCs generally have seek times of about 12 milliseconds or less. Hard disk drives are sometimes called Winchester drives. Winchester is the name of one of the first popular hard disk drive technologies developed Ьу IBM in 1973. Monitor with cathode ray tube
Monitor is another term for display screen. First monitors were black-and-white with cathode ray tube. Nowadays most monitors are colour monitors. Besides, colour LCD monitors are becoming more and more popular. Monitors have different screen sizes. Like televisions, screen sizes are measured in inches from one corner of the screen to the opposite corner diagonally.А typical size for small monitors is 14 inches. Monitors that are 16 or more inches diagonally are often called full-page monitors.
alphanumeric keys- буквенно-цифровые клавиши
Answer the questions:
1. How are the keys on computer keyboards classified?______________________________
2. How is the standard layout of keys on а keyboard called?___________________________
3. How many keys has enhanced keyboard?________________________________________
4. How are hard disk drives sometimes called?_______________________________________
5. What is hard disk drive?_______________________________________________________
6. How are monitor screen sizes measured?________________________________________
А mouse is а device to move the cursor or pointer on а display screen. As you move the mouse, the pointer on the display screen moves in the same direction. You can roll а mouse on а hard, flat surface. It looks а bit like а real mouse because the connecting wire looks like а mouse tail. Mice usually have two buttons and sometimes as many as three, which have different functions depending on what program is running. Some newer mice also have а scroll wheel for scrolling through long documents. The mouse was invented bу Douglas Engelbart of Stanford Research
Center in 1963. The mouse frees the user from using the keyboard. Mouse is important because you саn simply point to objects on the screen and click а mouse button. Мiсе саn be:
1. Mechanical with а rubber or metal ball that can roll in all directions. Mechanical sensors in the mouse detect the direction the ball is rolling and move the screen pointer.
2. Optomechanical with optical sensors to detect motion of the ball.
3. Optical with а laser to detect the mouse’s movement. Optical mice have no mechanical moving parts but they are more expensive.
4. Cordless infrared mice send infrared or radio waves to communicate with the computer.
Мicroprocessor is а silicon chip that contains а CPU. The terms microprocessor and CPU are used interchangeably. At the heart of all personal computers sits а microprocessor.
Мicroprocessors have basic characteristics:
Computational bandwidth: The number of bits processed in а single instruction. Speed: Given in megahertz (MHz), the speed determines how many instructions per second the processor can execute.
Printer is а device that prints text or illustrations on paper. There are many different types of printers but the most widely used printers are:
Dot-matrix printer strikes pins against an ink ribbon. Each pin makes а dot, and combinations of dots form letters and illustrations.
Ink-jet printer sprays ink at а sheet of paper. Ink-jet printers produce high-quality text and graphics.
Laser printer uses the sаmе technology as сору machines. Laser printers produce very high quality text and graphics. The speed of printers varies widely. Dot-matrix printers саn print up to 500 letters per second, and laser printers can print froт about 4 to 20 text pages per minute.
What ls an Optical Scanner?
Optical scannеr is а device that can read text or illustrations printed оn paper and translate the information into а form the computer can use. А scannеr works bу digitizing ап image. Sоmе scanners are sтall hand-held devices that you тоvе across the paper. Тhese hand held scanners are often called half-page scanners because they can only scan 2 to 5 inches at а time. Наnd-held scanners are good for scanning small pictures and photos, but they are difficult to use if you need to scan а large page. Larger scanners include machines into which you can feed sheets of paper. These are called sheet-fed scanners. Sheet-fed scanners are excellent for loose sheets of paper, but they are unable to handle bound documents. Large scanners are called flatbed scanners. They consist of а board оn which you lay books, magazines, and other documents that you want to scan.
CD-ROMs cannot bе erased and filled with new data. То read а CD, you need а CD-ROM player. АВ CD-ROMs have а standard size and forтat, so you can load any type of CD-ROM into any CD-ROM player. In addition, CD-ROM players are сараblе of playing audio CDs. CD-ROMs are good to store information that requires large storage capacity.
What ls Operating System?
Every computer must have ап operating system to run other programmes. Operating system is the most important programme that runs on а computer. Operating systems perform basic tasks, such as recognizing input from the keyboard, sending output to the display screen, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers. Operating systems provide а software platform on top of which other programmes, called application programmes, can run. The application programmes must be written to run on top of а particular operating system. Your choice of operating system, therefore, determines to а great extent the applications you can run. For PCs, the most popular operating systems are DOS, OS/2, and Windows.
pointer- указатель (курсор в форме стрелки, следующий за движениями мыши)
computational bandwidth- диапазон вычислительных возможностей
dot-matrix printer- матричный принтер
ink-jet printer- струйный принтер
Answer the questions:
1. What is а mouse?______________________________________________________
2. How many buttons are there on а serial mouse?_______________________________
3. Who invented а mouse?___________________________________________________
4. What are the types of mice?_________________________________________________
5. What are the basic characteristics of microprocessors?_____________________________
6. What are the types of the most widely used printers?______________________________
7. What printers are the fastest?________________________________________________
8. What is an optical scanner?___________________________________________________
9. What is а floppy disk?_______________________________________________________
10. What is CD-ROM?________________________________________________________
11. What basic tasks do operating systems perform?_________________________________
12. What are the most popular operating systems?___________________________________
13. What are application programmes?____________________________________________
1) Personal computer______________ used in business for _____________________________________
2) At home, the most popular use for personal computers ______________ for ____________________
3) The ___________ ____________________________ bу _________________________________
of __________________ _____________________________________Center in ________________.
4) The ________________mouse ________________ а laser to _________________ the mouse’s
5) Some ________________________ also _______________ а scroll _________________ for scrolling
through ______________________________ documents.
6) Software is __________________________________for _________________________to do work.
7) What is hardware?_______________________________________________________________
8) Monitors that are 16 or more inches ____________________________ ________________ often
called _____________________________________ monitors.
9) Software is a ____________________________________.
10)The standard ____________________ of letters, ________________, and numbers _____________
called _______________ because the first ________ keys оn the top row of letters ________________
Учебное пособие для студентов компьютерных специальностей
Учебное пособие по дисциплине «Профессиональный английский язык» раздается студентам в печатном виде в начале изучения курса. Каждый студент должен выполнять задания по мере изучения дисциплины.
Каждое задание должно выполняться студентом самостоятельно в процессе изучения аналогичного раздела курса. В учебном пособии подобраны задания различной сложности. Учебное пособие содержит профессионально-ориентированные тексты, новые слова к тема, вопросы к текстам.
Просмотр содержимого документа
«Учебное пособие для студентов компьютерных специальностей»
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И НАУКИ ДНР
Донецкий политехнический техникум
по дисциплине «Английский язык»
«Программирование в компьютерных системах»
Методические указания студентам по работе с учебным пособием………4
Раздел 1: Компьютер и его комплектующие…………………………………6
Периферийные устройства…………………………………………………. 8
Хост (компьютер, подключенный к сети)…………………………………..20
ISP (Internet Service Provider)…………………………………………………21
Билл Гейтс – основатель Microsoft…………………………………………..24
Английский язык – это язык высоких технологий, программирования и Интернета. Поэтому в профессии программиста роль иностранного языка постепенно начинает играть одну из лидирующих:
так как все языки программирования, являющиеся средством работы программиста, основаны на лингвограмматических конструкциях английского языка;
от уровня владения зависит быстрота запоминания и истолкования вновь осваиваемых конструкций языков программирования;
у программиста, владеющего английским языком, улучшается реакция при общении с операционной системой в процессе интерактивного диалога;
намного быстрее решаются проблемы отладки и редактирования программы;
быстрее осознается процесс реакции системы на ошибочные ситуации и многие другие, чисто профессиональные аспекты деятельности программиста.
Следовательно, владение программистом профессионально ориентированным английским языком является одной из составляющих его профессиональной компетентности.
Цель учебного пособия – развить у студентов навыки чтения и перевода, извлечение, обработки и передачи информации на английском языке, а также подготовить к экзаменам по английскому языку.
Учебное пособие содержит: профессионально-ориентированные тексты, новые слова по темам, вопросы по текстам.
Учебное пособие состоит из двух разделов:
— первый раздел: Компьютер и его комплектующие, который включает следующие темы:
— второй раздел: Интернет, который включает следующие темы:
— Хост (компьютер, подключенный к сети)
— ISP (Internet Service Provider)
Билл Гейтс – основатель Microsoft
Выполнение студентами заданий способствуют активизации самостоятельной работы, развитию творческих способностей, формирует высокую степень ответственности за конечный результат, повышает мотивацию к совершенствованию знаний.
Положительным при выполнении заданий из учебного пособия является закрепление пройденного материала, стимулирование студента к изучению дополнительной литературы по каждому разделу.
Методические указания студентам по работе с учебным пособием.
Учебное пособие по дисциплине «Профессиональный английский язык» раздается студентам в печатном виде в начале изучения курса. Каждый студент должен выполнять задания по мере изучения дисциплины.
Каждое задание должно выполняться студентом самостоятельно в процессе изучения аналогичного раздела курса. В учебном пособии подобраны задания различной сложности. Учебное пособие содержит профессионально-ориентированные тексты, новые слова к тема, вопросы к текстам. Некоторые задания можно выполнить, имея минимальные знания и навыки по дисциплине, решение других требует приобретения знаний, умений и навыков в процессе практических занятий, самостоятельного знакомства с литературой.
При выполнении заданий необходимо внимательно прочитать текст задания, чтобы не допустить ошибок при его выполнении.
По завершении изучения раздела, студенты самостоятельно проверяют задания и результаты заносятся преподавателем в журнал. Преподаватель проверяет задания студентов, разбирает общие ошибки, дает рекомендации по их исправлению.
W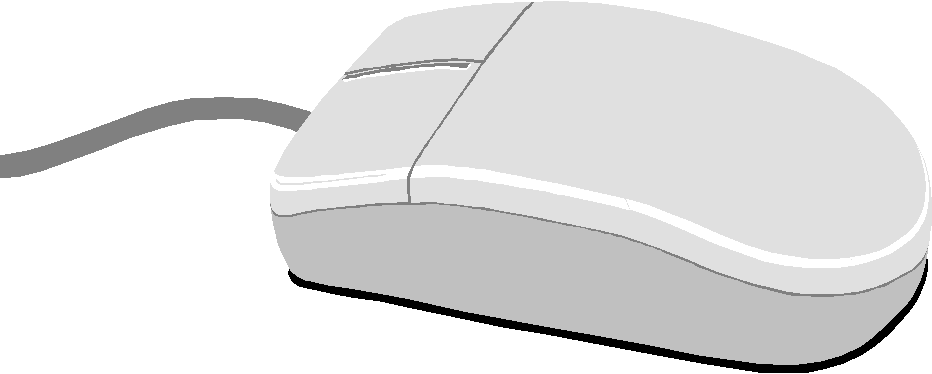
P

C
Systems software: the operating system and all the utilities that enable the computer to function.
Applications software: programs that do real work for users. F or example, word processors, spreadsheet programmes, and games are applications software.
What is Hardware?
Hardware are computer components that you can touch, like disks, disk drives, monitors, keyboards, printers, boards, and chips. But you cannot touch software. Software exists as ideas, concepts, and symbols. A computer without software is dead — you need software to make the computer work.
What are Peripheral Devices?
Peripheral devices are computer devices, such as a CD-ROM drive or printer. Peripheral devices can be external, such as a mouse, keyboard, printer, monitor, and scanner. Peripheral devices can be internal, such as a CD-ROM drive or internal modem.
individual — индивидуальный, личный
microprocessor = chip — микропроцессор
CPU (central processing unit) — центральный процессор
word processig — электронная обработка текста
accounting — бухгалтерское дело
desktop publishing — настольные издательские средства
software — компьютерные программы, программное обеспечение
hardware — оборудование, «железо»
systems software — системное программное обеспечение
applications software — прикладные программы
utility — обслуживающая программа, утилита
word processor — текстовой процессор (программа подготовки и редактирования текста)
spreadsheet — программа, работающая с таблицами
disk drive — дисковод
monitor — монитор printer — принтер
chip — процессор, микросхема
peripheral device — периферийное устройство
CD—ROM drive — дисководдля компакт-дисков internal modem — встроенный модем.
What is a personal computer?
What are personal computers used for?
What were the first models of PC?
What are computer programs called?
What is hardware?
Computer keyboard is the set of typewriter-like keys that enables you to enter data into a computer. Computer keyboards are similar to electric-typewriter keyboards but contain additional keys. The keys on computer keyboards are often classified as follows:
alphanumeric keys — letters and numbers
punctuation keys — comma, period, semicolon, and so on.
special keys — function keys, control keys, arrow keys, Caps Lock key, and so on.
The standard layout of letters, numbers, and punctuation is called QWERTY keyboard because the first six keys on the top row of letters spell QWERTY. The QWERTY keyboard was designed in the 1800s for mechanical typewriters.
There is no standard computer keyboard, although many manufacturers imitate the keyboards of PCs. There are actually three different PC keyboards: the original PC keyboard, with 84 keys; the AT keyboard, also
W
In addition to these keys, IBM keyboards contain the following keys: Page Up, Page Down, Home, End, Insert, Pause, Num Lock, Scroll Lock, Break, Caps Lock, Print Screen.
W
Hard disk drive is the mechanism that reads and writes data on a hard disk. Hard disk drive has many inflexible platters (discs) coated with magnetic material. Read/write heads can record computer data on these discs. Atypical hard disk rotates at 3,600 revolutions per minute, and the read/ write heads ride over the surface of the disk on a cushion of air 25 micron deep. Hard disk drives (HDDs) for PCs generally have seek times of about 12 milliseconds or less. Hard disk drives are sometimes called Winchester drives. Winchester is the name of one of the first popular hard disk drive technologies developed by IBM in
What is a Monitor?
M
alphanumeric keys — буквенно-цифровые клавиши
punctuation keys — клавиши пунктуации
semicolon — точка с запятой
function key — функциональная клавиша
control key — клавиша управления
arrow key — клавиша с изображением стрелки
Caps Lock key — клавиша фиксации регистра заглавных букв
enhanced keyboard — расширенная клавиатура
return key — клавиша возврата каретки
shift key — клавиша переключения регистра
num lock — фиксация числового регистра
revolutions per minute — оборотов в минуту
cushion of air — воздушная подушка
seek time — время поиска
cathode ray tube — электронно-лучевая трубка
How are the keys on computer keyboards classified?
How is the standard layout of keys on a keyboard called?
How many keys has enhanced keyboard?
How are hard disk drives sometimes called?
What is hard disk drive?
How are monitor screen sizes measured?
What is a Mouse?
A mouse is a device to move the cursor or pointer on a display screen. As you move the mouse, the pointer on the display screen moves in the same direction. You can roll a mouse on a hard, flat surface. It looks a bit like a real mouse because the connecting wire looks like a mouse tail. Mice usually have two buttons and sometimes as many. as three, which have different functions depending on what program is running. Some newer mice also have a scroll wheel for scrolling through long documents.
The mouse was invented by Douglas Engelbart of Stanford Research Center in 1963. The mouse frees the user from using the keyboard. Mouse is important because you can simply point to objects on the screen and click a mouse button.
1. Mechanical with a rubber or metal ball that can roll in all directions. Mechanical sensors in the mouse detect the direction the ball is rolling and move the screen pointer.
2. Optomechanical with optical sensors to detect motion of the ball.
3. Optical with a laser to detect the mouse’s movement. Optical mice have no mechanical moving parts but they are more expensive.
4. Cordless infrared mice send infrared or radio waves to communicate with the computer.
What is a Microprocessor?
Microprocessor is a silicon chip that contains a CPU. The terms microprocessor and CPU are used interchangeably. At the heart of all personal computers sits a microprocessor.
Microprocessors have basic characteristics:
C
Speed: Given in megahertz (MHz), the speed determines how many instructions per second the processor can execute.
What is a Printer?
Printer is a device that prints text or illustrations on paper. There are many different types of printers but the most widely used printers are:
Dot-matrix printer strikes pins against an ink ribbon. Each pin makes a dot, and combinations of dots form letters and illustrations.
Ink-jet printer sprays ink at a sheet of paper. Ink-jet printers produce high-quality text and graphics.
L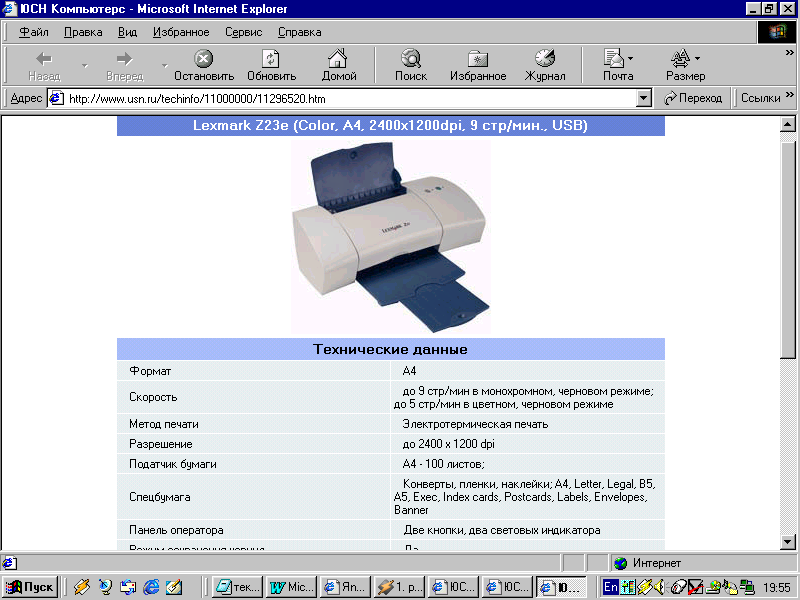
What is an Optical Scanner?
Optical scanner is a device that can read text or illustrations printed on paper and translate the information into a form the computer can use. A scanner works by digitizing an image.
Some scanners are small hand-held devices that you move across the paper. These hand held scanners are often called half-page scanners because they can only scan 2 to 5 inches at a time. Hand-held scanners are good for scanning small pictures and photos, but they are difficult to use if you need to scan a large page.
Larger scanners include machines into which you can feed sheets of paper. These are called sheet-fed scanners. Sheet-fed scanners are excellent for loose sheets of paper, but they are unable to handle bound documents.
L
What is a Floppy Disk?
A soft magnetic disk is called floppy because it flops if you bend it. Floppy disks (often called floppies or diskettes) have less storage capacity than hard disks butyou can remove them from a disk drive and they are portable. Disk drives forfloppy disks are called floppy drives.
Most common floppies come in size 3,5-inch. They have a rigid plastic envelope. Despite their small size, floppies have a large storage capacity — from 400K to 1.4MB of data. The most common sizes for PCs are 1.44MB (high-density).
CD-ROM is an abbreviation for Compact Disc- Read-Only Memory, a type of optical disk capable of storing large amounts of data — up to 1GB, although the most common size is 650MB (megabytes). A single CD-ROM has the storage capacity of 700 floppy disks, enough memory to store about 300,000 text pages.
CD-ROMs cannot be erased and filled with new data. To read a CD, you need a CD-ROM player. All CD-ROMs have a standard size and format, so you can load any type of CD-ROM into any CD-ROM player. In addition, CD-ROM players are capable of playing audio CDs.
CD-ROMs are good to store information that requires large storage capacity.
What is Operating System?
Every computer must have an operating system to run other programmes. Operating system is the most important programme that runs on a computer. Operating systems perform basic tasks, such as recognizing input from the keyboard, sending output to the display screen, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers.
Operating systems provide a software platform on top of which other programmes, called application programmes, can run. The application programmes must be written to run on top of a particular operating system. Your choice of operating system, therefore, determines to a great extent the applications you can run. For PCs, the most popular operating systems are DOS, OS/2, and Windows.
to run a programme — работать с программой
scroll wheel — колесико или кнопка на мыши для прокрутки длинных текстов
to click — сделать щелчок мышью
pointer — указатель (курсор в форме стрелки, следующий за дви- кениями мыши)
computational bandwidth — диапазон вычислительных возмож- юстей
dot—matrix printer — матричный принтер
pin — штифт, игла
laser printer — лазерный принтер
flatbed scanner — планшетный сканер
storage capacity — емкость запоминающего устройства
What is a mouse?
How many buttons are there on a serial mouse?
Who invented a mouse?
What are the types of mice?
What are the basic characteristics of microprocessors?
What are the types of the most widely used printers?
What printers are the fastest?
What is an optical scanner?
What is a floppy disk?
What basic tasks do operating systems perform?
What are the most popular operating systems?
What are application programmes?
Задание: Что из ниже перечисленного относится к оборудованию, а что к программному обеспечению?
14. Applications software
What is Internet?
Internet is a global network connecting millions of computers. More than 100 countries are linked into exchanges of data, news and opinions.
Each Internet computer, called a host, is independent. Its operators can choose which Internet services to use. The Internet is not synonymous with World Wide Web.
A host is a computer system that is accessed by a user when there are two computer systems connected by modems and telephone lines. The computer system that contains the data is called the host, and the computer at which the user sits is called the remote terminal.
What is World Wide Web?
A system of Internet servers that support specially formatted documents. The documents are formatted in a markup language called HTML (HyperText Markup Language) that supports links to other documents, as well as graphics, audio, and video files. This means you can jump from one document to another simply by clicking the mouse button.
There are several applications called Web browsers that make it easy to access the World Wide Web. Two of the most popular browsers are Netscape Navigator and Microsoft’s Internet Explorer.
What is the Difference Between the Internet and the World Wide Web?
Many people use the terms Internet and World Wide Web (or simply the Web) interchangeably, but in fact the two terms are not synonymous. The Internet and the Web are two separate but related things.
The Internet connects millions of computers together globally, forming a network in which any computer can communicate with any other computer as long as they are both connected to the Internet. Information travels over the Internet in many languages known as protocols.
The World Wide Web, or simply Web is built on top of the Internet. The Web also utilizes browsers, such as Internet Explorer or Netscape, to access Web documents called Web pages. Web documents also contain graphics, sounds, text and video.
The Web is just one of the ways that information can be sent and received over the Internet. Internet is used for e-mail, not the Web. So the Web is just a portion of the Internet, but the two terms are not synonymous and should not be confused.
Who Invented the World Wide Web?
Tim Berners-Lee (born 1955) invented the World Wide Web. His first version of the Web was a program named «Enquire». At the time, Berners-Lee was working at CERN, the European Particle Physics Laboratory located in Geneva, Switzerland. He invented the system as a way of sharing scientific data (and other information) around the world, using the Internet, a world-wide network of computers and hypertext documents. He wrote the language HTML (HyperText Mark-up Language), the basic language forthe Web, and devised URL’s (universal resource locators) to designate the location of each web page. HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) was his set of rules for linking to pages on the Web. After he wrote the first browser in 1990, the World Wide Web was up and going. Its growth was (and still is) phenomenal, and has changed the world, making information more accessible than ever before in history.
Berners-Lee is now a Principal Research Scientist at the Laboratory for Computer Science at MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) and the Director of the W3 Consortium.
global network — глобальная сеть
to link — соединять, связывать
host — хост (компьютер, подключенный к сети Интернет)
to gain, get access — получить доступ
remote terminal — дистанционный (удаленный) терминал
hypertext document — гипертекстовый документ
markup — разметка документа в
HTML-формате HTML (HyperText Markup Language) — язык
HTML (стандартный язык, используемый для создания страниц WWW)
URL (Universal Resource Locator) — универсальный указатель информационного ресурса (стандартизованная строка символов, указывающая местонахождение документа в сети Internet)
application — приложение, прикладная программа
browser (Web browser) — Web-броузер (программы для просмотра Web-страниц в сети Internet)
as long as — пока; до тех пор, пока
There are many ways to gain access the Internet. One of the ways is to gain access with the help of commercial Internet Service Provider (ISP). ISPs are also called JAPs (Internet Access Providers).
ISP is a company that provides access to the Internet. For a monthly fee, the service provider gives you a username, password and access phone number. Equipped with a modem, you can then log on to the Internet and browse the World Wide Web, and send and receive e-mail.
What is a Browser?
Short for Web browser, a software application used to locate and display Web pages. The two most popular browsers are Netscape Navigator and Microsoft Internet Explorer. Both of these are graphical browsers, which means that they can display graphics as well as text. In addition, most modern browsers can present multimedia information, including sound and video.
E-mail is the abbreviation for electronic mail, the transmission of messages over communications networks. The messages can be notes entered from the keyboard or electronic files stored on disk. Most computer networks have an e-mail system. All Internet Service Providers (ISPs) offer e-mail services so that you can exchange mail with other us ers. Usually, it takes only a few seconds or minutes for mail to arrive at its destination. Companies that are fully computerized widely use of e-mail because it is fast, flexible, and reliable.
Sent messages are stored in electronic mailboxes until the recipient fetches them. To see if you have any mail, you may have to check your electronic mailbox periodically, although many systems tell you when mail is received. After reading your mail, you can store it in a text file, forward it to other users, or delete it.
What is IP Address?
IP address is an identifier for a computer in network. Networks using the TCP/IP protocol route messages based on the IP address of the destination. IP address is written as four numbers separated by periods. Each number can be zero to 255. For example, 1.160.10.240 could be an IP address.
What is Web Server?
Web server is a computer that delivers (serves up) Web pages. Any computer can be turned into a Web server by installing server software and connecting the machine to the Internet. Every Web server has an IP address and possibly a domain name.
What is Domain Name?
A name that identifies one or more IP addresses. There are only a limited number of such domains. For example:
gov — Government agencies
edu — Educational institutions
org — Organizations (nonprofit)
com — commercial business
net — Network organizations
communication network — сеть связи
IP (Internet protocol) — Internet-протокол
IP address — IP-адрес (используется для идентификации узла в сети и для определения информации маршрутизации; состоит из идентификатора сети (network ID) и идентификатора хоста (host ID), присвоенного сетевым администратором)
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol) — протокол управления передачей IP-адреса
to route messages — прокладывать маршрут передачи сообщения
What is Internet?
What is World Wide Web?
What is Web browser?
What is Internet provider?
What are the types of domain names?
Задание: Прочтите, переведите и ответьте на вопросы.
How did Bill Gates begin his career?
What is Microsoft now?
Bill Gates — the Founder of Microsoft
William Henry Gates was born in Seattle, Washington, in 1955. He is a chairman and chief executive officer of the Microsoft Corporation. Gates was the founder of Microsoft in 1975 together with Paul Allen, his partner in computer language development. While attending Harvard in 1975, Gates together with Allen developed a version of the BASIC computer programming language for the first personal computer.
In the early 1980s, Gates led Microsoft’s evolution from the developer of computer programming languages to a large computer software company. This transition began with the introduction of MS-DOS, the operating system for the new IBM Personal Computer in 1981. Gates also led Microsoft towards the introduction of application software such as the Microsoft Word Processor.
Much of Gates’ success is based on his ability to use market strategy. Gates has accumulated great wealth from his holdings of Microsoft stock. Gates still continues to work personally in product development at Microsoft.
chief executive officer — главный исполнительный директор корпорации (обычно президент)
BASIC — Бейсик (язык программирования)
Word Processor — текстовой процессор (программа подготовки и редактирования текста)
market strategy — рыночная стратегия








