How to add list to list in python
How to add list to list in python
How to Add List to List in Python
Appending an element to the list is a common operation, but when it comes to adding a list to a list, there are two variations to that. The first is whether you want to add all the elements of a list to another list. The second is whether you want to add the complete list to a list as an element.
In this example, we will see both variations, and according to your requirement, you can use one of them. Let’s see the complete tutorial.
Python add a list to list
To add a list to the list in Python, use the list.extend() method. The extend() is a built-in Python function that adds all the items of an iterable (list, tuple, string, etc.) to the end of the list.
The extend() method takes an iterable as an argument and returns the list.
Syntax
Arguments
The extend() method takes an iterable such as list, tuple, string, etc.
Return Value
The extend() method modifies the original list. It doesn’t return any value.
Implementation of adding a list to list
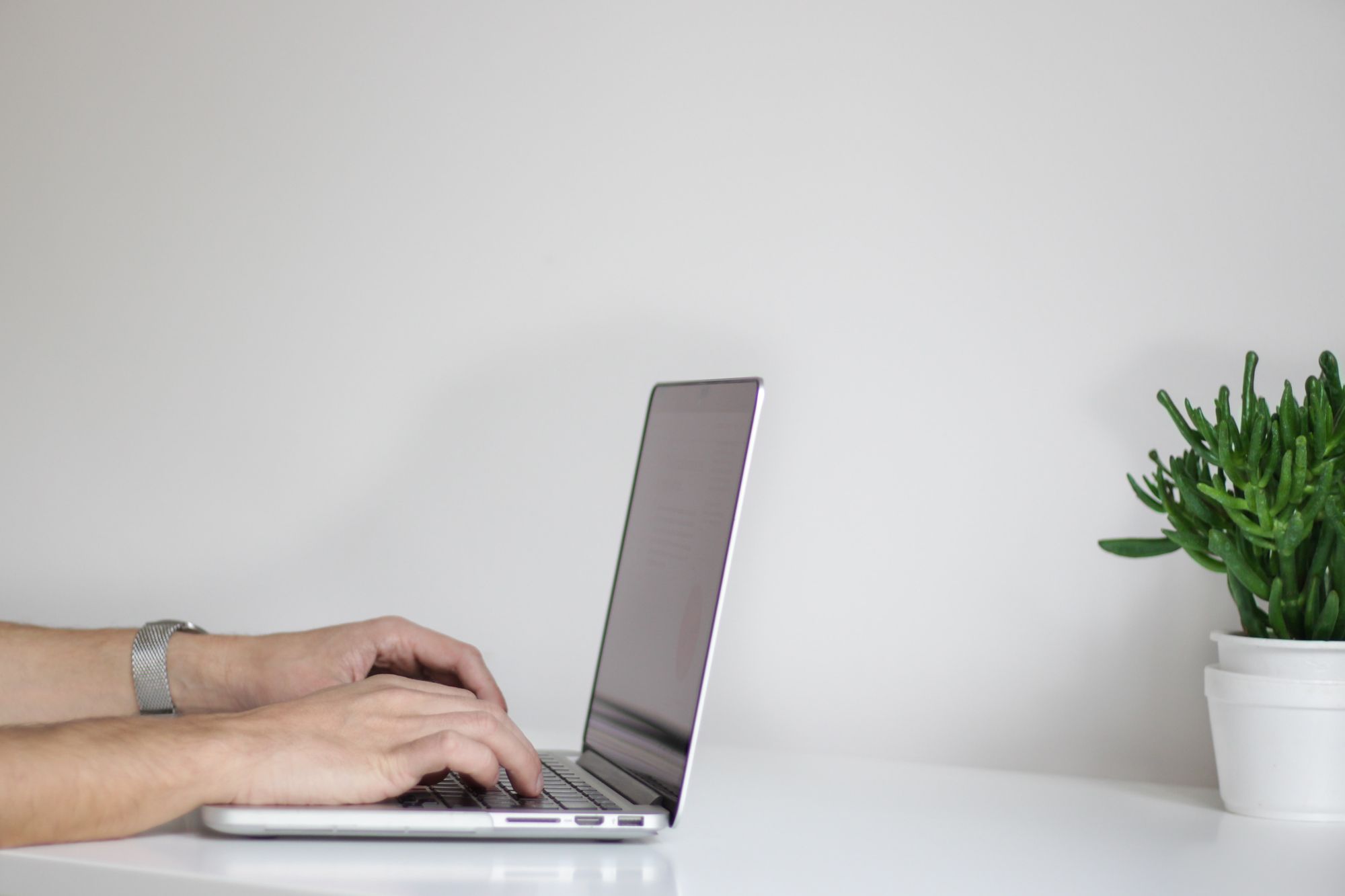
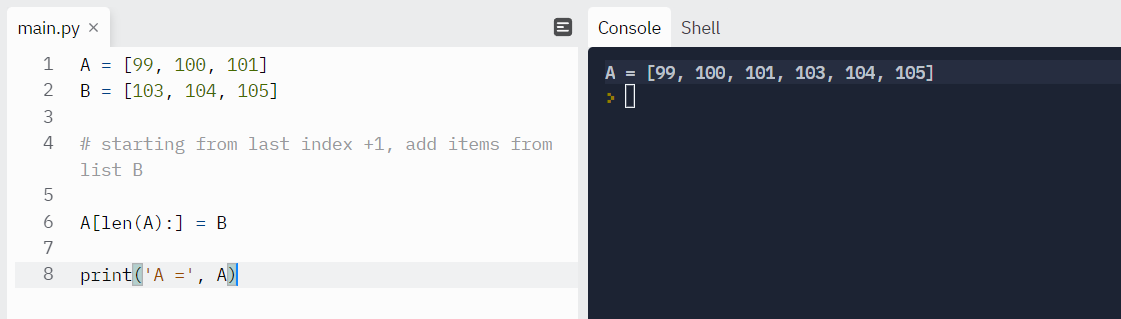
Let’s create two lists using square brackets([ ]).
Now, append the listB to a listA using the extend() function.
Output
You can see that the listA is modified and added all the elements of the listB.
The list.extend() method does not return a new list; it modifies the existing list.
The extend() method does not add the complete list inside the list. Instead, it adds all the elements of the second list to the first list. It does not add the complete list as an element.
Using list.append() to add a list inside of a list
To add a list inside a list as an element, use the list.append() method. The list append() is a built-in Python function that adds a single element to the existing list.
Syntax
Arguments
The list.append() function takes a single item and adds it to the end of the list.
Example
Let’s take the above example, and instead of using extend(), let’s use the append() function.
Output
You can see that it appended a list as an element to the listA.
You can use this approach to add a complete list to a list and not its elements.
That’s it for appending a list to a list tutorial.
How to Append List to Another List in Python? – list.extend(list)
Python – Append List to Another List – extend()
To append a list to another list, use extend() function on the list you want to extend and pass the other list as argument to extend() function.
In this tutorial, we shall learn the syntax of extend() function and how to use this function to append a list to other list.
Syntax – extend()
Following is the syntax of extend() function.
where elements of list2 are appended to the elements of list1.
Example 1: Append a list to another list
In the following example, we will create two lists and append the second list to the first one.
Python Program
Output
The contents of the list1 are modified.
Example 2: Append a list to another list keeping a copy of original list
If you would like to keep the contents of original list unchanged, copy the list to a variable and then add the other list to it.
Python Program
Output
Example 3: Append a list to another list – For Loop
You can also use a For Loop to iterate over the elements of second list, and append each of these elements to the first list using list.append() function.
Python Program
Output
Summary
In this tutorial of Python Examples, we learned how to extend a list with another list appended to it, with the help of well detailed example programs.
Append a List to Another List in Python
This tutorial will demonstrate ways to append a list into an already existing list in Python.
Use the extend() Method to Append a List Into Another List in Python
Python has a built-in method for lists named extend() that accepts an iterable as a parameter and adds it into the last position of the current iterable. Using it for lists will append the list parameter after the last element of the main list.
Please enable JavaScript
The extend() method provides a straightforward way to append a list into an existing list with a simple function call.
Use chain() Function in the itertools Module to Append Into a List in Python
itertools is a Python module containing fast and efficient utility methods for iterables. This module has the function chain() that accepts a variable number of same-type iterables and concatenates them together in sequence based on the parameters.
We can use the chain() function to append multiple lists and form them into a single list.
Use the Concatenation + Operator to Append Multiple Lists in Python
Another simple method of appending multiple lists together is to use the + operator, which supports list concatenation in Python.
Simply perform the concatenation + operation on existing list variables, and the output will be a single combined list in order of the operands inputted in the code.
In summary, three simple and efficient ways to append a list or multiple lists into a main list are extending, chaining, and using the concatenation + operator.
All three solutions perform reliably, and the comparative performance regarding time is relatively trivial, so it’s a matter of personal preference and convenience.
Lists are one of the most useful and versatile data types available in Python. Lists are a collection of arbitrary objects, just like arrays in other programming languages.
In this tutorial you will learn:
Prerequisites
For this tutorial, you need:
Lists in Python
Lists have the following properties that make them powerful and flexible:
How to create a list in Python
You create a list using square brackets in Python.
We can leave them empty and supply values later in the program:
We can also provide values while creating a list:
This would create a list as shown in the image below:

How to access items in a list
As list items are ordered, you can access them using their index.
In the image below, «P» is at index «0» whereas «H» is at index «3».
Let’s write a short program to define a list and access its items:
Defining and printing a list
Output:
Accessing list via negative index.
Output:
How to find the length of a list
We can easily find the length of a list using the len() method.
Finding the length of a list
Output:

Methods to Add Items to a List
We can extend a list using any of the below methods:
How to insert items in a list with insert()
You can insert items in a list at any index using the insert() method. There are more insertion methods and we will look at them later in this post.
Example of insert():
Output:
How to append an item to a list using list.append()
Example:
Output:
⚠️Note that trying to append more than one item gives an exception, as list.append() takes only a single argument.
How to add multiple items in a list using list.extend()
We can add multiple items to a list using the extend() method.
The below example combines two lists into a single list.
Output:
Other ways to extend lists in Python:
List slicing
Slicing allows us to select a range of values in a list.
The syntax is shown below:
list[starting index:upto index]
Let’s see how we can add lists using slicing.
Example:
Output:
Combining arrays using the + operator
Let’s combine two arrays odd and even into a single list using the + operator.
Example:
Output:
How to populate an empty list using for loop and append()
There are two ways to populate empty lists: using a for loop with append() and using list comprehension.
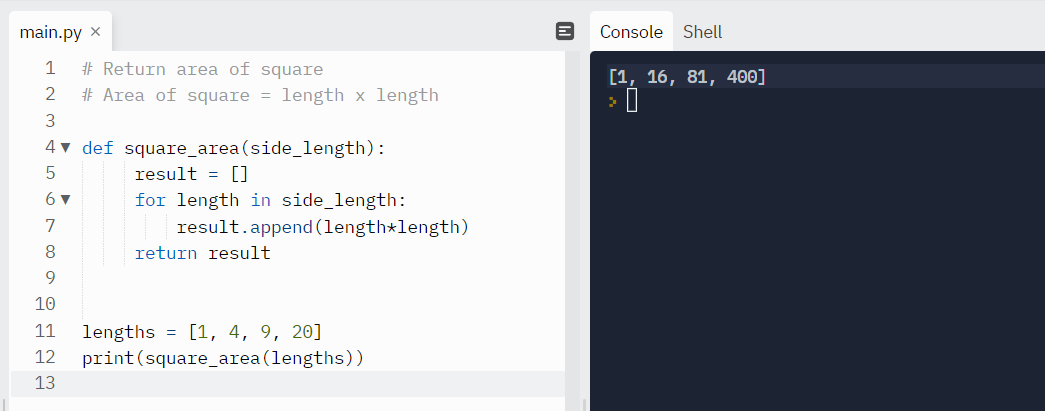
Example:
In this example, we are calculating area of a square and appending the result in an array.
Output:
How to populate an empty list using list comprehension
List comprehension makes the code simple and readable by combining the for loop and append() into a single line.
We can modify our previous example to achieve list comprehension. Notice the commented out lines here:
return [length*length for length in side_length] is list comprehension.
Output:
Both of the methods for filling an empty list are valid and suitable in different scenarios.
Append() vs Insert() vs Extend()
Append() always adds a single item at the end of a list. It is useful when only a single item needs to be inserted.
But if you need to make multiple additions, extend() is a better option as it adds iterable items in one batch.
You should use Insert() when insertion is required at a specific index or range of indexes.
How to Implement a Stack (LIFO)
What is a stack (LIFO)?
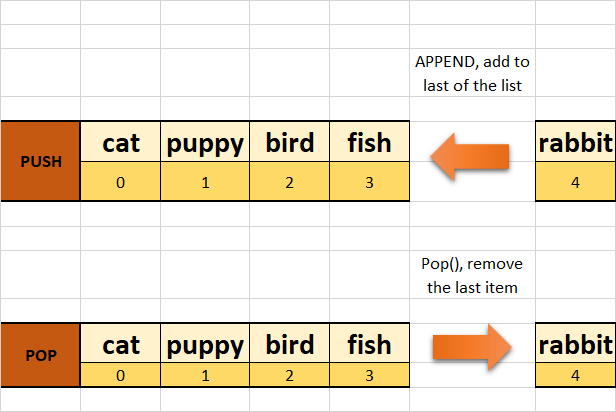
Stack is an arrangement of items that follows a last-in-first-out order. The item that goes last is the one that comes out first. An example of a stack would be the undo/redo stack in photo editing apps.
The diagram below visually explains a stack.
Coding stacks
Let’s create a stack class where we first declare an empty list in the init method.
The push() method appends an item to the list.
The __ len __ method determines the length of the stack.
Lastly, __ repr __ returns the output in a readable format.
Class definition:
Code body:
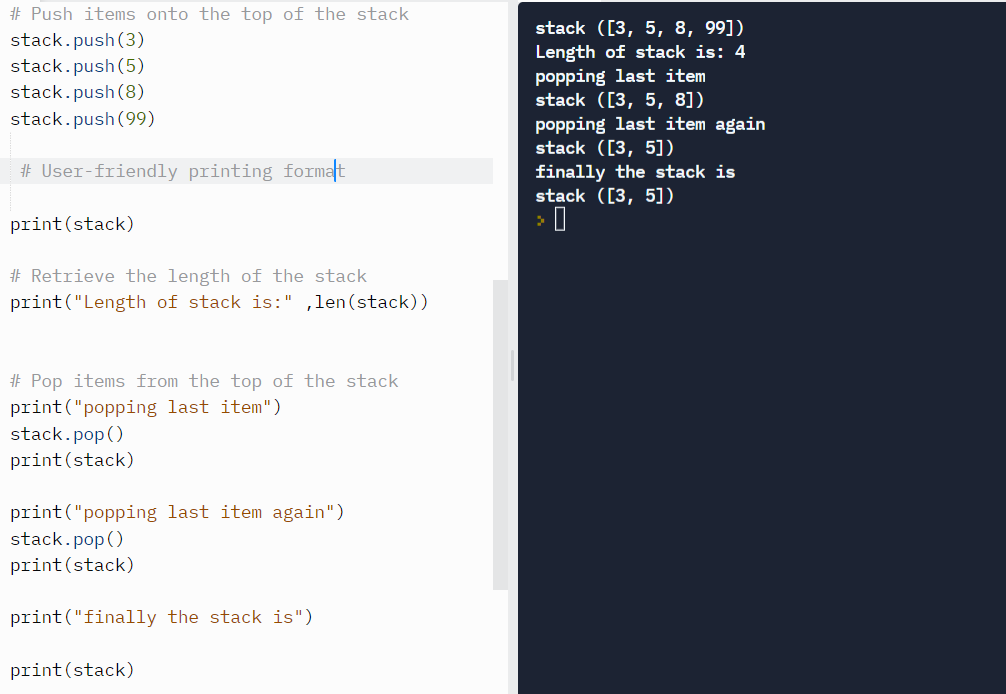
Let’s call the class functions and see the output in action.
Output:
We have added 3, 5, 8, 99 to the stack. Next we printed the stack and its length. Afterwards, we popped two items and printed the stack each time.
Wrapping up
In this tutorial, we learned list creation methods. We also looked at some examples along with a practical implementation of stacks to see how it all works.
What’s your favorite thing you learned from this tutorial? Let me know on Twitter!
Append in Python – How to Append to a List or an Array
Let’s get started!
What are lists in Python? A definition for beginners
An array in programming is an ordered collection of items, and all items need to be of the same data type.
However, unlike other programming languages, arrays aren’t a built-in data structure in Python. Instead of traditional arrays, Python uses lists.
Lists are essentially dynamic arrays and are one of the most common and powerful data structures in Python.
You can think of them as ordered containers. They store and organize similar kind of related data together.
The elements stored in a list can be of any data type.
There can be lists of integers (whole numbers), lists of floats (floating point numbers), lists of strings (text), and lists of any other built-in Python data type.
Although it is possible for lists to hold items of only the same data type, they are more flexible than traditional arrays. This means that there can be a variety of different data types inside the same list.
Lists have 0 or more items, meaning there can also be empty lists. Inside a list there can also be duplicate values.
How to create lists in Python
To create a new list, first give the list a name. Then add the assignment operator( = ) and a pair of opening and closing square brackets. Inside the brackets add the values you want the list to contain.
How lists are indexed in Python
Lists maintain an order for each item.
Each item in the collection has an its own index number, which you can use to access the item itself.
Indexes in Python (and every other modern programming language) start at 0 and increase for every item in the list.
For example, the list created earlier on had 4 values:
The first value in the list, «Jimmy», has an index of 0.
The second value in the list, «Timmy», has an index of 1.
The third value in the list, «Kenny», has an index of 2.
The fourth value in the list, «Lenny», has an index of 3.
To access an element in the list by its index number, first write the name of the list, then in square brackets write the integer of the element’s index.
For example, if you wanted to access the element that has an index of 2, you’d do:
Lists in Python are mutable
In Python, when objects are mutable, it means that their values can be changed once they’ve been created.
Lists are mutable objects, so you can update and change them after they have been created.
Lists are also dynamic, meaning they can grow and shrink throughout the life of a program.
Items can be removed from an existing list, and new items can be added to an existing list.
There are built-in methods for both adding and removing items from lists.
The general syntax looks something like this:
Let’s break it down:
If you wanted to add an extra name to the list created from earlier on, you would do the following:
The general syntax looks like this:
Let’s break it down:
For example, say you had the following list of programming languages:
If you instead had wanted «JavaScript» to be the first item in the list, and then add «Python» as the new item, you would specify the position as 1 :
What if you want to add more than one item to a list at once, instead of adding them one at a time?
Say you have one list that contains only two programming languages:
You then want to add two more languages, at the end of it.
Say you already had two lists, like so:
The general syntax looks like this:
Let’s break it down:
So, the example from above would look like this:
Conclusion
When it is used for adding a list to another list, it creates a list within a list.
If you want to learn more about Python, check out freeCodeCamp’s Python Certification. You’ll start learning in an interacitve and beginner-friendly way. You’ll also build five projects at the end to put into practice what you learned.
Источники информации:
- http://pythonexamples.org/python-append-list-to-another-list/
- http://www.delftstack.com/howto/python/python-append-list-into-another-list/
- http://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-list-append-how-to-add-an-item-to-a-list-in-python/
- http://www.freecodecamp.org/news/append-in-python-how-to-append-to-a-list-or-an-array/