How to add ssh key to gitlab
How to add ssh key to gitlab
How to Generate and Use GitLab SSH Keys
Read more tutorials by Kelvin Kipkorir!
Table of Contents
Repeated username and password prompts are annoying and time-wasting. If you use password authentication with your Gitlab account, each action requires you to send over your credentials, whether as part of the command or through an interactive prompt.
Especially when automating the CI/CD pipelines in GitLab, password authentication can be inefficient and a possible security risk. Why not end your suffering and switch to Secure Shell (SSH) authentication using Gitlab SSH keys? Read on and learn how!
By the end of this tutorial, you will have generated an SSH key pair, used the key to authenticate and publish a new Gitlab project.
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
This tutorial is a hands-on demonstration. To follow along, be sure to prepare the following requirements.
Visual Studio Code (VS Code). The example in this tutorial will be using VS Code 1.62.3.
Generating a Gitlab SSH Key Pair
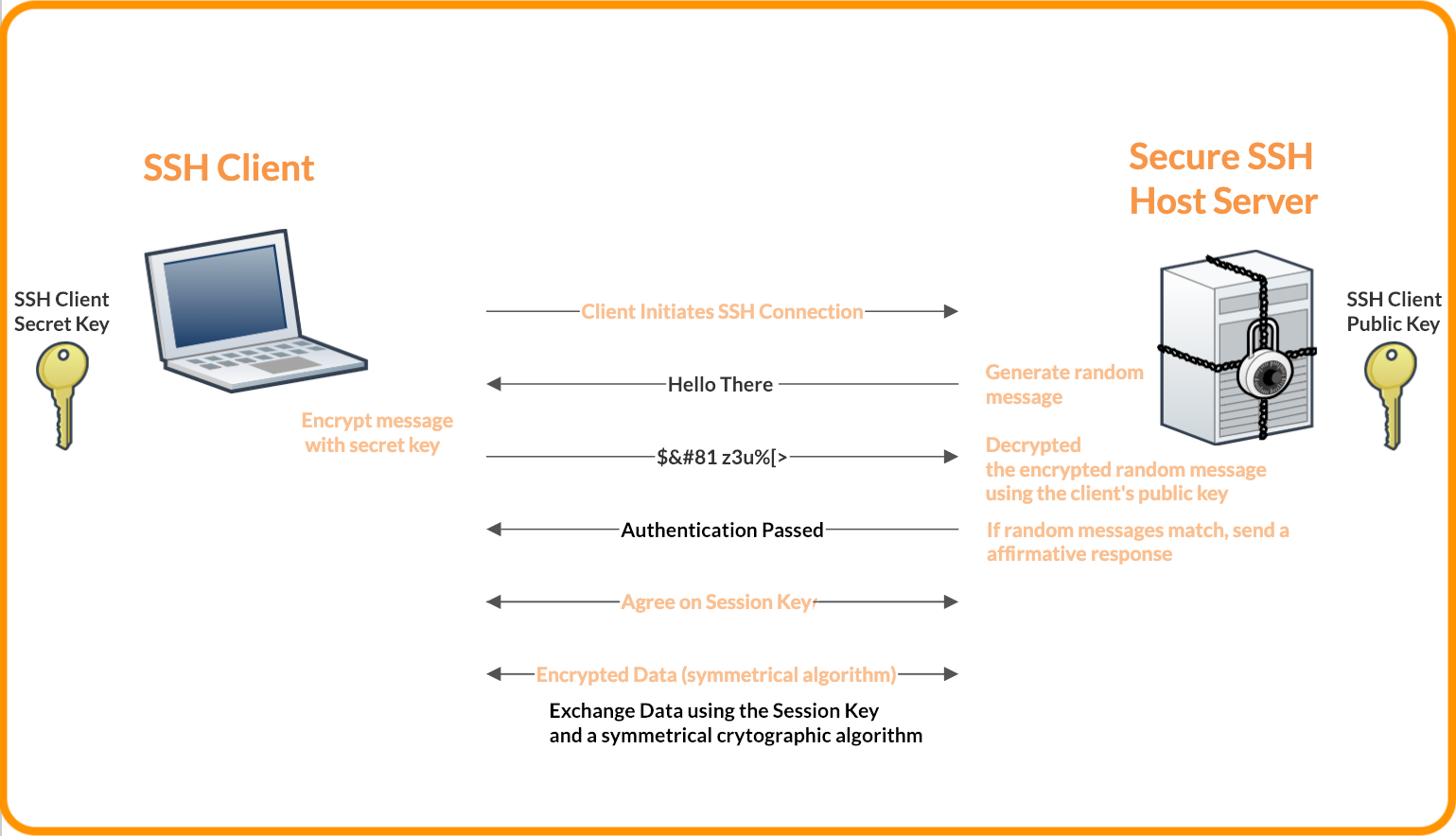
SSH keys or a key pair is consists of private and public keys. In a nutshell, the private key is what the client (your computer) presents to the server (Gitlab) for authentication, and the public key is what the server uses to decode your private key. And if both keys match, the authentication passes.
GitLab supports two types of SSH key pairs, the RSA and ED25519 SSH keys. But in this example, you’ll generate the ED25519 key pair as it is considered more secure than RSA keys. Follow the steps below to generate an SSH key pair.
1. On your desktop, open a terminal session and run the command below. This command opens your home directory in VS Code.
2. On the VS Code, click Terminal —> New Terminal.
4. At the next prompt asking where to save the key, press Enter to accept the default filename. The filename should be similar to /home/ /.ssh/id_ed25519, where is your username.
5. Next, leave the passphrase empty, and press Enter twice. As a result, you’ll be creating a passwordless SSH key pair.
You should see a similar result to the screenshot below showing the private key (id_ed25519) and public key (id_ed25519.pub) locations.
Adding the Gitlab SSH Key to Your Profile
Remember that the private key stays on your computer, while the public key should be on the Gitlab server. So after generating the SSH Keys, your next step is to upload the public key to your Gitlab account. To do so, proceed as follows.
1. Open your public key file in VSCode. On the Explorer pane, expand the .ssh folder and click id_es25519.pub. Next, select the public key and copy it to the clipboard.
2. Now, open a web browser, navigate to https://gitlab.com, and log in to your Gitlab account.
3. After login, navigate to the SSH Keys profile settings at https://gitlab.com/-/profile/keys.
Using Your Gitlab SSH Key
So far, you’ve generated the SSH key and uploaded it to your Gitlab account. What’s left is to test whether your SSH key works by using it to connect and authenticate to Gitlab.
Signing In
On the VS Code terminal, connect to your Gitlab account by running the command below.
Assuming you’re connecting for the first time, the command prompts you to verify the host’s authenticity and confirm the connection. Type yes at the prompt and press Enter to confirm.
Notice that you did not have to enter a username and password to log in? Instead, the ssh command automatically uses your SSH keys for authentication. After a successful login, you should see a welcome message saying, “Welcome to Gitlab @username!“.
Publishing a New Project
You’ve confirmed that your Gitlab SSH key works and lets you authenticate successfully. But does it also work when you interact with Gitlab through Git? Why not test by publishing a new Gitlab repository?
1. First, initialize the Git configuration and set it up with your Gitlab account’s username and email address. On the VS Code terminal, run the git config commands below to specify your Gitlab username and email address, respectively.
The command you ran should update or create the
/.gitconfig file with the information you provided.
2. Next, create a folder under your home directory for your new repository. Name the new folder as my-first-project.
The folder name will also become your Gitlab repository project name.
3. Initialize the repository by running the command below. Make sure to change the with your Gitlab username.
You should see a similar confirmation message to the screenshot below.
4. Next, specify the remote Git repository address for your project. This repository address determines whether you’ll authenticate with SSH keys or with username and password.
Find the syntax below, where is your Gitlab username and
5. Run the command below to create an empty file in your repository called README.md.
6. Open the README.md file for editing and paste the following content into the file. Save the file after editing. My first project to demonstrate Gitlab SSH keys.
7. Now, tell Git to add the new README.md file to the repository and commit the changes.
You should see a similar output as shown below.
8. Finally, time to publish your new repository. Run the command below to push the repository from your computer to your Gitlab account.
As you can see below, the project creation was successful, and there were no credential prompts! Git used your SSH keys to authenticate with Gitlab.
9. Finally, confirm that your new Gitlab project exists online. Using your browser, navigate to https://gitlab.com/dashboard/projects to view a list of your existing projects. You should then see the my-first-project name on the list.
10. Furthermore, click on the project name, and you should see the README.md file and contents on display.
Conclusion
Congratulations on having made this far in this tutorial! Throughout this step-by-step tutorial, you’ve learned how to generate and use SSH keys to make secure version control deployments to your GitLab repository.
With this knowledge, you can now perform tasks on your Gitlab repositories without worrying about inadvertently exposing your username and password.
Have you used Gitlab SSH key authentication before? How was the experience? Do you recommend others to use SSH keys, too, or is there any reason they should stay away from it? Let us know.
Hate ads? Want to support the writer? Get many of our tutorials packaged as an ATA Guidebook.
More from ATA Learning & Partners
Recommended Resources!
Recommended Resources for Training, Information Security, Automation, and more!
Get Paid to Write!
ATA Learning is always seeking instructors of all experience levels. Regardless if you’re a junior admin or system architect, you have something to share. Why not write on a platform with an existing audience and share your knowledge with the world?
ATA Learning Guidebooks
ATA Learning is known for its high-quality written tutorials in the form of blog posts. Support ATA Learning with ATA Guidebook PDF eBooks available offline and with no ads!
How do I add an SSH key in gitlab?
Part of GitLab Collective
Here is what my dashboard looks like:
Not really sure where to add an SSH key. Anyone have any idea?
5 Answers 5
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
Go to your GitLab account: https://gitlab.com/
Click on Settings on the top right drop-down, which will appear once you select the icon(white-fox image [specific to my profile]).
Click on Settings on the top right drop-down, which will appear once you select the icon(white-fox image).
Click on SSH Keys:
Add/Paste the SSH Key.
How to generate the ssh key: Download gitbash or putty:
After downloading gitbash/putty follow the steps:
Generate a new ED25519 SSH key pair:
Or, if you want to use RSA:
It will generate the key in => C:\Users\yourname.ssh directory.
Copy the public key and paste in the gitlab location:
Command to run on gitbash to clone the repository:
How to add SSH key to a GitLab account
How to add SSH key to a GitLab account
Git is a distributed version control system, which means the user can work locally but also can share or » push» any changes to other servers. Before the user can push any changes to a GitLab server, it may need a secure communication channel for sharing information.This SSH protocol provides this security and allows the user to authenticate to the GitLab remote server without supplying the username or password each time. This tutorial covers the configuration process of adding SSH key to a GitLab account.
Configuration procedure
Before starting the configuration procedure, first generate the SSH key in the target local machine which has to be added to the GitLab account.
Run the following command to open the SSH public key file. Now copy the SSH key to the user account.
In the GitLab account, go to Settings option in the profile tab.
The key has been copied to the GitLab account. Click the Add key option to add the copied key and establish a connection between the GitLab and the local server.
The key has been successfully added in the GitLab account.
Once the SSH key is added logout from the account and login to GItLab again. Now the user can directly clone the project or do any other process without any authentication.
Wasn’ t that an easy configuration process? Stay connected to know more about various other aspects of GitLab from our future articles.
Using SSH keys with GitLab CI/CD
GitLab currently doesn’t have built-in support for managing SSH keys in a build environment (where the GitLab Runner runs).
If anything of the above rings a bell, then you most likely need an SSH key.
How it works
/.ssh/authorized_keys ) or add it as a deploy key if you are accessing a private GitLab repository.
SSH keys when using the Docker executor
When your CI/CD jobs run inside Docker containers (meaning the environment is contained) and you want to deploy your code in a private server, you need a way to access it. In this case, you can use an SSH key pair.
You first must create an SSH key pair. For more information, follow the instructions to generate an SSH key. Do not add a passphrase to the SSH key, or the before_script will prompt for it.
Create a new CI/CD variable. As Key enter the name SSH_PRIVATE_KEY and in the Value field paste the content of your private key that you created earlier.
The before_script can be set globally or per-job.
Make sure the private server’s SSH host keys are verified.
As a final step, add the public key from the one you created in the first step to the services that you want to have an access to from within the build environment. If you are accessing a private GitLab repository you must add it as a deploy key.
That’s it! You can now have access to private servers or repositories in your build environment.
SSH keys when using the Shell executor
If you are using the Shell executor and not Docker, it is easier to set up an SSH key.
You can generate the SSH key from the machine that GitLab Runner is installed on, and use that key for all projects that are run on this machine.
First, log in to the server that runs your jobs.
Then, from the terminal, log in as the gitlab-runner user:
Generate the SSH key pair as described in the instructions to generate an SSH key. Do not add a passphrase to the SSH key, or the before_script will prompt for it.
As a final step, add the public key from the one you created earlier to the services that you want to have an access to from within the build environment. If you are accessing a private GitLab repository you must add it as a deploy key.
After generating the key, try to sign in to the remote server to accept the fingerprint:
Verifying the SSH host keys
It is a good practice to check the private server’s own public key to make sure you are not being targeted by a man-in-the-middle attack. If anything suspicious happens, you notice it because the job fails (the SSH connection fails when the public keys don’t match).
To find out the host keys of your server, run the ssh-keyscan command from a trusted network (ideally, from the private server itself):
If you must connect to multiple servers, all the server host keys must be collected in the Value of the variable, one key per line.
Example project
We have set up an Example SSH Project for your convenience that runs on GitLab.com using our publicly available shared runners.
Want to hack on it? Fork it, commit, and push your changes. In a few moments the changes is picked by a public runner and the job starts.
Help & feedback
Product
Feature availability and product trials
Get Help
If you didn’t find what you were looking for, search the docs.
If you want help with something specific and could use community support, post on the GitLab forum.
For problems setting up or using this feature (depending on your GitLab subscription).
The complete guide to SSH keys in GitLab
No one wants to send their precious information over unencrypted channels. This is why most websites and web services use HTTPS to encrypt data by default.
When it comes to connecting to GitLab, many users and developers default to using HTTPS. Why? Because everyone knows how a username and password work. Albeit maybe not on a technical level but intuitively it makes sense.
Things tend to get a little more complicated when sending Git commands to a server over HTTPS demands the user submit their username and password in order to perform each action. This can result in quite a lot of prompts. Moreover, when using CI/CD and automation tools, SSH keys are a much better choice for securely authenticating your GitLab account.
In this article, we’ll review what SSH keys are in the context of GitLab authentication, how to create them, and how to keep them safe.
What are SSH Keys?
In order to communicate over SSH (Secure Shell), you must have an SSH key pair. Each SSH key pair has a public and a private key.
Public Key – Can be used to encrypt data in such a way so only the holder of the corresponding private key can decrypt it.
Private Key – Can be used as proof of identity, and is used to authenticate a user’s connection to the server.
When using an SSH key pair as a method of authentication, the public key is stored on the server. It doesn’t really matter if it can be viewed as it is public information. The private key, however, is kept by the user and should not be copied or exposed in any way.
Once this is set up, the server can ask the user for proof of identity using the public key and the user can prove it using the private key.
What are SSH keys in GitLab?
SSH keys are one of the choices for authentication against GitLab servers. The vast majority of actions you will be taking on GitLab via SSH will be pushing changes from your local git repository to the hosted repository on GitLab.
Although there are other actions you can take, such as starting the GitLab CI/CD pipeline, once started you’re not going to need to interact with the GitLab runner often. Whenever you push code to the hosted repository, it will trigger the pipeline and it will be automated from there, and that action might be scheduled to run many times a day.
Types of SSH keys and options supported
It is generally recommended you use ED25519 SSH keys, which are more secure, and should be available on any system.
However, if you have a good reason to, there are also RSA SSH keys, which would work just as well on GitLab. Although it is recommended you use an SSH key of at least 2048 bits. Do note that by default, a 1024 bit key is generated, so make sure to not use the default.
Why should you use SSH keys in Gitlab?
Aside from the comfort provided by not having to submit your username and password for each action you take, SSH keys are generally much more secure than a username and password. Humans aren’t very good at remembering a large number of secure passwords so they tend to reuse passwords over multiple sites, resulting in many vulnerabilities. No system connected to the internet is truly secure, but with an SSH key you greatly reduce the chance of human error giving away your access privileges.
How to generate an SSH key pair for your GitLab account
The official documentation is fairly comprehensive, but for completeness sake, I will walk you through the process.
One thing you won’t find in the above page, since it shows up in another place in the documentation, is where to type in the commands.
I’m assuming you are using GitBash, as it is the terminal that is supplied with git. For MacOS, Windows PowerShell or Linux terminals instructions, please see the documentation.
How to generate an ED25519 SSH key
To generate ED25519 SSH key you will need to run the following terminal command:
You should see the following response after typing the above command:
How to generate an RSA SSH key pair
If you wish to generate an RSA key pair, use the following command:
The output should look like this:
Where to save your SSH key pair
Unless you know you need to use a different one, use the default path. But whatever you choose, do not use a network path (more on security later). Your chosen terminal will also use the generated SSH key without further input.
After generating the pair, you will be prompted to optionally add a passphrase:
This is optional, but recommended if others may have access to your computer where the key is stored.
How to configure an SSH key in GitLab
The first thing you’ll need is your public ED25519 SSH key in text form, to get this, you can use this command it Git Bash:
Or if you’re using RSA:
Which will copy the SSH key in text form to your clipboard.
While logged into your GitLab account on gitlab.com, follow these steps:
Keeping GitLab SSH keys safe
SSH keys are far less prone to human error, but they are not foolproof. If you’re going to use SSH keys you should have a general idea about the security risks and how to mitigate them. Why? Because not doing so may cost you. In 2019 GoDaddy, one of the largest domain registrars in the world, suffered a critical security breach due to mismanaged SSH keys.
There are many things you could do in order to make your SSH communications more secure, but most of them are done from the server side, not the client side. As an admin, you may want to set up expiration policies, so that new keys need to be generated, and old keys will no longer be valid. This greatly reduces the risk of the keys falling into the wrong hands.
As a user on GitLab though, the main thing you need to concern yourself with is that the private key generated and stored locally should never ever be copied or moved. If you feel your private key may have been compromised, remove the corresponding public key from the server. You might want to do this periodically regardless, to ensure your server’s safety.
If you ever find yourself on a different computer, simply generate a new SSH key pair and upload the public key to GitLab. If a computer is lost, simply delete the public key from your GitLab account and all is well.
Do not backup your SSH keys as the only thing that does is create a vulnerability. As a rule, creating new keys and revoking old ones is a lot less painful than dealing with the fallout of a leaked SSH key pair.