How to check gpu temperature
How to check gpu temperature
How To Monitor Your GPU and CPU Temperature
Keeping is an eye out on the temperatures of your CPU and GPU is vital if you want your PC to have a great amount of longevity. Here’s a simple guide on how you can monitor your CPU and GPU temperature.
Is your PC/laptop feeling hotter than usual? Any alarms beeping inside the case?
If so, you might want to take a closer look at those temperatures!
After all, overheating is the primary cause of hardware failure and it can drastically reduce your setup’s lifespan.
So, here’s a couple of suggestions as to how you can monitor your GPU and CPU temperatures, as well as some pointers on how to keep the temperatures within the acceptable range.
Table of Contents Show
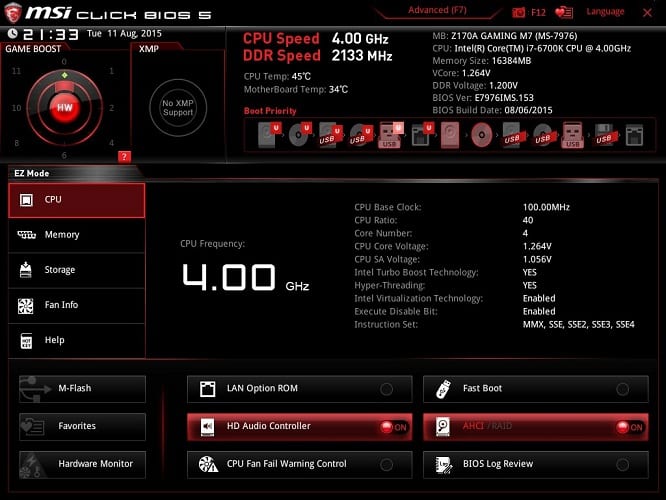
The easiest way to check the CPU temperature is through your motherboard’s BIOS.
To access the BIOS:
Not every BIOS will look the same, especially when it comes to gaming motherboards, as OEMs often equip them with a unique GUI these days.
However, they are all fairly simple to navigate — just glance over the different tabs and sections until you get to the CPU settings. The temperature will be displayed here if it is not already shown on the first screen.
The BIOS might look scary if you’ve never accessed it before, but don’t worry too much about changing something that you shouldn’t tamper with. When exiting the BIOS, a prompt asking whether you wish to save your alterations will always be displayed, so it’s quite easy to rectify any mistakes you might have made.
The obvious disadvantage of using the BIOS for temperature monitoring is that you need to restart your computer every time that you want to check the temperatures. If you need to do this more frequently, then read on for some solutions that are available straight from your desktop.
CPU Utility
Both AMD and Intel have their own overclocking utilities — the Ryzen Master and the Extreme Tuning Utility, respectively. Chances are you have them installed already.
Both of these utilities are quite straightforward. Besides allowing you to monitor your temperature, they also offer extensive overclocking options, although you’d do best to stay away from these unless you know what you’re doing or you’ll risk worsening your temperature problems.
GPU Utility
There are also various GPU monitoring and overclocking utilities that can serve this purpose well, and graphics card OEMs inevitably include their own with each graphics card.
However, any utility will work on any graphics card regardless of the manufacturer, so you can download and use whichever one you want. This is a very good thing as some utilities are inevitably better than others.
So, for example, you are free to use the MSI Afterburner (which is often regarded as the best GPU utility) on an Asus card instead of the Asus GPU Tweak, and vice versa.
Other Utilities
Finally, there are also many other utilities that can be used to monitor system temperatures, including Open Hardware Monitor, HWMonitor or AIDA64, among many others.
Depending on which utility you ultimately pick, they will display both CPU and GPU temperatures, along with more potentially useful data.
What Causes High Temperatures and How to Prevent Them
The most common reason for CPUs and GPUs to overheat after a certain amount of time is dust build-up. Every computer that relies on active cooling will eventually accumulate large amounts of dust, something that will eventually affect the cooler’s effectiveness by limiting airflow.
And what to do when that occurs? Why, clean it, of course! To find out the correct way to clean the dust off your computer, check out our guide on that very subject. Also, if you are a laptop owner, you might also want to cast a glance at another article of ours that will tell you how to keep your laptop cool while gaming.
If dust build-up is not the culprit, other potential reasons could be poor airflow or defective hardware.
To ensure proper ventilation, the air inside the PC case shouldn’t be obstructed and it shouldn’t be kept in a closed space. Moreover, if the power supply is mounted at the bottom of the case, the PC should also be placed on a solid surface, as soft surfaces such as carpets can block the PSU’s air intake.
As for potentially defective hardware, there could be various reasons behind the heat build-up. If you’re lucky, the problem will be one of the easily replaceable case fans or the CPU cooler.
Case-mounted fans are generally a very good way to improve your PC’s cooling, as even a single fan can greatly help. They are fairly cheap, too, so they could very well end up helping your PC run cooler and more quietly.
Conclusion
Those would be our top choices when it comes to all the ways you can monitor your CPU and GPU temperatures. However, keep in mind that they are, of course, far from being the only options out there.
Also, be sure to check out the following video from LinusTechTips if you’re interested in discovering some additional helpful system monitoring utilities:
How To Monitor Your GPU Temperature
Keeping your GPU temperature in check is the key to getting the best visual performance out of your graphics card. Here’s how you monitor it.
This author has been vetted and has the necessary know-how or education to be able to write about this topic. Learn more on our about page.
Your GPU temperature getting too high can be a sign of more serious problems developing under the hood.
Therefore, it’s crucial to keep that in check, especially when your GPU is placed under a lot of strain, for example, when running resource-heavy games. Here’s how to monitor your GPU temperature.
Table of Contents Show
Why Is It Important To Monitor Your GPU Temperature?
There are different reasons why you might need to monitor your GPU temperature, but they all boil down to the same old goal: getting the best performance.
Overclocking
If you have tried overclocking your GPU, you will need to keep a close eye on the temperature that your graphics card’s slightly increased clock is producing. Keeping the temperature of the GPU in that sweet spot is a necessity when overclocking it.
Today, graphics card manufacturers are well aware of the overclocking community among gamers. This has led to them carefully designing their graphics cards to accommodate overclocking while also keeping their product’s integrity intact.
A key thing you will need to consider when overclocking your GPU is the possible need for additional cooling. This is the key to keeping your GPU running at an optimal temperature. If you’re experiencing overheating, this is probably the first thing you should consider in order to fix the problem.
Playing Resource-Heavy Games
Even if you’re simply playing a game with higher-quality graphics for a longer period of time, it could place a strain on the GPU. This, in turn, can lead to more severe problems.
The key here is knowing how well your graphics card can handle the load. In many situations, your GPU will fulfill the minimum system requirements or even recommended system requirements but might still have trouble running the game at higher graphical settings for a few hours.
Depending on how long you ignore the obvious problems while playing (such as stuttering or beeping from inside the PC case), you could end up with different levels of damage. Fortunately, most modern GPUs are built in a way that prevents the graphics card from suffering physical damage by turning it off before things get too heated.
On the other hand, that doesn’t stop other related hardware from malfunctioning. Also, the GPU shutting off when hitting dangerous temperatures doesn’t completely prevent it from being damaged. Ignoring the problem and having the GPU shut off multiple times can eventually wreck the card and leave you looking for a replacement.
Best Ways To Monitor Your GPU Temperature
As mentioned earlier, an overheating GPU can cause some serious issues. Fortunately, there are multiple ways to keep an eye on the GPU temperature and ensure that it doesn’t cross that dangerous threshold.
Each of these options has its own pros and cons and we hope to teach you these well enough to make an informed decision.
Manufacturer-Specific Software
Both AMD and NVIDIA have companion software for their graphics cards. This is mostly used for tasks such as keeping your drivers up to date and enabling some additional performance-enhancing features specific to the respective brand.
Both NVIDIA and AMD have bundled an overclocking tool together with the drivers (you will need GeForce Experience for NVIDIA GPUs).
AMD’s solution allows the user to adjust the fan speeds, clock speeds, and power delivery. There is also the option for automatic overclocking.
NVIDIA was a bit late to the party and their OC tool still isn’t as good as AMD’s. There is an ‘Automatic Tuning‘ option to automatically overclock the GPU clock speeds, but there’s no option to do it yourself.
As both companies have delivered some kind of overclocking tool with their drivers, they have also added a feature for performance monitoring.

Both monitoring tools deliver plenty of information, including fan RPM, memory clock, GPU clock, temperature, etc. If you need even more data than that, you should consider third-party software.
Third-Party Solutions
With technological developments, there were unsurprisingly many enthusiastic people willing to learn all the ins and outs of how a PC works. Thanks to those people, we first saw component monitoring software, some of which are still in use today.
Disclaimer: Most of these tools will include some other functions, enabling you to monitor other parts of your PC, which is always a plus.
HWiNFO
HWiNFO has to be the best of the bunch, considering you can get temperature readings on almost every component in your computer. This includes everything from your GPU to your drives.
Additionally, there is an option to oversee clock speeds, voltage, and even your RAM timings. It is also customizable, so you can easily remove the sensors you aren’t interested in.
That’s not all. Add-ons are also available for HWiNFO, for example, an add-on to use Riva Tuner’s, MSI Afterburner’s, or EVGA Precision’s On-Screen Display tool. There are many more add-ons for extra information and features.
Open Hardware Monitor
This tool is another old-school looking piece of software but is just as reliable as the first one. Like HWMonitor, it can also keep your RAM in check but, most importantly in today’s context, it allows you to manually adjust the fan speed.
This is quite useful as the fan speed isn’t always automatically adjusted when the card is placed under more strain. At the cost of extra electricity, you can crank up those RPMs and enjoy a smooth gaming experience.
SpeedFan
Continuing the theme of old-school software, SpeedFan is another reliable solution. In addition to the standard monitoring of voltage, fan speed, and temperature, it can adjust the RPM of fans as well as help to reduce the noise.
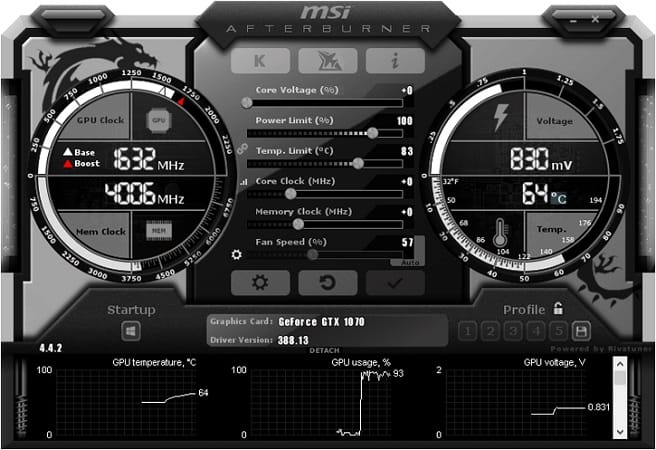
MSI Afterburner
It’s impossible to discuss hardware monitoring software without mentioning MSI Afterburner.
This tool is the perfect solution for measuring the performance of your GPU while you’re playing a game, as it features a nifty overlay that tells you exactly how hot your GPU temperature is.
You obviously won’t want to run every game constantly with this overlay, but it’s a great solution for a stress test that can help you either adjust your in-game settings or fan speed, something MSI Afterburner can also help with.
HWMonitor
HWMonitor is a relatively old tool but is still incredibly reliable. In addition to the ability to monitor your GPU temperature, HWMonitor can also help you keep an eye on voltages and fan speed of other PC hardware such as the CPU, hard drive and the motherboard.
How to check your GPU temperature
Fortunately, keeping an eye on its temperatures isn’t difficult and can be accomplished in just a few moments with helpful tools. But there are a few other things to keep in mind, so let’s dig in.
How to monitor your GPU’s temperature
By far, the easiest tool to check your GPU’s temperature in Windows 10 can be found by firing up Windows Task Manager and jumping to the Performance tab. At the bottom of the list, you’ll find your GPU listed with its temperature between brackets. Use this to check your GPU temperature under a heavy gaming load, ensuring it is operating at or very close to 100% utilization.

But this isn’t the best tool, as it’s difficult to monitor in-game. The moment you Alt + Tab out of a game, the GPU temperature drops immediately, so you won’t be able to view a live reading like this unless you have a second monitor, making it difficult to see what your GPU’s temperature is like under load.

However, there is another tool that you may prefer that’s built into the Nvidia GPU drivers, and AMD’s GPUs have a similar utility. To get to Nvidia’s overlay, make sure you have GeForce Experience installed and are logged in. Use Alt + Z to open the overlay in-game, click the Cog icon on the right, and set up the advanced performance monitor in the corner of your choosing. It will look like the above window, and you can spot the GPU temperature on the fourth line from the bottom.
AMD’s GPUs also have an in-game overlay for monitoring hardware, and there are also alternative third-party monitoring tools such as HWiNFO, MSI Afterburner, and Evga’s Precision X1.
The real test is synthetic
All that being said, the aforementioned tools and tests generally don’t cut it entirely, as different games may lead to different temperatures. Or, if your processor isn’t up to snuff, some games may not even tax your GPU at 100%, which may give a false sense of security. Instead, the real test for whether a GPU’s cooling solution is adequate is to run Furmark, a brutal synthetic torture test built to bring out the worst of your GPU.
The test is easy to run — just install Furmark, open it, and run the test at standard settings. You should see a screen like pictured above. Let this run for about 10 to 15 minutes until the temperature has stabilized and you have a good idea of where you’re at. While running the benchmark, Furmark also tells you the GPU’s clock speeds, temperatures, and more.
Do keep in mind that Furmark is harder on the GPU than your average game, so it will bring out the worst and result in lower clocks than games generally achieve. Therefore, it is also a riskier test to run, and it does warn you about this before starting a test, but as long as you keep an eye on the temperatures and ensure they don’t exceed 90 degrees Celsius, there is nothing to fear.
Today’s GPUs target 85 degrees Celsius
The vast majority of today’s graphics cards have a target temperature of about 82 to 85 degrees Celsius, meaning they will either overclock until they reach that temperature or have reached their maximum overclock. The reason for this is simple: If there is thermal headroom, the GPU will try to run at a higher frequency in order to boost performance and/or reduce fan speeds to quiet things down if the power limit has been reached.
But, this can make it a bit difficult to tell whether your GPU’s temperature is within norms. Of course, if the temperature you spot is below 80 degrees Celsius, you generally have no reason to worry — all is good — but if it is at exactly 85 degrees, it could be fine, but it could also be a sign of a problem.
This is because just as a GPU can overclock when it hasn’t reached the thermal threshold yet, it can also underclock itself as protection from overheating when it needs to. Therefore, if your GPU temperature is at or very close to 85 degrees, you will want to double-check whether its clock speeds match the design specifications.
For example, according to Nvidia’s website, the RTX 2070 Super is set to run at a base clock of 1605 MHz with a boost clock of 1770 MHz, and this GPU has no problem meeting those figures in any of the aforementioned tests. In fact, it happily boosts to 1890 MHz in Horizon Zero Dawn, and in the synthetic Furmark test, it runs at a perfect, on-point 1605 MHz, all at about 72 degrees, so this is a healthy GPU.
However, if its temperature were to jump to 85 degrees, and its achieved clock speed under load were to drop far below the factory base clock of 1605 MHz, then there would be a problem.
One more thing to keep in mind is that although many tools don’t display it, some may display a “junction temperature” that comes out higher than the GPU temp reading you see elsewhere. This value measures the hottest temperature on your GPU rather than the GPU’s edge temperature, and while the higher figure may look scary, it’s not one you generally need to worry about unless you’re pushing heavy overclocks well beyond factory specifications.
So, what if the temperatures aren’t right?
If you find that your GPU runs at or above 85 degrees and its clock speed under load is lower than the advertised base clock, then there is work to be done. The first thing to check is whether there is enough airflow in your case and whether the dust filters have been cleaned. At the same time, check the GPU’s heatsink for dust buildup, and remove it if present. Clean your PC, reassemble, and test again.
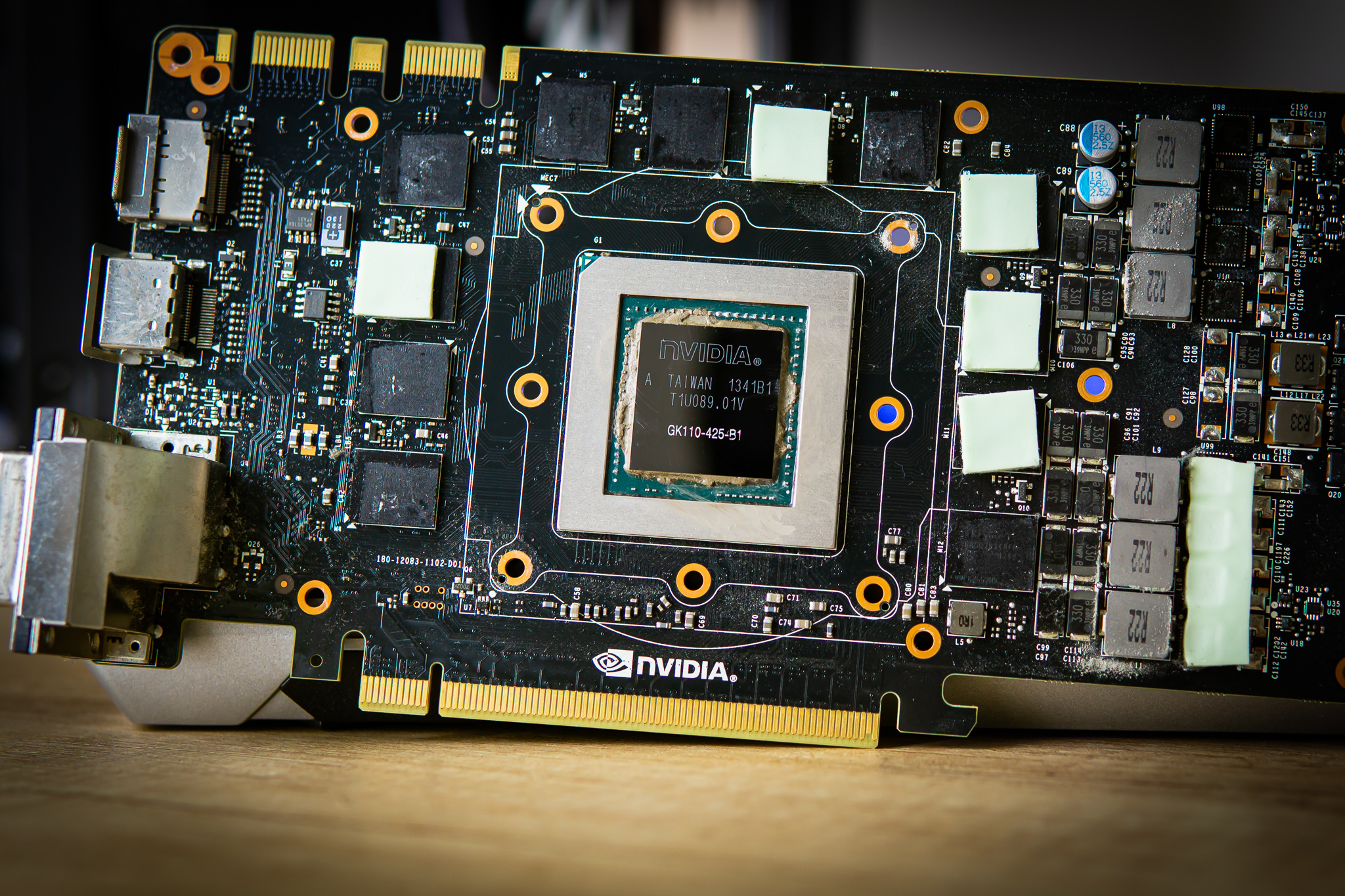
If this doesn’t solve your GPU temperature problem, there is a high chance of bad contact between your GPU’s cooler and the GPU’s core itself, either from a bad install from the factory or dried-out paste from old age. Under heavy use, thermal grease will begin to dry out and degrade after about two years, and from then on, it can lead to significant performance loss from about four years onward.

Pictured above is a GTX 780 Ti that was disassembled after about four years of leaving it untouched, and you can clearly tell that the thermal paste is no longer in order and needs to be replaced. After replacement, not only did the GPU run cooler, it also ran much quieter, as the GPU was finally able to properly move its heat into the heatsink for dissipation, which means its fan didn’t have to work as hard. Better yet, this also led to a significant performance increase.
Keep in mind that disassembling a GPU is a specialist procedure and is best done by someone with an affinity for disassembling electronics. If you’re not comfortable taking electronics apart and your GPU is still within its warranty period, your best bet is to send the card to the manufacturer for repair or bring it to a local PC hardware shop.
Как проверить температуру видеокарты
Если у вас возникли проблемы с производительностью компьютера, он стал часто «тормозить», «заикаться», особенно когда вы играете в компьютерные игры, редактируете или воспроизводите видео, первое что вам нужно сделать — это проверить температуру видеокарты.
Во-первых, следует отметить, что работа большинства видеокарт рассчитана на довольно высокие температурные пороги. Многие видеоадаптеры работают при температуре 60-70 градусов Цельсия и это абсолютно нормально.
Если все же вы подозреваете, что с вашей видеокартой не все в порядке, следует узнать ее температуру и если она окажется выше 100 градусов, то следует принять меры по охлаждению или замене видеоадаптера. Выявить и устранить проблему нужно как можно скорее, т.к. перегрев видеокарты может привести к ее поломке и выводу из строя остальных составных частей компьютера.
Также, следует отметить, что порог 100 градусов Цельсия не является эталонной величиной. Предельные значения температур зависят от производителя видеокарты и ее типа (встроенные, дискретные, для стационарного ПК, ноутбука и т.д.).
Самым простым способом проверить температуру видеокарты является использование специализированных программ. Давайте рассмотрим несколько утилит, с помощью которых можно это сделать.
GPU-Z — очень простая и на мой взгляд лучшая программа для определения температуры видеочипа. Скачать ее можно по этой ссылке: http://www.techpowerup.com/gpuz/
На первой вкладке «Graphics Card» отображаются основные характеристики видеокарты, такие как тактовая частота, объем памяти, версия драйвера и т.д. Если у вас 2 видеоадаптера (например, встроенный и дискретный), то в нижнем левом углу окна можно выбрать исследуемую карту.
Но нас больше будет интересовать вторая вкладка «Sensors». Здесь вы увидите искомый параметр «GPU Temperature», который будет показывать текущее значение температуры видеочипа.
Если последовательно щелкать мышью на значении температуры, то будет отображаться минимальное, максимальное и среднее значение за измеряемый период.
Speccy
Скачайте и установите программу, используя эту ссылку: http://www.piriform.com/Speccy
После запуска приложения вы увидите основные характеристики вашего компьютера. В разделе «Graphics» или «Графические устройства» (в зависимости от выбранного языка интерфейса) будет отображаться текущая температура вашего видеоадаптера.
В меню слева расположены пункты, отвечающие за другие компоненты вашего компьютера. Выбрав соответствующий пункт, можно посмотреть более детальную информацию по отдельным комплектующим.
Недостатком этой программы является то, что она не всегда отображает температуру видеокарт, особенно встроенных.
HWMonitor
Далее рассмотрим еще одну простую утилиту HWMonitor. Инсталлятор или portable-версию можно скачать с официального сайта: http://www.cpuid.com/softwares/hwmonitor.html
Тут, как и в предыдущей программе, будут отображены значения датчиков основных компонентов компьютера. Текущую, минимальную и максимальную температуру видеочипа можно посмотреть в соответствующем пункте.
SpeedFan
На первой вкладке справа будет отображаться список температурных датчиков и их значения.
Нас будет интересовать только пункт «GPU», в котором и будет отображаться текущая температура видеокарты.
HWinfo
На выбор можно скачать portable или install версии для 32 и 64-битных систем.
Как и большинство аналогичных программ HWinfo служить для просмотра информации о различных компонентах компьютера. Чтобы найти показания температуры видеоадаптера нужно нажать кнопку «Sensors» и найти необходимый раздел в списке датчиков.
AIDA64
Это платная программа для тестирования и диагностики компьютера с помощью которой также можно посмотреть температуру видеочипа. Хотя приложение платное, у него есть пробный 30-дневный период, которого вполне достаточно, чтобы посмотреть и протестировать нужный показатель.
Существуют еще специализированные утилиты для определенных моделей видеокарт, (например, NVIDIA Control Panel, NVIDIA GPU Temp, ATI Tool, ATI Tray Tools и др.) с помощью которых также можно определить температуру видеокарты, но т.к. она подходят не для всех видеоадаптеров, мы не будем рассматривать их в рамках данной статьи.
В заключение хотелось бы сказать, что основными причинами слишком высокой температуры видеокарты являются: пыль на вентиляторе карты и в системном блоке, плохой воздухообмен, выход из строя кулера и высыхание термопасты на графическом процессоре.
How to check your graphics card’s GPU temperature
How hot is your PC’s graphics card temperature? During normal operations, your GPU temperature shouldn’t matter much—your graphics card should simply drive monitors and play games without overheating and shutting down. But if you have an older PC, a case with poor airflow, or if you want to try your hand at graphics card overclocking, being able to monitor your GPU temperature is vital—especially when the summer heat is scorching indoors and out. There’s a reason that “may your temperatures be low” is a common saying among PC enthusiasts.
The good news? Checking your PC’s graphics card temperature is dead simple, especially now that Windows finally includes a native way to keep tabs on temps. All sorts of free GPU monitoring tools are also available, and many of them can help you check your PC’s CPU temperature, too.
How to check your graphics card temperature
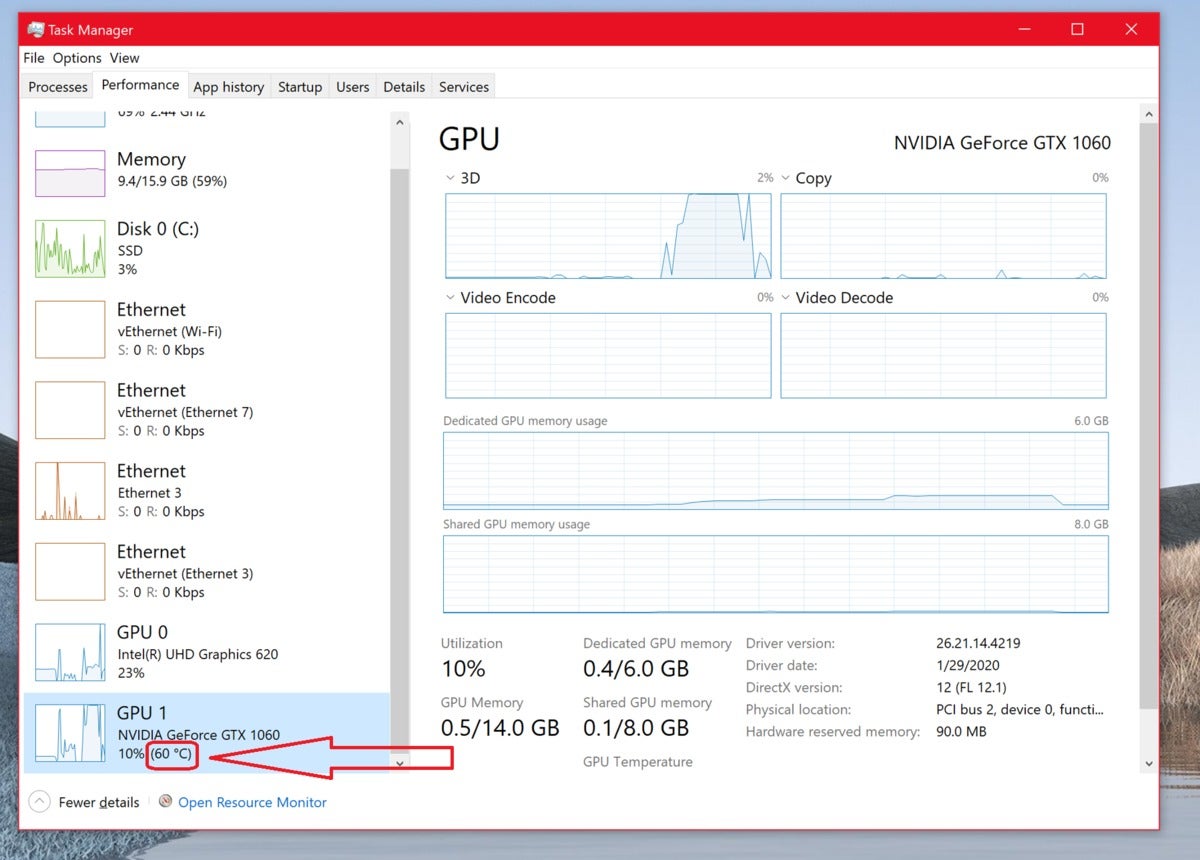
You can now find your discrete GPU’s temperature in the Windows 10 Task Manager.
Microsoft finally answered our prayers with the Windows 10 May 2020 Update, adding a GPU temperature monitoring tool in the Task Manager. Sure, it took 24 years, but it’s here now!
To see how hot your graphics card is running, open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc, by pressing Crtl + Alt + Delete and selecting Task Manager, or by right-clicking on the Windows Start menu icon and selecting Task Manager. Once you’re in, simply head to the Performance tab and look for your current GPU temperature listed in the GPU section, as shown in the image above. This works only if you have the Windows 10 May 2020 Update or a newer version of Windows installed; older versions lack the capability.
It’s a bare-bones feature, showing only the current temperature rather than tracking it over time. It can also be annoying to keep Task Manager open while you’re gaming or fine-tuning an overclock. While we’re very glad to see the option finally included in Windows itself, third-party tools offer more robust GPU temperature options. Read on for alternatives if you need more oomph.
Other GPU temperature monitoring tools
AMD’s Radeon RX 6900 XT.
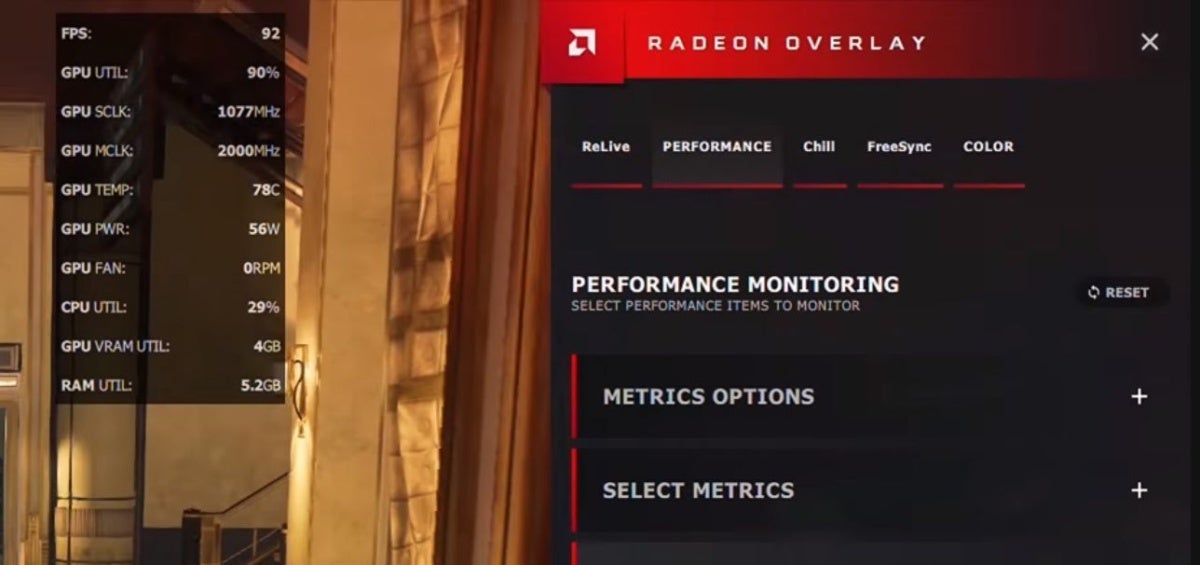
If you’re running an AMD Radeon graphics card with an up-to-date version of the Radeon Settings app, keeping tabs on your graphics card temperature is simple. AMD’s Radeon Overlay provides handy-dandy tools to tweak your game’s visual settings when you summon it. It also includes a Performance Monitoring tool that displays your GPU temperature and other crucial information while you’re playing games.
Radeon RX 6600 Swft 210
To activate the tool, summon the Radeon Overlay by pressing Alt + R and select which performance aspects you’d like to keep tabs on in the Overlay’s Performance Monitoring section. Once it’s set up, you can bring up the Performance Monitoring tool alone by pressing Crtl + Shift + 0.
What if you’re not actively playing a game? You can still check your Radeon GPU’s temperature by wading into the Wattman overclocking tool in Radeon Settings. Right-click on the Windows desktop, select Radeon Settings, and then head to Gaming > Global Settings > Global Wattman. After promising not to blow up your graphics card if you apply a wild overclock with the tool, you’ll gain access to Wattman, which tracks GPU temperature and other key statistics in graph form. Done!
The Radeon Overlay’s performance monitoring tool tracks GPU temperature by default.
But what if you aren’t packing Radeon hardware? Nvidia’s GeForce graphics comprise a whopping 75 percent of all GPUs in gaming PCs, according to the Steam hardware survey. After years of ignoring performance overlays, Nvidia’s GeForce Experience software now includes those metrics, including the crucial GPU temperature, though it involves jumping through a few more hoops for now.
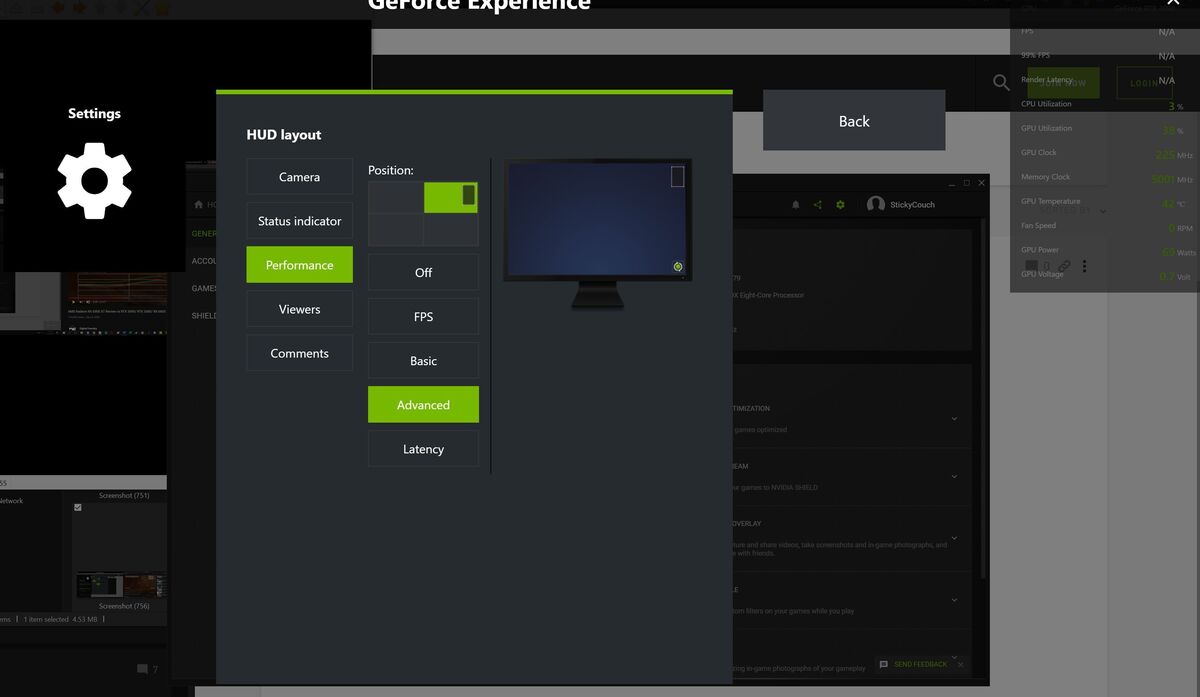
To enable it, make sure you have GeForce Experience installed. Once it is, open it up, then click the cog icon next to your name to open the Settings. Turn on the “In-game overlay” option.
A screenshot showing how to enable GeForce Experience’s performance overlay.
Click the Settings button, and in the overlay that appears, select HUD Layout > Performance > Advanced, and select where you’d like the overlay to appear on-screen. You’ll see the overlay appear in the chosen place with several metrics visible, including your GPU temperature. Press Alt + R to summon or dismiss GFE’s performance overlay at will once you’ve got it set up.
Many graphics card makers also offer specialized software that enable GPU overclocking. These tools usually include persistent on-screen display (OSD) options that show your graphics card’s most critical measurements, similar to AMD’s Radeon Overlay. Tons are available, but we tend to recommend MSI’s Afterburner tool for its versatility. This long-popular utility works with both Nvidia GeForce and AMD Radeon graphics cards, and provides several additional features gamers will welcome.
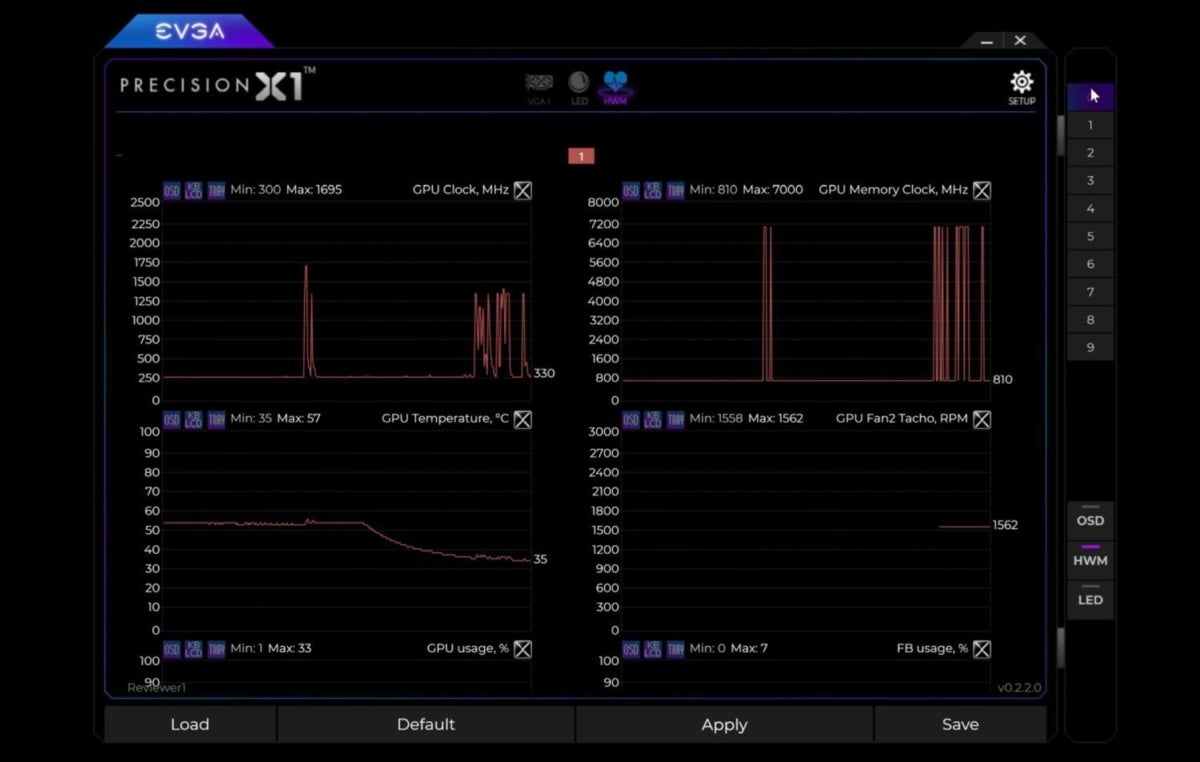
EVGA’s Precision X1 lets you check your GPU temperature either in-app or via an on-screen display while gaming.
If you prefer a more polished-looking app, we adore EVGA’s Precision X1, which was overhauled from the ground up for the release of Nvidia’s new GeForce RTX 20-series graphics cards. It’s seriously slick, though EVGA’s software only works with Nvidia-brand graphics cards.
Mentioned in this article
GeForce RTX 3050
You’ll need to dive into the settings options of each of those programs to activate and fine-tune their OSD performance monitoring tools, which prove very helpful indeed when you’re trying to dial in an aggressive overclock. As with AMD and Nvidia’s tools, you can also open Afterburner and Precision X1 outside of games to check your graphics card’s temperature outside of games.
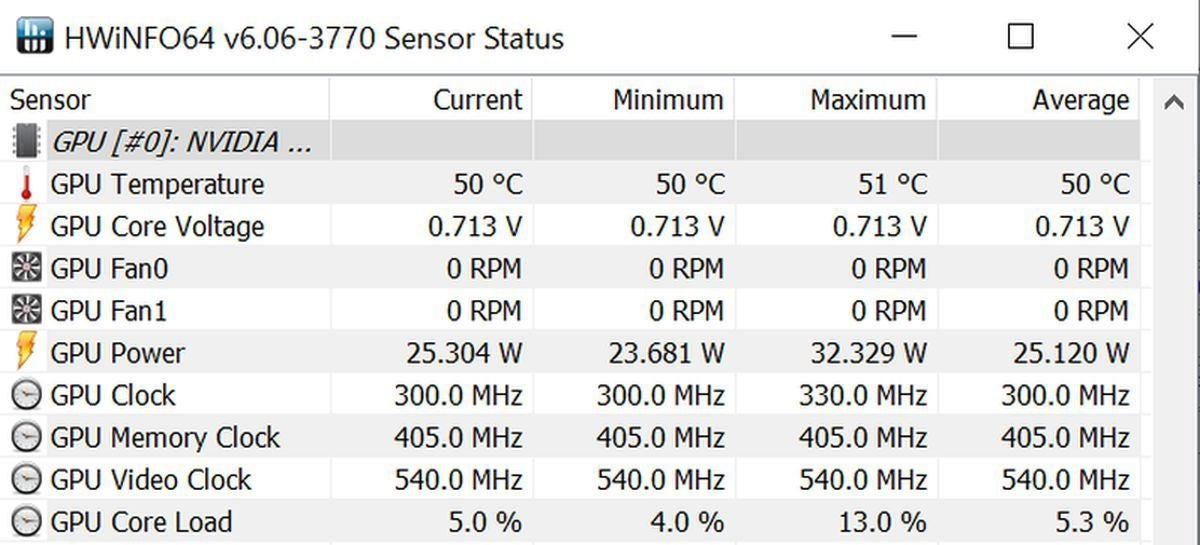
What if you’re not a gamer or don’t care about checking your GPU temperature in-game? Then you’ll want to install hardware monitoring software that taps into your system’s temperature sensors. HWInfo is our go-to monitoring program, because it provides a snapshot of virtually every aspect of your PC (click the Sensors icon to see temps), but SpeedFan and Open Hardware Monitor are solid options, too. Open Hardware Monitor also supports Linux.
HWInfo’s sensor info includes GPU temperatures and a lot more. A whole lot more.
If the sparse, information-dense look of those enthusiast-focused apps don’t work for you, NZXT’s superb CAM software performs the same task, even if you don’t have any NZXT hardware in your PC. It offers a clean, straightforward aesthetic and a handy mobile app for remote monitoring, but you’ll need to create an account to use CAM.
What’s a good GPU temperature?
So now you know what tools can help you monitor your graphics card temperature, but numbers on a screen mean nothing without context. How hot should your graphics card run?
There’s no easy answer; it varies from GPU to GPU. Google is your friend. Most modern chips can run at temperatures in the mid-90 degrees Celsius, though, and you’ll often see them hit those temperatures in gaming laptops. In desktops, however, a graphics card running at 90-plus degrees is screaming for help. In single-GPU systems with decent airflow, your graphics card temperatures shouldn’t wander above the 80-degree range unless you’re using a model with a single blower-style cooler, or an exceptionally powerful GPU. Custom graphics cards with multiple fans often hover in the 60s and 70s, even under full load, and water-cooled GPUs can run even cooler.
Some graphics cards, like this iteration of the Radeon Vega 64, include integrated closed-loop liquid coolers for even cooler temperatures.
If your graphics card was released in the last five years and runs hotter than 90 degrees Celsius, or you’ve observed a steep incline in your GPU temperature over several weeks or months of monitoring it, consider taking steps to help cool it down.
How to lower your graphics card temperature
If your graphics card temperature runs hot, there’s not much you can do to improve it aside from paying for hardware upgrades. But before you invest more money into lowering your GPU temperature, make sure that you really need to. Again: Graphics chips are designed to handle hot temperatures. If your PC isn’t shutting down in the middle of intense gaming or video editing sessions, you probably don’t have much to worry about.
PCWorld’s staff loves these fans
be quiet! Pure Wings 2 120mm PWM high-Speed, BL081, Cooling Fan
First, double-check your system’s wiring to make sure the GPU is getting good airflow from your fans. Assuming your PC isn’t a rat’s nest of cables, you’ll likely need to consider adding more fans to your case to improve airflow. Every PC should have at least intake and outtake fans for optimal performance, and that goes doubly so for gaming PCs.
Your hot graphics card could cool down in a more spacious case.
Small form factor systems can deliver a big punch these days, but the constrained space can send hardware temperatures skyrocketing. If you have a particularly small case, and your graphics card keeps overheating and shutting down, consider upgrading to a more spacious model. Even larger cases can strangle airflow if they’re poorly designed, however. Our guide to picking the perfect PC case can help.
A great, affordable case with a focus on airflow
Corsair 4000D Airflow Tempered Glass Mid-Tower ATX PC Case – Black
Finally, sometimes the thermal paste between the GPU and the heatsink can become dry and lose its effectiveness, most commonly in graphics cards that are many years old. And sometimes, graphics cards ship with poor thermal paste application, though it’s very rare. You could try to replace it if all else fails, though the process is highly technical, varies card-by-card, and voids the hell out of your warranty. Our guide to making your old graphics card run like new is several years old, but the basic technique still applies to today’s GPUs.
Just be sure to Google a disassembly guide for your specific graphics card model before you start tearing your precious, pricey hardware apart willy-nilly. And if you don’t want to go to all that hassle, our constantly updated guide to the best graphics cards for PC gaming can help you pick out an all-new GPU lickity-split.