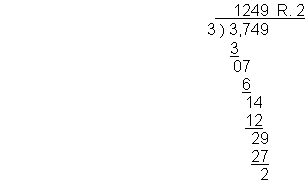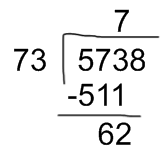How to do division
How to do division
How to do division
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 |
| 4 Dogs | 4 Dogs | 4 Dogs |
12 
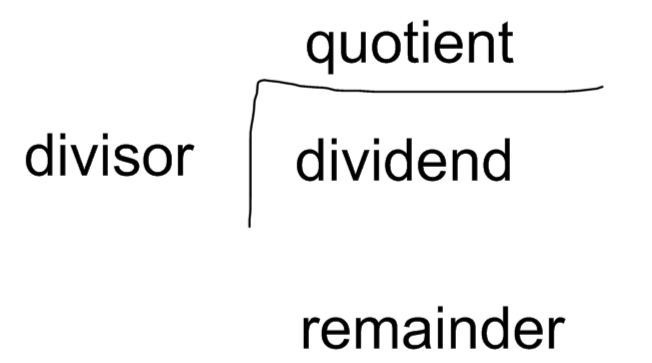
| Terms – Divisor, Dividend, Quotient, Remainder |
There are four main terms to describe the parts of division. The dividend is the number that is being divided. The divisor is the number that will be doing the dividing. The quotient is the answer, or the number of times the divisor goes into the dividend. In the problem, 12 
If we have the problem 23 
| Division Facts |
Division is quicker and easier once you know and memorize the basic facts. The division facts are the inverses of the multiplication facts. For example, if 9 x 6 = 54, then 54 
Flash cards are a great aid in learning division facts.
Division by zero would be the inverse of multiplying by zero. 7 x 0 = 0. This corresponds to 0/7 = 0 or 0 

Division of zero is considered undefined. It is impossible to divide nothing into groups of nothing.
a x 1 = a
5 x 1 = 5 and 25 x 1 = 25
A 
5 

| Multiplicative inverse |
A multiplicative inverse, or reciprocal, for a number (such as a) is denoted by 1/a such that the number, a, and its reciprocal, 1/a, yield 1 when multiplied.
For example, the multiplicative inverse of 8 is 1/8. When you multiply 8 x 1/8, the answer is 8/8 which is 1, or 1 whole.
For the multiplicative inverse or reciprocal of any number, divide 1 by that number.
| Division with a Single Digit Divisor |
To check your answer, multiply the quotient by the divisor. If the dividend is your answer, your quotient is correct. 2 x 23 = 46.
This is a fairly simple problem which works out evenly. Let’s try a problem which is not so straightforward. Let’s divide 3,749 by 3.
How many times will 3 go into 29? 3 x 9 = 27. So we will put the 9 above the 9, multiply and subtract again. Since we have no more digits to bring down, we will have a remainder of 2.
In real life situations, a remainder does not work out very well. When you start to do decimals, you will use another method to work with remainders.
To check your answer, multiply the quotient by the divisor, then add the remainder:
| Division with a Multiple Digit Divisor |
Sometimes your divisor has two or three digits. This really isn’t difficult to work with; it simply takes a little more thought. Let’s look at 2,892 
1. A number is evenly divisible by 2 if it ends in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8.
2. A number is evenly divisible by 3 if the sum of the digits is a multiple of 3.
3. A number is evenly divisible by 4 if the lasts two digits are a number that is a multiple of 4.
4. A number is evenly divisible by 5 if it ends with 5 or 0.
5. A number is evenly divisible by 6 if the sum of the digits of the number is a number that is a multiple of 3 and the last digit is an even number (divisible by 2).
6. A number is evenly divisible by 9 if the sum of the digits are a multiple of 9.
Long Division
Long Division is a method for dividing large numbers, which breaks the division problem into multiple steps following a sequence. Just like the regular division problems, the dividend is divided by the divisor which gives a result known as the quotient, and sometimes it gives a remainder too. Let us learn more about the long division method along with its steps and examples in this article.
| 1. | What is Long Division Method? |
| 2. | Parts of Long Division |
| 3. | How to do Long Division? |
| 4. | FAQs on Long Division |
What is Long Division Method?
In math, long division is a method for dividing large numbers into steps or parts, breaking the division problem into a sequence of easier steps. It is the most common method used to solve problems based on division. Observe the following long division to see the divisor, the dividend, the quotient, and the remainder.
Parts of Long Division
While performing long division, we need to know the important parts of long division. The basic parts of long division can be listed as follows:
The following table describes the parts of long division with reference to the example shown above.
| Dividend | The number which has to be divided. | 75 |
|---|---|---|
| Divisor | The number which divides the dividend. | 4 |
| Quotient | The result of division. | 18 |
| Remainder | The leftover part or the number left after the division which cannot be divided further. | 3 |
How to do Long Division?
Division is one of the four basic mathematical operations, the other three being addition, subtraction, and multiplication. In arithmetic, long division is a standard division algorithm for dividing large numbers, breaking down a division problem into a series of easier steps. Let us learn about the steps that are followed in long division.
Long Division Steps
In order to perform division, we need to understand a few steps. The divisor is separated from the dividend by a right parenthesis 〈)〉 or vertical bar 〈|〉 and the dividend is separated from the quotient by a vinculum (an overbar). Now, let us follow the steps of the long division given below to understand the process.
Let us have a look at the examples given below for a better understanding of the concept. While performing long division, we may come across problems when there is no remainder, while some questions have remainders. So, first, let us learn division in which we get remainders.
Division with Remainders
Case 1: When the first digit of the dividend is equal to or greater than the divisor.
Example: Divide 435 ÷ 4
Solution: The steps of this long division are given below:
Division
The division is one of the four basic mathematical operations, the other three being addition, subtraction, and multiplication. In simple words, division can be defined as the splitting of a large group into smaller groups such that every group will have an equal number of items. It is an operation used for equal grouping and equal sharing in math. Let us learn about division operation in math in detail in this article.
| 1. | What is Division? |
| 2. | Parts of Division |
| 3. | Division Algorithm |
| 4. | How to do Division? |
| 5. | Division with Remainders |
| 6. | Properties of Division |
| 7. | FAQs on Division |
What is Division?
The division is one of the basic arithmetic operations in math in which a larger number is broken down into smaller groups having the same number of items. For example, for a sports event, if 30 students need to be divided into groups of 5 students, then how many total groups will be formed? Such problems can be solved easily using the division operation. Here we need to divide 30 by 5. The result will be 30 ÷ 5 = 6. So, there will be 6 groups of 5 students in each. You can verify this value by multiplying 6 and 5, which will give you the original number, 30.
Division Definition
The division is the process of repetitive subtraction. It is the inverse of the multiplication operation. It is defined as the act of forming equal groups. While dividing numbers, we break down a larger number into smaller numbers such that the multiplication of those smaller numbers will be equal to the larger number taken. For example, 4 ÷ 2 = 2. This can be written as a multiplication fact as 2 × 2 = 4.
Division Symbol
The division is denoted by a mathematical symbol that consists of a small horizontal line with a dot each above and below the line. There are two basic division symbols that represent the division of two numbers. They are ÷ and /. For example, 4 ÷ 2 = 2, and 4/2 = 2.
Parts of Division
Parts of division mean the name of the terms associated with the division process. There are four parts of the division, which are dividend, divisor, quotient, and remainder. Let us look at an example of division given below and understand the meanings of these four parts of the division.
Here, when we divide 105 by 8, we get the values of a divisor, dividend, quotient, and remainder. Look at the table below to understand the meaning of these terms.
| Terms | Descriptions | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Dividend | The number that is to be divided | 105 |
| Divisor | The number of equal groups that are to be made, or the number by which we divide the dividend | 8 |
| Quotient | The value/answer obtained after performing the division | 13 |
| Remainder | The remaining or left out value that is not a part of any group | 1 |
In the above image, it is written that «Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder». This equation satisfies the above values but will it be satisfying for values of dividend, divisor, quotient, and the remainder in every division? Let’s find out.
Division Algorithm
The division algorithm is an equation that forms a relationship between all four parts of the division. In any division fact, the product of divisor and quotient added to the remainder is always equal to the value of the dividend. Thus, the general formula of division is: Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder. This is known as the division algorithm.
The above formula helps us to verify the values of quotient and remainder obtained after performing division. We can substitute the values of the quotient, remainder, and divisor in the above equation and check whether the result is the same as dividend or not. If we get the dividend, it means we have done the steps of division correctly. If not, it means there is an error in our calculations that we need to rectify. Let us take one example and see if it satisfies the above division algorithm or not. Divide 17 by 3. 17 divided by 3 will give us 5 as the quotient and 2 as the remainder.
Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder
How to do Division?
One-digit division can be done using multiplication tables. For example, to solve 24 ÷ 6, we just need to see what we need to multiply by 6 to get 24 as the answer. Clearly, 6 × 4 = 24, therefore 24 ÷ 6 = 4. When it comes to the division of numbers with greater numbers, then we can use the long division method. Let us take the example of 65 divided by 5 to understand it. Follow the steps below to learn how to do division:
Look at the image given below showing the above steps of division.
Division with Remainders
It is not always mandatory to have 0 as the remainder. If the dividend is not a multiple of the divisor, then we get a non-zero remainder. When we get a non-zero remainder while dividing a number by another, it is known as a division with remainders. Let us take an example of distributing 9 balloons to 2 children equally such that both children will have an equal number of balloons with them. Is it possible to do that without getting a leftover?
Dividing 9 by 2 will give us 4 as the quotient and 1 as the remainder. We can make 2 groups having 4 balloons in each but 1 balloon will be left. Look at the image below showing division with remainders (9 ÷ 2).
Go ahead and try out the following division questions and observe whether you get a non-zero remainder or not: 63 ÷ 9, 76 ÷ 13, 89 ÷ 8, 34 ÷ 5, and 27 ÷ 3.
Properties of Division
Now let us look at some of the properties of division operation that will help you understand this operation even better. Listed below are a few properties of division:
☛ Related Articles
To know more about the division facts check out a few more interesting articles listed below and learn the basics.
Division Examples
Example 1: Liza has 2 puppies. She bought 8 chewable bones to feed them both equally. How many bones will each puppy get?
Solution:
Given, number of puppies = 2,and number of bones = 8. Thus, number of bones for each puppy = 8 ÷ 2 = 4. Therefore, each puppy will get 4 bones.
Example 2: Eva’s father baked some cookies for her. Pal and Akon, her best friends, decided to give her a surprise by visiting her unannounced. If there were 9 cookies, how many did Eva’s father give Eva, Pal, and Akon so that they were equally shared between them? Use the division algorithm to check your answer.
Solution:
Given, the number of cookies = 9, and number of people to share cookies = 3. Cookies divided equally among Eva, Pal, and Akon = 9 ÷ 3 = 3. To check division, we will put the values in the formula, Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder. So, 9 = 3 × 3 + 0 = 9. Hence, verified.
Example 3: Find the values of quotient and remainder when 75 is divided by 3? Verify the answers using the division algorithm.
Solution:
Here, we have to divide 75 by 3. So, dividend = 75 and divisor = 3. Let us divide 75 by 3 using the steps of division.
Hence, we get, Quotient = 25 and Remainder = 0.
To check division, we will put the values in the formula, Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder. So, 75 = 3 × 25 + 0 = 75. Hence, verified.
How to Do Division
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Christopher M. Osborne, PhD. Christopher Osborne has been a wikiHow Content Creator since 2015. He is also a historian who holds a PhD from The University of Notre Dame and has taught at universities in and around Pittsburgh, PA. His scholarly publications and presentations focus on his research interests in early American history, but Chris also enjoys the challenges and rewards of writing wikiHow articles on a wide range of subjects.
This article has been viewed 202,962 times.
Division is one of the 4 major operations in arithmetic, alongside addition, subtraction, and multiplication. In addition to whole numbers, you can divide decimals, fractions, or exponents. You can do long division or, if one of the numbers is a single digit, short division. Start by mastering long division, though, because it is the key to the entire operation.
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
\u00a9 2022 wikiHow, Inc. All rights reserved. wikiHow, Inc. is the copyright holder of this image under U.S. and international copyright laws. This image is not licensed under the Creative Commons license applied to text content and some other images posted to the wikiHow website. This image may not be used by other entities without the express written consent of wikiHow, Inc.
\n
You Might Also Like
About This Article
To do simple division, think about how many times one number can go into another number. For example, 6 ÷ 2 is 3, because 3 goes into 6 two times. For larger numbers, it’s helpful to spend time reviewing the multiplication tables. To do long division, write the number you want to divide under the division bar, and place the number you want to divide by outside of the bar. For example, if you want to calculate 72 ÷ 3, place 72 under the division bar and 3 outside of it. Then, calculate how many times 3 goes into the first number under the division bar. In this case, you’re calculating how many times 3 goes into 7. The answer is 2, with 1 left over. Write the number 2 above the bar, and the remainder – in this case, 1 – below the 7. Then, if there are any numbers left under the division bar, bring them down to the same row as the remainder. So in this case, you’d write a 2 beside the 1 to get 12. Then, repeat the process: how many times does 3 go into 12? In this example, 3 goes into 12 four times, so you’d write 4 on the line above the problem, beside the other numbers. Therefore, 72 ÷ 3 = 24. If you want to learn how to divide fractions, keep reading the article!
How to Solve Double Digit Division
In today’s post we are going to explain how to solve double digit division.
Before beginning to learn how to solve double digit division, it is important that you become familiar with these terms, because we will use them later.
Dividend: the number that is being divided.
Divisor: the number by which the dividend is divided.
Quotient: the result of division.
Remainder: the amount that is left over after division.
Once you have seen this, you know where to place each number in the division. Now, we have to follow these steps:
That’s the concept, but we are going to go through it with an example.
We are going to solve the following double digit division:
But 584 is bigger than 573; therefore, 8 “does not fit”. You have to choose the preceding number and multiply again:
511 is smaller than the dividend; therefore 7 “does fit”. We write 511 beneath the digits of the dividend and then divide and subtract:
Divide the first two digits of the dividend by the first digit of the divisor and write it in the space of the quotient:
Multiply that digit by the divisor:
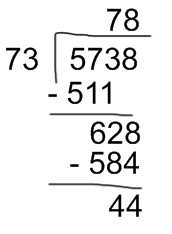
584 is less than 628; therefore, we can subtract:
The result of this division is 78 and a remainder of 44.
I hope that you have learned with this post how to do double-digit division.
Do not hesitate to leave your comments!
And if you want to learn more math, sign in Smartick