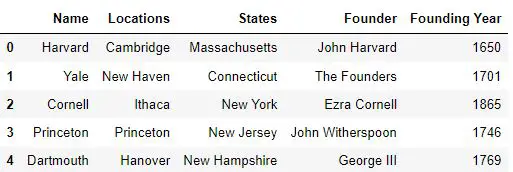
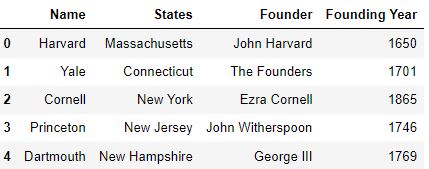
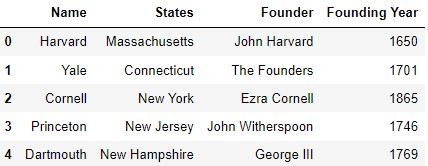
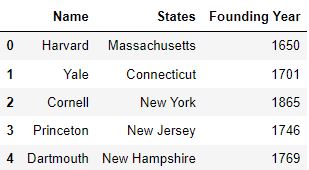
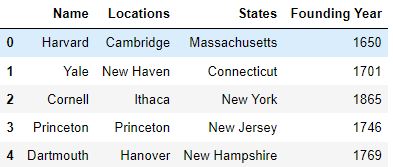
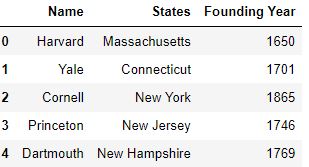
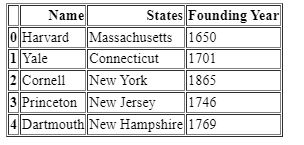
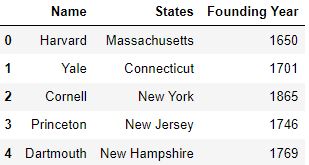
How to drop columns pandas
How to drop columns pandas
Pandas drop column : Different methods
To drop a single column or multiple columns from pandas dataframe in Python, you can use `df.drop` and other different methods.
During many instances, some columns are not relevant to your analysis. You should know how to drop these columns from a pandas dataframe. When building a machine learning models, columns are removed if they are redundant or doesn’t help your model.
Creating a Basic DataFrame
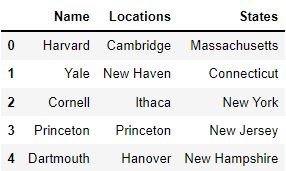
To understand how to drop a column, let us start by creating a basic pandas dataframe.
Using the del command to drop coloumn
To drop a single column in a pandas dataframe, you can use the del command which is inbuilt in python.
Using the drop method
You can use the drop method of Dataframes to drop single or multiple columns in different ways.
pandas.DataFrame.drop(labels=None, axis=0, index=None, columns=None, level=None, inplace=False, errors=’raise’)
Purpose: To drop the specified rows or columns from the DataFrame.
Parameters:
labels: single label or list (default: None). Used to specify the row or column index labels which are to be dropped.
axis: 0 or 1 (default: 0). Specify the orientation along which the labels are to be dropped. If the value of this parameter is set to 0 then the labels will be dropped along the rows and if it is set to 1, then the labels will be dropped along the columns.
index: single label or list (default:None). Alternative to the axis parameter for specifying the orientation along which the labels are to be dropped.
columns: single label or list (default: None). Alternative to specifying the orientation along which the labels are to be dropped.
level: int or level name (default: None). Specify the level in case multi-level indices are present from which the labels are to be removed.
inplace: Boolean (default: False). Specify if a copy of the DataFrame is to be returned or not. If the value of this parameter is set to ‘False’ then a copy of the original DataFrame will be returned. If it is set to ‘True’ then the changes will be made in the original DataFrame.
errors: ‘ignore’ or ‘raise’ (default: raise). Specify if the errors are to be raised or ignored. If the ‘ignore’ value is passed to this parameter then the error is suppressed and only the existing labels are dropped.
Dropping a single column
For dropping a single column, specify the name of that column in the label parameter.
Dropping multiple columns
For dropping multiple columns, pass the list of column names that are to be dropped in the label parameter.
Using the columns argument
By using the columns argument, you do not need to specify the axis parameter to be 1 to remove the columns.
Passing the arguments here ensures that only column labels are targeted
For dropping multiple columns using the columns argument, you can pass a list of column names which are to be dropped.
Dropping columns using column indices
The elements of this array can be accessed via indexing. Therefore, you can drop columns using the column indices as well.
Using loc indexing
You can access rows and columns of a DataFrame using the loc indexing.
The loc indexing method accepts the names of the index labels to access them.
You need to pass the label names of both the row labels and column labels for accessing rows and columns using this method.
You can also pass name patterns as label names to the loc index.
Using name patterns, you can remove all the columns from a DataFrame which have the specified pattern in them.
Want to become awesome in ML?
Hi! I am Selva, and I am excited you are reading this!
You can now go from a complete beginner to a Data Science expert, with my end-to-end free Data Science training.
No shifting between multiple books and courses. Hop on to the most effective way to becoming the expert. (Includes downloadable notebooks, portfolio projects and exercises)
Sold already? Start with the Complete ML Mastery Path
Using iloc indexing
You can also access rows and columns of a DataFrame using the iloc indexing.
The iloc method is similar to the loc method but it accepts integer based index labels for both rows and columns instead of label names.
To learn more about accessing the rows and columns of a DataFrame using the iloc method, click here.
Using the DataFrame.columns.difference method
The DataFrame.columns.difference function is used as a negation operation to the DataFrame.columns method which is used to access the array of column names.
By using this function, you can mention the column names that you want to retain and the remaining columns will be removed.
Using the pop method
The pop method is used to remove the specified column from the DataFrame and return the removed column as a pandas Series.
Practical Tips
Conclusion
In this article, you learnt how to drop columns using the methods:
Test Your Knowledge
Q1: The pop function removes the specified column from the DataFrame, and returns the DataFrame. True or False?
Answer
Q2: Which function is the inbuilt function in Python that is used to drop columns from a pandas Dataframe?
Answer
Q3: Identify the error in the code and write the code for the following:
Answer
Q4: You have a DataFrame df which has three columns: ‘col_A’, ‘col_B’ and ‘col_c’. Write the code to remove the column ‘col_C’ and return it as a pandas Series ‘ser_col_c’
Answer
Q5: You have a DataFrame df which has three columns: ‘col_A’, ‘col_B’ and ‘col_c’. Write the code to remove the column ‘col_A’ and ‘col_B’ using the loc function. Make sure that the columns are removed in the same DataFrame and a copy of the DataFrame is not formed
Answer
This article was contributed by Shreyansh.
Delete Rows & Columns in DataFrames Quickly using Pandas Drop
At the start of every analysis, data needs to be cleaned, organised, and made tidy. For every Python Pandas DataFrame, there is almost always a need to delete rows and columns to get the right selection of data for your specific analysis or visualisation. The Pandas Drop function is key for removing rows and columns.
Pandas Drop Cheatsheet
Removing columns and rows from your DataFrame is not always as intuitive as it could be. It’s all about the “DataFrame drop” command. The drop function allows the removal of rows and columns from your DataFrame, and once you’ve used it a few times, you’ll have no issues.
Sample DataFrame
For this post, we’re using data from the WHO COVID tracker, downloaded as at the 1st January 2020 (data here). If you’d like to work with up-to-date data, please change the source URL for the read_csv function in the loading script to this one.
Delete or Drop DataFrame Columns with Pandas Drop
Delete columns by name
Deleting columns by name from DataFrames is easy to achieve using the drop command. There are two forms of the drop function syntax that you should be aware of, but they achieve the same result:
Delete column with pandas drop and axis=1
The default way to use “drop” to remove columns is to provide the column names to be deleted along with specifying the “axis” parameter to be 1.
Delete column with pandas drop “columns” parameter
Potentially a more intuitive way to remove columns from DataFrames is to use the normal “drop” function with the “columns” parameter specifying a single column name or a list of columns.
Delete columns by column number or index
WARNING: This method can end up in multiple columns being deleted if the names of the columns are repeated (i.e. you have two columns with the same name as the one at index 3).
When you have repeating columns names, a safe method for column removal is to use the iloc selection methodology on the DataFrame. In this case, you are trying to “select all rows and all columns except the column number you’d like to delete”.
To remove columns using iloc, you need to create a list of the column indices that you’d like to keep, i.e. a list of all column numbers, minus the deleted ones.
Delete DataFrame Rows with Pandas Drop
There are three different ways to delete rows from a Pandas Dataframe. Each method is useful depending on the number of rows you are deleting, and how you are identifying the rows that need to be removed.
Deleting rows using “drop” (best for small numbers of rows)
Delete rows based on index value
To delete rows from a DataFrame, the drop function references the rows based on their “index values“. Most typically, this is an integer value per row, that increments from zero when you first load data into Pandas. You can see the index when you run “data.head()” on the left hand side of the tabular view. You can access the index object directly using “data.index” and the values through “data.index.values”.

To drop a specific row from the data frame – specify its index value to the Pandas drop function.
It can be useful for selection and aggregation to have a more meaningful index. For our sample data, the “name” column would make a good index also, and make it easier to select country rows for deletion from the data.
Delete rows based on row number
At times, the DataFrame index may not be in ascending order. To delete a row based on it’s position in the DataFrame, i.e. “delete the second row”, we still use the index of the DataFrame, but select the row from the index directly as we delete. We can also use these index selections to delete multiple rows, or index from the bottom of the DataFrame using negative numbers. For example:
Deleting rows based on a column value using a selection (iloc/loc)
The second most common requirement for deleting rows from a DataFrame is to delete rows in groups, defined by values on various columns. The best way to achieve this is through actually “selecting” the data that you would like to keep. The “drop” method is not as useful here, and instead, we are selecting data using the “loc” indexer and specifying the desired values in the column(s) we are using to select.
There is a full blog post on Pandas DataFrame iloc and loc selection on this blog, but a basic example is here:
Deleting rows by truncating the DataFrame
One final way to remove rows from the DataFrame is to use Python “slice” notation. Slice notation is well summarised in this StackOverflow post:
The slice notation makes it easy to delete many rows from a DataFrame, while retaining the selected “slice”. For example:
Dropping “inplace” or returning a new DataFrame
The drop function can be used to directly alter a Pandas DataFrame that you are working with, or, alternatively, the return the result after columns or rows have been dropped. This behaviour is controlled with the “inplace” parameter. Using inplace=True can reduce the number of reassignment commands that you’ll need in your application or script. Note that if inplace is set as True, there is no return value from the drop function.
Further Reading and Links
As deleting columns and rows is one of the key operations for DataFrames, there’s a tonne of of excellent content out there on the drop function, that should explain any unusual requirement you may have. I’d be interested in any element of removing rows or columns not covered in the above tutorial – please let me know in the comments.
How to use Pandas drop() function in Python [Helpful Tutorial]
This Python tutorial is all about the Python Pandas drop() function. We will see how to use the Pandas drop() function in Python. Also, we will cover these topics:
In this tutorial, we will learn about how to use drop in pandas. Drop is a major function used in data science & Machine Learning to clean the dataset. Also, we will cover these topics
Pandas drop() function
The Pandas drop() function in Python is used to drop specified labels from rows and columns. Drop is a major function used in data science & Machine Learning to clean the dataset.
Pandas Drop() function removes specified labels from rows or columns. When using a multi-index, labels on different levels can be removed by specifying the level.
New to Python Pandas? Check out an article on Pandas in Python.
Pandas drop syntax
Below is the Pandas drop() function syntax.
| Options | Explanation |
|---|---|
| labels | Single label or list-like Index or Column labels to drop. |
| axis | the drop will remove provided axis, the axis can be 0 or 1. axis = 0 refers to rows or index (verticals) axis = 1 refers to columns (horizontals) by default, axis = 0 |
| index | single label or list-like. the index is the row (verticals) & is equivalent to axis=0 |
| columns | Single label or list-like. the columns are horizontals in the tabular view & are denoted with axis=1. |
| level | int or level name, optional For MultiIndex, the level from which the labels will be removed. |
| inplace | accepts bool (True or False), default is False Inplace makes changes then & there. don’t need to assign a variable. |
| errors | the error can be ‘ignored‘ or ‘raised‘. default is ‘raised’ if ignored suppress error and only existing labels are dropped if raised then it will show the error message & won’t allow dropping the data. |
Pandas drop column
Let us see how to use Pandas drop column.
Pandas drop column by index
Pandas drop columns with condition
In this section, we will learn how to drop columns with condition in pandas.
Pandas drop column if exists
In this section, we will learn how to drop column if exists.
Pandas drop column with nan
Pandas drop columns with all zeros
In this section, we will learn how to delete columns with all zeros in Python pandas using the drop() function.
Pandas drop column while reading CSV
Pandas drop column with no name
Pandas drop columns except
Pandas drop non numeric columns
In this section, we will learn to drop non numeric columns
Pandas drop rows
In this section, we will learn how to drop rows in pandas
Pandas drop rows with condition
In this section, we will learn how to drop rows with condition.
Pandas drop rows with nan in column
Pandas drop rows with nan
Pandas drop rows with nan in specific column
Pandas drop rows with condition string
In this section, we will learn how to drop rows with condition string
Pandas drop rows with value in any column
In this section, we will learn how to drop rows with value in any column
Pandas drop range of rows
Pandas drop rows with zero in column
Pandas drop header row
In this section, we will learn how to drop the header rows. In our demonstration we will create the header row then we will drop it.
Pandas drop non-integer rows
In this section, we will learn how to drop non integer rows.
Pandas drop non numeric rows
In this section, we will learn how to drop non numeric rows.
Pandas drop blank rows
In this section, we will learn how to remove blank rows in pandas. Blank rows are represented with nan in pandas. So ultimately we will be removing nan or missing values.
Pandas drop missing rows
Drop Column with NaN values in Pandas DataFrame
In this section, we will learn about columns with nan values in pandas dataframe using Python. NaN is missing data.
Drop Column with NaN Values in Pandas DataFrame Replace
In this section, we will learn about removing the NAN using replace in Python Pandas.
Drop Column with NaN Values in Pandas DataFrame Get Last Non
In this section, we will learn about Drop column with nan values in Pandas dataframe get last non.
Check out the below Python tutorials:
In this tutorial we have learned how to drop data in python pandas also we have covered these topics.
Entrepreneur, Founder, Author, Blogger, Trainer, and more. Check out my profile.
How to Use the Pandas Drop Technique
In this tutorial, I’ll explain how to drop rows and columns from a dataframe using the Pandas drop method.
I’ll explain what the drop method does, explain the syntax, and show you clear examples.
If you need something specific, you can click on any of the following links.
Table of Contents:
The drop technique is fairly simple to use, but there are a few important details that you should know. So, let’s start with a quick explanation of what it does and how it works.
A quick introduction to Pandas Drop
The Pandas drop method deletes rows and columns from Python dataframes and Series objects.
You can acutally use this technique to:
Although, I use this technique most frequently to delete columns (i.e., variables).
Deleting rows and columns is very common when you’re doing “data wrangling” or data cleaning. So to master data wrangling in Python, you really need to know how to use this technique.
Having said that, exactly how you use it depends on the syntax. That being the case, let’s take a look at the syntax of the drop() method.
The Syntax of Pandas drop
In this section, I’ll show you the syntax to:
We’ll look at those separately, and then I’ll explain some optional parameters afterwards.
A quick note
One quick note before we look at the syntax.
All of these syntax explanations assume that you’ve already imported Pandas and that you have a Pandas dataframe available (or a Series).
You can import Pandas with the following code:
And if you need a refresher on how to create dataframes, you can read our tutorial on Pandas dataframes.
syntax: delete a column
First, let’s look at the syntax to delete a single column.
Inside the parenthesis, you need to use the columns parameter.
The argument to the parameter will be the name of the column that you want to delete. The name of the column should be enclosed inside quotation marks.
I’ll show you an example of this in example 1.
syntax: delete multiple columns
The syntax to delete multiple columns is similar to the syntax to delete a single column.
But here, to drop multiple columns, you provide a list of column names.
I’ll show you an example of this in example 2.
syntax: delete rows
Finally, let’s look at the syntax to delete a row or rows.
The syntax to delete rows is very similar to the previous to syntax variations.
But here, to delete rows, you use the labels parameter.
The argument to the labels parameter is the ‘label’ of the row from the dataframe index. You can use either a single row label, or multiple labels inside of a Python list.
This is fairly simple to do, but to do it properly, you really need to understand Python dataframe indexes. If you need a refresher, you can read our tutorial on Pandas indexes.
I’ll show you an example of how to delete rows in example 3.
The parameters of Pandas drop
Now that we’ve looked at the basic syntax of Pandas drop, let’s look at some parameters.
The important parameters that I think you should know are:
There are a few other parameters, but I think several of them are simply confusing for most beginners and there are a few unnecessary parameters. So, the three above are the ones I recommend using.
Let’s discuss each of them.
columns
The columns parameter enables you to specify the columns that you want to delete.
The argument to this parameter can be a single column name or a list of column names. The column names themselves must be enclosed inside quotes.
I’ll show you how to use the columns parameter in example 1 and example 2.
labels
The labels parameter enables you to specify the rows that you want to delete.
The argument to this parameter can be a single row label or a list of row labels.
The format of the labels depends on how you’ve structured the index. If the labels are integers, the labels you provide will be integers. But if the index labels are strings, then you’ll provide strings to this parameter.
I’ll show you how to use the labels parameter in example 3.
inplace
The inplace parameter enables you to modify your dataframe directly.
Be careful when you use this parameter, since it will overwrite your data.
The output of Pandas drop
By default, the drop() technique outputs a new dataframe and leaves your original dataframe unchanged.
Examples: how to drop rows and columns of a Pandas dataframe
Now that we’ve looked at the syntax, let’s take a look at how we can use the drop() method to delete rows and columns of a Python dataframe.
Examples:
Run this code first
Before you run any of the examples, you’ll need to run some preliminary code first.
Specifically, you need to:
Import Pandas
Fist, let’s import Pandas.
You can do that with the following code:
Obviously, we’ll need Pandas to use the Pandas drop technique. We’ll also need Pandas to create our data. Let’s do that next.
Create Dataframe
To do this, we’ll call the pd.DataFrame() function, but we’ll also set the dataframe index with the set_index() method.
This dataframe contains mock sales data. We’ll be able to use this in our examples.
Let’s quickly print it out so we can see the contents:
The dataframe also has an index with the names of the salespeople in the data. We’ll be able to use the index to reference the rows and delete specific rows.
So now that we have our dataframe, let’s run some examples.
EXAMPLE 1: Delete a single column from a dataframe
First, let’s start very simple.
Here, we’re going to delete a single column from our dataframe.
To do this, we’ll call the drop method, and we’ll use the columns parameter.
Let’s take a look:
Explanation
This is fairly simple, but let me explain.
Here, we deleted the expenses column.
Inside the parenthesis, we used the code columns = ‘expenses’ to specify that we want to drop the expenses column. Note that the name of the column is inside quotation marks (i.e., it’s presented as a string).
In the output, we see that the entire expenses column has been removed.
I’ll show you how to directly modify the original dataframe in example 4.
EXAMPLE 2: Delete multiple columns from a dataframe
Next, let’s delete multiple columns from a Pandas dataframe.
To do this, we’ll still use the columns parameter.
But instead of providing a single column name as the argument, we’ll provide a list of column names.
Specifically, here, we’ll delete the region variable and the expenses variable.
Let’s take a look:
Explanation
In the output we see that both the region variable and the expenses variable have been removed.
To do this, we called the drop() method, but we used the columns parameter to specify multiple variables to drop.
Specifically, inside the parenthesis, we used the code columns = [‘region’,’expenses’] to indicate that we want to remove the region variable and the expenses variable. Notice that the names of these variables are inside quotations (i.e., they are presented as strings). Furthermore, they are passed to the columns parameter as a list of variable names.
Keep in mind that here, we only deleted two variables. But if you have a larger dataframe and you want to delete many more variables, you can simply create a list of all of the names you want to delete.
EXAMPLE 3: Drop specific rows from a dataframe
Now, let’s drop some rows from our dataframe.
Deleting rows is very similar to deleting columns. But instead of using the columns we’ll use the labels parameter.
By using the labels parameter, we can specify specific rows to delete by the index label.
Let’s take a look:
Explanation
The labels parameter enables us to delete rows by index label and the list of values (i.e., [‘William’,’Paulo’] ) indicate exactly which rows to remove.
This is fairly simple, but to really understand it, you need to understand what a dataframe index is. If you need a refresher, you should check out our tutorial on Pandas indexes.
Note that in this example, we deleted multiple rows, so we presented the labels inside of a Python list, similar to deleting multiple columns like we did in example 2.
EXAMPLE 4: Delete columns and modify the data “in place”
Finally, let’s directly modify our data by deleting a column “in place.”
Remember: when we use the drop() method, the technique produces a new dataframe as the output by default, and leaves the original dataframe unchanged.
Let’s take a look, and then I’ll explain.
Create dataframe copy
Before we run the example, we’ll first create a copy of the data.
That’s because we’ll be directly modifying our data. As a safeguard, we’ll work with a copy right now.
Drop column “in place”
And let’s print out the data:
Explanation
Frequently asked questions about Pandas drop
Now that we’ve looked at some examples, let’s look at some common questions about the drop() technique.
Frequently asked questions:
Question 1: I used the drop method, but my dataframe is unchanged. Why?
If you use the drop method, you might notice that your original dataframe remains unchanged after you call the method.
For example, in example 1, we used the following code:
If you print out sales_data after you run the code, you’ll realize that sales_data is unchanged. The expenses column is still there.
That’s because the drop() method produces a new dataframe, and leaves both original dataframes unchanged.
By default, the output of the method is sent to the console. We can see the output in the console, but to save it, we need to store it with a name.
For example, you could store the output like this:
But be careful, if you use either of these techniques, they will overwrite your original dataset. Make sure that you check your code so it works properly before you overwrite an input dataframe.
Question 2: What does the axis parameter do?
The axis parameter is an alternative way of controlling whether you delete rows or columns.
Personally, I think that the use of the axis parameter for the drop() method is very poorly designed. I won’t go into the details, but the way the Pandas developers implemented this parameter makes it very confusing to work with.
The good news is that there’s another way. You can completely skip using the axis parameter.
Instead, you can use the columns parameter when you want to delete columns, and you can use the labels parameter when you want to delete rows.
I show the syntax for using these other parameters these in the syntax section, and I show examples of deleting columns and rows in example 1, example 2, and example 3.
Leave your other questions in the comments below
Do you have any other questions about the Pandas drop method?
Is there something else that you need to understand that I haven’t covered here?
If so, leave your question in the comments section below.
To learn more about Pandas, sign up for our email list
This tutorial should have given you a good introduction to the Pandas drop technique, but if you really want to master data manipulation and data science in Python, there’s a lot more to learn.
So if you’re ready to learn more about Pandas and more about data science, then sign up for our email newsletter.
We publish FREE tutorials almost every week on:
When you sign up for our email list, we’ll deliver these free tutorials directly to your inbox.
Sign up for FREE data science tutorials
If you want to master data science fast, sign up for our email list.
When you sign up, you’ll receive FREE weekly tutorials on how to do data science in R and Python.
Pandas Delete Column
In this Python Pandas tutorial, we will discuss everything on Pandas Delete column and how to Drop column in DataFrame using Pandas.
We have used Electric Car Dataset downloaded from Kaggle.
Pandas Delete Column DataFrame
In this section, we will learn about Pandas Delete Column from DataFrame using Python.
Syntax:
This is the the syntax for drop() method in Python Pandas.
In our example on the jupyter notebook, we have demonstrated all of these methods.
Pandas Delete Column by Name
In this section, we will learn about Pandas Delete Column by Name.
Implementation on Jupyter Notebook
Please read the comments to understand the use of that code snippet.
Pandas Delete Column by Index
In this section, we will learn about Pandas Delete Column by index.
Implementation on Jupyter Notebook
Please read the comments to understand the use of that code snippet.
Pandas Delete Column if Exists
In this section, we will learn about Pandas delete column if exists.
Implementation on Jupyter Notebook
Please refer to the examples to understand the use of code snippets.
Pandas Delete Column by Condition
In this section, we will learn about Pandas Delete Column by Condition.
Implement on Jupyter Notebook
Pandas Delete Columns with NaN
In this section, we will learn about Pandas Delete Columns with NaN.
Implementation on Jupyter Notebook
Pandas Delete Column if all nan
In this section, we will learn about Pandas Delete Column if all nan.
Pandas Delete Column by Position
In this section, we will understand about Pandas Delete column by Position. Position can also be referred to as an index.
Pandas Delete Column with no Name
In this section, we will learn about Pandas Delete Column with No Name.
Implementation on Jupyter Notebook
Pandas Delete Column Header
In this section, we will learn about Pandas delete column header in Python.
Implementation using Jupyter Notebook
Pandas Delete Columns Except
In this section, we will learn about Pandas Delete Columns Except.
Implementation on Jupyter Notebook
Drop column in Pandas DataFrame
Syntax:
Here is the Syntax of Pandas.drop() method
Source Code:
In the above code first, we have imported a Pandas package and then create a dictionary in which we have inserted five fields in each column.
Now we want to convert the dictionary into a dataframe by using the pd.Dataframe() method.
Now in this example, we want to remove the column name ‘val2’. To do this we can use the df.drop() method to remove columns for the dataframe.
You can refer to the below Screenshot
Drop first column in Pandas DataFrame
Syntax:
Here is the Syntax of DataFrame.iloc() method
Example:
Let’s take an example and understand how to drop the first column from Dataframe.
Here is the Screenshot of the following given code
In the above Screenshot as you can see the output of the first column ‘stu_name’ has been removed from DataFrame.
Drop the first column from DataFrame
By using the df.drop() method we can perform this particular task and in this example, we will use parameter axis=1 and inplace =True.
Source Code:
In the above code, we have dropped the first column based on the column index. In this example, we have mentioned the index number along with the axis and inplace parameter in the df.drop() method.
Once you will print ‘df’ then the output will show the modifying dataframe.
Here is the implementation of the following given code
Drop last column in Pandas DataFrame
Syntax:
Example:
Let’s take an example and check how to drop the last column of the DataFrame
In the above code, we have created a list of tuples and then create a Dataframe object. Now we want to drop the last column of the dataframe we can simply apply the df.columns[-1] method in the del keyword.
Here is the execution of the following given code
Drop the last column of Pandas DataFrame
By using the df.drop() method we can solve this problem and in this example, we have mentioned the index number along with the axis and inplace parameter in the df.drop() method.
Source Code:
Here is the Screenshot of the following given code
As you can see in the Screenshot the last column ‘val5’ has been removed from Pandas DataFrame.
Drop multiple columns in Pandas DataFrame
Source Code:
In the above code, we have created a dataframe and then use the drop() function on the Pandas DataFrame to remove multiple columns.
Once you will print ‘df’ then the output will display the updated dataframe that contains only a specific ‘designation’ column.
You can refer to the below Screenshot
How to drop multiple columns in Pandas
By using the Python Pandas df.pop() method we can perform this particular task and this function is used to remove a specific column.
Syntax:
Here is the Syntax of DataFrame.pop() method
Source Code:
Here is the Screenshot of the following given code
Drop duplicate columns in Pandas DataFrame
Syntax:
Here is the Syntax of Pandas.DataFrame.duplicate() method
Source Code:
Here is the implementation of the following given code
Remove first column in Pandas DataFrame
In this topic, you can use the drop() function, and also you can refer to the above topic Drop the first column in Pandas DataFrame.
Remove column names in Pandas DataFrame
Source Code:
Here is the implementation of the following given code
Drop column Pandas series
Syntax:
Here is the Syntax of Pandas.Series.drop() method
Example:
In the above code first, we have imported numpy and Pandas library and then create a Pandas series by using pd. series and assign a number of values by applying np.arange() function.
Here is the Output of the following given code
Drop one column in Pandas DataFrame
Example:
You can refer to the below Screenshot
Drop list of column in Pandas DataFrame
Example:
In the above code, we have removed two specific columns that are ‘Stu_name’ and ‘Stu_id’. Once you will print ‘new_val’ then the output will display the updated dataframe.
Here is the execution of the following given code
You may like the following Python tutorials:
In this tutorial, we have learned about Pandas Delete Column. Also, we have covered these topics.
Entrepreneur, Founder, Author, Blogger, Trainer, and more. Check out my profile.