How to enable ssh on ubuntu
How to enable ssh on ubuntu
Installing and Configuring OpenSSH on Ubuntu and Debian-based Distributions
If you want to enable SSH on Ubuntu desktop, use the following command:
sudo apt install openssh-client
If you want to enable SSH on Ubuntu server, use the following command:
sudo apt install openssh-server
Read the rest of the article for more detailed information.
Every system admin and developer has experienced the need for remote logins into the systems for quicker administration and debugging purposes.
In an IT environment, almost all the sysadmin tasks these days are performed via remote logins.
And not just sysadmins, even normal users sometimes need to remote login to the servers.
So how do you remotely connect to a Linux system? There are multiple tools available for remote logins but when it comes to Linux, SSH is the most popular choice.
SSH, short for secure shell, is a protocol that allows remote login securely from one computer to another.
Now the question is how do you enable SSH on Ubuntu or Debian or any other Linux distributions you are using?
Remember that SSH is only a protocol and this can protocol can be implemented via a number of tools such as lsh, Dropbear etc., but the most widely used tool for SSH is the open source software OpenSSH.
In this tutorial, you’ll see how to install OpenSSH and configure it to enable SSH on Ubuntu and Debian based Linux distributions. The steps mentioned are applicable to both desktop and server versions of Ubuntu/Debian.
I also advise reading this article to get acquainted with the basics of SSH.
Enable SSH on Ubuntu and Debian with OpenSSH
As I mentioned earlier, OpenSSH is the software for making SSH logins. It listens on a port and authenticates the incoming users and creates a new shell for the remote user.
For SSH to work, an ssh server needs to be running on the remote system to which the user needs to log in. You also need to have an ssh client in the local system from which the user will log into the remote system.
OpenSSH provides both of these functionalities. There is openssh-client for end-users and openssh-server for the remote servers.
Before you install OpenSSH, you should check if SSH is already installed and running on your system.
Check if SSH is already enabled and running
It’s more likely that SSH is already enabled on your system. To verify, run the following command on either of the remote server or the end user system:
If SSH is enabled, you should see an information about SSH agent on your desktop:
On the server, you should see the information about a SSH daemon running:
If you don’t see an output similar to the ones mentioned above, you don’t have SSH running on your system. It’s time to install OpenSSH.
Installing OpenSSH on Ubuntu and Debian
A quick note about openssh-client and openssh-server before you go on installing OpenSSH.
openssh-client: This is the package you need if you want to connect to a remote Linux system using SSH. This is what you need as the end-user/desktop user.
openssh-server: This is the package you need if you want to allow remote logins via SSH to your system. This is what you need on your Linux server.
Note that installing openssh-server also enables you to remote login to other systems via SSH. In other words, openssh-server consists openssh-client. But if you are just an end user with a Linux desktop, there is (mostly) no need to install openssh-server and allow remote login to your system.
Now that you know the difference between the two, it’s time to see how to install them.
Note that to install OpenSSH on Ubuntu or Debian, you need to have sudo/root rights. If you don’t have such permission, contact your system administrator. You may also read this article about creating sudo users.
Installing OpenSSH for desktop or end users
If you just want to connect to other remote systems over SSH, you should install the openssh-client package using the following command:
Once you have installed ssh on your system, you are read to use it. Please refer to this detailed article to know how to use SSH.
Installing OpenSSH for servers
If you are setting up an Ubuntu/Debian server, should install the openssh-server package so that other remote users can connect to your system.
Once you have installed openssh-server, it’s time to learn how to tweak it and configure it as per your need.
Controlling the SSH daemon sshd (for servers)
You’ll have the SSH daemon named sshd installed and enabled to be started on reboot automatically by default. systemctl is one of the several ways to control the SSH daemon. To know more about systemctl, please refer to this article.
Start the sshd service
The service can be started by simply issuing:
Stop the sshd service
The service can be stopped in a similar way:
Restart the sshd service
If you want the sshd service to be stopped and started (usually needed in the case of changing configurations to sshd service), you can simply use this command:
Enable SSH on Ubuntu automatically at each boot
Some services need to be started on rebooting itself to avoid manual interaction and if it is very frequently used. It is very essential for services like Apache, mongod, mysqld, sshd in servers.
If you want to enable such auto start for sshd, use:
Disable SSH auto start on reboot
If you don’t want the sshd to be started on reboot automatically, use
Above said four tips are necessary whenever you make a change to the ssh service such as changing the port. You can make use of the above commands to manage any service (like mysqld, mongod, apache) with the service name sshd replaced with the target service.
Tip: You can use nohup command to keep on running commands even if your SSH connection disconnects.
Configuring SSH (for servers)
As of now, our ssh service will be listening on port 22 and ready to authenticate any user (also root) once a key is stored.
If you want to change any of the configurations such as port to listen for connections, you can edit the file “/etc/ssh/sshd_config” by adding, deleting, commenting or uncommenting the lines and then restart the sshd service.
There are many options to configure. I have created a list of configurations that will be most likely needed.
1. Change the default SSH port
Usually, the sshd service listens on TCP port 22. If you want, you can change the SSH port to say 5678 by adding/editing the following line in /etc/ssh/ssh_config.
Restart the service to see the change immediately.
2. Disable root login via SSH
Allowing root users to authenticate by ssh is not a good idea due to security reasons. sudo users can be logged in remote but not root as root is in the top of security food chain.
Root Login can be disabled by adding (if not already present) the following line and restarting the service.
If the line is already present, then ensure it is not commented out.
3. Allow SSH Key-Based Authentication on
You may want to allow ssh key-based authentication so that end user won’t have to enter the password all the time. Just using the ssh [email protected] will be enough for logging into the remote system.
For this, you should configure SSH to allow public key authentication:
If the line is already present, then ensure it is not commented out.
Now if you want to allow a particular system to log in via public key, you need to add that public key of the end user in the file .ssh/authorized_keys.
You can make ssh keys (public key and private key) with the help of ssh-keygen. To know more about key-gen, refer to this great resource.
You can transfer the public key of the end-user to the remote server by any means you prefer. You may use scp command if you like or simply get it via FTP. It’s really up to you.
Above three are most needed, but if you want to change further, please refer the manpage of sshd_config.
Conclusion
I think that’s a good enough reading material to know how to enable SSH on Ubuntu/Debian and how to configure SSH on your server for remote logins.
In a related article, you can refer to this article detailing a SSH error that arises due to copying public key between systems.
If you found this article useful, Share it with your friends. If you have any suggestions or comments or if you think I missed something, feel free to drop a comment below.
How to Enable SSH on Ubuntu 18.04
Home » Security » How to Enable SSH on Ubuntu 18.04
When establishing a remote connection between a client and a server, a primary concern is ensuring security. For Linux users, the best practice of accessing and managing your server remotely is through the cryptographic protocol known as Secure Shell (SSH).
SSH encrypts all data transferred from one machine to another, making sure that no sensitive information is compromised during the process. As a desktop client, you can safely run a command line, transfer files, secure network services, and much more.
By following the steps below, you will learn how to enable SSH on Ubuntu 18.04.
Enable SSH on Ubuntu
The SSH server is not installed by default on Ubuntu systems. To install and enable SSH on Ubuntu follow the steps found below:
1. Open the terminal either by using the CTRL+ALT+T keyboard shortcut or by running a search in Ubuntu Dash and selecting the Terminal Icon.
2. Before starting the installation process, check if an SSH server has already been installed on your computer. Use the following command:
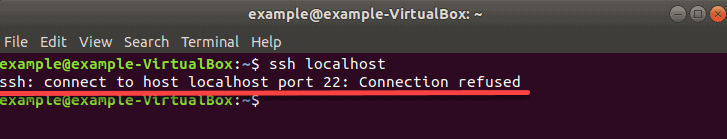
If you see the SSH “Connection Refused” message, you will have to go through the SSH installation process.
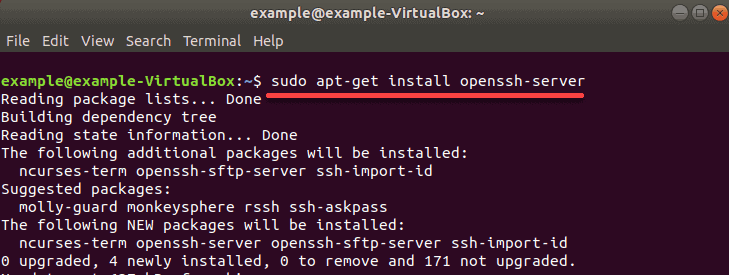
3. To install SSH, first update the package repository cache with:
4. Now install the OpenSSH software package by entering:
If prompted, type in your password and press y (yes) to permit the installation.
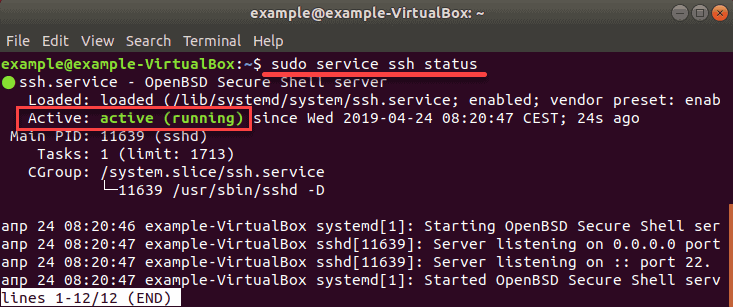
5. To verify the installation was successful and SSH is running use the command:
The confirmation message that you are looking for is: Active: active (running)
This means you have installed and enabled SSH on your remote machine, which can now accept commands from your SSH client.
Log into Remote Server with SSH
Once you have gone through the process of enabling SSH on Ubuntu 18.04, you are ready to log into your remote machine.
1. Open the terminal (CTRL+ALT+T) and type the following command:
Change the username and IP address to the username and IP address of the Ubuntu computer on which you have installed SSH.
2. If you do not know the IP address, you can quickly identify it through the terminal by typing the command:
This should display the public IP address of the machine where SSH was installed.
Once you have identified and typed in all the information, you have officially logged into your server. You are free to manage it from the comfort of your workstation safely.
SSH Configuration Options
Edit Configuration File
After successfully installing OpenSSH on Ubuntu, you can edit its configuration file.
You can change the default port (generally a good idea, as a precautionary security measure), disable the “root ” user or make other configuration adjustments.
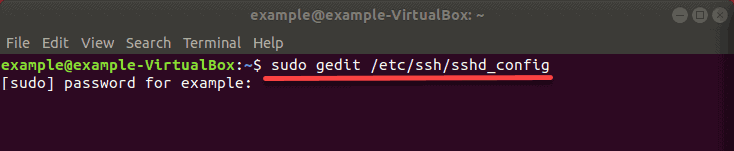
1. Open your SSH configuration file with the command:
Gedit is a text editor which comes by default in Ubuntu, but you can also use other text editors such as nano. If you prefer using nano, you can easily install it by running the following command:
2. When prompted, type in your password and press y (yes) to permit the installation.)
3. Then replace “gedit ” with “nano” type in the command:
4. Now that you have opened the file (using any of the text editors recommended above) find and make any necessary changes.
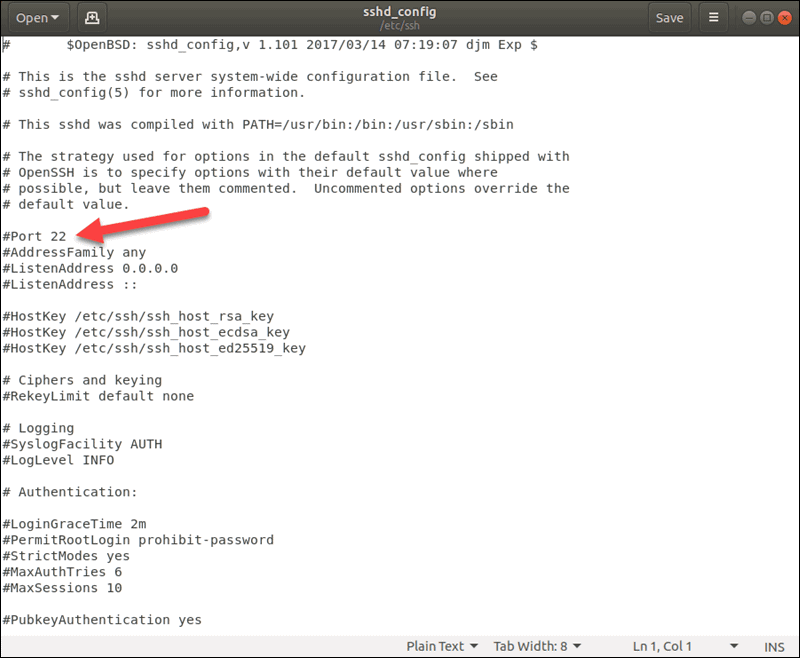
For example, if you wish to change the port number to listen on TCP port 2222 instead of the default TCP port 22, find the line in which Port 22 is specified by default, and change it to Port 2222.
Important: Changing the default port number is an SSH security best practice. Everyone is aware of the default port number so changing it is a recommended security precaution.
Disable Root
Another critical security precaution is to make sure that the root is disabled. That way, the root user cannot be invoked remotely, and security will be significantly improved.
2. After you have made the desired changes, save and close the file by using the CTRL+W keyboard shortcut (or the commands to save and close in your editor of choice).
3. For the changes to take into effect, restart SSH with the following command:
Configure Firewall
If you have decided to change the default port number, you must configure your firewall to allow traffic via the specified port.
Let’s use the example of Port 2222.
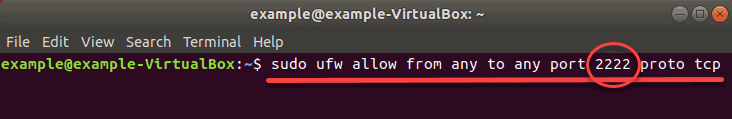
The default firewall configurations tool in Ubuntu is UFW, configure it with the command:
Some firewalls may require allowing traffic to the public IP address of the machine running SSH.
Note: The “p2222” is the port number we have defined in the Configure SSH section. If you used the default port 22, then it is not necessary to put the port number.
How to Disable SSH on Ubuntu
To temporarily disable SSH:
To start SSH again:
To completely disable SSH after reboot:
To enable SSH on Ubuntu host again:
By following the simple steps above, you now know how to enable SSH on Ubuntu 18.04. Now you can establish a reliable and secure protocol between you and a remote device.
Get started by logging to your machine to perform sysadmin tasks with the command prompt.
Как включить SSH в Ubuntu 20.04
Secure Shell (SSH) — это сетевой протокол, используемый для безопасного соединения между клиентом и сервером. Каждое взаимодействие между сервером и клиентом зашифровано.
В этом руководстве объясняется, как включить SSH на компьютере с Ubuntu.
Включение SSH в Ubuntu
По умолчанию при первой установке Ubuntu удаленный доступ через SSH не разрешен. Включение SSH в Ubuntu довольно просто.
Выполните следующие шаги от имени пользователя root или пользователя с правами sudo для установки и включения SSH в вашей системе Ubuntu:
Откройте терминал с помощью Ctrl+Alt+T и установите пакет openssh-server :
При появлении запроса введите свой пароль и нажмите Enter, чтобы продолжить установку.
После завершения установки служба SSH запустится автоматически. Вы можете убедиться, что SSH работает, набрав:
Вывод должен сообщить вам, что служба запущена и разрешена для запуска при загрузке системы:
Нажмите q чтобы вернуться в командную строку.
Подключение к SSH-серверу
Чтобы подключиться к вашей машине Ubuntu по локальной сети, вызовите команду ssh, за которой следует имя пользователя и IP-адрес в следующем формате:
Если вы не знаете свой IP-адрес, вы можете легко найти его с помощью команды ip :
Найдя IP-адрес, войдите на удаленный компьютер, выполнив следующую команду ssh :
При первом подключении вы увидите такое сообщение:
Введите yes и вам будет предложено ввести пароль.
После ввода пароля вы увидите сообщение Ubuntu по умолчанию:
Теперь вы вошли в систему на своей машине с Ubuntu.
Подключение к SSH за NAT
Чтобы подключиться к домашней машине с Ubuntu через Интернет, вам необходимо знать свой общедоступный IP-адрес и настроить маршрутизатор на прием данных через порт 22 и их отправку в систему Ubuntu, где работает SSH.
После того, как вы нашли IP-адрес и настроили маршрутизатор, вы можете войти в систему, набрав:
Если вы открываете свою машину для доступа в Интернет, рекомендуется принять некоторые меры безопасности. Самый простой — настроить маршрутизатор на прием трафика SSH на нестандартный порт и пересылку его на порт 22 на машине, на которой запущена служба SSH.
Вы также можете настроить аутентификацию на основе ключа SSH и подключиться к компьютеру с Ubuntu без ввода пароля.
Отключение SSH в Ubuntu
Чтобы отключить SSH-сервер в вашей системе Ubuntu, просто остановите службу SSH, запустив:
Позже, чтобы снова включить его, введите:
Выводы
Мы показали вам, как установить и включить SSH на вашем Ubuntu 20.04. Теперь вы можете войти на свой компьютер и выполнять повседневные задачи системного администратора через командную строку.
Если у вас есть вопросы, оставьте комментарий ниже.
How to Enable SSH Access on Ubuntu?
There are a few features that are not available out of the box in Ubuntu. One such feature is SSH. If you ever install Ubuntu desktop on your machine and expect the ssh to work by default, it doesn’t. You would get an error message that says ‘The remote system refused the connection’ However, in the Ubuntu server you would get an option to choose SSH service during the installation.
Also if you try to open winscp on your local machine and tried to access the Ubuntu that wont work either.
You will get Network error, connection refused.
Even when you try to transfer the file using the SCP command, it will still not work and throw the same error message that says connection refused lost connection, because SCP also use the same ssh port number 22.
And for me, being from the network background I really needed this ssh access as well as I should have the ability to transfer data over SCP. To fix the SCP access, we have to just enable the SSH on Ubuntu.
In this blog, we are going to enable ssh access on Ubuntu, and secure the ssh access. By doing that SCP access also will be enabled for the users.
What is SSH in Ubuntu?
An SSH (secure shell) is a protocol that lets you securely connect to remote hosts’ command-line interface. Since it is encrypted, no one can read the data between the SSH server and the ssh clients. The default port that is used by the SSH is 22.
Is SSH enabled by default on Ubuntu?
The SSH service is not enabled on the Ubuntu desktop by default. However, when you install the Ubuntu server, you will get an option to install the OpenSSH service during the installation, and if you do not choose that option, ssh service will not be enabled.
You can follow the steps here to install the ssh service on the Ubuntu machine.
We are using Ubuntu version 20.04 for this lab, if you have another version of Ubuntu such as 20.10, 19.10, 19.04, 18.10, 18.04. The steps mentioned here would work just fine.
Steps to enable SSH access on Ubuntu.
To enable SSH service on the Ubuntu machine, you will have to download and install the utility called OpenSSH service on your Ubuntu machine. Let’s go ahead and install the OpenSSH utility on my Ubuntu machine.
1. Verify the SSH service installed or not.
When you get the error message that says the remote system refused the connection, which doesn’t mean the ssh service is not installed on the machine. It could also mean that the ssh service may be blocking the connection.
You can check the status by typing service ssh status or systemctl status ssh.
As you can see, in my case, the ssh service is not installed, so let’s go ahead and install the ssh service on Ubuntu.
Note: If you have already installed the SSH service, you don’t have to install the service again, and you can go to the step4.
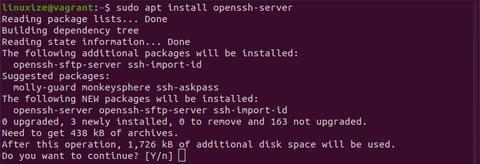
2. Ubuntu enable SSH – By installing OpenSSH-Server.
Log in to the terminal and enter the below commands to install the OpenSSH service on your ubuntu machine.
3. Check the SSH service status.
As you can see the ssh service not only installed, it has also been started automatically.
At any point, if the ssh service has not started you can enter the command service ssh start to start the service.
To stop the service type service ssh stop and you can also restart the services by typing service ssh restart just like how you would manage any other services in Linux.
4. Start ssh on boot ubuntu.
You also need to make sure the SSH service starts during the boot.
If you don’t do that when the system reboots and you try to access the Ubuntu machine via ssh, you cannot get in, and it will throw an error saying connection refused.
The problem is the SSH service wouldn’t have started during the boot.
5. Verify the ssh access from localhost.
To verify the SSH access you can do the SSH to the same ubuntu host by typing ssh localhost
As you can see, I was able to ssh into the ubuntu localhost using ssh.
This means, the ssh service is working and you are able to ssh from your local machine.
6. Verify the ssh access from the remote.
Now lets go to any remote host and try to ssh again, this time of course you have to use the IP address of the Ubuntu host.
Type IP addr and get the IP address, first make sure you are able to reach the remote IP by pinging the IP.
Yes, we are able to reach the ubuntu host from the remote machines.
By this point, you should be able to access the Ubuntu host via SSH. Read on to secure the SSH access and test the SCP connection.
7. Secure the SSH access.
We are able to access the ssh and it works just fine. Next, let’s take a look at how you can secure ssh access.
We can secure the ssh access multiple ways, and we are looking into two options here. First, change the default ssh port number from 22 to something different. In our example, let’s use port number 2222.
Second, Allow only specific users to the ssh, let’s see how we can achieve that.
If you wanted to tighten the security more, you could even allow only a specific IP address to SSH into the host. We are not going to do that here.
a. Change SSH port to 2222
Changing the default ssh port number is very easy. You have to open the ssh sshd config file and replace port number 22 with a different one.
The ssh configuration file is located in /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Edit the configuration file using an ubuntu editor nano.
You should be able to see the port 22 is commented, you have to uncomment that line and change the port number.
For this test, I am using the port number 2222.
After you made the change, go ahead and restart the ssh service in Ubuntu.
The current session would continue even if you change the port number and restart the services. You can now exit out of the current session and try to ssh again.
As you can see, when I tried to ssh again, it didn’t let me in.
That’s because, by default, the ssh service would start the session with port number 22. So anytime you want to ssh into this box, you will have to add the ssh port number manually before proceeding.
And we are able to ssh into the Ubuntu machine successfully this time after modified the port number.
b. Restrict the access to specific users.
To restrict the access to specific users in Ubuntu you can add a line that says Allowusers and the username.
For eg: Allowusers user1
After you made the change, you can go ahead and restart the ssh service.
Try to ssh with the old username and see if you can still access the system via ssh.
I have tried to ssh and it prompted me for the password three times and it failed, though I enterered the currecct credentails.
Which means we restricted the access on the user level.
How do I allow the old user again?
You can add the old username to the allow list. Just below the allowusers line you can add the same line, but this time with the old username.
If you have multiple users, you can keep adding the usernames in here.
As soon as I made the changes and restarted the ssh services, I am now able to to authenticate using the my old username.
8. Verify the SCP access.
Now that we have configured the SSH access, we should be able to start transferring files over the SCP protocol as well.
Open the WinSCP and try to access the Ubuntu machine, and you should be able to access it.
Note : Remember to put the port number 2222 while accessing it.
I am also able to transfer files using SCP on CLI.
OpenSSH Server
Introduction
OpenSSH is a powerful collection of tools for the remote control of, and transfer of data between, networked computers. You will also learn about some of the configuration settings possible with the OpenSSH server application and how to change them on your Ubuntu system.
OpenSSH is a freely available version of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol family of tools for remotely controlling, or transferring files between, computers. Traditional tools used to accomplish these functions, such as telnet or rcp, are insecure and transmit the user’s password in cleartext when used. OpenSSH provides a server daemon and client tools to facilitate secure, encrypted remote control and file transfer operations, effectively replacing the legacy tools.
The OpenSSH server component, sshd, listens continuously for client connections from any of the client tools. When a connection request occurs, sshd sets up the correct connection depending on the type of client tool connecting. For example, if the remote computer is connecting with the ssh client application, the OpenSSH server sets up a remote control session after authentication. If a remote user connects to an OpenSSH server with scp, the OpenSSH server daemon initiates a secure copy of files between the server and client after authentication. OpenSSH can use many authentication methods, including plain password, public key, and Kerberos tickets.
Installation
Installation of the OpenSSH client and server applications is simple. To install the OpenSSH client applications on your Ubuntu system, use this command at a terminal prompt:
To install the OpenSSH server application, and related support files, use this command at a terminal prompt:
Configuration
There are many directives in the sshd configuration file controlling such things as communication settings, and authentication modes. The following are examples of configuration directives that can be changed by editing the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file.
Prior to editing the configuration file, you should make a copy of the original file and protect it from writing so you will have the original settings as a reference and to reuse as necessary.
Copy the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file and protect it from writing with the following commands, issued at a terminal prompt:
Furthermore since losing an ssh server might mean losing your way to reach a server, check the configuration after changing it and before restarting the server:
The following are examples of configuration directives you may change:
After making changes to the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file, save the file, and restart the sshd server application to effect the changes using the following command at a terminal prompt:
Many other configuration directives for sshd are available to change the server application’s behavior to fit your needs. Be advised, however, if your only method of access to a server is ssh, and you make a mistake in configuring sshd via the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file, you may find you are locked out of the server upon restarting it. Additionally, if an incorrect configuration directive is supplied, the sshd server may refuse to start, so be extra careful when editing this file on a remote server.
SSH Keys
SSH allow authentication between two hosts without the need of a password. SSH key authentication uses a private key and a public key.
To generate the keys, from a terminal prompt enter:
During the process you will be prompted for a password. Simply hit Enter when prompted to create the key.
By default the public key is saved in the file
/.ssh/id_rsa is the private key. Now copy the id_rsa.pub file to the remote host and append it to
/.ssh/authorized_keys by entering:
Finally, double check the permissions on the authorized_keys file, only the authenticated user should have read and write permissions. If the permissions are not correct change them by:
You should now be able to SSH to the host without being prompted for a password.
Import keys from public keyservers
These days many users have already ssh keys registered with services like launchpad or github. Those can be easily imported with:
The prefix lp: is implied and means fetching from launchpad, the alternative gh: will make the tool fetch from github instead.
Two factor authentication with U2F/FIDO
OpenSSH 8.2 added support for U2F/FIDO hardware authentication devices. These devices are used to provide an extra layer of security on top of the existing key-based authentication, as the hardware token needs to be present to finish the authentication.
Once the keypair is generated, it can be used as you would normally use any other type of key in openssh. The only requirement is that in order to use the private key, the U2F device has to be present on the host.
For example, plug the U2F device in and generate a keypair to use with it:
Now just transfer the public part to the server to
/.ssh/authorized_keys and you are ready to go:
FIDO2 esident keys
FIDO2 private keys consist of two parts: a “key handle” part stored in the private key file on disk, and a per-device key that is unique to each FIDO2 token and that cannot be exported from the
token hardware. These are combined by the hardware at authentication time to derive the real key that is used to sign authentication challenges.
For tokens that are required to move between computers, it can be cumbersome to have to move the private key file first. To avoid this, tokens implementing the newer FIDO2 standard support resident keys, where it is possible to retrieve the key handle part of the key from the hardware.
Using resident keys increases the likelihood of an attacker being able to use a stolen token device. For this reason, tokens normally enforce PIN authentication before allowing download of keys, and users should set a PIN on their tokens before creating any resident keys. This is done via the hardware token management software.
which will download the resident key from the token and write public/private key files for them. It is also possible to download and add resident keys directly to ssh-agent by running