How to get ip address mac address
How to get ip address mac address
How to Find Your IP and MAC Addresses in Windows
Locate an IP address using these steps
What to Know
This article explains how to locate your computer’s MAC and IP addresses by using the ipconfig command or through the network adapter’s settings. Instructions apply to Windows 10, 8, Vista, 7, and XP.
Use the ipconfig Command
The ipconfig utility is accessible from Command Prompt and is easy to use. It displays address information for all active network adapters.
Open Command Prompt. In Windows 10, open the Start menu and search for cmd. In Windows 8, open the Apps screen to find Command Prompt in the Windows System section.
For older versions of Windows like Windows 7, Vista, and XP, open the Start menu and go to All Programs > Accessories to open Command Prompt.
Type this command and press Enter.
ipconfig /all
Locate Physical Address to see the network adapter’s MAC address. The IPv4 address is listed beside IPv4 Address, while Link-local IPv6 Address shows the IPv6 address.
Many Windows PCs include more than one network adapter (such as separate adapters for Ethernet and Wi-Fi support) and report several active IP or MAC addresses.
Open the Network Adapter’s Settings
Another way to find the MAC address in Windows or to see the IP address, is through the network adapter’s settings, something you can do through Control Panel.
Select Network and Internet. If you don’t see that option, go to Network and Sharing Center, then skip to Step 4. In Windows XP, select Network and Internet Connections or Network Connections, then skip to Step 5.
Choose Network and Sharing Center. In Windows XP, select Network Connections.
Select Change adapter settings. In Windows XP, skip this step. In Windows Vista, click Manage network connections.
Double-click the adapter for which you want to see the MAC address and local IP address.
Select Details. In Windows XP, go to the Support tab.
Locate IPV4 Address or Link-local IPv6 Address for the IP address, or Physical Address to see the MAC address for that adapter.
Virtual adapters used in virtual machines and other virtualization software usually possess software-emulated MAC addresses and not the physical address of the network interface card.
Find Device or IP Address using MAC Address Free – Here’s a Quick Tutorial & Guide!
How would you communicate with a device when you don’t have the IP?
You might be in a situation where you don’t have the IP address of a device in a local network, but all you have is records of the MAC or hardware address.
Or your computer is unable to display its IP due to various reasons, and you are getting a “No Valid IP Address” error.
Finding the IP from a known MAC address should be the task of a ReverseARP application, the counterpart of ARP. But RARP is an obsolete protocol with many disadvantages, so it was quickly replaced by other protocols like BOOTP and DHCP, which deal directly with IP addresses.
In this article, we’ll show you how to find all ip addresses on a network along with device vendors using MAC addresses with different methods for free.
Understanding ARP
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is the protocol in charge of finding MAC addresses with IPs in local network segments.
It operates with frames on the data link layer. As you might already know, devices in the data link layer depend on MAC addresses for their communication. Their frames encapsulate packets that contain IP address information.
A device must know the destination MAC address to communicate locally through media types like Ethernet or Wifi, in layer 2 of the OSI model. Understanding how ARP works can help you find IPs and MAC addresses quickly.
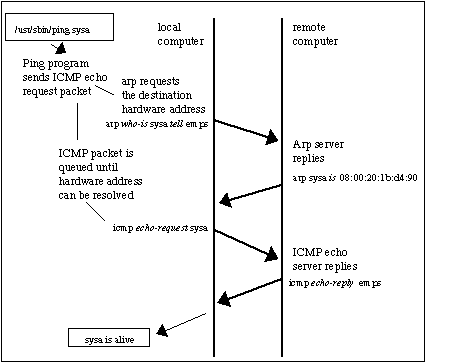
The following message flow diagram can help you understand the concept:
The local computer sends an ARP REQUEST message to find the owner of the IP address in question.
This message is sent to all devices within the same segment or LAN through a broadcast MAC (FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF) as the destination.
Finding IPs with ARP
You can use ARP to obtain an IP from a known MAC address.
But first, it is important to update your local ARP table in order to get information from all devices in the network.
For Windows:
Step 1
This will open the command-line interface in Windows.
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4.
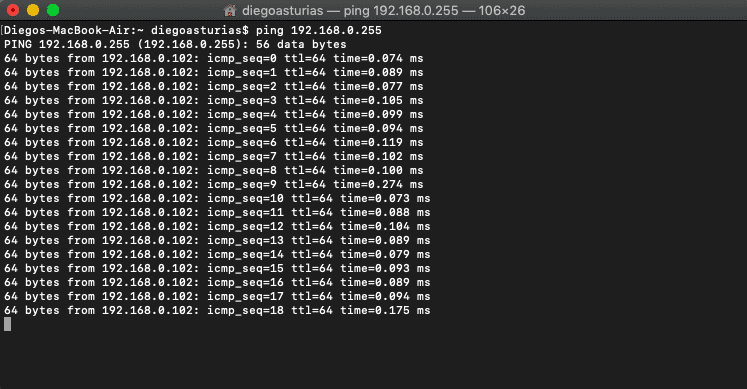
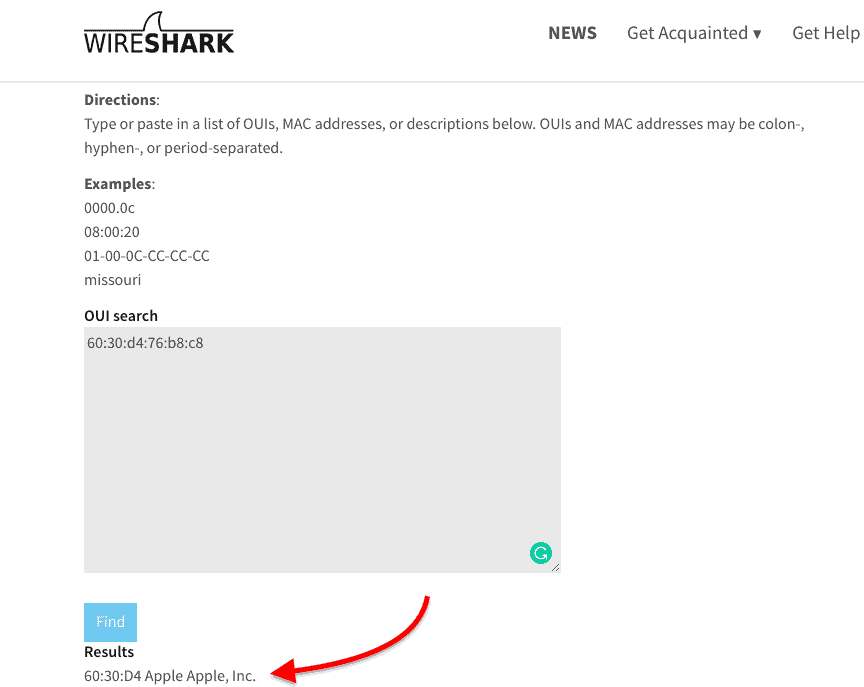
Let’s say you have the MAC address 60-30-d4-76-b8-c8 (which is a macOS device) and you want to know the IP.
From the results shown above, you can map the MAC address to the IP address in the same line.
The IP Address is 192.168.0.102 (which is in the same network segment) belongs to 60-30-d4-76-b8-c8.
You can forget about those 224.0.0.x and 239.0.0.x addresses, as they are multicast IPs.
For macOS:
Step 1
Step 2
Finding IPs with the DHCP Server
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is the network protocol used by TCP/IP to dynamically allocate IP addresses and other characteristics to devices in a network. The DHCP works with a client/server mode.
The DHCP server is the device in charge of assigning IP addresses in a network, and the client is usually your computer.
For home networks or LANs, the DHCP Server is typically a router or gateway.
If you have access to the DHCP Server, you can view all relationships with IPs, MACs, interfaces, name of the device, and lease time in your LAN.
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Using Sniffers – Nmap
If you couldn’t find the IP in the ARP list or unfortunately don’t have access to the DHCP Server, as a last resort, you can use a sniffer.
Packet sniffers or network analyzers like Nmap (or Zenmap which is the GUI version) are designed for network security.
They can help identify attacks and vulnerabilities in the network.
With Nmap, you can actively scan your entire network and find IPs, ports, protocols, MACs, etc.
If you are trying to find the IP from a known MAC with a sniffer like Nmap, look for the MAC address within the scan results.
How to find the Device and IP with a Sniffer?
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Finding out the device vendor from a MAC address
But what if you want to know more details about that particular device?
What vendor is it?
Your network segment or LAN might be full of different devices, from computers, firewalls, routers, mobiles, printers, TVs, etc.
And MAC addresses contain key information for knowing more details about each network device.
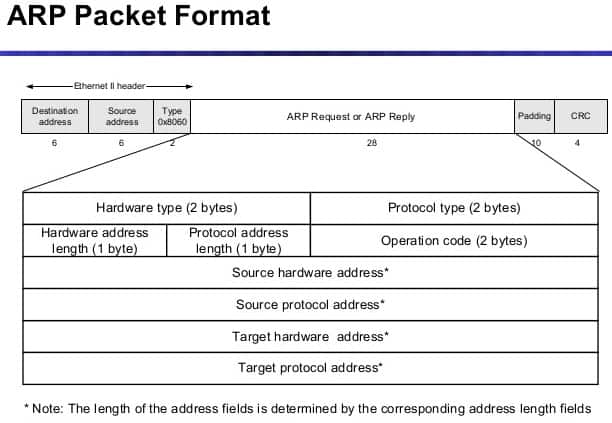
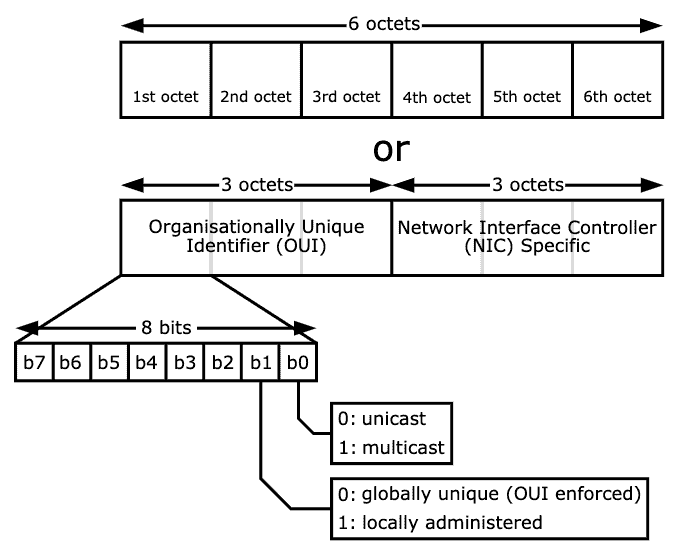
First, it is essential to understand the format of the MAC address.
Traditional MAC addresses are 48 bits represented in 12-digit hexadecimal numbers (or six octets).
The first half of the six octets represent the Organizational Unique Identifier (OUI) and the other half is the Network Interface Controller (NIC) which is unique for every device in the world.
There is not much we can do about the NIC, other than communicating with it.
But the OUI can give us useful information about the vendor if you didn’t use Nmap, which can also give you the hardware vendor.
Using Wireshark OUI Lookup
A free online OUI lookup tool like Wireshark OUI Lookup can help you with this.
Just enter the MAC address on the OUI search, and the tool will look at the first three octets and correlate with its manufacturing database.
Using DHCP to view IP info
Although the RARP (the counterpart of ARP) was specifically designed to find IPs from MAC addresses, it was quickly discontinued because it had many drawbacks.
RARP was quickly replaced by DHCP and BOOTP. But ARP is still one of the core functions of the IP layer in the TCP/IP protocol stack. It finds MAC addresses from known IPs, which is most common in today’s communications. ARP works under the hood to keep a frequently used list of MACs and IPs.
Aside from ARP, you can also use DHCP to view IP information. DHCP Servers are usually in charge of IP assignments. If you have access to the DHCP server, go into the DHCP Client list and identify the IP with the MAC address. Finally, you can use a network sniffer like Nmap, scan your entire network, and find IPs, and MACs.
If you only want to know the vendor, an online OUI lookup like Wireshark can help you find it quickly.
Find a Device or IP Address FAQs
Can you find an IP address from a MAC address?
How can I access a device by MAC address?
How can I find a device by IP address? (cmd instructions)
You can follow a path to a device if you know its IP address by using the tracert command at the command prompt (cmd). Open a Command Prompt window and type in tracert followed by the IP address that you know. The output will show each router that has a connection to that device will pass through.
Find your IP Address on a Mac

This works the same in all versions of Mac OS X on all Macs.
How to Find the IP Address on a Mac
You can find any Macs IP, or your IP address from the Mac System Preferences Network configuration screen:
Your IP address is the number listed, in the above case it is 192.168.0.100
Now we’ll cover the more technical approaches to getting your IP address using the Mac OS X command line:
Find your IP Address via the Mac OS X Terminal
This is how to find the IP address of your Mac through the Terminal, this is often the quickest way for those that are more technically inclined.
ifconfig |grep inet
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128
inet6 fe80::1%lo0 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x1
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 0xff000000
inet6 fe80::fa1e:dfff:feea:d544%en1 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x5
inet 192.168.0.100 netmask 0xffffff00 broadcast 192.168.0.255
The other command line option is to use: ipconfig getifaddr en1 which reports back only your en1 (usually wireless) IP address. You can change this to en0 for wired/ethernet too. I have heard ipconfig is not supported in all versions of Mac OS X so I did not recommend this as the first choice. However, using ipconfig you can also set your IP address from the command line.
Find your External Public IP Address in Mac OS X
Your external IP address is what is broadcast to the world rather than your local network (behind a wireless router, for instance).
You can find your external IP address easily by going to a website like Google and typing “what is my IP address” or by going to websites like “whatismyipaddress.com” and checking there.
This is easiest to find through a Terminal command a well:
curl ipecho.net/plain ; echo
This will instantly report back your external IP address. We covered this command when finding your external IP address in the past.
How do I find my IP Address from the command line?
9 Answers 9
Use ipconfig getifaddr en1 for wireless, or ipconfig getifaddr en0 for ethernet.
ipconfig getifaddr en0 is default for the Wi-Fi network adapter.
Alternatively you can also do:
The following works for me on 10.8 and on 10.10 Yosemite.
If you find the above gives you more than one answer, save the following to a script, and run it instead
ip_address.sh
Just type curl ifconfig.me in the terminal.
You can do the following:
Typically, when you have SSH daemon running on a box, it will listen on all available interfaces, ie. you can use any IP address that’s configured on your machine to connect to that machine via SSH (this, obviously, subject to Firewall rules). If you’re after what the OS calls a Primary interface and primary IP address, you can use the scutil command like this:
Please note, that the above, even though is a command-line command, is also interactive (so you run scutil and then enter its own commands into it). The first show command tells you the name of the primary interface for the OS (i.e. this will be the one on top of the list in your System Preferences / Network Preferences window), as well as the IP address of your default router. The second show command takes State:/Network/Interface/ /IPv4 argument (in this case, en0 ) and gives you the IP addresses assigned to it. You’re looking for the address in the Addresses array, the other two entries are broadcast addresses and the netmasks.
Hope that helps, but if anything is not clear, let me know.
Find IP address by MAC address
Sometimes it is needed to determine IP address of a network device or a PC but only MAC address is known.
This is mostly problem for network devices like network printers or IP CCTV cameras. For example we connected such a device to a network with DHCP and we’d like to know what IP address the device got from DHCP server. May be a device has a static IP address configured but we can’t remember it while MAC address is known (labeled on the box). Same question may be for remote computers.
A simple way to find IP address works on any PC and requires no administrative permissions – find IP address from ARP cache list by filtering the list by known MAC address:
This is simple but the record for a particular address may not present in the list.
The main reason for that is Windows keeps ARP cache records for 15-45 seconds, see Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) caching behavior in Windows Vista TCP/IP implementations for more details. That means a record related to the particular MAC address could be deleted and therefore unavailable.
To get full list of ARP records one can use standard ping utility. The simplest way is to ping all possible IP addresses in the LAN. For a network like 192.168.1.1 / 255.255.255.0 the command would be like that:
Important that ping utility processes would be started with do @start /b ping because:
Below is a batch file ip_by_mac.cmd to perform these actions. MAC address to search expected in command line argument:
Please note for statement uses double percentage sign – that’s correct for batch files.
Starting the batch file:
The file is small and simple in use but can be used in networks 255.255.255.0.
The video shows how to find IP address in 192.168.0.x network for known 00-0C-29-01-7C-3F MAC address from command line window:
The video shows three steps.
Firstly checking ARP cache if it already contains a record for MAC 00-0C-29-01-7C-3F:
The empty output means there’s no records for MAC 00-0C-29-01-7C-3F in ARP cache.
Next polling all 254 addresses in FOR /L loop:
The output is again empty, that’s OK.
Finally checking ARP cache again:
This time the output is not empty telling correct IP address:
See also
The batch file to find IP address can be downloaded by this link
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ryanperiansquare-de5f69cde760457facb17deac949263e-180a645bf10845498a859fbbcda36d46.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/001-how-to-find-your-ip-and-mac-addresses-in-windows-4d361aa9c84240ceabf4c635f035018c.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/002-how-to-find-your-ip-and-mac-addresses-in-windows-2f1026e8fa334963b1c65c40f663adec.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/003-how-to-find-your-ip-and-mac-addresses-in-windows-76b63bc2b2ad46c8b159663d2ee62c52.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/004-how-to-find-your-ip-and-mac-addresses-in-windows-c330d46ba261403682f66473acb7a9ac.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/005-how-to-find-your-ip-and-mac-addresses-in-windows-5d6a4e191fd74830b400466c308e3259.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/006-how-to-find-your-ip-and-mac-addresses-in-windows-81c1584cc643430e88bcf1cb8f4ea87f.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/007-how-to-find-your-ip-and-mac-addresses-in-windows-07a155d82a2f408fb150ecf90df7a6e6.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/008-how-to-find-your-ip-and-mac-addresses-in-windows-0dcb87f0dd2d42d3a3b19fae122bebf1.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/009-how-to-find-your-ip-and-mac-addresses-in-windows-3fa8853ed5c54b4f8b88a9e7d74c746f.jpg)