How to install phpmyadmin
How to install phpmyadmin
How to Install PHPMyAdmin on a Server?
Updated on May 21, 2021
Database is an essential part of any web based application for saving records and user data. Previously, I’ve written about how you can setup MySQL on debian based servers. MySQL is actually a part of LAMP/LEMP stack, both of which form an integral part of PHP applications. Hence, once you install MySQL on any web hosting for PHP, you can carry out your job using MySQL commands in terminal.
Developers can perform all the above mentioned tasks easily. They can easily find and run commands on the terminal to work with MySQL queries. But sometimes, there are non-tech people too who do not want to go in technical details to perform some simple database operations. This is where PHPMyAdmin comes into play as a handy tool for them to work with pre-defined MySQL queries. The platform gives you the ease to perform complex database operations in just a few clicks and write queries with debugging.
Let’s see how you can install PHPMyAdmin on debian based cloud servers. The process is quite easy followed by some commands. I’m assuming here that you have already installed MySQL on your hosting server.
Nothing as Easy as Deploying PHP Apps on Cloud
With Cloudways, you can have your PHP apps up and running on managed cloud servers in just a few minutes.
Install PHPMyAdmin on Debian
There are not only non-techie people who want a better GUI to handle complex database functions, but developers too need such a kind of platform to save their precious time. That’s why the best platform recommended for handling database jobs is PHPMyAdmin. It’s is an open source GUI which helps in managing MySQL database. Let’s first setup an SSL with Apache, so that our password isn’t sent in plain text form. Type the following command to install an SSL with Apache server.
Now, restart your Apache server with the following command.
Now, begin PHPMyAdmin installation by typing the following command.
During PHPMyAdmin installation process, a prompt will open which will ask you about the web server you are using. Select Apache and press the Enter key. After that it will ask about the root user password. Enter the password and press Enter, once again.
PHPMyAdmin will be installed in /usr/share/phpmyadmin. We will create its symlink inside the public_html folder. Type the following commands to route to public_html folder and create a symlink:
Now type ‘ ls ’ to verify whether the symlink has been created or not. Once verified, open this in browser through [server ip address] /phpmyadmin where you’ll see that it is installed. Now, let’s secure it by creating a .htaccess file using vim file inside PHPMyAdmin folder and allow only your server IP to access it.
Now, you can easily use PHPMyAdmin and work with databases.
But, the next question is how to open PHPMyAdmin on Cloudways managed servers? To do that you need to follow some steps.
Install PHPMyAdmin on Cloudways
You can install PHPMyAdmin on the app you are using or can launch a new PHP stack application.
Once you have launched the PHP stack application, follow the following steps in order to install PHPMyAdmin.
Improve Your PHP App Speed by 300%
Cloudways offers you dedicated servers with SSD storage, custom performance, an optimized stack, and more for 300% faster load times.
Step 1: Launch SSH Terminal
Login to Cloudways Platform, launch SSH terminal and login using Master Credentials.
After successful login, head to the application folder where you want to download PHPMyAdmin by using the following command.
Step 2: Downloading And Installing PHPMyAdmin
Now go to PHPMyAdmin website and copy the download URL of the latest version of PHPMyAdmin (zipped format)
Now go to SSH Terminal, type the following command and paste the download URL.
Press Enter and let the server download the file.
Once the file has been downloaded, run the following command to unzip it.
Wait for the command to finish its process.
Once done, run the following command to delete the zip.
Let’s rename the folder so that we can access it easily by running the following command.
Now head to the application URL and add /phpmyadmin at the end of URL. You will see that PHPMyAdmin has been installed and you will see its login page.
Now login using the database credentials.
Once you have logged in with your database credentials, you can successfully access PHPMyAdmin page.
You have successfully installed PHPMyAdmin. You can use it to access all your applications’ databases on the server on which it is installed.
Q: How to use PHPMyAdmin after installation?
A: Once phpMyAdmin installation is completed, visit your staging app link to access it. For example http://phpstack-123.cloudwaysapps.com/phpmyadmin.
Q: How to find the port for PHPMyAdmin?
A: On the PHPMyAdmin home screen, click on Home, move to Variables option available on top. Search for port settings, the values are available there.
Q: How to start/install the phpMyAdmin from the command line on Ubuntu?
Q: How to start phpMyAdmin on a Linux based System?
A: To start the phpMyAdmin, type in the URL: http://
Share This Article
“Cloudways hosting has one of the best customer service and hosting speed”
Sanjit C [Website Developer]
Ahmed Khan
How To Install and Secure phpMyAdmin on Ubuntu 20.04
An earlier version of this tutorial was written by Brennan Bearnes.
Introduction
While many users need the functionality of a database management system like MySQL, they may not feel comfortable interacting with the system solely from the MySQL prompt.
phpMyAdmin was created so that users can interact with MySQL through a web interface. In this guide, we’ll discuss how to install and secure phpMyAdmin so that you can safely use it to manage your databases on an Ubuntu 20.04 system.
Prerequisites
In order to complete this guide, you will need:
Additionally, there are important security considerations when using software like phpMyAdmin, since it:
For these reasons, and because it is a widely-deployed PHP application which is frequently targeted for attack, you should never run phpMyAdmin on remote systems over a plain HTTP connection.
If you do not have an existing domain configured with an SSL/TLS certificate, you can follow this guide on securing Apache with Let’s Encrypt on Ubuntu 20.04. This will require you to register a domain name, create DNS records for your server, and set up an Apache Virtual Host.
Step 1 — Installing phpMyAdmin
You can use APT to install phpMyAdmin from the default Ubuntu repositories.
As your non-root sudo user, update your server’s package index:
Following that you can install the phpmyadmin package. Along with this package, the official documentation also recommends that you install a few PHP extensions onto your server to enable certain functionalities and improve performance.
If you followed the prerequisite LAMP stack tutorial, several of these modules will have been installed along with the php package. However, it’s recommended that you also install these packages:
Run the following command to install these packages onto your system. Please note, though, that the installation process requires you to make some choices to configure phpMyAdmin correctly. We’ll walk through these options shortly:
Here are the options you should choose when prompted in order to configure your installation correctly:
Note: Assuming you installed MySQL by following Step 2 of the prerequisite LAMP stack tutorial, you may have decided to enable the Validate Password plugin. As of this writing, enabling this component will trigger an error when you attempt to set a password for the phpmyadmin user:
To resolve this, select the abort option to stop the installation process. Then, open up your MySQL prompt:
Or, if you enabled password authentication for the root MySQL user, run this command and then enter your password when prompted:
From the prompt, run the following command to disable the Validate Password component. Note that this won’t actually uninstall it, but just stop the component from being loaded on your MySQL server:
Following that, you can close the MySQL client:
Then try installing the phpmyadmin package again and it will work as expected:
The installation process adds the phpMyAdmin Apache configuration file into the /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/ directory, where it is read automatically. To finish configuring Apache and PHP to work with phpMyAdmin, the only remaining task in this section of the tutorial is to is explicitly enable the mbstring PHP extension, which you can do by typing:
Afterwards, restart Apache for your changes to be recognized:
phpMyAdmin is now installed and configured to work with Apache. However, before you can log in and begin interacting with your MySQL databases, you will need to ensure that your MySQL users have the privileges required for interacting with the program.
Step 2 — Adjusting User Authentication and Privileges
When you installed phpMyAdmin onto your server, it automatically created a database user called phpmyadmin which performs certain underlying processes for the program. Rather than logging in as this user with the administrative password you set during installation, it’s recommended that you log in as either your root MySQL user or as a user dedicated to managing databases through the phpMyAdmin interface.
Configuring Password Access for the MySQL Root Account
In Ubuntu systems running MySQL 5.7 (and later versions), the root MySQL user is set to authenticate using the auth_socket plugin by default rather than with a password. This allows for some greater security and usability in many cases, but it can also complicate things when you need to allow an external program — like phpMyAdmin — to access the user.
In order to log in to phpMyAdmin as your root MySQL user, you will need to switch its authentication method from auth_socket to one that makes use of a password, if you haven’t already done so. To do this, open up the MySQL prompt from your terminal:
Next, check which authentication method each of your MySQL user accounts use with the following command:
In this example, you can see that the root user does in fact authenticate using the auth_socket plugin. To configure the root account to authenticate with a password, run the following ALTER USER command. Be sure to change password to a strong password of your choosing:
Then, check the authentication methods employed by each of your users again to confirm that root no longer authenticates using the auth_socket plugin:
You can see from this output that the root user will authenticate using a password. You can now log in to the phpMyAdmin interface as your root user with the password you’ve set for it here.
Configuring Password Access for a Dedicated MySQL User
Alternatively, some may find that it better suits their workflow to connect to phpMyAdmin with a dedicated user. To do this, open up the MySQL shell once again:
If you have password authentication enabled for your root user, as described in the previous section, you will need to run the following command and enter your password when prompted in order to connect:
From there, create a new user and give it a strong password:
Note: Again, depending on what version of PHP you have installed, you may want to set your new user to authenticate with mysql_native_password instead of caching_sha2_password :
Then, grant your new user appropriate privileges. For example, you could grant the user privileges to all tables within the database, as well as the power to add, change, and remove user privileges, with this command:
Following that, exit the MySQL shell:
You can now access the web interface by visiting your server’s domain name or public IP address followed by /phpmyadmin :
Log in to the interface, either as root or with the new username and password you just configured.
When you log in, you’ll see the user interface, which will look something like this:
Now that you’re able to connect and interact with phpMyAdmin, all that’s left to do is harden your system’s security to protect it from attackers.
Step 3 — Securing Your phpMyAdmin Instance
Use your preferred text editor to edit the phpmyadmin.conf file that has been placed in your Apache configuration directory. Here, we’ll use nano :
Add an AllowOverride All directive within the section of the configuration file, like this:
To implement the changes you made, restart Apache:
In order for this to be successful, the file must be created within the application directory. You can create the necessary file and open it in your text editor with root privileges by typing:
Within this file, enter the following information:
Here is what each of these lines mean:
When you are finished, save and close the file.
You will be prompted to select and confirm a password for the user you are creating. Afterwards, the file is created with the hashed password that you entered.
Now, when you access your phpMyAdmin subdirectory, you will be prompted for the additional account name and password that you just configured:
After entering the Apache authentication, you’ll be taken to the regular phpMyAdmin authentication page to enter your MySQL credentials. By adding an extra set of non-MySQL credentials, you’re providing your database with an additional layer of security. This is desirable, since phpMyAdmin has been vulnerable to security threats in the past.
Conclusion
You should now have phpMyAdmin configured and ready to use on your Ubuntu 20.04 server. Using this interface, you can create databases, users, and tables, as well as perform the usual operations like deleting and modifying structures and data.
Want to learn more? Join the DigitalOcean Community!
Join our DigitalOcean community of over a million developers for free! Get help and share knowledge in our Questions & Answers section, find tutorials and tools that will help you grow as a developer and scale your project or business, and subscribe to topics of interest.
How to Install phpMyAdmin on Any Operating System
Managing a database is a complex but necessary part of running a website. Luckily, software like phpMyAdmin exist to make the process much easier. This popular administration tool may seem challenging to learn, but accessing and modifying your database will be a breeze once you have the hang of it.
The most difficult part is knowing how to install phpMyAdmin and setting it up on your web server. If you’re having trouble, you’re certainly not the only one.
In this article, we’ll show you step by step how to install phpMyAdmin on all major operating systems, plus how to configure it from there.
Prefer to watch the video version?
What Is phpMyAdmin?
Behind every website is a database. This database allows you to store data ranging from user account information to the posts you make on your site. While there are many database services, MySQL is the most popular one. And most likely, it’s the one your website is using. MariaDB is a common alternative.
Kinsta spoiled me so bad that I demand that level of service from every provider now. We also try to be at that level with our SaaS tool support.

Interacting directly with MySQL can be complicated and confusing, especially if you’re new to website administration. But interacting with your databases is often a necessary part of site maintenance.
phpMyAdmin was created to bring a browser-based visual interface to MySQL and make it easier to work with your database. Due to its popularity, many web hosting services include access to phpMyAdmin, including Kinsta.
Why Do You Need phpMyAdmin?
Without a tool like phpMyAdmin, your only option for accessing the database is with the command line. It means you have no visual interface — just a text prompt where you put in commands. Doing it this way can be confusing and may even lead to accidentally breaking your site.
phpMyAdmin is free and open source. A wide range of web hosts supports it, and you can even install it yourself without paying a single cent. And once you’ve installed it, executing database commands from the visual interface is much more intuitive.
Still on the fence? You can try phpMyAdmin yourself to see if it’s a database manager you’d like to use. Once you’ve given it a test drive and decided you’d like it, you can install the tool on your server.
phpMyAdmin Requirements
The requirements to install phpMyAdmin are, luckily, relatively simple. If you have a web server of any kind, you should almost certainly be able to get it running. Here are the detailed requirements:
Before you try to install phpMyAdmin, remember that many web hosts already come with it installed. Kinsta is among them; if you want to access the database manager, log into your Kinsta account, then go to the Info tab and look for Database Access.
Before installing phpMyAdmin, check your web host’s documentation to ensure they’ve not installed it already.
Step By Step: Installing phpMyAdmin
Once you’ve checked to make sure your server supports phpMyAdmin, it’s time to get to work installing it. Web servers come in a wide range of operating systems, so we’ve included all the most popular ones, including Windows, Mac, and multiple distributions of Linux.
With that, here are the step-by-step instructions for installing phpMyAdmin.
How to Install phpMyAdmin on Windows 10
As the requirements state, you’re going to need a web server with PHP and a database to use phpMyAdmin. While you can undoubtedly download Apache, PHP, and MySQL manually, there’s a much simpler option to get a server up and running on a Windows computer.
WAMP (Windows, Apache, MySQL, and PHP) is free software that easily allows you to create a server with all prerequisites. You can also try XAMPP for Windows (Apache, MariaDB, PHP, and Perl) if it suits your needs better.

Once you have one of these downloaded, it’s just a matter of installing it and walking through the setup process.
Suppose you’re using WAMP or XAMPP. Both of these come with phpMyAdmin already! In your browser, navigate to http://localhost/phpMyAdmin , and you should see the login screen, confirming that you’ve installed everything correctly.
How to Install phpMyAdmin on Mac
Getting phpMyAdmin on a Mac is a little different. All the prerequisites are the same. But as macOS ships with both Apache and PHP, you don’t need to download them.
With Mac, you have two options: You can use XAMPP just like with other operating systems or install everything manually.

Download XAMPP for OS X, open it, and drop it into your Applications folder.
If you’d instead install phpMyAdmin manually, the process is simple. Since you already have Apache and PHP, you only need to download MySQL. Make sure you select macOS from the dropdown. Download and install the file, follow the instructions, and record any usernames and passwords given to you.
You can then open System Preferences and launch MySQL to start a server. You can also start Apache by running this command in the Terminal:

With that, all that’s left is installing phpMyAdmin. Rename the folder to “phpMyAdmin” and move it to /Library/WebServer/Documents/. Check to make sure it’s installed correctly by visiting http://localhost/phpMyAdmin in the browser.
If you have Homebrew installed, another option is to put in the command: brew install phpMyAdmin.
How to Install phpMyAdmin on Ubuntu
As one of the most popular and most accessible to use Linux distributions, Ubuntu is a good choice for your server.
While manual installation of Apache and MySQL is always possible, Linux has its own “stack” of standard server software known as LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP). Unlike WAMP and XAMPP, this does not come with phpMyAdmin, so you’ll need to install it manually. Luckily, Ubuntu allows you to do all of your installations through the command line.
First, check that tasksel is enabled. Server editions of Ubuntu should come with it installed, but if you have a desktop edition, you can enable it with this command:
After that, you can use tasksel to install a LAMP server with this command:

Now, you can install phpMyAdmin:
With that, you have all the necessary files to run a server on your computer.
How to Install phpMyAdmin on CentOS 7
Installing phpMyAdmin on CentOS 7 is very similar to other distributions, but the commands are slightly different as this OS uses Yum rather than the typical apt command.
There’s also no simple LAMP stack that installs all the server components you need at once, so you’ll need to download Apache, MySQL, and PHP manually. Thankfully these can be easily obtained through the command line.
First, let’s get a LAMP stack downloaded using the command line, beginning with Apache:
To start the Apache server and ensure it runs on boot, use these commands:
Now it’s time to install a database. CentOS 7 defaults to installing MariaDB. It is also fully compatible with phpMyAdmin, so it’s safe to use. While it’s possible to download MySQL instead, it’s a much more complicated process. Let’s use MariaDB:
sudo yum install mariadb-server mariadb
Now we can run it and cause it to start at boot:
To finish installing MariaDB and ensure it’s secure, run the secure installation setup with the following command.
Last, we can install PHP with the additional MySQL package.
You’ll also need to restart the Apache server, so it works properly with PHP.
With that, you have the LAMP stack you need and can finally get to downloading phpMyAdmin. As it isn’t in the Yum repository, you’ll need to install the EPEL repository instead with this command:
And install phpMyAdmin.
It takes a few more steps on CentOS 7, but you should now have a server ready for configuration.
How to Install phpMyAdmin on Debian
Much like CentOS 7, you’ll need to install a LAMP stack using the command line manually. First, let’s get Apache with this command:
Next, we’ll install MariaDB. Like CentOS 7, this Linux distribution works better with MariaDB, and we recommended you use that one instead.
And like with CentOS 7, you should run the secure installation to add a database password and ensure that everything is secure.
Finally, we can install PHP and a few extra packages your server will need to work.
And we can finish off by installing phpMyAdmin.
How to Access phpMyAdmin
Once you have phpMyAdmin appropriately installed, accessing it and logging in is the same on any operating system.
You’ll need your web server’s address, then append /phpMyAdmin/ to the end of it. If you just set up a server on your computer, the address is very likely simply “localhost,” so visit this link:
It may also be an IP, or even a named address if this is a server you already have running on the web. If you’re not sure, you can likely find the address in your Apache or MySQL config files.
Once you’re on the login screen, you’ll need a username and password. If this is a fresh installation, the username is likely “root,” and you can leave the password blank. If that doesn’t work, the password may be “password.”

If you can’t log in, check the phpMyAdmin or MySQL config files to find your login info. You may have also changed the login info during the installation process.
Linux users should try the following Linux command if they’re having trouble accessing the page or logging in:
Lastly, you should note that if you’re using a web host such as Kinsta with phpMyAdmin preinstalled, you can usually find login info and links in your hosting dashboard. In this case, you don’t need to install phpMyAdmin on the server manually.
Configuring phpMyAdmin
With the database manager installed and ready to go on your system, you should know how to configure phpMyAdmin. Like with any server software, you’re certainly going to want to do plenty of tinkering with the settings.
An unconfigured phpMyAdmin can also pose a potential security risk. There are a few extra steps you need to take to lock down your system.
If you ever need to restore a backup of your database, you can always use phpMyAdmin to import a new SQL file. Always make frequent backups before doing any significant modifications to the database or its settings, especially if you’re not just working on a test server.
How to Run SQL Queries
Now that you have phpMyAdmin working, you should know how to do what it’s made for: running SQL queries.
You can run queries either on the homepage (this will apply to the entire site), or in a specific database or table. Click the SQL tab at the top of the screen, type in your command, and press Go.

There are certainly more commands to learn, but those are a few to start with.
How to Change the Default phpMyAdmin URL
Leaving the phpMyAdmin access link on its default setting ( http://website.com/phpMyAdmin ) can pose a security risk.
If you make this page easy to find, hackers will be able to visit it and attempt to brute force down your username and password. It can be even worse if you’ve left the credentials on the default “root” and “password.”
But by changing the URL to something only you know, you can make it much more difficult for unknown users to access this page and try to guess the password.
Open phpMyAdmin.conf in a text editor, which you can find under C:\wamp\alias on Windows/WAMP, xampp\apache\conf\extra on XAMPP, /etc/httpd/conf.d on Linux, or /usr/conf/extra on Mac.
You should see this line in there:
Change the /phpMyAdmin path to the new address of your choice. For instance:
Now you can access this unique URL for phpMyAdmin by visiting the custom address you set ( http://website.com/exampleURL ).
How to Set Up an NGINX Authentication Gateway
Another option is to set up a second layer of security with an authentication gateway. After moving the phpMyAdmin login page to a secret location, you can password protect this page to make it even less likely for attackers to get through.
Users of Linux on an NGINX server can run the following commands in the command line to create an authentication gateway (this is also possible on Apache servers).
Start by creating an encrypted password (change “example” to whatever you like) and noting down the result:
Create a configuration file in NGINX’s folder and give it a name:
Enter the username and password into this file like this, being careful to leave in the colon:
Now open the NGINX configuration file.
Within the “server” block, we’ll add our gateway by pasting the following code (make sure to change the values).
The first /example should be whatever you set your phpMyAdmin URL to, and you can adjust the auth_basic variable name to anything you want, and the final /examplename should be the name of the password file you created earlier.
Now upon login, you should be required to enter the credentials you set before even seeing the phpMyAdmin login.
Adminer: A Simpler Alternative to phpMyAdmin
Adminer is a free, open source database management tool similar to phpMyAdmin. Formerly called phpMinAdmin, Adminer was explicitly designed as a simpler, better alternative to phpMyAdmin.
It’s effortless to deploy on any web server. All it takes is uploading a single, lightweight PHP file.

Even DevKinsta, Kinsta’s free suite of local development tools, uses Adminer to run its database manager. It supports many powerful database management features such as easy database switching, viewing and editing tables, manipulating database values, importing and exporting databases, running SQL queries, and much more.

You can learn more about Adminer, its features, and how to use it in our dedicated Adminer article.
Summary
Your first time using phpMyAdmin can be intimidating. But once you know how to install and configure it, accessing your database will be as easy as logging into WordPress.
Windows, Mac, and Linux users alike can all make use of this invaluable database manager. As long as you have a web server with PHP installed, getting it running should be simple if you follow our instructions. Remember to configure it properly and make sure it’s secure, and you’ll never have trouble modifying your database again.
Save time, costs and maximize site performance with:
All of that and much more, in one plan with no long-term contracts, assisted migrations, and a 30-day-money-back-guarantee. Check out our plans or talk to sales to find the plan that’s right for you.
How to install phpmyadmin
Last updated on: 2019-12-20
Authored by: Paul Dolbear
phpMyAdmin® is a free and open source administration tool for MySQL® and MariaDB®. As a portable web application written primarily in PHP, phpMyAdmin has become one of the most popular MySQL administration tools, especially for web hosting services.
This article describes how to install and configure phpMyAdmin on your web server for CentOS® 7, Red Hat® Enterprise Linux® (RHEL) 7, and Ubuntu® 16.04 LTS.
Prerequisites
Before you can install phpMyAdmin, you must have the following installed on your server:
Check whether a web server is installed
Use the commands in the following table to check whether a web server is installed:
Check whether PHP is installed
Use the following command to check whether PHP is installed on CentOS or RHEL:
Use the following command to check whether PHP is installed on the Ubuntu operating system:
Install phpMyAdmin
Use the instructions in the following sections to install phpMyAdmin.
CentOS and RHEL
Install phpMyAdmin by using the following command:
The output should be similar to the following example:
The Ubuntu operating system
Install phpMyAdmin by using the following command:
The output should be similar to the following example:
Press Y and then press Enter to continue to the configuration process. See the Configure phpMyAdmin on the Ubuntu operating system section for further instructions.
Configure phpMyAdmin on CentOS and RHEL
After you have installed phpMyAdmin on your web server, use the instructions in the following sections to configure phpMyAdmin.
Apache web server
You first need to add the Internet Protocol (IP) address that you want to use to access phpMyAdmin to the /etc/phpMyAdmin/config.inc.php configuration file.
Open the /etc/phpMyAdmin/config.inc.php file in a text editor.
Save and close the file.
Set a URL alias (optional)
The standard URL for a phpMyAdmin installation is https://ipaddress/phpMyAdmin, where ipaddress is the IP address that you added to the configuration file in the previous section. If you want to change the URL, you can set an alias.
Open the /etc/httpd/conf.d/phpMyAdmin.conf file in a text editor.
Find the lines beginning with Alias and change /phpMyAdmin to the alias of your choice, as shown in the following example:
Save and exit the file.
Database configuration file
If the MySQL or MariaDB database server that you want to use with phpMyAdmin is not located on the same server as your web server, you must edit the database configuration file to define the database server location.
There are two configuration options:
Use the following steps to define the location of your database server:
Open the /etc/phpMyAdmin/config.inc.php file in a text editor.
Edit the file as shown in the following example:
Save and exit the file.
To make the changes live, you must check the syntax of the web engine daemon and then gracefully restart or reload it.
Check the syntax by using the following command:
If there are no errors in the configuration file, you should see Syntax OK in the output.
Reload the Apache web server by using the following command:
CentOS and RHEL 6
CentOS and RHEL 7
Check the status of the httpd service to ensure that it is functioning as expected by using the following command:
CentOS and RHEL 6
CentOS and RHEL 7
You should now be able to view phpMyAdmin through a web browser, as shown in the following image:
NGINX web server
On NGINX, the phpMyAdmin package doesn’t come with a configuration file, so you have to create a server block to point at the phpMyAdmin configuration file.
Open a text editor and create the file /etc/nginx/conf.d/phpMyAdmin.conf.
Enter the following configuration settings:
Save and exit the file.
To make the changes live, you must check the syntax of the web engine daemon and then gracefully restart or reload it.
Use the following command to check the syntax:
If there are no errors in the configuration file, you should see Syntax OK in the output.
Reload the NGINX web server by using the following command:
CentOS and RHEL 6
CentOS and RHEL 7
Check the status of the NGINX service to ensure that it is functioning as expected by using the following command:
CentOS and RHEL 6
CentOS and RHEL 7
You should now be able to view phpMyAdmin through a web browser, as shown in the following image:
Configure phpMyAdmin on the Ubuntu operating system
Use the steps in the following sections to configure phpMyAdmin on the Ubuntu operating system.
Apache web server
The installation process adds the phpMyAdmin Apache configuration file to the /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/ directory, where it is read automatically. The only thing you need to do is to enable the mbstring PHP extension, which you can do by running the following command:
After installing phpMyAdmin, the package configuration screen displays, as shown in the following image.
Use the space bar to select apache2, press Tab to select Ok, and then press Enter.
Select Yes, and then press Enter.
You are prompted for your database administrator password. Input your password, press Tab to select Ok, and then press Enter.
Next, enter a password for the phpMyAdmin application itself, press Tab to select Ok, and then press Enter.
Confirm the password by selecting Ok, and then press Enter.
After the installation process is complete, the phpMyAdmin configuration file is added to /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/phpmyadmin.conf.
If this file doesn’t exist after the installation is complete, you can copy it from /etc/phpmyadmin/apache.conf to /etc/apache2/conf-enabled. If that file doesn’t exist, you must create a virtual host for phpMyAdmin with the following settings:
If at any time you need to reconfigure phpMyAdmin, you can use the following command:
Remote database configuration
If the database server that you want to manage with phpMyAdmin is remote, you must configure phpMyAdmin differently. The configuration files are located in the /etc/phpmyadmin directory. The main configuration file is /etc/phpmyadmin/config.inc.php, which contains the configuration options that apply globally to phpMyAdmin.
To use phpMyAdmin to administer a MySQL database hosted on another server, open /etc/phpmyadmin/config.inc.php in a text editor and then edit the following line:
| Old line | New line |
|---|---|
| $cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘host’] = ‘$dbserver’; | $cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘host’] = ‘192.168.71.21’; |
The other configuration file that you must edit is /etc/phpmyadmin/apache.conf. This file is linked symbolically to /etc/apache2/conf-available/phpmyadmin.conf. After it is enabled, it is used to configure Apache2 to serve the phpMyAdmin site. The file contains directives for loading PHP, directory permissions, and so on.
Run the following command to enable the configuration file, and then reload the service:
Now that phpMyAdmin is installed on the client computer, connect to the remote server where the MySQL or MariaDB database is installed. Open the file /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysql.cnf and edit the following line:
Replace 0.0.0.0 with the IP address of the remote server, and then save and exit the file.
Run the following command to allow the root user to access the server from the client computer:
Replace the IP address with the address of the remote server, and root_password_here with the root user password.
After you edit the configuration settings, open a browser and navigate to https://clientPC/phpmyadmin, using the client computer IP address or host name. You should be able to log on remotely to the server from the client phpMyAdmin web portal.
Reload the web server
To make the changes to the configuration files live, you must first check the syntax of the file and then gracefully restart or reload the web server.
Use the following command to check the syntax of the configuration files:
Then reload the Apache web server by running the following command:
Check the status of the service to ensure that it is functioning as expected by running the following command:
You should now be able to view phpMyAdmin through a web browser, as shown in the following image:
NGINX web server
After installing phpMyAdmin, the package configuration screen displays, as shown in the following image:
Use the space bar to select apache2, press Tab to select Ok, and then press Enter.
Select Yes, and then press Enter.
You are prompted for your database administrator password. Input your password, press Tab to select Ok, and then press Enter.
Next, enter a password for the phpMyAdmin application itself, press Tab to select Ok, and then press Enter.
Confirm the password by selecting Ok, and then press Enter.
After the installation process is complete, you must create the phpMyAdmin configuration file here: /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/phpmyadmin.conf.
Enter the following information in the file and then save it:
Your phpMyAdmin files are located in the /usr/share/phpmyadmin/ directory. The configuration above tells NGINX that if visitors enter https://ip_address/phpmyadmin in the browser address bar, it should find the index.php file in the /usr/share/phpmyadmin/ directory and display it.
Reload the web server
To make the changes to the configuration files live, you must first check the syntax of the file and then gracefully restart or reload the web server.
Use the following command to check the syntax of the configuration files:
Then reload the Apache web server by running the following command:
RHEL and CentOS 6
RHEl and CentOS 7
Check the status of the service to ensure that it is functioning as expected by running the following command:
RHEL and CentOS 6
RHEL and CentOS 7
You should now be able to view phpMyAdmin through a web browser, as shown in the following image:
Configure additional security (optional)
htpasswd is used to create and update the flat files that store usernames and passwords for the basic authentication of HTTP users. If htpasswd cannot access a file (cannot write to the output file or read the file in order to update it), it returns an error status and makes no changes.
Use the steps in the following sections to set up basic authentication on a web server running phpMyAdmin.
Apache web server
For RHEL and CentOS, the configuration file is /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf.
For the Ubuntu operating system, the configuration file is /etc/apache2/conf/httpd.conf.
Save and close the file.
The htpasswd command is used to create and update the files that store usernames and passwords for the basic authentication of Apache users. Use the following command to create a hidden file to store the username and encrypted password for each user:
After you create a user, run the following command to see the username and password in the /etc/phpMyAdmin/.phpmyadmin-htpasswd file:
The output should be similar to the following example:
Finally, you must uncomment the following lines from the phpMyAdmin configuration files:
NGINX web server
The htpasswd command is used to create and update the files that store usernames and passwords for the basic authentication of Apache users. Use the following command to create a hidden file to store the username and encrypted password for each user:
After you create a user, run the following command to see the username and password in the /etc/nginx/.pma_pass file:
The output should be similar to the following example:
Finally, you must uncomment the following lines from the phpMyAdmin configuration files:
Share this information:
©2020 Rackspace US, Inc.
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License
Как установить phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin – простое приложение с открытым исходным кодом, позволяющее управлять базами данных MySQL. С его помощью можно администрировать пользователей, создавать и редактировать таблицы, а также проводить экспорт и импорт данных в них. Удобство состоит в том, что все эти операции можно проводить в веб-интерфейсе. Я расскажу, как установить phpMyAdmin на компьютер и на сервер.
Установка phpMyAdmin на компьютер
Прежде чем начать установку phpMyAdmin, убедитесь, что у вас установлены и настроены сервер Apache, PHP и базы данных MySQL. Еще нужно соединение с сервером по защищенному туннелю SSH. Этот способ скорее можно назвать ручным.
Сперва советуем скачать архив приложения с официального русскоязычного сайта. Выбираем любую удобную версию и жмем по ссылке для начала загрузки.
Как только процесс загрузки завершится, распакуем архив. Затем переходим в папку htdocs, расположенную на системном диске в директории «Apache». Сюда вставляем папку из архива, потом переименовываем ее в phpmyadmin.
Теперь открываем папку «PHP» и находим в ней файл «php.ini-production». Переименовываем его в php.ini, а потом открываем с помощью «Блокнота». Находим в тексте строчки «extension=php_mysqli.dll» и «extension=php_mbstring.dll» и удаляем в них символ точки с запятой. Сохраняем изменения, выходим из блокнота.
Если все сделано правильно, то после введения в адресной строке браузера запроса http://localhost будет открываться страница авторизации phpMyAdmin.
Установка phpMyAdmin на сервер
Процедура установки инструмента phpMyAdmin на сервер отличается для разных операционных систем. Требования примерно те же – соединение по защищенному туннелю SSH, предустановленное программное обеспечение PHP, MySQL, Nginx или Apache.
Ubuntu
Перед установкой phpMyAdmin на сервере с ОС Ubuntu прежде всего необходимо проверить, имеется ли расширение PHP для редактирования текстовых строк в формате юникода. Для этого в командной строке вводим вот такой запрос:
После завершения обновления можно приступать к установке нужного нам инструмента на сервер.
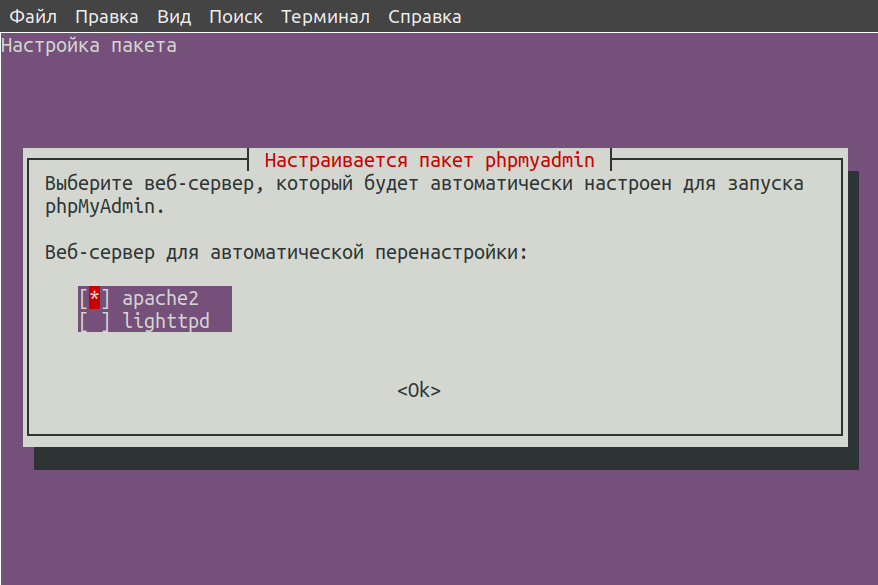
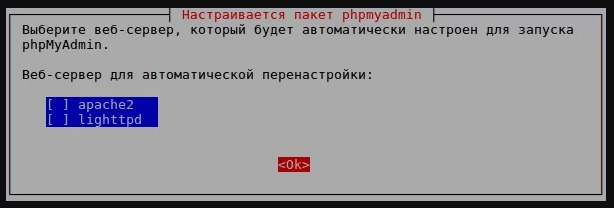
Как только данная команда активируется, откроется установщик. В нем будет предложен выбор веб-сервера для работы с приложением в дальнейшем. С помощью пробела выбираем пункт «apache», потом отмечаем кнопку ОК для применения изменений.
Если на вашем сервере установлен Nginx, на этом моменте просто выберите соответствующий пункт.
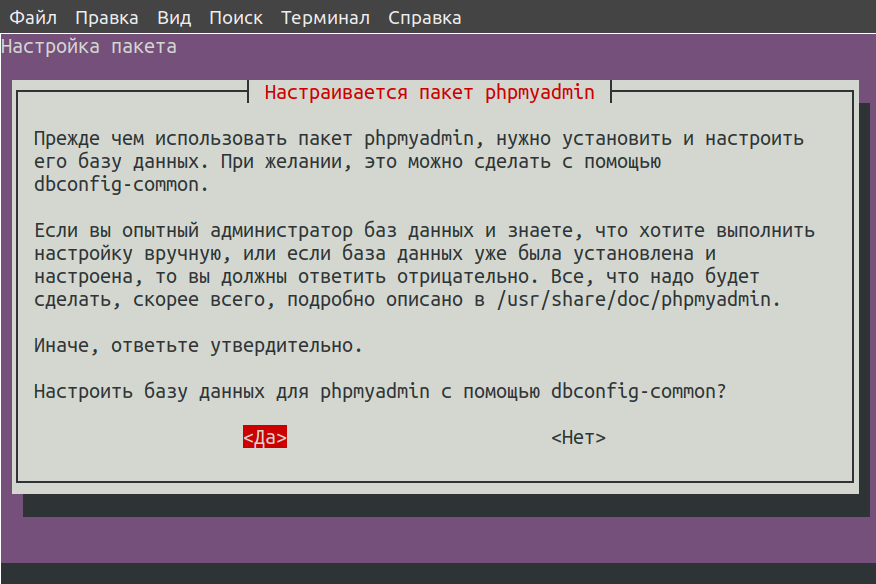
Далее будет предложено создание баз данных для данного ПО, в которой будет вся служебная информация. Соглашаемся, нажав на кнопку «Да», и идем дальше.
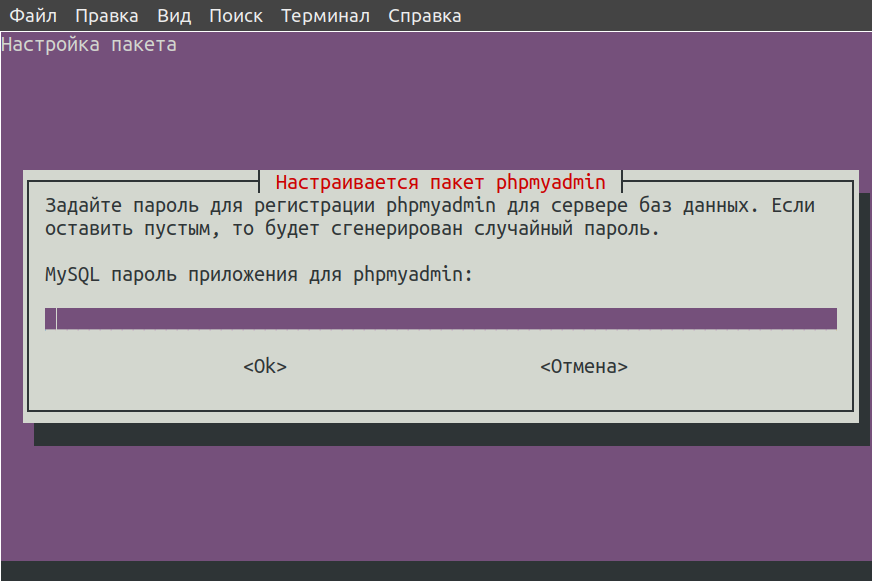
Следующий этап – создание пароля для собственного профиля. Можно придумать новый или оставить поле пустым, чтобы сервис сгенерировал случайную комбинацию. Потом, если мы все же придумали свой пароль, его следует подтвердить.
Но установка phpMyAdmin на сервер не завершена. Нам необходимо включить расширения PHP mcrypt и mbstring, используя для этого нижеуказанные команды:
Чтобы применить все изменения, перезапускаем сервер Apache с помощью специального запроса:
Debian
В случае с Debian был заранее предустановлен стек LEMP, включающий NGINX, MySQL и PHP. Но если что-то из всего этого на сервере отсутствует, можно задать в терминале вот такую команду:
Ждем завершения скачивания и установки всех пакетов. Еще для защиты аутентификации рекомендуется установить сертификат SSL/TLS для передачи зашифрованного трафика.
Так как в Debian большинство программ в репозиториях отсутствует, необходимо будет вручную добавить пункт с phpMyAdmin. Сперва открываем файл «sources.list» в редакторе вот такой командой:
Теперь вносим кое-какие изменения в самом конце файла, добавив следующие строчки:
Сохраняем изменения и выходим из редактора. Теперь надо обновить базы данных в терминале с помощью такого запроса:
А вот теперь можно приступать непосредственно к скачиванию нужного нам приложения. Вписываем следующую команду:
Так как у нас заранее предустановлен Nginx, в момент настройки нам не нужно будет выбирать веб-сервер. Просто пропускаем этот пункт, нажав на кнопку «Tab», а затем кликнув на ОК.
Выйдет новое окно в мастере установки, запрашивающее разрешение на использование «dbconfig-common». Данный параметр позволит настроить базу данных и пользователя с правами администратора для программы phpMyAdmin. Поэтому выбираем пункт «Да» и идем дальше.
Точно так же, как было описано ранее, создаем собственный пароль или оставляем поле пустым для генерации случайного. Теперь ждем, когда все пакеты ПО будут до конца установлены. Для проверки в адресной строке браузера вбиваем адрес http://доменное_имя или IP/phpmyadmin.
CentOS
Здесь тоже заранее инсталлированы модули PHP и Apache. Чтобы установить phpMyAdmin на CentOS, прежде всего понадобится скачать расширенный репозиторий EPEL. Для этого мы задаем вот такую команду:
Если указанный репозиторий не скачать, командная строка может дать ошибку типа «пакета с названием phpmyadmin не найдено».
Скачивание пакета завершено, теперь можем приступать к скачиванию самой программы, и даем для этого следующий запрос:
Потом устанавливаем модули PHP для нормальной работы панели управления базами данных, и делается это одним запросом:
Возможно, они уже были установлены ранее, но все же стоит дополнительно выполнить проверку. Потом перезапускаем сервер для принятия всех внесенных изменений.
Понадобится настроить виртуальный домен, создав для этого специальный конфигурационный файл.
Содержание его при этом должно быть таково:
Сохраняем изменения и закрываем редактор. Затем проверяем корректность настроек вот такой командой:
Если ошибки не возникли, перезапускаем сервер. Если же возникли, заново вносим изменения в только что созданный файл.
Дополнительно можно еще создать отдельный каталог для хранения временных файлов с помощью такого запроса:
Потом потребуется задать для нее владельца и соответствующие права специальными командами:
Настройка завершена. Теперь можно открыть страницу с виртуальным доменом. В результате мы должны попасть на страницу с формой для ввода имени пользователя и пароля.