How to reinstall python
How to reinstall python
Python 3 Installation & Setup Guide
Table of Contents
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: Python Basics: Setting Up Python
Installing or updating Python on your computer is the first step to becoming a Python programmer. There are a multitude of installation methods: you can download official Python distributions from Python.org, install from a package manager, and even install specialized distributions for scientific computing, Internet of Things, and embedded systems.
This tutorial focuses on official distributions, as they’re generally the best option for getting started with learning to program in Python.
In this tutorial you’ll learn how to:
No matter what operating system you’re on, this tutorial has you covered. Find your operating system below and dive in!
Free Bonus: Click here to get a Python Cheat Sheet and learn the basics of Python 3, like working with data types, dictionaries, lists, and Python functions.
How to Install Python on Windows
There are three installation methods on Windows:
In this section, you’ll learn how to check which version of Python, if any, is installed on your Windows computer. You’ll also learn which of the three installation methods you should use. For a more comprehensive guide, check out Your Python Coding Environment on Windows: Setup Guide.
How to Check Your Python Version on Windows
To check if you already have Python on your Windows machine, first open a command-line application, such as PowerShell.
Tip: Here’s how you open PowerShell:
Alternatively, you can right-click the Start button and select Windows PowerShell or Windows PowerShell (Admin).
You can also use cmd.exe or Windows Terminal.
With the command line open, type in the following command and press Enter :
Note: If you don’t have a version of Python on your system, then both of the above commands will launch the Microsoft Store and redirect you to the Python application page. You’ll see how to complete the installation from the Microsoft Store in the next section.
If you’re interested in where the installation is located, then you can use the where.exe command in cmd.exe or PowerShell:
Note that the where.exe command will work only if Python has been installed for your user account.
What Your Options Are
As mentioned earlier, there are three ways to install the official Python distribution on Windows:
Microsoft Store package: The most straightforward installation method on Windows involves installing from the Microsoft Store app. This is recommended for beginner Python users looking for an easy-to-set-up interactive experience.
Full Installer: This approach involves downloading Python directly from the Python.org website. This is recommended for intermediate and advanced developers who need more control during the setup process.
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL): The WSL allows you to run a Linux environment directly in Windows. You can learn how to enable the WSL by reading the Windows Subsystem for Linux Installation Guide for Windows 10.
In this section, we’ll focus on only the first two options, which are the most popular installation methods in a Windows environment.
If you want to install in the WSL, then you can read the Linux section of this tutorial after you’ve installed the Linux distribution of your choice.
Note: You can also complete the installation on Windows using alternative distributions, such as Anaconda, but this tutorial covers only official distributions.
Anaconda is a popular platform for doing scientific computing and data science with Python. To learn how to install Anaconda on Windows, check out Setting Up Python for Machine Learning on Windows.
The two official Python installers for Windows aren’t identical. The Microsoft Store package has some important limitations.
Limitations of the Microsoft Store Package
The official Python documentation has this to say about the Microsoft Store package:
The Microsoft Store package is an easily installable Python interpreter that is intended mainly for interactive use, for example, by students. (Source)
The key takeaway here is that the Microsoft Store package is “intended mainly for interactive use.” That is, the Microsoft Store package is designed to be used by students and people learning to use Python for the first time.
In addition to targeting beginning Pythonistas, the Microsoft Store package has limitations that make it ill-suited for a professional development environment. In particular, it does not have full write access to shared locations such as TEMP or the registry.
Windows Installer Recommendations
If you’re new to Python and focused primarily on learning the language rather than building professional software, then you should install from the Microsoft Store package. This offers the shortest and easiest path to getting started with minimal hassle.
On the other hand, if you’re an experienced developer looking to develop professional software in a Windows environment, then the official Python.org installer is the right choice. Your installation won’t be limited by Microsoft Store policies, and you can control where the executable is installed and even add Python to PATH if necessary.
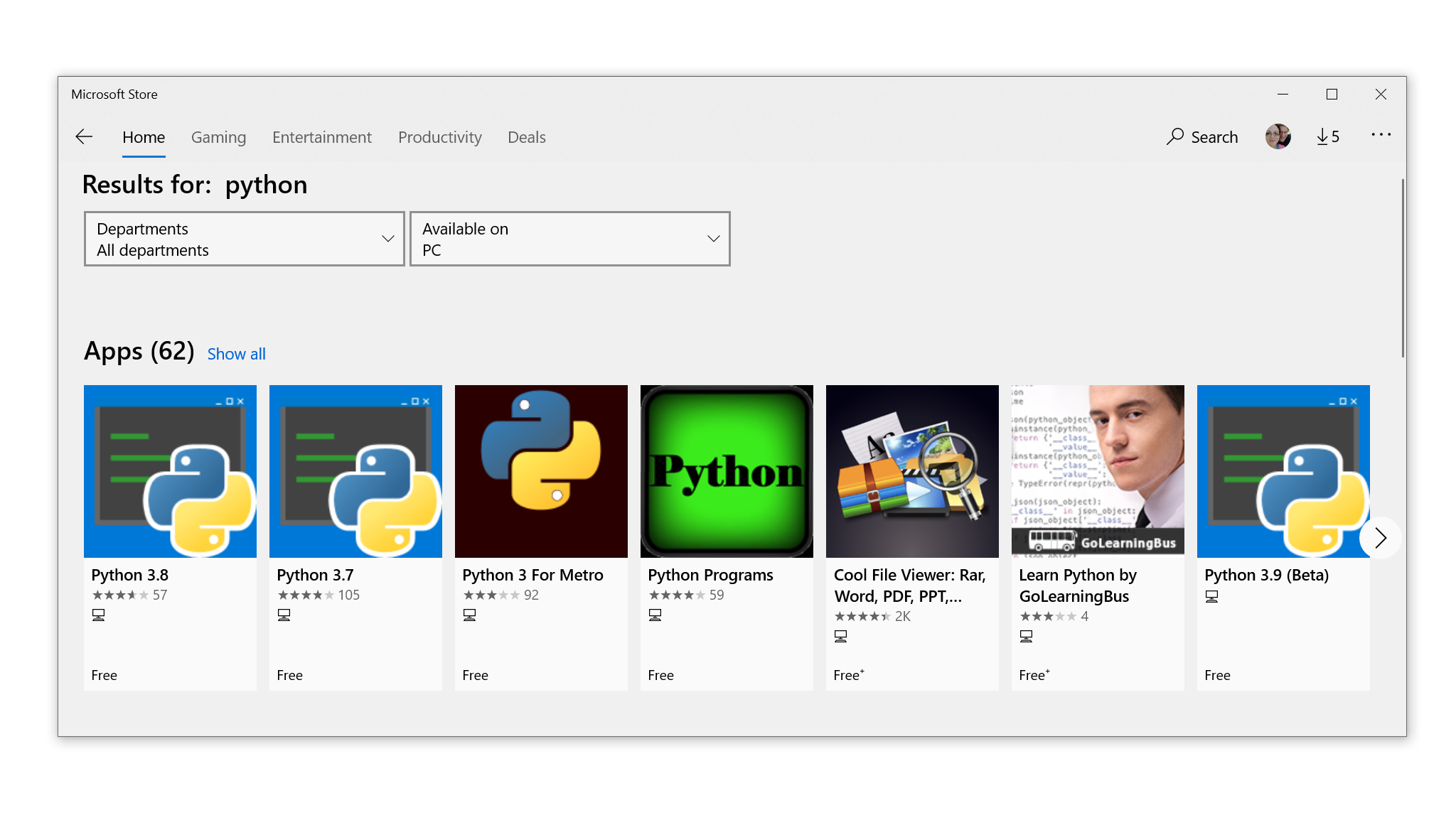
How to Install From the Microsoft Store
If you’re new to Python and looking to get started quickly, then the Microsoft Store package is the best way to get up and running without any fuss. You can install from the Microsoft Store in two steps.
Step 1: Open the Python App Page in the Microsoft Store
You’ll likely see multiple versions that you can choose to install:
Select Python 3.8, or the highest version number you see available in the app, to open the installation page.
Warning: Make sure that the Python application you’ve selected is created by the Python Software Foundation.
The official Microsoft Store package will always be free, so if the application costs money, then it’s the wrong application.
Alternatively, you can open PowerShell and type the following command:
Step 2: Install the Python App
After you’ve selected the version to be installed, follow these steps to complete the installation:
Wait for the application to download. When it’s finished downloading, the Get button will be replaced with a button that says Install on my devices.
Click Install on my devices and select the devices on which you’d like to complete the installation.
Click Install Now and then OK to start the installation.
If the installation was successful, then you’ll see the message “This product is installed” at the top of the Microsoft Store page.
Congratulations! You now have access to Python, including pip and IDLE!
How to Install From the Full Installer
For professional developers who need a full-featured Python development environment, installing from the full installer is the right choice. It offers more customization and control over the installation than installing from the Microsoft Store.
You can install from the full installer in two steps.
Step 1: Download the Full Installer
Follow these steps to download the full installer:
Open a browser window and navigate to the Python.org Downloads page for Windows.
Scroll to the bottom and select either Windows x86-64 executable installer for 64-bit or Windows x86 executable installer for 32-bit.
If you aren’t sure whether to select the 32-bit or the 64-bit installer, then you can expand the box below to help you decide.
32-bit or 64-bit Python? Show/Hide
For Windows, you can choose either the 32-bit or the 64-bit installer. Here’s the difference between the two:
If your system has a 32-bit processor, then you should choose the 32-bit installer. If you attempt to install the 64-bit version on a 32-bit processor, then you’ll get an error at the beginning and the install will fail.
On a 64-bit system, either installer will work for most purposes. The 32-bit version will generally use less memory, but the 64-bit version performs better for applications with intensive computation.
If you’re unsure which version to pick, go with the 64-bit version.
If you have a 64-bit system and would like to switch from 64-bit Python to 32-bit (or vice versa), then you can just uninstall Python and then reinstall it by downloading the other installer from Python.org.
When the installer is finished downloading, move on to the next step.
Step 2: Run the Installer
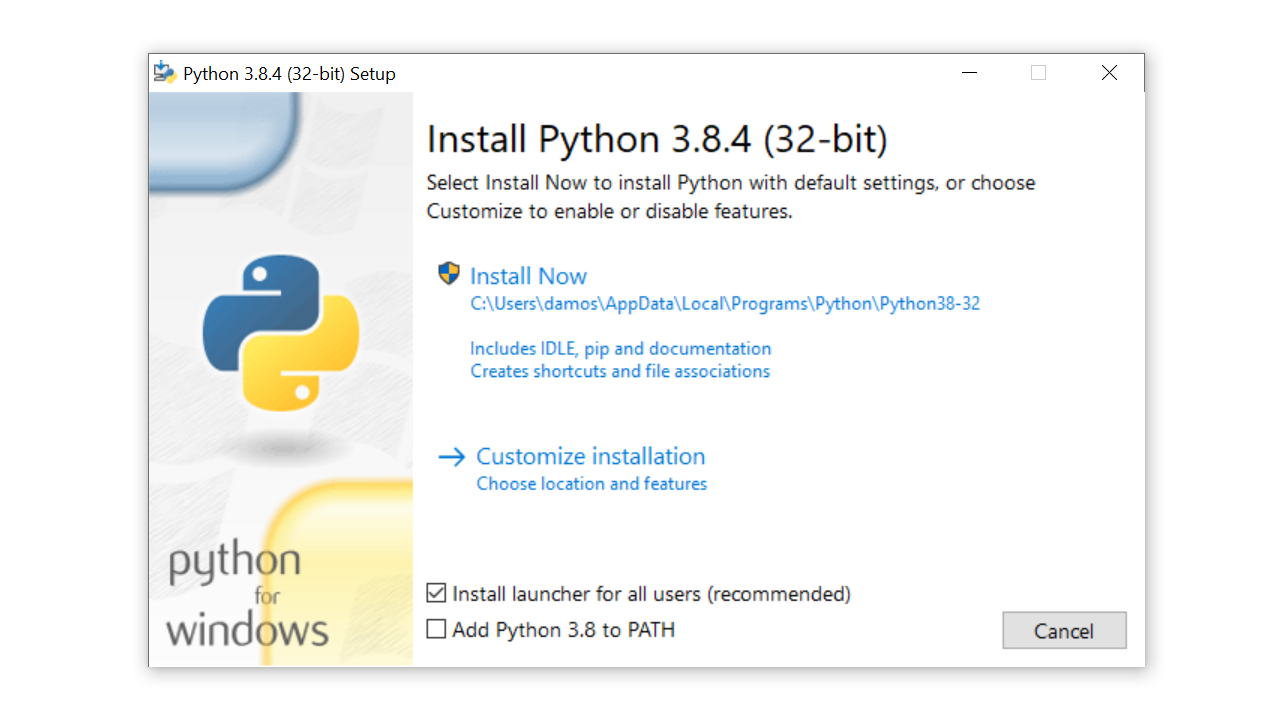
Once you’ve chosen and downloaded an installer, run it by double-clicking on the downloaded file. A dialog box like the one below will appear:
There are four things to notice about this dialog box:
The default install path is in the AppData/ directory of the current Windows user.
The Customize installation button can be used to customize the installation location and which additional features get installed, including pip and IDLE.
The Install launcher for all users (recommended) checkbox is checked default. This means every user on the machine will have access to the py.exe launcher. You can uncheck this box to restrict Python to the current Windows user.
The full installer gives you total control over the installation process.
Warning: If you don’t know what PATH is, then it’s highly recommended that you do not install with the full installer. Use the Microsoft Store package instead.
Customize the installation to meet your needs using the options available on the dialog box. Then click Install Now. That’s all there is to it!
Congratulations—you now have the latest version of Python 3 on your Windows machine!
How to Install Python on macOS
Python 2 comes preinstalled on older versions of macOS. This is no longer the case for current versions of macOS, starting with macOS Catalina.
There are two installation methods on macOS:
In this section, you’ll learn how to check which version of Python, if any, is installed on your macOS device. You’ll also learn which of the two installation methods you should use.
How to Check Your Python Version on a Mac
To check which Python version you have on your Mac, first open a command-line application, such as Terminal.
Tip: Here’s how you open Terminal:
Alternatively, you can open Finder and navigate to Applications → Utilities → Terminal.
With the command line open, type in the following commands:
If you have Python on your system, then one or more of these commands should respond with a version number.
For example, if Python 3.6.10 were already set up on your computer, then the python3 command would display that version number:
What Your Options Are
There are two ways to install the official Python distribution on macOS:
The official installer: This method involves downloading the official installer from the Python.org website and running it on your machine.
The Homebrew package manager: This method involves downloading and installing the Homebrew package manager if you don’t already have it installed, and then typing a command into a terminal application.
Both the official installer and the Homebrew package manager will work, but only the official installer is maintained by the Python Software Foundation.
Note: You can also complete the installation on macOS using alternative distributions, such as Anaconda, but this tutorial covers only official distributions.
Anaconda is a popular platform for doing scientific computing and data science with Python. To learn how to install Anaconda on macOS, check out the macOS installation guide from the official Anaconda documentation.
The distributions installed by the official installer and the Homebrew package manager aren’t identical. Installing from Homebrew has some limitations.
Limitations of Installing From Homebrew
The Python distribution for macOS available on Homebrew doesn’t include the Tcl/Tk dependency required by the Tkinter module. Tkinter is the standard library module for developing graphical user interfaces in Python and is in fact an interface for the Tk GUI toolkit, which isn’t part of Python.
Homebrew doesn’t install the Tk GUI toolkit dependency. Instead, it relies on an existing version installed on your system. The system version of Tcl/Tk may be outdated or missing entirely and could prevent you from importing the Tkinter module.
macOS Installer Recommendations
The Homebrew package manager is a popular method for installing Python on macOS because it’s easy to manage from the command line and offers commands to upgrade Python without having to go to a website. Because Homebrew is a command-line utility, it can be automated with bash scripts.
However, the Python distribution offered by Homebrew isn’t controlled by the Python Software Foundation and could change at any time. The most reliable method on macOS is to use the official installer, especially if you plan on doing Python GUI programming with Tkinter.
How to Install From the Official Installer
Installing Python from the official installer is the most reliable installation method on macOS. It includes all the system dependencies needed for developing applications with Python.
You can install from the official installer in two steps.
Step 1: Download the Official Installer
Follow these steps to download the full installer:
Open a browser window and navigate to the Python.org Downloads page for macOS.
Scroll to the bottom and click macOS 64-bit installer to start the download.
When the installer is finished downloading, move on to the next step.
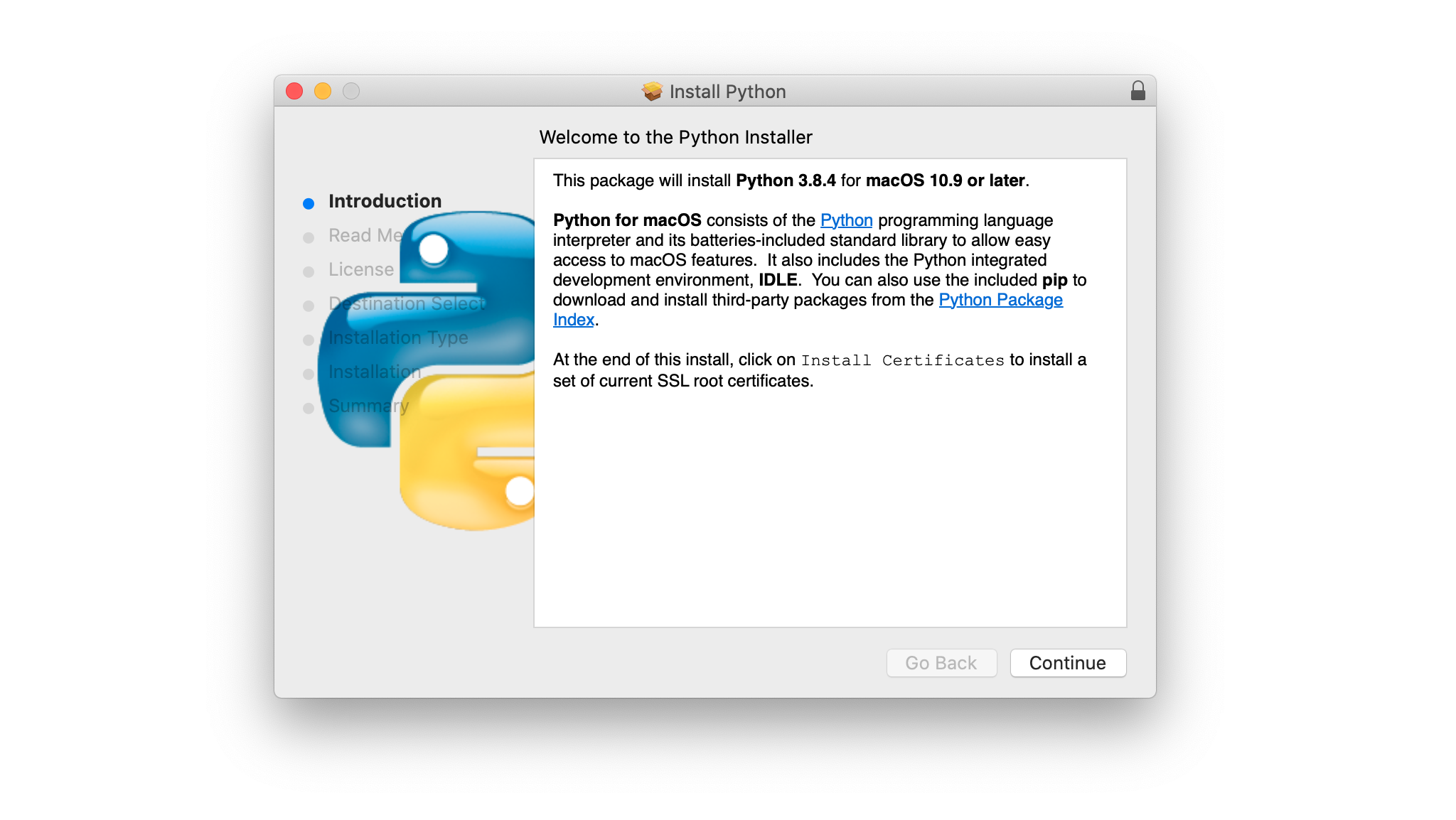
Step 2: Run the Installer
Run the installer by double-clicking the downloaded file. You should see the following window:
Follow these steps to complete the installation:
Press Continue a few times until you’re asked to agree to the software license agreement. Then click Agree.
You’ll be shown a window that tells you the install destination and how much space it will take. You most likely don’t want to change the default location, so go ahead and click Install to start the installation.
When the installer is finished copying files, click Close to close the installer window.
Congratulations—you now have the latest version of Python 3 on your macOS computer!
How to Install From Homebrew
For users who need to install from the command line, especially those who won’t be using Python to develop graphical user interfaces with the Tkinter module, the Homebrew package manager is a good option. You can install from the Homebrew package manager in two steps.
Step 1: Install Homebrew
If you already have Homebrew installed, then you can skip this step. If you don’t have Homebrew installed, then use the following procedure to install Homebrew:
Open a browser and navigate to http://brew.sh/.
You should see a command for installing Homebrew near the top of the page under the tile “Install Homebrew.” This command will be something like the following:
Highlight the command with your cursor and press Cmd + C to copy it to your clipboard.
Enter your macOS user password when prompted.
Depending on your Internet connection, it may take a few minutes to download all of Homebrew’s required files. Once the installation is complete, you’ll end up back at the shell prompt in your terminal window.
Note: If you’re doing this on a fresh install of macOS, you may get a pop-up alert asking you to install Apple’s command line developer tools. These tools are necessary for installation, so you can confirm the dialog box by clicking Install.
After the developer tools are installed, you’ll need to press Enter to continue installation of Homebrew.
Now that Homebrew is installed, you’re ready to install Python.
Step 2: Install Python
Follow these steps to complete the installation with Homebrew:
Open a terminal application.
Type in the following command to upgrade Homebrew:
You can make sure everything went correctly by testing if you can access Python from the terminal:
Open a terminal.
Congratulations—you now have Python on your macOS system!
How to Install Python on Linux
There are two installation methods on Linux:
In this section, you’ll learn how to check which version of Python, if any, is on your Linux computer. You’ll also learn which of the two installation methods you should use.
How to Check Your Python Version on Linux
Many Linux distributions come packaged with Python, but it probably won’t be the latest version and may even be Python 2 instead of Python 3. You should check the version to make sure.
To find out which version of Python you have, open a terminal window and try the following commands:
If you have Python on your machine, then one or more of these commands should respond with a version number.
You’ll want to get the latest version of Python if your current version is in the Python 2.X series or is not the latest version of Python 3 available, which was 3.8.4 as of this writing.
What Your Options Are
There are two ways to install the official Python distribution on Linux:
Install from a package manager: This is the most common installation method on most Linux distributions. It involves running a command from the command line.
Build from source code: This method is more difficult than using a package manager. It involves running a series of commands from the command line as well as making sure you have the correct dependencies installed to compile the Python source code.
Not every Linux distribution has a package manager, and not every package manager has Python in its package repository. Depending on your operating system, building Python from source code might be your only option.
Note: You can also complete the installation on Linux using alternative distributions, such as Anaconda, but this tutorial covers only official distributions.
Anaconda is a popular platform for doing scientific computing and data science with Python. To learn how to install Anaconda on Linux, check out the Linux installation guide in the official Anaconda documentation.
Which installation method you use mainly boils down to whether your Linux OS has a package manager and whether you need to control the details of the installation.
Linux Installation Recommendations
The most popular way to install Python on Linux is with your operating system’s package manager, which is a good choice for most users. However, depending on your Linux distribution, Python may not be available through a package manager. In this case, you’ll need to build Python from source code.
There are three main reasons that you might choose to build Python from source code:
You can’t download Python from your operating system’s package manager.
You need to control how Python gets compiled, such as when you want to lower the memory footprint on embedded systems.
You want to try out beta versions and release candidates of the latest and greatest version before it’s generally available.
To complete the installation on your Linux machine, find your Linux distribution below and follow the steps provided.
How to Install on Ubuntu and Linux Mint
In this section, you’ll learn how to install Python using Ubuntu’s apt package manager. If you’d like to build Python from source code, skip ahead to the How to Build Python From Source Code section.
Note: Linux Mint users can skip to the “Linux Mint and Ubuntu 17 and below” section.
Depending on the version of the Ubuntu distribution you run, the process for setting up Python on your system will vary. You can determine your local Ubuntu version by running the following command:
Follow the instructions below that match the version number you see under Release in the console output:
Ubuntu 18.04, Ubuntu 20.04 and above: Python 3.8 doesn’t come by default on Ubuntu 18.04 and above, but it is available in the Universe repository. To install version 3.8, open a terminal application and type the following commands:
Once the installation is complete, you can run Python 3.8 with the python3.8 command and pip with the pip3 command.
Linux Mint and Ubuntu 17 and below: Python 3.8 isn’t in the Universe repository, so you need to get it from a Personal Package Archive (PPA). For example, to install from the “deadsnakes” PPA, use the following commands:
Once the installation is complete, you can run Python 3.8 with the python3.8 command and run pip with the pip3 command.
Congratulations! You now have Python 3 set up on your machine!
How to Install on Debian Linux
Before you can install Python 3.8 on Debian, you’ll need to install the sudo command. To install it, execute the following commands in a terminal:
After that, open the /etc/sudoers file using the sudo vim command or your favorite text editor. Add the following line of text to the end of the file, replacing your_username with your actual username:
Now you can skip ahead to the How to Build Python From Source Code section to finish installing Python.
How to Install on openSUSE
Building from source is the most reliable way to set up Python on openSUSE. To do that, you’ll need to install the development tools, which can be done in YaST via the menus or by using zypper :
This might take a while to complete as it installs over 150 packages. Once it’s completed, skip ahead to the How to Build Python From Source Code section.
How to Install on CentOS and Fedora
Python 3.8 isn’t available in the CentOS and Fedora repositories, so you’ll have to build Python from source code. Before you compile Python, though, you need to make sure your system is prepared.
Once yum finishes updating, you can install the necessary build dependencies with the following commands:
When everything is finished installing, skip ahead to the How to Build Python From Source Code section.
How to Install on Arch Linux
Arch Linux is fairly diligent about keeping up with Python releases. It’s likely you already have the latest version. If not, use the following command to update Python:
When Python is finished updating, you should be all set!
How to Build Python From Source Code
Sometimes your Linux distribution doesn’t have the latest version of Python, or maybe you just want to be able to build the latest, greatest version yourself. Here are the steps you need to take to build Python from source:
Step 1: Download the Source Code
To start, you need to get the Python source code. Python.org makes this fairly straightforward. If you go to the Downloads page, then you’ll see the latest source for Python 3 at the top. Just make sure you don’t grab Legacy Python, Python 2!
When you select the Python 3 version, you’ll see a “Files” section at the bottom of the page. Select Gzipped source tarball and download it to your machine. If you prefer a command-line method, you can use wget to download the file to your current directory:
When the tarball finishes downloading, there are a few things you’ll need to do to prepare your system for building Python.
Step 2: Prepare Your System
There are a few distro-specific steps involved in building Python from scratch. The goal of each step is the same on all distros, but you might need to translate to your distribution if it doesn’t use apt-get :
First, update your package manager and upgrade your packages:
Next, make sure you have all of the build requirements installed:
It’s fine if you already have some of the requirements installed on your system. You can execute the above commands and any existing packages will not be overwritten.
Now that your system is ready to go, it’s time to start building Python!
Step 3: Build Python
Once you have the prerequisites and the TAR file, you can unpack the source into a directory. Note that the following command will create a new directory called Python-3.8.3 under the one you’re in:
The enable-optimizations flag will enable some optimizations within Python to make it run about 10 percent faster. Doing this may add twenty or thirty minutes to the compilation time. The with-ensurepip=install flag will install pip bundled with this installation.
It might take a while to finish installation. Once it’s done, you can verify that Python is set up correctly.
Step 4: Verify Your Installation
If you have some extra time on your hands, you can also run the test suite to make sure everything is working properly on your system.
To run the test suite, type the following command:
You’ll probably want to find something else to do for a while, as your computer will be running tests for some time. If all the tests pass, then you can be confident that your brand-new Python build is working as expected!
How to Install Python on iOS
The Pythonista app for iOS is a full-fledged Python development environment that you can run on your iPhone or iPad. It features a Python editor, technical documentation, and an interpreter all rolled into a single app.
Pythonista is surprisingly fun to use. It’s a great little tool when you’re stuck without a laptop and want to work on your Python skills on the go. It comes with the complete Python 3 standard library and even includes full documentation that you can browse offline.
To set up Pythonista, you need to download it from the iOS app store.
How to Install Python on Android
If you have an Android tablet or phone and want to practice Python on the go, there are several options available. The one that we found most reliably supports Python 3.8 is Pydroid 3.
Pydroid 3 features an interpreter that you can use for REPL sessions, and it also allows you to edit, save, and execute Python code.
You can download and install Pydroid 3 from the Google Play store. There is a free version and also a paid Premium version that supports code prediction and code analysis.
Online Python Interpreters
If you want to try out the examples in this tutorial without setting up Python on your machine, then there are several websites that offer an online Python interpreter:
These cloud-based Python interpreters may not be able to execute some of the more complex examples in this tutorial, but they’re adequate for running most of the code and may be a nice way to get started. More information on using these sites is presented in the next tutorial in this series.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You now have access to the latest version of Python for your system. Your Python journey is just beginning.
In this tutorial you’ve learned how to:
You’re now ready to get started programming in Python! Be sure to share your progress and any questions you may have in the comments below.
How to install Python in Linux correctly
I am confident, even if you are new to Python, you will be able to install it easily, following this post step by step. So let’s deep dive in.
What are Python and pip
Python is a simple, Object-oriented, interpreted, high-level programming language with dynamic semantics. Due to its non-complicated syntax and fast edit-test-debug cycle, the Programmer community loves it. Python also reduces the cost of software management due to its simple nature.
Pip is a package manager for python, it allows you to install and manage additional libraries and dependencies that are not distributed or part of the standard library.
Pre-requisite to install Python 3.9
How to check Python and pip version
Approximately all Linux versions are shipped with python by default. Earlier it was Python2.x but now everyone is moving towards Python3. Depending upon your distro, it may be the n-1 or older version of Python. I will recommend you to check the existing version of Python already installed in ubuntu 20.04.
1.) Open Terminal in Ubuntu
Press on your keyboard to open terminal.
2.) Run python3 command to check the default version
As you can see in image, Python 3.8.5 is already installed in my Ubuntu 20.04.
3.) Check for existing pip version in ubuntu 20.04
While writing this article, Python 3.9.1 is the latest version available. I will show you the correct way to install Python 3.9.1 and pip 20.3.3 in Linux.
How to install Python on Linux using apt
Step1- Install supporting additional packages
Install software-properties-common package, which provides an abstraction of used apt repositories. It allows you to manage distribution and independent software vendors by adding or removing PPAs.
Step2- Add deadsnakes ppa repository to install latest Python 3.9
Deadsnakes repository contains the latest Python version. Run add-apt-repository command to add deadsnakes ppa to ubuntu 20.04.
Press Enter to continue adding the repository.
Step3- Update ubuntu repository
Run apt command to update or refresh ubuntu repository after adding new deadsnakes ppa.
Step4- Install latest Python 3 (Version 3.9.1)
Type «Y» and press Enter to install the package.
Step5- Check python version
Step6- Open python and run your first program
Open python and type print(«My First Python Program») in python3.9 console and check the output. It will print the statement «My First Python Program«.
Python 3.9.1 (default, Dec 8 2020, 02:26:20)
[GCC 9.3.0] on linux
Type «help», «copyright», «credits» or «license» for more information.
print(«My First Python Program»)
My First Python Program
Type exit() or press to come out from python shell.
How to install the latest python3-pip in Linux
By default, python3-pip is not installed in Ubuntu 20.04 and installing it from apt will install the old pip package. So let’s see step by step installation of the latest python3-pip version (20.3.3). It will be a two-step process, first, we will install pip 20.0.2 using the apt repository. Then, download and install the latest pip package i.e. 20.3.3 version.
Step7- Install python3-pip package using apt command
Step8- Check python3-pip version
Here pip version 20.0.2 got installed and we need to upgrade it to version 20.3.3. Installing package 3.8 from apt will help to meet all dependent packages and libraries which will be required for pip 20.3.3. If you will skip this step, you may get dependent modules error.
Step9- Install curl command first.
If curl is already installed in your system, you can skip this step. Most of the Ubuntu 20.04 don’t have curl installed by default. So use apt install command to install it. Curl is required to execute step 10.
Step10- Download pip from bootstrap.pypa.io website
Now you need to download get-pip from the bootstrap.pypa.io website using the curl command as shown in the image.
Step11- Upgrade python3-pip version to pip-20.3.3
Run the python3.9 command to execute the » get-pip.py » package file you downloaded. It will automatically download and install the latest pip in your Ubuntu.
Step12 (optional)- Add pip3.9 directory to PATH.
This can be achieved by editing /etc/environment files using your favourite editor. Otherwise, exporting and appending the «PATH» variable for the local user profile will also do the trick. Make sure you add
/.local/bin/ in PATH variable.
Step13- Check pip version
Congrats!! till this point, you have installed the latest Python 3.9.1 and pip 20.3.3 successfully.
Further, I want to draw your attention to the problems of uninstalling the default python package. So keep reading, it will definitely save your from breaking your system in future.
How to uninstall Python3 from Ubuntu 20.04
I always provide uninstallation steps of all software in my posts. But I will ask you to avoid this in the case of python. If you will try removing the default python shipped with ubuntu, it will break your system.
Don’t uninstall default python shipped with ubuntu
It’s my recommendation, not to uninstall default python released with your Ubuntu Linux distro. In my case, python3.8 got shipped with my ubuntu 20.04. Running «sudo apt-get remove python*» can break your system. A lot of packages including firefox, gnome and many core packages are dependent on python.
Below mentioned is the list of dependent packages shown in the image. These packages will also remove with the uninstall of default Python 3.8. Which is shipped with Ubuntu 20.04 and it will break our system.
You can keep more than one version of python in your Linux distro. So there is no problem keeping the default Python3.8 and the latest Python3.9 version. You can simply change the default path or alias if required. Additionally, if you work on different projects which, require a different version of Python. I will recommend using a virtual environment (Python—venv).
To avoid all kinds of mess with your system and to perform testing like me. I will suggest you install VMware workstation player in your system and install ubuntu 20.04 on it.
How to Fix or restore, if you have broken your system already while removing the default python package?
Video Tutorial
If you don’t like reading, watch out for this quick video on «How to install the latest Python and pip in Ubuntu 20.04«.
How to reinstall system python 2.7 on Linux Mint 18.3 WITHOUT reinstalling the OS?
On a clean install of Linux Mint 18.3 I ran the following commands through the terminal:
Now when I run pip install
or sudo pip install
neither works. Generally I’ll get an error message that looks like this:
2 Answers 2
If you’re issue is being on too-modern a version of pip (10+), you can always revert it to the previous version (e.g., pip 9.0.3 which was the last version prior to pip 10). You can do this from the command line:
I am on a virtualbox linuxmint 18 Sarah installation. I got into a real mess when I tried to update pip. (eventually a missing frozen keyword when using the new pip for installations)
After trying to follow the various instructions like the one above, I did a brute force reinstall until I could run my python tests again and continue development.
then remove all python installations brute force
(uninstalling python2.7 with the package manager will leave many broken packages behind)
reinstall python from linux packages giving a working pip
reinstall needed python package from using pip, e.g.:
The python packages you need to reinstall might vary obviously for your setup. I hope I didn’t miss anything important from my command history, but you should get the general idea. The longest was the system upgrade. Everything else wen quite quick
How do I install the latest Python 2.7.X or 3.X on Ubuntu?
I want to install the latest Python tarball on Ubuntu, downloaded from http://python.org/download/.
Is this is a correct way to install?
If not, how do I do that?
6 Answers 6
First, install some dependencies:
Then download using the following command:
Extract and go to the directory:
Now, install using the command you just tried, using checkinstall instead to make it easier to uninstall if needed:
Unless you really have a burning desire to compile it yourself, the preferred way is to use the DeadSnakes PPA to install versions of Python that aren’t included by default:
Continuing to document this for the latest Ubuntu releases 1 : for Ubuntu 16.04.1 server, the default Python is version 3.5, and Python 2.7 is not installed by default. On a fresh install (note that there’s not even a python executable):
Installing python 2.7 is as easy as:
The initial output of installing python 2.7 is as follows:
After installing python 2.7,
So to install pip, again, it’s as easy as sudo apt-get install python-pip :
An interesting thing happens as a result of this: you now have the «standard» (and PEP recommended) python2 and python3 (which are just symlinks to python 2.7 and python 3.5):
You’ll also want to sudo apt-get install python3-pip ; before you install, you have:
The resulting versions:
And one last thing before you can go and start installing all your favorite python PyPI modules: you’ll probably have to upgrade pip itself (both pip2 and pip3, separately; also, it doesn’t matter if pip is invoked via the python executables or the pip executables, the actual upgrades are stored in /usr/lib ):
Python download and Installation steps (Windows 10/Unix/Mac/Ubuntu/CentOS )
In this Python tutorial, We will discuss Python download and installation steps. Also we will cover below things.:
You can also check a very good article in How does python work?.
If you want to learn Python and machine learning, check out Python and Machine Learning Training Course.
How to install python on windows?
Let’s discuss, Python 3.8.2 download and installation in Windows 10. Please follow the below steps to do so.
Open the Python official site for downloading the python updated version. The current version in April 2020 is 3.8.2.
Now click on the “Windows” link to download the python version for windows.
From Python stable version 3.8.2 version section, Click on Download “Windows x86-64 executable installer”. Now Python-3.8.2-amd64.exe file will get download. Copy that file to your desktop or some other location.
Now double click on the downloaded file.The below window will open. Click on “Install now“.
Ensure that the Install launcher for all users (recommended) and the Add Python 3.8 to PATH check boxes at the bottom are checked.
Do you want to allow this app to make changes to your device. Please click on yes option.Then the installation will start.
Now the below pop up window will open saying “Setup is successful”.
If you will search for Python in your machine, Python 3.8 (64-bit) will display. Now if you will double click on that below terminal will open.
Now let’s check what is the exact python version installed in my system. To check that I entered the below command
But unfortunately, I got the below error
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “ ”, line 1, in
NameError: name ‘python’ is not defined
Now why this error?
Actually, We are trying to start the Python interpreter by running the command “python”.
However the interpreter is already started. It is interpreting python as a name of a variable, and that name is not defined here so it is showing “name python is not defined”.
But don’t worry python is installed correctly. To verify that, what I did is I entered print(“pythonguides”) and I got the expected output as “pythonguides”.
Now in two ways we can see the python version in this case
1- Please enter the below line of codes in the python terminal
Now see the below screen shot, It is showing my python version is “python 3.8.2”.
2- The other approach here to see the python version is to open the system command prompt and enter the below command. You can see the it will display the version is Python 3.8.2.
How to install python on Linux?
Please follow the below steps to do Python download and installation on Linux.
You should install the build-essentials, bzip2, SQLite as a prerequisite, If you are building this software for the first time in your system as it’s mandate or else you will get errors during installation of python. If you have already done it before then you can ignore the below three steps.
Open the terminal and enter the command “sudo apt-get install build-essential”.This will install all the build essentials in your system.
Now on the terminal enter the command “Sudo apt-get install libbz2-dev”. This will install bzip2 support which is needed.
Now on the terminal enter the command “Sudo apt-get install libsqlite3-dev”. This will install SQ Lite support which is also needed.
So Now you are done with the prerequisite. Now follow the below steps
Open the Python official site for downloading the python updated version. The current version in April 2020 is 3.8.2. But it’s up to you which version you want to download.
Click on the “Linux\Unix” link and download the needed version.
There will be many versions so click on the version you need. It will be downloaded as Python-version and save it in your local folder. Double click on that it will extract and copy to the folder Python-version.
Note: Version here is the version of python you downloaded (Ex : 3.8.2 so you folder \file name will be Python-3.8.2)
Now open the terminal then enter the below command. Now it will point to the folder where your downloaded file is present.
Now type the below command and press enter and wait for some time. Once the system will check everything then you go to the next step.
Now enter the below command and press enter.Linux will make the python software.
Now in your terminal enter the below command. Which will install Python in your system.
Note: Few commands may be different based on your Linux version.
Install Python 3.6 on Ubuntu 16.10 and 17.04
Let’s discuss how we can install Python 3.6 on Ubuntu 16.10 and 17.04. Python 3.6 is by default present there in the repository of Ubuntu 16.10 and 17.04. So please follow the below steps to find the update and install python 3.6.
First open the terminal in your system.
Now check the update. Please use the below command for the same
Use the below command to install python 3.6 on your machine.
Now to make sure the correct version is installed in your machine. You can check the version of python using the below command.
You will get the out put as below
How to install Python 3.8 on Ubuntu, Centos?
Let’s discuss Python 3.8 download and installation steps on Ubuntu. 3.8.2 is the latest version now(April 2020). Please follow the below steps for the same.
Before going to the actual installation We need to install the prerequisites else it will show you so many errors during installation.
Open the terminal and run the below commands.This will download and install the packages needed for the installation.
Open the Python official site for downloading the python 3.8 version. Click on the “Linux\Unix” link and download the 3.8 version.
It will be downloaded as Python-version and save it in your local folder. Double click on that it will extract and copy to the folder Python-3.8.
Now open the terminal then enter the below command. Now it will point to the folder where your downloaded file is present.
Now type the below command and press enter and wait for some time. Once the system will check everything then you go to the next step.
Now in your terminal enter the below command. Which will install Python in your system.
Now to make sure the correct version is installed in your machine. You can check the version of python using the below command.
You will get the below output.
Python 3 Installation on mac
Let’s discuss here how to install Python 3 on macOS? Before going to the actual installation we need to install some prerequisites needed.
Open your terminal and type the below command to install XCode. Which is needed.
Now we need to install Homebrew.To install this, run the below command in your terminal
Now open your terminal and type the below command that will install the latest version of python 3 in your mac
To confirm the version of the python installed in your mac, please type the below command
It will show the latest python version as the output.
How to Install Python 3 on CentOS 7?
Let’s discuss here how to install Python 3 via the CentOS 7 package manager Yum.In Centos 7.7, Python 3 is available in the repository. So let’s follow the below steps
To update the environment, Please use the below command.
Now we need to do the actual installation of python.To do so please use the below command.
Now to make sure python3 got installed correctly, Please run the below command. That will show you the python3 version installed in your machine.
Install Python 3.8 on CentOS 7 / CentOS 8
Let’s discuss here on Python 3.8 download and installation steps on Centos 7 / Centos 8. Please follow the below steps to do so.
We need to install the packages needed before the actual installation of python. To do that please run the below commands.
Open the Python official site for downloading the python 3.8 version. Click on the “Linux\Unix” link and download the 3.8 version.
It will be downloaded as Python-version and save it in your local folder. Double click on that it will extract and copy to the folder Python-3.8.
Now open the terminal then enter the below command. Now it will point to the folder where your downloaded file is present.
Now type the below command and press enter and wait for some time. Once the system will check everything.
Now in your terminal enter the below command. Which will install Python in your system.
Now to verify that you have installed the python 3.8 version correctly. Please use the below command.
You will get the below output
Now we are don with the installation of python 3 in different operating systems. So the next that we need to start the development activities is we need to install one IDE or code editor where we will write and execute our code.
Python IDEs and Code Editors
We will discuss about the different python IDEs and code editors needed for the development of python.
What are IDEs and Code Editors?
When we start working with any of the programming languages, We need some tools or editors where we need to write and execute our programs.
IDE is nothing but an “Integrated Development Environment”. This is a software that is designed for software development. This tool helps to write, design, debug the code easily.
When you are getting an error you can put a debugger and check line by line where the issue is from. Not only this much, An IDE will highlight the code and has auto-suggestion features etc.
Where as the code editors are simple text editors which can highlight the code syntax as well as can format your code easily.
There are few good code editors that can support the debugging as well.
If you are using python for a normal programming purpose then you can choose a good code editor instead of going for an IDE. But if you are building any complex project using python then IDE is the best choice.
There are many IDEs and code editors are available in the market. Some are for general purpose and supports many languages and few you can only use for python development.
1- PyCharm:
Pycharm is one of the best development IDE for python.
This IDE has lots of good features like Code editor, Error highlighting capability, Code debugging capability,supports source controls as well.
Pycharm is available in both paid (Professional) and free open-source (Community) editions.
This is one of the simple IDE and supports in Windows,Linux and Mac platforms.
Let’s discuss the steps to install pycharm community version 2020.1 which is free in Windows 10.
Download the Pycharm executable file from the official site. Click on the “Download” button under the community option.
Python-community-2020.1 file will get downloaded. Copy to a proper location for example desktop or any drive and then double click on that file. Click yes when it will ask “Do you want to allow this app to make changes to your device?”
The below popup will appear, Please click on next.
Now the below pop up will appear, Please click on next button again.
Now you will see the below pop up and check the checkbox 64-bit launcher if you want a desktop short cut and then click next.
Now see the below pop up choose JetBrains and click on install
Now you can see the installation in progress. Please wait for it to complete 100%.
Now if you want to run the Pycharm community version immediately you can check the option or else click on Finish button.
Now your installation is done.Search for Pycharm in your computer and click on that you will get the below popup. Check the check box and click on continue.
The below popup will appear. Click on don’t send button.
Now the IDE will open like below just click on “skip remaining set defaults” button.
Step-12: Congratulation, Now here is the Pycharm IDE version 2020.1.
2- Spyder
One of the best thing in case of Spyder is, It is an open source Python IDE.
Spyder has all the common features which all the IDEs are providing such as code editing, Syntax highlighting, Auto-completion, etc.
Spider is mainly targeted for data scientists using python as It integrates well with common Python data science libraries like SciPy, NumPy, etc.
It looks very simple and easy to use for python development.
3- Visual Studio
Visual studio is one more IDE which is from Microsoft. This is a very reach IDE with all the features like code editor, Highlighting the errors, Autocomplete, Intellisense support, Debugging feature and many more.
This is and IDE with fully loaded feature. You can do what ever you want with this IDE.
Both free version(Community) and paid versions( Professional and Enterprise) are available for visual studio. The current version vs is 2019 as of now.
4- Visual studio code
Visual studio code is a code editor which you can use for python development.This is not only mean for python, It supports other languages also.
Mainly uses for many scripting language as well as for share point framework development purposes.
One more good thing with VSC is it is an open-source tool and has many features like syntax highlighting, bracket-matching, auto-indentation, box-selection etc.
5- Sublime Text
This is one more code editor used for the python development.
It has all the common features like Auto-Completion, selecting multi-line, Formatting, Syntax highlighting, etc
It has build in support to many packages which makes the sublime text editor very rich.
Sublime Text is not totally free, you can use the evaluation version as free but it has less features compared to the paid ones.
6- Atom
Atom is mainly used for developing many desktop applications using HTML,javascript, CSS etc. But you need to install an extension then only you can able to use Atom for python development.
It is a light weight tool and you can install it in many platforms. Only thing is compare to other editors it has less inbuilt features.
7- Thonny
Thonny is one IDE that you can use for the development of python.
It is mainly targeted for beginners for writing python programming.
It has features like Debugging, Highlighting syntax errors, Autocomplete, Variable scope highlighting feature etc
How to Uninstall Python 2.7
To Uninstall Python 2.7 from windows, follow these steps:
Python disable path length limit
In windows 10 latest update have a setting option for path length, follow these steps:
You may like following below Python Tutorials:
Conclusion
Python is the most popular open-source object-oriented programming language. Python is easy to learn and syntax wise it is very simple.
We can install python on different operating system like windows,Linux,Ubuntu,Mac,CentOS7 etc.
We learned about different IDE and code editors for the development of python like Pycharm, Spyder, Atom, Visual Studio, visual studio code, Sublime Text, Thonny etc
The latest python version on April 2020 is 3.8.2.
Python is the best.
This python tutorial explains the below points:
Entrepreneur, Founder, Author, Blogger, Trainer, and more. Check out my profile.
Источники информации:
- http://cloudlinuxtech.com/how-to-install-python/
- http://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/449167/how-to-reinstall-system-python-2-7-on-linux-mint-18-3-without-reinstalling-the-o
- http://askubuntu.com/questions/101591/how-do-i-install-the-latest-python-2-7-x-or-3-x-on-ubuntu
- http://pythonguides.com/python-download-and-installation/