How to report financial report
How to report financial report
Search the Blog
Breaking Down the Basics of a Financial Analysis Report
If you want someone to invest in your company, you need to be able to tell them why it’s worth the investment. And, you must be able to back up your claims with strong financial data. To show investors why your business is a good investment, develop a financial analysis report.
Financial analysis report
Your financial analysis report highlights the financial strengths and weaknesses of your business. Essentially, the report communicates the financial health of your company to investors.
You can use a financial analysis report to attract the interest of investors and help grow your business further.
Even though business owners can build their own financial analysis report, sometimes other individuals may create reports about companies. Then, the individuals creating the reports can use the research to recommend the business’s stock to investors.
How to conduct a financial analysis report
Follow these four steps to conduct a financial analysis report for your small business.
1. Gather financial statement information
To begin conducting your financial analysis report, you must collect data. Gather financial statements and other documentation.
Examples of financial reports include your income statement, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. Consider also gathering any financial notes, quarterly or annual records, and government reports (if applicable).
2. Calculate ratios
Calculate ratios that give a snapshot of your business’s financial health. For example, you might calculate and include your business’s return on investment ratio. That way, you can show investors the profitability of your investments.
Find what ratios matter most to your business. Add your ratios and calculations to your financial analysis report.
3. Conduct a risk assessment
How risky is your business? Investors want to see if your business is worth the risk.
To show investors your business is worth investing in, conduct a risk assessment. You can analyze your business’s risk by doing the following:
4. Determine the value of your business
Lastly, estimate how much your business is worth. Determine the price of your business’s stock and the value it can bring to investors.
Financial analysis report sections
To begin attracting investors, you must learn how to make a financial analysis report. Review the common sections of a financial analysis report below.
Company overview
To start a financial analysis report, start with a description of your business. The company overview helps investors understand the business, industry, and the company’s competitive advantage. These factors help investors determine if your business is a good investment or not.
Gather this information from your company’s quarterly or annual financial statements.
Investment
The investment section addresses the pros and cons of investing in the company.
Investment analysis includes reviewing your business’s cash flow, liquidity, and levels of business debt. And, this section should give projections for how the information might change in the future.
Go into detail about your company’s growth trends, financial statement analysis, and how it compares to the competition.
Consider also including details like turnover ratios, return on investment (ROI), and other financial components.
The more information you have, the better. Using past financial trends in your analysis can help define the likelihood of future financial success.
Valuation
One of the most important parts of a financial analysis report is the valuation section. In this section, you must include how much your business’s stock is worth.
There are three methods for stock valuation, including discounted cash flow analysis, relative value, and book value.
Discounted cash flow
Using the discounted cash flow method, estimate the value of stocks and investments based on the business’s future cash flows. When using this method, find the present value of expected future cash flow using a discount rate.
Relative value
To use the relative value method, compare your business’s fundamental metrics and key financial ratios to your competitors.
Typically, the price-to-earnings ratio is included in the financial analysis report. This ratio compares the market price of a business’s stock to its earnings per share.
Book value
To find book value, compare the business’s book value to the current price of the stock. Book value allows you to see if the stock is overvalued or undervalued.
Risk analysis
Your risk analysis section includes risks that may prevent your company from achieving its valuation.
Detail all key factors that may derail your business. Remember that factors can vary from business to business. And, they can range anywhere from lack of supplies to the loss of patent protection on a product.
Analyze the main risks and summarize them in your report. Consider also looking at the type of industry to determine other potential risks (e.g., technology industry).
Details
In the details section, include summaries of your financial statements and documents. And, incorporate interpretations of the statements using ratios, pie charts, and other graphs.
Consider including a summary or shortened versions of the following financial statements:
The information you include in the details section should support other information presented in your report.
Summary
At the end of the report, give a brief recap of the sections you discussed. Summarize the key points made in the analysis.
Do you need an easy way to keep track of your business’s finances? Patriot’s online accounting software lets you keep track of your income and expenses. And, we offer free, U.S.-based support. Try it for free today!
This is not intended as legal advice; for more information, please click here.
How to Prepare a Financial Report
This article was co-authored by Alan Mehdiani, CPA and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD. Alan Mehdiani is a certified public accountant and the CEO of Mehdiani Financial Management, based in the Los Angeles, California metro area. With over 15 years of experience in financial and wealth management, Alan has experience in accounting and taxation, business formation, financial planning and investments, and real estate and business sales. Alan holds a BA in Business Economics and Accounting from the University of California, Los Angeles.
There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 97,017 times.
A financial report, or financial statement, consists of a balance sheet, an income statement, a statement of retained earnings, and a statement of cash flows. These 4 documents together communicate a company’s performance over a period of time. [1] X Expert Source
Alan Mehdiani, CPA
Certified Public Accountant Expert Interview. 9 July 2020. Private companies may need to distribute quarterly or annual financial reports to banks or lenders. Publicly-traded corporations in the US are required to submit audited financial reports to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). If you’re a small business owner, you may choose to prepare your own financial reports. However, if your business is large or complex, you’d likely be better off to hire an accountant. [2] X Research source
How To Prepare Organized Financial Reporting
Learn how to prepare financial reporting in a standardized and organized way so you can gain the trust of potential investors and creditors.
In this article:
Financial Reporting Standards: What You Need to Know
Financial Reporting: How to Prepare Financial Statements
To prepare the financial statements, you need to compile information from your general ledger and accounting journals into a standard financial report. The purpose of financial reporting is for investors, creditors, and lenders to be able to properly evaluate a company’s capacity.
Businesses distribute their financial statements to these parties so they can check their performance, cash flows, and liquidity. If the company passes the evaluation, they’ll be eligible to get investors’ funding or apply for loans.
When preparing the financial reporting requirements, it’s important to take into account the order of how you need to present your financial statements. In this way, whoever will receive the financial report can precisely analyze your business’ financial position in a faster way.
There are four types of financial statements we’ll talk about today:
1. Income Statement (Profit and Loss)
When you create your Income Statement, organize the items under it this way:
| COST OF GOODS SOLD (COGS) | EXPENSES |
| Used to determine the Gross Profit | Used to determine the Net Profit |
| Predictable and based on sales | Semi-predictable and based on the manager’s discretion |
| Typically variable | Typically fixed |
| Direct | Indirect |
| Unallocated |
| OTHER INCOME AND EXPENSES |
| Amortization |
| Capital Gains / Losses |
| Depreciation |
| Extraordinary Items |
| Interest Expenses |
| Interest Income |
| Income Tax |
Noteworthy Items Under the Income Statement
What Is Gross Profit? This refers to the company’s profit after deducting the costs they incurred in manufacturing and selling their products or providing their services. To calculate this, subtract the COGS from the revenue (sales).
What Is Net Profit? This refers to the company’s remaining profit after deducting the following from the total revenue: operating expenses, taxes, interest, and preferred stock dividends. To calculate this, subtract the Total Expenses from the Total Revenue.
What Is Gross Margin? This is the sales revenue retained by the company after incurring the COGS. To calculate this, subtract the COGS from the Net Sales Revenue.
It’s important to appropriately identify the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) versus Operating Expenses (or simply “Expenses”). This will help you properly analyze the Gross Profit and Gross Margin.
The percentage of the Gross Margin is a good indicator of the business’ characteristics.
Investors, creditors, and lenders alike are all interested in the Net Profit a.k.a. “The Bottom Line.” This is where they’ll be able to determine how lucrative the business is or if they’ll be able to repay their loan.
Remember as well that you should properly identify your business’ Non-operating and Extraordinary Items. This is especially important if you incurred a big loss in the past but it isn’t expected to recur.
The bank, in particular, may consider not including that factor in the calculation of your Net Profit.
2. Statement of Retained Earnings
The first step to prepare this part of the financial reporting is to calculate the Net Profit or Loss. This statement determines your company’s total retained earnings to date and the amount of dividends you’ll pay your investors.
What is retained earnings? Retained earnings are the profit your company keeps for growth. This is different from earnings distributed as dividends to stakeholders or distributed profit share to investors.
3. Balance Sheet
There are three buckets under the Balance Sheet, namely:
Through the Balance Sheet, investors, creditors, and lenders can determine a business’s financial position as a whole since inception. Unlike Profit and Loss Statement, Balance Sheet is a real account which means permanent, as opposed to a nominal account which is temporary in nature.
Here’s how you can organize these three buckets in your financial reporting:
Assets
If you’re applying for a bank loan, you should know that banks mostly focus on the liquidity of the business. They prefer businesses with a higher amount of Current Assets, or highly liquid assets, as they’ll have a better chance to get their funds back if the business fails to pay their loan.
What is liquidity? Liquidity is how quickly a business converts assets into cash like Marketable Securities and Accounts Receivable.
Meanwhile, Fixed Assets serve as collateral. Businesses can use their equipment or real estate assets to back their loans.
Liabilities
| CURRENT LIABILITIES These refer to claims against your assets that are payable within an operating cycle. | NON-CURRENT LIABILITIES Liabilities payable not due within one year |
| Credit card | |
| Credit lines | |
| Loans payable within one year |
Lenders like banks aren’t open to lend to businesses that have high debt as they know they might have a tough time paying back all their loans. They’re well aware that businesses can file for bankruptcy.
During bankruptcy proceedings, shareholders aren’t held personally liable to pay the lenders back. That’s why having a high debt is a red flag.
Another issue that lenders watch out for is the blanket lien. This means that the potential lender is second in position for the collateral, as previous lenders are the priority.
The probability of collecting their loan payment is lower with the blanket lien in place. Lenders also know that if a single loan defaults, then all of the others do the same.
Equity
| EQUITY – NET WORTH Companies increase their Net Worth with Shareholder’s Equity and Net Income and/or Retained Earnings. |
The business’ net worth is the Equity. If the business owners opt to retain their profit and let it circulate within the business, equity grows and maintains.
4. Statement of Cash Flows
In this statement, you compare financial data from two time periods. Here you show how cash changed in the following areas:
The Cash Flow Statement comes last because it needs data from the first three financial statements. Then you divide the cash flows into the following:
What you’ll determine is the net change in cash flows in a given period of time. This statement shows your company’s cash basis financial position or a record of the revenue you actually received in cash.
The Credit Philosophy
If you’re planning to use your financial reports to apply for a bank loan, it’s good to know the five C’s of Credit. This is how they measure risk prior to issuing credit to businesses:
You can present a stronger case by including a narrative that’s similar to the “Notes to Financial Statements” that accountants prepare for audit. Do this in the form of a Business Plan and include the following details:
These are the standard contents you can expect to find in a business financial reporting. The highlights of the report may vary depending on the end-user, but all financial statements include the Income Statement and Balance Sheet.
Always keep in mind the objectives of financial reporting so you can present accurate and useful data.
Do you have other tips in preparing organized financial reporting? We’d love to read about them in the comments section below.
Financial Reporting
What is Financial Reporting?
Financial reporting is a systematic process of recording and representing a company’s financial data. The reports reflect a firm’s financial health and performance in a given period. Management, investors, shareholders, financiers, government, and regulatory agencies rely on financial reports for decision-making.
Table of contents
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution link How to Provide Attribution? Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Financial Reporting (wallstreetmojo.com)
Key Takeaways
Understanding Financial Reporting
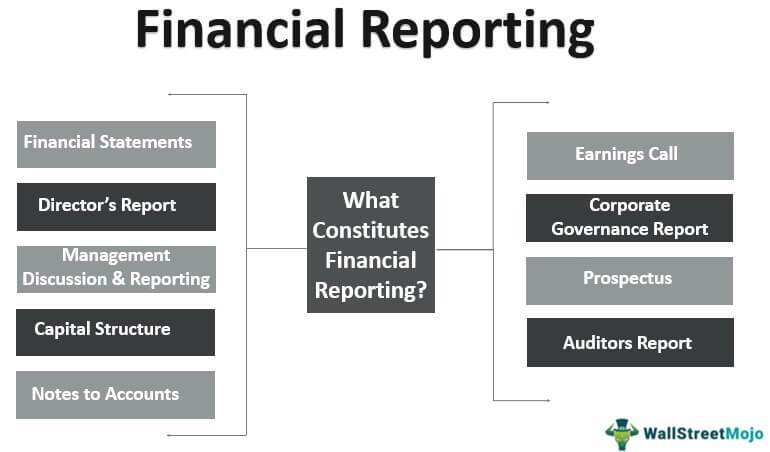
Types of Financial Reporting
Given below are its different reporting methods:
#1 – Financial Statement
#2 – Director’s Report
#3 – Management Discussion and Analysis
Financial reporting and analysis provide information on the current position and performance of a company—in comparison to the competition. In addition, the report focuses on industry trends, future strategies, and future opportunities.
#4 – Notes to Accounts
#5 – Auditors’ Report
This report contains the independent opinion of the statutory auditor. It is the auditors who take the company’s financials and accounting principles.
#6 – Corporate Governance Report
#7 – Prospectus
A company planning to issue an IPO releases a prospectus to promote the securities. It contains all the information about the company’s financials, operations, management, and business goals.
Purpose
Financial reports mirror business performance in terms of numerical figures. It aims to fulfill the following goals:
Examples
Let us see some financial reporting and analysis examples. Given below are financial statements of Verizon Communication Inc., for the year ending on December 31, 2020:
Income Statement:

Balance Sheet:
Cash Flow Statement:
Statement of Change in Equity:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) has standardized worldwide accounting and auditing practices by issuing International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
Financial reporting and analysis facilitate the preparation of financial records, financial ratio analysis, tax return filing, strategic planning, decision-making, and capital acquisition. In addition, shareholders, investors, and regulatory institutions rely on the reports for decision-making and analysis.
Following audit measures determining the veracity of financial reporting and analysis:
• Accrual ratio,
• Profit decline avoidance ratio,
• Loss avoidance ratio,
• Non-big Four auditor ratio,
• Qualified audit opinion ratio,
• Audit-fee ratio.
Financial Reporting Video
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is Financial Reporting. We explain its meaning, analysis, types, standards, and directives using examples. You may learn more about Accounting from the following articles –
How to Write a Great Financial Report? Tips and Best Practices

To make informed financial decisions in your company, you first have to be, well, informed.
Understanding the financial activity of your company sets the foundation for identifying good business opportunities and making the right decisions to ensure future growth.
By tracking, organizing, and analyzing financial performances, you will have a clearer picture of where the money is going and where it’s coming from.
To stay on top of numbers, companies use financial reports.
Financial reports are formal documents that capture all the significant financial activities within a business in a specific period.
While these reports are extremely useful for you and your key stakeholders, you won’t be the only one reaping the fruits. Financial statements are also examined by potential investors and banks since they provide them with enough insight to determine whether they want to invest in your business.
In this article, we are going to walk you through what financial reports are, why they are significant and show you a step-by-step guide that will take your financial reports and business reporting as a whole, to the next level.
What Is a Financial Report?
Financial reports are official company documents that showcase all the financial activities and performances of your business over a specific period. Usually, they are created on a quarterly or yearly basis.
Every business is legally obliged to use financial reporting to display its current financial status and organize financial data.
The documents are available for public view which means that potential banks and investors will most likely analyze them before they decide to work with you and invest in your business.
They are also important for tracking future profitability estimates, business growth, and overall financial health.
At bottom, financial reports provide you with insight into how much money you have, how much did you spend, and where it is coming from. Based on the data within the report, you can make informed business decisions and create plans for future spending.
The key things a financial report should include are:
What Is the Purpose of Financial Reporting?
Understanding how your business is performing from a financial standpoint can seem like an impossible task without these reports.
However, financial reports aren’t used only because they are practical; you are legally required to include them.
Here are some of the main ways in which financial reports can help your business:
Communicate essential data
Having an insight into the current financial situation of your business is important to each high-ranking member of the company (stakeholders, executives, investors, and partners).
You will use this financial data to create budget plans and monitor the company’s overall performance. When you establish an open communication and transparency policy within your business, you are more likely to attract new investors and enhance funding.
The information communicated in financial statements is what investors rely on when they are assessing risks, profitability, and future returns.
Monitors income and expenses
Financial reporting involves tracking incomes and expenses for a specific time period. To establish efficient debt management and budget allocation, you will need an insight into the most important spending areas.
By tracking income and expenses, you will also understand current liabilities and assets. Analyzing financial documentation will provide you with a bigger picture regarding the key metrics such as debt-to-asset ratios that investors use to calculate potential profitability.
All of this is information is crucial for staying ahead of your competitors.
Supports financial analysis and decision-making
The performance analysis in financial reports is what you rely on to make better business decisions.
Considering the different data that financial reports include, you can check out real-time information regarding historical performances, key spending areas, and use them to create accurate financial forecasts.
Implementing detailed financial analysis and using developed data models can help any business better evaluate current activities and make future business growth decisions.
You will be able to recognize trends, potential problems, and stay on top of your financial performances in real-time. This sets the foundation for quick and accurate economic decisions.
Compliance
The main purpose of financial reports is to make sure your business is in compliance with the law and regulations of government agencies.
Regulatory institutions examine every document that evaluates the financial activities of your company. This is why making accurate financial documentation is crucial for the well-being of your business.
Aside from accuracy, you will also have to follow certain deadlines that these institutions set. This sometimes causes pressure in accounting departments to create complex financial reports quickly and accurately, which is why regular bookkeeping is immensely important.
In the US, private and public companies have to be compliant with the GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles), while international companies mostly report under the IRFS (International Reporting Financial Standards).
Both of these organizations provide some standard guidelines but there are a few differences you will have to pay attention to when creating your financial statements.
Simplify your taxes
No matter how big or small your business is, doing taxes can be a stressful task.
By creating accurate financial reports, you can make tax calculation a lot easier since you will minimize any chances of error and save time by including all financial data in one document.
Not only that, since financial reports are a legal requirement, the IRS uses them to evaluate the tax income of each individual company.
What Are the Types of Financial Reporting?
While financial reports all have the same goal, there are a few different types that you should know about.
This isn’t only a matter of compliance or best practice, these reports are key for understanding the different segments of cash flow.
Here are the main types of financial reporting:
Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is a financial statement that tracks the total amount of assets, liabilities, and shareholder equities within your company. They also provide you with a real-time evaluation of asset liquidity and debt coverage.
Most companies create balance sheets on a quarterly basis and include the data from each quarter in the annual report.
When creating a balance sheet, there is an asset page (includes available cash, equipment value, inventory value, etc.) and a liability page (includes accounts payable, credit card balances, bank loans, etc.) that you need to fulfill.
Once you total these assets and liabilities, you will subtract liabilities from the assets. The amount you get is what is called ‘owner’s equity’.
Cash Flow Statement
This is a financial statement that records all the different cash flow activities in the company.
Cash flow statements track cash generated and cash spent amounts in a specific time period. This report is crucial for measuring whether companies generate enough cash to cover their debts. Also, it provides insight into fund operations, investments, and the overall activities that are generating revenue.
This statement is helpful for investors since they can use it to determine whether your business presents a good investment opportunity.
While balance sheets incorporate certain calculations to determine financial values, cash flow statements are consisted of three main elements:
Income Statement
The income statement records the company’s expenses, revenue, and net loss/income over a specific time period.
Balance sheets focus on the current activities and performances while income sheets track them over a longer period. Businesses tend to track income statements each quarter to gain better insight into the different financial processes that occur.
Income statements include profits and losses, which is why they are also called P&L statements (Profits & Losses).
The main elements included on the income statement are:
Shareholder Equity Statement
Even though shareholder’s equity is usually included on the balance sheet, larger companies tend to report these activities on a separate statement.
This statement tracks the amount of money key stakeholders invest in the business. The investments most commonly include company stocks and securities. After dividends are released to stockholders, the retained earnings in the company change.
Stakeholder equity statement includes these key components:
Pro Tip: How to Stay on Top of the Financial Health of Your Business
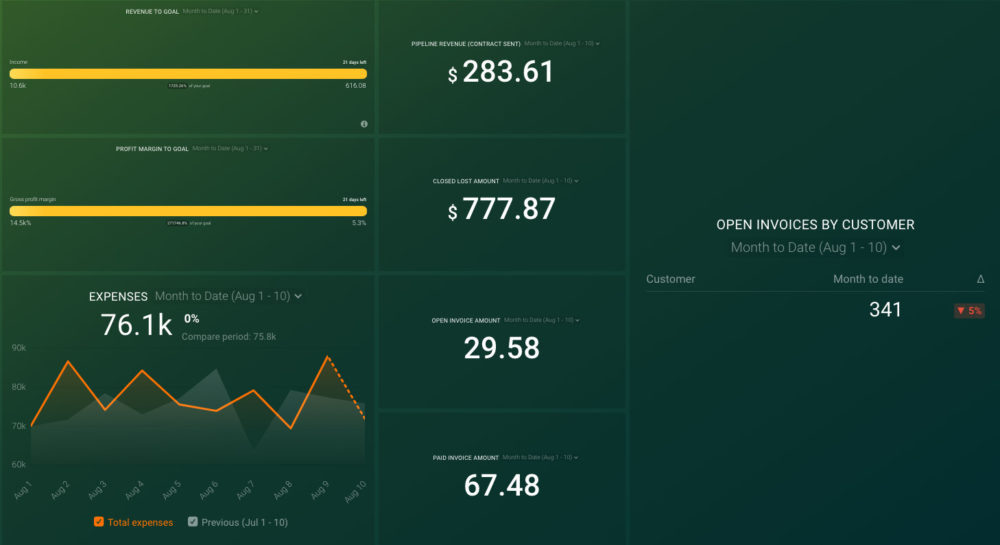
Do you own and manage a small business? Then you know how much of a struggle it can be to stay on top of the financial health of your business on a daily basis. Now you can pull data from QuickBooks and HubSpot’s CRM to track your key business metrics in one convenient dashboard, including:
Now you can benefit from the experience of our HubSpot CRM and QuickBooks experts, who have put together a plug-and-play Databox template that helps you monitor and analyze your key financial metrics. It’s simple to implement and start using, and best of all, it’s free!
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your HubSpot and Quickbooks accounts with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.