How to restart ubuntu from terminal
How to restart ubuntu from terminal
Shutdown or Restart Ubuntu Using Linux Command Line [Beginner’s Tip]
This quick tutorial teaches you how to shutdown Ubuntu or any other distributions from the Linux command line.
How to shutdown Ubuntu?
There are two ways to shutdown Ubuntu Linux. Go to the upper right corner and click the drop down menu. You’ll see the shutdown button here. You can also use the command ‘shutdown now’.
In this article, I’ll discuss both GUI and terminal way of shutting down an Ubuntu system.
1. Shutdown Ubuntu graphically
If you use Ubuntu desktop, you would have no problems in finding the shutdown and the restart option located in the top right corner. If you do, you can extend the next section to see what it looks like.
It may depend on the desktop environment but usually, you’ll see the option in the top right corner:
If you click on the power-off button, it will give you three options: Cancel, Restart and Power Off. You can choose the one you want.
This article is specifically focused on Ubuntu server editions. You are probably stuck in a terminal and wonder how to shutdown or restart the system from the command line.
2. Restart or Shutdown Ubuntu Linux in Terminal
There are multiple commands you can use to shutdown Linux from the terminal. I would recommend the shutdown command. It’s easy to remember and easy to use.
Let’s see how can you use this shutdown command for shutting down or restarting your system.
Shutdown Ubuntu Linux immediately
If you use shutdown command without any arguments, it will shutdown your system in one minute. You can change the behavior and shutdown Ubuntu immediately using:
Schedule a shutdown in Ubuntu Linux
You can schedule a shutdown in various ways.
For example, to schedule a shutdown at 03:30 PM, you can use the command in following fashion:
You don’t always have to specify the absolute time. You can provide a relative time as well.
For example, to schedule a shutdown 20 minutes from now, you can use shutdown command like this:
Restart Ubuntu Linux immediately
You can immediately restart Ubuntu from terminal using the now option like this:
Schedule a restart in Ubuntu Linux
You can also schedule a restart in the same way you scheduled a shutdown.
To schedule a restart at 3:30 PM, you can use:
To schedule a restart 20 minutes from now, you can use:
Cancel a schedule shutdown or reboot
I hope these quick tips helps you to shutdown and restart Ubuntu and other Linux distributions from the command line. Any questions or suggestions are always welcomed.
Creator of It’s FOSS. An ardent Linux user & open source promoter. Huge fan of classic detective mysteries ranging from Agatha Christie and Sherlock Holmes to Detective Columbo & Ellery Queen. Also a movie buff with a soft corner for film noir.
Similar Posts
How to Install Raspbian OS on Raspberry Pi
Install Raspberry Pi OS Raspbian “wheezy” using GUI tools in a safer and easier way. Ideal tutorial for beginner level Linux users.
7 Best Modern Open Source Text Editors For Coding in Linux
Looking for the best text editors in Linux for coding? Here’s a list of the best code editors for Linux. The best part is that all of them are free and open-source software. If you ask experienced Linux users, their answers would probably include Vim, Emacs, Nano, etc. No doubt these are exceptional editors, but…
6 Features That Windows 10 Has Taken From Linux
Microsoft has announced its upcoming operating system Windows 10. The name ‘Windows 10’ has surprised many as people were expecting it to be called Windows 9 as the current version is Windows 8.1. Most plausible reason for this is to avoid conflicts with old codes that dealt with Windows 95. Windows 10 promises some features…
Ubuntu 18.04 Will Get 10-Year Support
Ubuntu’s founder Mark Shuttleworth announced this news in a keynote at OpenStack Summit in Berlin. I’m delighted to announce that Ubuntu 18.04 will be supported for a full 10 years. A Move to lead the Internet of Things (IoT) We are living in a ‘connected world’. The smart devices are connected to the internet everywhere and…
Download YouTube Videos in Linux Command Line Using youtube-dl
Easily download YouTube videos in Linux using youtube-dl command line tool. With this tool, you can also choose video format and pixel size to download it in 1080p or 720p.
How To Watch Netflix on Ubuntu Linux
A few years back, it watching Netflix on Linux required tweaking your system, installing extra libraries, switching user agents in the web browser. The good news is that Netflix is now completely supported on Linux. You don’t need to do any extra efforts to watch Netflix on Linux anymore. Well, mostly. How to watch Netflix…
have updated to 21.10 but computer does not power off after clicking shutdown. have to long press the power button and then re-press to start
Don’t find what you are looking for?
Well done, Sherlock!
Your sharp observation skill and intellect have identified a potential issue with this article.
Is it a grammatical mistake or a simple typo? That happens from time to time.
Is there some incorrect technical information? It’s possible that we were not clear on the topic.
Part of the article contains outdated steps or commands? We have over 1500 articles in the last ten years. It’s possible that some articles that worked well five years ago won’t work today.
Is there an issue with the UI and UX of the website? Some button not working? Link leading to a dead page? Or any other issue with the website elements?
Dear Holmes, help your Watson (that’s us) by explaining the details.
How do I shut down or reboot from a terminal?
How can I shut down or reboot Ubuntu using terminal commands?
5 Answers 5
Open your terminal with CTRL + ALT + T and do these following commands
To shutdown the system:
& one more command for restart:
Another way as one of the user mentioned.
You can get more info on the shutdown command by using one of the following:
Hate passwords ( sudo ) and love one-liners?
For Ubuntu 15.04 and later
This is due to Ubuntu’s shift in using systemd instead of Upstart
Since hibernate is normally disabled by default in Ubuntu systems, you can enable this by checking this answer.
For Ubuntu 14.10 or earlier
Other commands you may like:
Hibernate: (if enabled on your system)
On 16.04 no need of sudo
To restart the computer, type
Now, instead of shutting it down and halting it, you will restart your computer once it’s shutdown. 🙂
Terminal or shell command to shutdown or reboot Ubuntu Linux
S o how do you shutdown or reboot the Ubuntu Linux server from a terminal or a shell prompt? If GUI is working you can always click on a shutdown button. If GUI is not working or if you are working remotely over ssh type the following commands to shutdown from a terminal:
How do I restart /shutdown from a terminal?
To reboot Ubuntu Linux
Type the command to restart Ubuntu box from the command line:
sudo reboot
More information can be found about these two commands by typing following commands (man page):
man reboot
man shutdown
Related posts:
Author: admin
I like chocolate, gadgets, open source software, photography, traveling and all shades of green colors. I love spending time with fun loving friends and family members. This is my own online journal. View all posts by admin
30 thoughts on “Terminal or shell command to shutdown or reboot Ubuntu Linux”
thank you. very usefull shell commands
What would be the shell command to get the shutdown/restart popup? The reason why I am asking is because I want to change the command on one of the applets on AWM from logout to shutdown/restart. I would rarely if ever use the logout feature since I am the sole user of my computer.
I have a dual booting machine having XP SP2 and UBUNTU 8.04. I have installed UBUNTU under XP. Now using secured Shell from an remote PC I want to logout from ubuntu such that it would not go to the dual boot screen where Windos XP is the firs option and I have no control over it from remote PC to stop the machine to to go to Windows. This is only possible if I use logout not restart or reboot. So, please tell me how is it possible from terminal?
Thank for the commands.
Was just browsing and saw this. I have a dual boot as well. and wanted to control the same problem when booting.
what I did was write a script that edits the grub configuration file. the file is in /boot/grub. I have 9.10 and the file is called grub.cfg, but in older versions it is called menu.lst.
you are looking for a line that says “default x” where x is the default row that grub starts on. starting from 0(in 9.10 this is “default = x”). soooooo…
note, this script has to be run with root permission to edit the file(and in ubuntu 9.10 the permissions have to be adjusted on the file to allow root to write to it).
What I did was attach this script to an launcher on my taskbar so whenever I click it it runs “gksu scriptname” note also that gksu must be used with the launcher because no terminal will appear for you to enter the root password if you just use “sude” here.
here it is written in perl, this should work on 8.04 without any changes assuming things are configured normally. just change the numbers “0” and “6” accordingly for your system.
How to Reboot Ubuntu through the Command Line
Although Linux does not require frequently restarting as opposed to Windows, sometimes major system updates or serious system glitches may require a system restart. With the introduction of ‘kptach’ by RedHat, system administrators can easily patch critical security updates to the Linux kernel. There is no need to look for the processes to complete, log off the system, or crontab any reboot task. It also increases system uptime without losing productivity. ‘Livepatch’ by Ubuntu also works in the same way. With Livepatch, vulnerability fixes can be patched on the Ubuntu Linux Kernels.
Reboot process helps deadlocked programs exit, apply critical patches, remove temporary files, repair damaged file systems, and perform many system management tasks.
What will we cover?
In this guide, we will see different ways of rebooting a Linux Ubuntu 20.04 machine from the command line and GUI. Let’s get started with this tutorial.
Using the Shutdown command
This command can be used to stop, power off or restart a machine. It uses a time argument to specify the time for execution. The time argument is ‘now’ for triggering immediate operation. For example, to immediately reboot a system use the ‘-r’ flag with the ‘now’ string:
In the same way, if you want to schedule a reboot after 5 minutes, use the below command:
The time format is “hh:mm” in 24-hr clock format. We can also use ‘+m’ to reboot after ‘m’ minutes from now.
It should be noticed that the ‘shutdown’ command itself also has the capability to shut down, reboot, stop and power off a system.
Using the Reboot command
From the terminal perspective, the reboot command is the fastest and easiest way to reboot a system. Simply type the below command to reboot:
Using ‘Init’ the command
In linux, ‘/sbin/init’ is the first process that executes once the kernel is loaded. It means the process has PID 1.
In Linux systems that do not have ‘systemd’, the ‘init’ command stops all running processes, and the disks are then synchronized prior to switching the init states or run levels. The run level 5 is the default run level. The ‘init 6’ command halts the running system and restarts the system to a state listed in ‘/etc/inittab’. To restart, simply use:
In case we want to reboot the Linux Ubuntu to a multiuser state, use the command:
Similarly, to reboot to a Single-User State (Runlevel S), use the command:
To reboot to single user mode is to use the command:
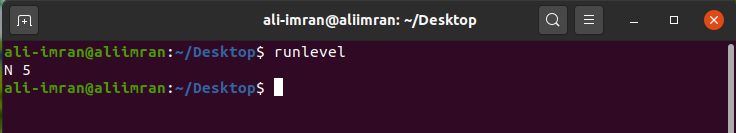
To check your current run level, run the following command:
If the output is like ‘N 1’, this means we have no old runlevel as we have just booted the system:
Now let us boot to runlevel 1 (also called runlevel s) and check the runlevel status:
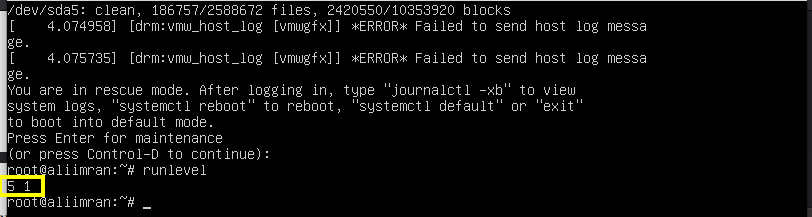
As you can see, the status has now changed to ‘5 1’. We can again switch back to runlevel 5 by running:
The ‘SYSTEMD’ Way
‘Systemd’ has replaced the init process, so the ‘/sbin/init’ has now become a symbolic link to systemd.
On systems having systemd ( as opposed to the init system), you may not find ‘/etc/inittab’. In such a case, use the below command to reboot a system:
Just like runlevels in the SysV init system, systemd uses the so-called “target” system. The above ‘systemctl’ command is the primary interface to systemd. The runlevel 6 of the SysV init system has its equivalent target in systemd as “reboot.target”. So you can also use the above reboot command as:
The Restart Button
The simplest and quickest solution is, of course, the reboot button. When you click on the right top corner of your Ubuntu 20.04 system, you will find the ‘Power Off / log Out’ option.
Now when you click on this option, you will see the last option as ‘Power Off’. Press this label, and it will bring you the Power Off window. Hit on the ‘Restart’ button to reboot the system.
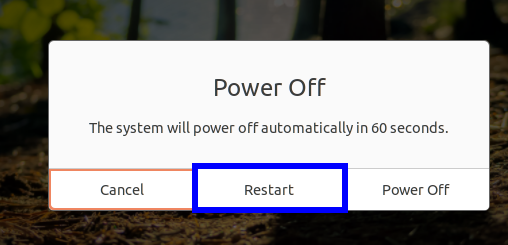
You can also find this window by typing ‘reboot’ in the Gnome search bar:

Another way is to use the physical power button; this will display the Power Off window. But beware, this may require first configuring the power button behavior from inside the system settings.
Conclusion
In this guide, we have learned about different ways of rebooting a Ubuntu machine. This guide can also be used for many other Linux distributions besides Ubuntu since all commands are generally the same for them. We have not provided many screenshots of the practicals because it’s not possible to snap a reboot process. But we are sure this guide will run smoothly for your system.
About the author
Ali Imran Nagori
Ali imran is a technical writer and Linux enthusiast who loves to write about Linux system administration and related technologies. You can connect with him on LinkedIn
.
How to Restart or Reboot Linux Server from the Command Line
Home » SysAdmin » How to Restart or Reboot Linux Server from the Command Line
It’s a cliché, but true – restarting a Linux server solves a wide variety of issues.
When a system is rebooted, any malfunctioning software is purged from active memory. When the system restarts, it loads a fresh, clean copy of the software into active memory. Also, some operating systems require a restart to process updates or configuration changes.
This guide will show you how to restart a Linux server using only the command-line or prompt.
Steps to Restart Linux using Command Prompt
Restarting Local Linux Operating System
Step 1: Open Terminal Window
If your version of Linux uses a graphical interface, you can open a terminal window by right-clicking the Desktop > left-clicking Open in terminal.
You can also click the main menu (usually found in the lower-left or upper-left corner) and type in terminal in the search bar. Click on the Terminal icon, as in the image below.
Step 2: Use the shutdown Command
Since powering off is one of the most basic functions of an operating system, this command should work for most distributions of Linux.
In a terminal window, type the following:
The sudo command tells Linux to run the command as an administrator, so you may need to type your password. The -r switch at the end indicates that you want the machine to restart.
Note: See our article for additional Linux shutdown command options.
Alternative Option: Restart Linux with reboot Command
In the terminal, type:
Many Linux versions do not require administrator privileges to reboot. If you get a message that you do not have sufficient privileges, type:
Your system should close out of all open applications and restart.
Reboot Remote Linux Server
Step 1: Open Command Prompt
If you have a graphical interface, open the terminal by right-clicking the Desktop > left-clicking Open in terminal.
You can also click the main menu (usually found in the lower-left or upper-left corner), and then click Applications > System Tools > Terminal.
If you prefer using a keyboard shortcut, press Ctrl+Alt+T.
Step 2: Use SSH Connection Issue reboot Command
In a terminal window, type:
Note: You may need to enter the password for the username you’ve used. Also, make sure you type the single-quote marks.
The ssh command tells your system to connect to another machine. The -t option forces the remote system to enter the command in a terminal. Replace [email protected] with the username @ server name that you want to restart.
The sudo reboot command can be switched out for sudo shutdown and the above options above can be used.
That is: -r tells it to restart, hh:mm sets a specific time, +mm sets a countdown.)
In this tutorial, you have learned how to restart a Linux server from the command prompt.
Rebooting a Linux system or server is designed to be simple, so you shouldn’t have any trouble. Just make sure you have saved all your work before restarting.