How to set environment variable in linux
How to set environment variable in linux
How to Set Environment Variables in Linux
Overview
In this tutorial, you will learn how to set environment variables in Ubuntu, CentOS, Red Hat, basically any Linux distribution for a single user and globally for all users. You will also learn how to list all environment variables and how to unset (clear) existing environment variables.
Environment variables are commonly used within the Bash shell. It is also a common means of configuring services and handling web application secrets.
It is not uncommon for environment specific information, such as endpoints and passwords, for example, to be stored as environment variables on a server. They are also used to set the important directory locations for many popular packages, such as JAVA_HOME for Java.
Setting an Environment Variable
To set an environment variable the export command is used. We give the variable a name, which is what is used to access it in shell scripts and configurations and then a value to hold whatever data is needed in the variable.
For example, to set the environment variable for the home directory of a manual OpenJDK 11 installation, we would use something similar to the following.
To output the value of the environment variable from the shell, we use the echo command and prepend the variable’s name with a dollar ($) sign.
And so long as the variable has a value it will be echoed out. If no value is set then an empty line will be displayed instead.
Unsetting an Environment Variable
To unset an environment variable, which removes its existence all together, we use the unset command. Simply replace the environment variable with an empty string will not remove it, and in most cases will likely cause problems with scripts or application expecting a valid value.
To following syntax is used to unset an environment variable
For example, to unset the JAVA_HOME environment variable, we would use the following command.
Listing All Set Environment Variables
To list all environment variables, we simply use the set command without any arguments.
An example of the output would look something similar to the following, which has been truncated for brevity.
Persisting Environment Variables for a User
When an environment variable is set from the shell using the export command, its existence ends when the user’s sessions ends. This is problematic when we need the variable to persist across sessions.
To make an environment persistent for a user’s environment, we export the variable from the user’s profile script.
Adding the environment variable to a user’s bash profile alone will not export it automatically. However, the variable will be exported the next time the user logs in.
To immediately apply all changes to bash_profile, use the source command.
Export Environment Variable
Export is a built-in shell command for Bash that is used to export an environment variable to allow new child processes to inherit it.
To export a environment variable you run the export command while setting the variable.
We can view a complete list of exported environment variables by running the export command without any arguments.
Setting Permanent Global Environment Variables for All Users
A permanent environment variable that persists after a reboot can be created by adding it to the default profile. This profile is loaded by all users on the system, including service accounts.
All global profile settings are stored under /etc/profile. And while this file can be edited directory, it is actually recommended to store global environment variables in a directory named /etc/profile.d, where you will find a list of files that are used to set environment variables for the entire system.
Conclusion
This tutorial covered how to set and unset environment variables for all Linux distributions, from Debian to Red Hat. You also learned how to set environment variables for a single user, as well as all users.
Setting environment variables in Linux using Bash
What is the equivalent to the tcsh setenv function in Bash?
Is there a direct analog? The environment variables are for locating the executable.
5 Answers 5
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
The reason people often suggest writing
instead of the shorter
Set a local and environment variable using Bash on Linux
Check for a local or environment variables for a variable called LOL in Bash:
Sanity check, no local or environment variable called LOL.
Set a local variable called LOL in local, but not environment. So set it:
Set a local variable, and then clear out all local variables in Bash
You could also just unset the one variable:
Local variable LOL is gone.
Promote a local variable to an environment variable:
Note that exporting makes it show up as both a local variable and an environment variable.
Exported variable DOGE above survives a Bash reset:
Unset all environment variables:
You have to pull out a can of Chuck Norris to reset all environment variables without a logout/login:
You created an environment variable, and then reset the terminal to get rid of them.
Or you could set and unset an environment variable manually like this:
How to set environment variable in Linux permanently
How I can set the new environment variables and their value permanently in Linux
I used export to set the env variables. But the problem is its session specific. If I open new session the values set will be gone. Thank you in advance
/.bashrc for bash or
6 Answers 6
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
with all the respect due to answers above, setting environnement variables is depending if you want to set to the user session or super user session.
1) input this command in the environement of your choice :
3) open this file in your favorite editor, for example :
4) then add at the end of the file your personnalized variable as following:
5) then save and close and open the terminal, check if your variable has been set:
Solution: In order to export and keep environment variables persistent on linux you should export variables decelration into one of the following files:
When bash is invoked as an interactive/non-interactive login shell, it first reads and executes commands from the file /etc/profile (if exists) and after looks for these following files ( in that order and do the same)
Example: adding secret token into my user profile.
The usual place is
/.bash_profile,.bashrc,/etc/environment. Is it still possible to set the path using command which will not be depend on session?
See how the environment variable PATH is being set above.
A note on export command
How to Set Environment Variables in Linux
Home » SysAdmin » How to Set Environment Variables in Linux
Every time you start a shell session in Linux, the system goes through configuration files and sets up the environment accordingly. Environment variables play a significant role in this process.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to set, view, and unset environment variables in Linux.
What Are Environment Variables: A Definition
Environment variables are variables that contain values necessary to set up a shell environment. Contrary to shell variables, environment variables persist in the shell’s child processes.
Structurally, environment and shell variables are the same – both are a key-value pair, separated by an equal sign.
If a variable has more than one value, separate them with a semicolon:
Variables that contain spaces are written under quotation marks:
Note: The convention is to use all caps for writing variable names, in order to distinguish them among other configuration options.
Most Common Environment Variables
Here are some environment variables that an average user may encounter:
How to Check Environment Variables
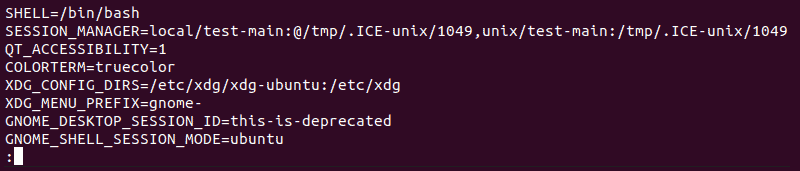
View All Environment Variables
Use the printenv command to view all environment variables. Since there are many variables on the list, use the less command to control the view:
The output will show the first page of the list and then allow you to go further by pressing Space to see the next page or Enter to display the next line:
Search a Single Environment Variable
To check a single environment variable value, use the following command:
The HOME variable value is the home folder path:
Alternatively, display the value of a variable by using the echo command. The syntax is:
Search Specific Environment Variables
To find all the variables containing a certain character string, use the grep command:
The search output for the USER variable shows the following lines:
Find an environment variable in the list that contains all the variables and shell functions by using set | grep :
Note: Take a look at our in-depth guide on how to use the Linux set command to learn more about it.
Set an Environment Variable in Linux
The simplest way to set a variable using the command line is to type its name followed by a value:
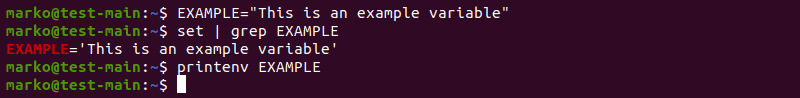
1. As an example, create a variable called EXAMPLE with a text value. If you type the command correctly, the shell does not provide any output.
2. The set | grep command confirms the creation of the variable. However, printenv does not return any output.
This is because the variable created in this way is a shell variable.
3. Another way to confirm this is to type bash and start a child shell session. Using the echo command to search for the EXAMPLE variable now returns no output:
Note: In a child process, EXAMPLE is not an existing variable.
How to Export an Environment Variable
1. If you want to turn a shell variable into an environment variable, return to the parent shell and export it with the export command:
2. Use printenv to confirm the successful export:
3. If you open a child shell session now, echo will return the environment variable value:
The environment variable created in this way disappears after you exit the current shell session.
Set an Environment Variable in Linux Permanently
If you wish a variable to persist after you close the shell session, you need to set it as an environmental variable permanently. You can choose between setting it for the current user or all users.
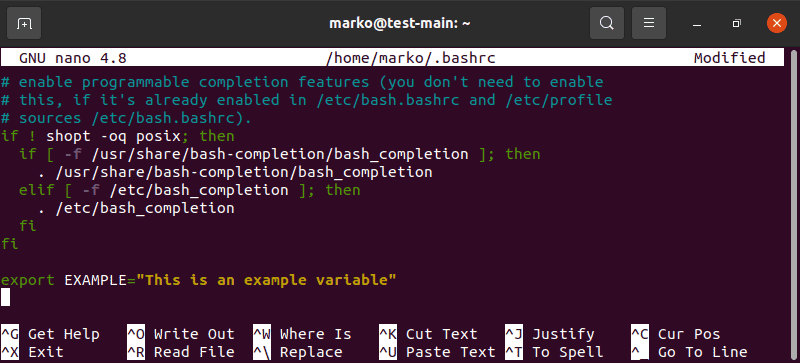
1. To set permanent environment variables for a single user, edit the .bashrc file:
2. Write a line for each variable you wish to add using the following syntax:
3. Save and exit the file. The changes are applied after you restart the shell. If you want to apply the changes during the current session, use the source command:
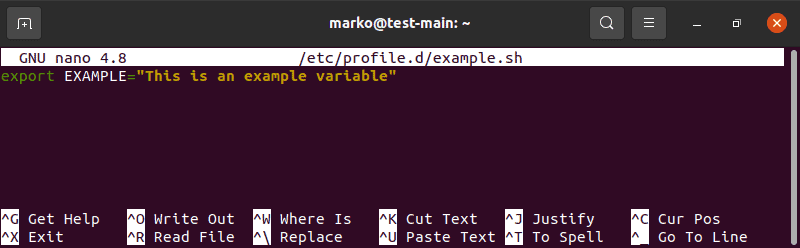
4. To set permanent environment variables for all users, create an .sh file in the /etc/profile.d folder:
5. The syntax to add variables to the file is the same as with .bashrc :
6. Save and exit the file. The changes are applied at the next logging in.
How to Unset an Environment Variable
To unset an environment variable, use the unset command:
This command permanently removes variables exported through a terminal command.
Variables stored in configuration files are also removed from the current shell session. However, they are set again upon next logging in.
To permanently unset a variable you stored in a file, go to the file, and remove the line containing the variable definition.
After reading this article, you should know how to set and unset environmental variables on a Linux system. Knowing how to set environment variables will help you more easily configure software packages in the future.
Переменные окружения в Linux
Например, команда PWD использует системную переменную, чтобы сохранять прежнюю рабочую директорию. Пользовательские переменные окружения устанавливаются пользователем, для текущей оболочки, временно или постоянно. Вся концепция добавления и удаления переменных оболочки крутится вокруг нескольких файлов, команд и различных оболочек.
Виды переменных окружения
Если смотреть более широко, переменная окружения может быть трех типов:
1. Локальные переменные окружения
Эти переменные определены только для текущей сессии. Они будут безвозвратно стерты после завершения сессии, будь то удаленный доступ или эмулятор терминала. Они не хранятся ни в каких файлах, а создаются и удаляются с помощью специальных команд.
2. Пользовательские переменные оболочки
3. Системные переменные окружения
Эти переменные доступны во всей системе, для всех пользователей. Они загружаются при старте системы из системных файлов конфигурации: /etc/environment, /etc/profile, /etc/profile.d/ /etc/bash.bashrc.
Конфигурационные файлы переменных окружения Linux
Здесь мы кратко рассмотрим различные конфигурационные файлы, перечисленные выше, которые используются для настройки переменных окружения для всей системы или конкретного пользователя.
.bashrc
Это файл переменных конкретного пользователя. Загружается каждый раз, когда пользователь создает терминальный сеанс, то есть проще говоря, открывает новый терминал. Все переменные окружения, созданные в этом файле вступают в силу каждый раз когда началась новая терминальная сессия.
.bash_profile
/etc/environment
Этот файл для создания, редактирования и удаления каких-либо переменных окружения на системном уровне. Переменные окружения, созданные в этом файле доступны для всей системы, для каждого пользователя и даже при удаленном подключении.
/etc/bash.bashrc
Системный bashrc. Этот файл выполняется для каждого пользователя, каждый раз когда он создает новую терминальную сессию. Это работает только для локальных пользователей, при подключении через интернет, такие переменные не будут видны.
/etc/profile
Системный файл profile. Все переменные из этого файла, доступны любому пользователю в системе, только если он вошел удаленно. Но они не будут доступны, при создании локальной терминальной сессии, то есть если вы просто откроете терминал.
Все переменные окружения Linux созданные с помощью этих файлов, могут быть удаленны всего лишь удалением их оттуда. Только после каждого изменения, нужно либо выйти и зайти в систему, либо выполнить эту команду:
Добавление пользовательских и системных переменных окружения в Linux
Теперь, когда вы знаете немного теории, перейдем к практике. Локальные переменные окружения в Linux можно создавать следующими командами:
var=значение
export var=значение
Эти переменные будут доступны только для текущей терминальной сессии.
Для удаления переменных окружения можно использовать несколько команд:
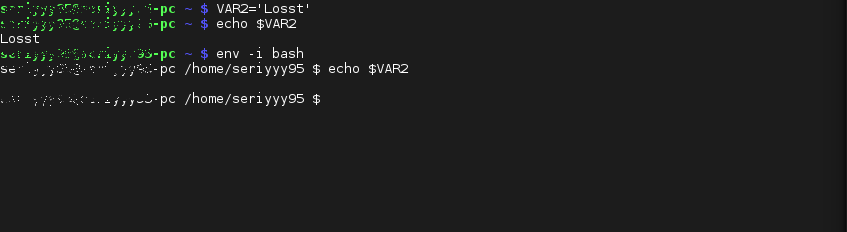
1. Использование env
Такая команда запустит оболочку вообще без переменных окружения:
После запуска такого окружения, не будет доступно никаких переменных, но после выхода все вернется на свои места.
2. Использование unset
Это другой способ удаления переменных окружения Linux. Unset удаляет переменную по имени до конца текущей сессии:
3. Установить значение переменной в »
Это самый простой способ удаления переменных окружения в Linux, устанавливая пустое значение переменной, вы удаляете ее до конца текущей сессии.
Замечание: С помощью таких способов вы можете изменять значения системных или пользовательских переменных, но они будут актуальны только для текущего сеанса.
Создание пользовательских и системных переменных окружения
В этом разделе рассмотрим как установить и удалить системные и пользовательские переменные не только для текущего сеанса, а так чтобы эффект сохранялся после перезагрузки.
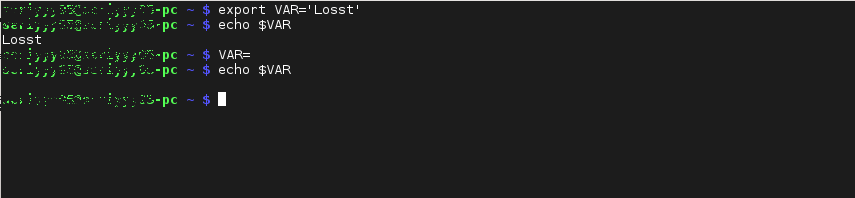
1. Устанавливаем и удаляем локальные переменные в Linux
Давайте создадим локальную переменную VAR и установим ей любое значение, затем удалим ее с помощью unset и убедимся что она удалена:
Установка и удаление пользовательских переменных
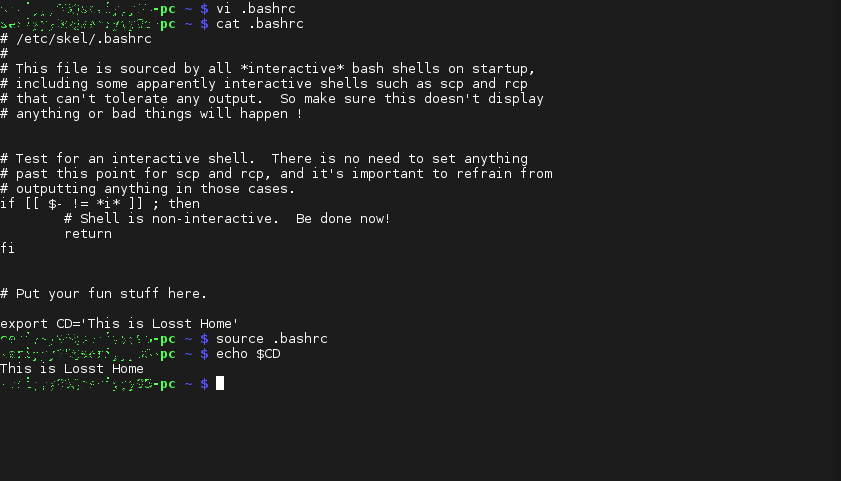
Добавьте такую строчку (o, затем вставить, затем Esc и :wq):
export CD=’This is Losst Home’
Теперь осталось обновить конфигурацию:
export VAR2=’This is Losst Home’
И выполните эти команды, чтобы применить изменения и проверить добавление переменной:
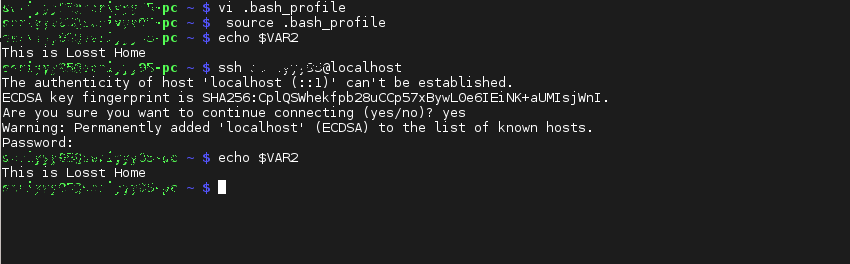
Переменная недоступна, так как вы создали локальную терминальную сессию, теперь подключитесь по ssh:
Удалить эту переменную окружения можно так же как и в предыдущем случае, удалив ее из файла.
Замечание: Эти переменные доступны всегда, но не для всех пользователей.
Установка и удаление системных переменных окружения
Создадим переменную, доступную для всех пользователей, во всех терминальных сессиях, кроме удаленных, добавлением ее в /etc/bash.profile:
vi /etc/bash.profile
export VAR=’This is system-wide variable’
Теперь эта переменная доступна для всех пользователей, во всех терминалах:
Если вы хотите сделать переменную окружения доступной для всех пользователей, которые подключаются к этой машине удаленно, отредактируйте файл /etc/profile:
export VAR1=’This is system-wide variable for only remote sessions’
Обновите конфигурацию, и проверьте доступность переменной, она будет доступна только удаленно:
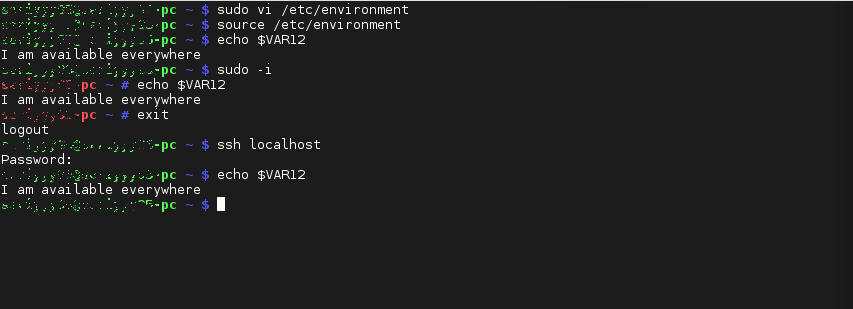
Если нужно добавить переменную окружения в Linux, так чтобы она была доступна и удаленно, и для локальных сессий, экспортируйте ее в /etc/environment:
export VAR12=’I am available everywhere’
Как видите, переменная доступна и для локальных пользователей и удаленно.
Выводы
С помощью этих нескольких способов мы можем изменить переменные окружения. Если вы знаете другие интересные способы это сделать, поделитесь в комментариях!
Оцените статью:
Об авторе
Основатель и администратор сайта losst.ru, увлекаюсь открытым программным обеспечением и операционной системой Linux. В качестве основной ОС сейчас использую Ubuntu. Кроме Linux, интересуюсь всем, что связано с информационными технологиями и современной наукой.
12 комментариев
/etc/profile
«Все переменные из этого файла, доступны любому пользователю в системе, только если он вошел удаленно. »
А что значит вошел удаленно? Через SSH?
Написанное справедливо для всех современных дистрибутивов?
«. добавлением ее в /etc/bash.profile
.
Затем обновляем:
source /etc/bash.bashrc»
я думал обновлять надо отредактированный файл, или это опечатка?
Позволю себе добавить к вышесказанному:
VAR=1 # переменная видна только для ТЕКУЩЕГО процесса
$VAR
>> 1: команда не найдена
set | grep VAR # set без параметров отобразит ВСЕ (как локальные так и глобальные) переменные
>> VAR=1
env | grep VAR
>>
bash # запустим дочерний процесс
$VAR # наша переменная в нем не видна
>>
exit # выходим
$VAR # переменная сохранилась в родительском процессе
>> 1: команда не найдена
VAR=2 bash # установим переменную для дочернего процесса
$VAR # она видна в дочернем процессе
>> 2: команда не найдена
set | grep VAR # так же видна в set
>> VAR=2
exit # закрываем дочерний процесс
$VAR # в родительском процессе хранится свой экземпляр переменной
>> 1: команда не найдена
unset VAR
$VAR
>> # значение переменной сброшено
export VAR=3 # переменная видна в ТЕКУЩЕМ и ДОЧЕРНИХ процессах
$VAR
>> 3: команда не найдена
set | grep VAR
>> VAR=3
env | grep VAR
>> VAR=3
printenv | grep VAR
>> VAR=3
bash # запускаем дочерний процесс
env | grep VAR
$VAR # переменная доступна
>> 3: команда не найдена
VAR=2 # можем изменить ее значение
$VAR
>> 2: команда не найдена
unset VAR # сбросим значение
$VAR
>> # переменная не определена
exit
$VAR
>> 3: команда не найдена # родительский процесс хранит значение переменной после сброса в дочернем
env | grep VAR
>> VAR=3
«Системный файл profile. Все переменные из этого файла, доступны любому пользователю в системе, только если он вошел удаленно. Но они не будут доступны, при создании локальной терминальной сессии, то есть если вы просто откроете терминал.» – неверно. Переменная будет доступна везде: в терминале, GUI программах, не важно. Только что проверял локально.
/.профиль; а иногда ничего этого не происходит и
Привет всем. А какая переменная отвечает за заголовок терминала? например PS1 отвечает за первое приглашение, а вот про заголовок окна терминала, что-то я не нашёл? или какими командами можно изменить этот самый заголовок? всем удачи.