How to stop bleeding
How to stop bleeding
How to Stop Bleeding
This article was medically reviewed by Luba Lee, FNP-BC, MS. Luba Lee, FNP-BC is a board certified Family Nurse Practitioner (FNP) and educator in Tennessee with over a decade of clinical experience. Luba has certifications in Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS), Emergency Medicine, Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS), Team Building, and Critical Care Nursing. She received her Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) from the University of Tennessee in 2006.
There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 18 testimonials and 100% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 2,127,634 times.
Experts agree that the first thing you should do if you’re bleeding is apply pressure to the area. Bleeding happens when the blood leaks from your blood vessels, often because of a wound. External bleeding occurs when you have a cut or bloody discharge, but you might also have internal bleeding, where you bleed under your skin. [1] X Trustworthy Source MedlinePlus Collection of medical information sourced from the US National Library of Medicine Go to source Research suggests uncontrolled or severe bleeding may lead to shock, which means you don’t have enough blood in your body. [2] X Research source You can likely treat mild bleeding injuries at home, but see a doctor immediately if you have severe bleeding or can’t get your bleeding under control.
How to Control Bleeding
4 First Aid Steps Everyone Should Know
Rod Brouhard is an emergency medical technician paramedic (EMT-P), journalist, educator, and advocate for emergency medical service providers and patients.
Michael Menna, DO, is a board-certified, active attending emergency medicine physician at White Plains Hospital in White Plains, New York.
Regardless of how severe a cut or laceration is, all bleeding can be controlled. With that said, some wounds can cause profuse bleeding, and it is only with the proper first aid interventions that the bleeding can be stopped.
Preparation and awareness are key to treating any wound properly. This starts with having a fully stocked first aid kit close at hand wherever you are. It is equally important to recognize when bleeding requires emergency care.
Bleeding Emergencies
People don’t always know if a wound is serious enough to warrant a call to 911. Or, they may be reluctant to make the call because of a lack of insurance. If in doubt, though, it is always best to err on the side of caution and make the call.
As a general rule, you need to call 911 or rush the injured party to the nearest emergency room if:
Even if you are able to stop the bleeding, don’t assume that medical care is no longer needed. The wound may still require stitches to heal properly. Certain wounds require vaccination to reduce the risk of tetanus or rabies. Lacerations or puncture wounds on the joints and other vulnerable parts of the body can cause permanent nerve, ligament, or tendon damage if not treated appropriately.
It is therefore important to seek immediate medical care if:
Symptoms to Watch For
Even if the bleeding is stopped, it should almost invariably be seen by a healthcare provider if the wound is deep or there was profuse, spurting blood. The same applies if there was a significant loss of blood, which could lead to a potentially life-threatening condition known as hypovolemic shock.
Call 911 if the injured party experiences signs of shock, including:
You should also seek care if the wound becomes infected. See a healthcare provider immediately if the injured party experiences a high fever, chills, nausea or vomiting, and a rapidly expanding area of hot, swollen, and tender skin. These could be signs of a potentially deadly infection known as cellulitis.
How to Stock a First Aid Kit
While you can certainly purchase a fully stocked first aid kit online and in most drugstores, you can put one together on your own. If you do decide to make your own kit (for the house, car, office, etc.), the American Red Cross suggests that you include the following:
How to Stop Bleeding: Direct Pressure
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
» data-caption=»» data-expand=»300″ data-tracking-container=»true» />
The first step in controlling a bleeding wound is to plug the hole. Blood needs to clot in order to stop the bleeding and start the healing process. Just like ice won’t form on the rapids of a river, blood will not coagulate when it’s flowing.
The best way to stop it is to:
If the gauze or towel soaks through with blood, add another layer. Never take off the gauze. Peeling blood-soaked gauze off a wound removes vital clotting agents and encourages bleeding to resume.
Once bleeding is controlled, take steps to treat the victim for shock.
How to Stop Bleeding: Elevate Above the Heart
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
» data-caption=»» data-expand=»300″ data-tracking-container=»true» />
Gravity makes blood flow down easier than it flows up. If you hold one hand above your head and the other at your side, the lower hand will be red while the higher one is pale.
Step two to control bleeding uses this principle.
How to Stop Bleeding: Use Pressure Points
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
» data-caption=»» data-expand=»300″ data-tracking-container=»true» />
Pressure points are areas of the body where blood vessels run close to the surface. By pressing on these blood vessels, blood flow further away will be slowed, allowing direct pressure to stop bleeding.
When using pressure points, make sure you are pressing on a point closer to the heart than the wound. Pressing on a blood vessel farther from the heart than the wound will have no effect on the bleeding.
Remember to also keep the wound elevated above the heart and keep pressure directly on the wound.
Common pressure points:
How to Stop Bleeding: Tourniquets
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
» data-caption=»» data-expand=»300″ data-tracking-container=»true» />
When should you use a tourniquet? The simple answer: almost never.
Tourniquets severely restrict or occlude blood flow to the arm or leg to which they are applied. Using a tourniquet to stop bleeding has the potential to damage the entire arm or leg. People lose limbs from the use of tourniquets.
If a tourniquet doesn’t cause a loss of function in the extremity, then it probably wasn’t applied correctly.
Applying a tourniquet is a desperate move—only for dire emergencies where the choice between life and limb must be made.
To use a tourniquet:
Frequently Asked Questions
To treat a nosebleed, sit down and firmly press the soft part of your nose just above the nostrils for 10 minutes or more. Instead of tilting your head back, lean forward and breathe through your mouth. This will allow the blood to drain into the nose, speeding coagulation, rather than letting it run freely down the back of your throat.
In addition to using tampons and doubling up pads, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like Advil (ibuprofen) may help reduce bleeding. If you are prone to frequent heavy flows, your healthcare provider may prescribe an oral contraceptive that can correct the hormonal imbalances that promote bleeding. There is also a drug called Lysteda (tranexamic acid) that can be taken during menstruation to reduce the flow.
Bleeding gums can be treated by rinsing your mouth with water and gently pressing a moistened gauze against the gums until the bleeding stops. Afterward, rinse with salt water or an antiseptic mouthwash to reduce bacteria and inflammation. If the bleeding is significant, you can hold an ice pack against the gums (but for no longer than 10 minutes to avoid frostbite).
Smaller cuts are treated similarly to larger wounds. Place pressure on the cut with a clean tissue. When the bleeding stops, place the cut under cold running water to remove any debris. Gently apply antiseptic cream, and cover with an adhesive bandage.
There are many different home remedies that people turn to stop bleeding, some of which work better than others. Some of the more common include:
How to Stop Bleeding?
We are all human, and what do humans do all the time? Bleed. Of course, this isn’t something any of us enjoying having happen to us, but life is unpredictable, and bleeding can occur to any of us at any time.
When it comes to external bleeding, three different types of blood flow can occur. Knowing what kind of bleeding you are experiencing is vital in order to figure out how to fix it. A simple definition of external bleeding is when blood comes out of some wound. So, whenever you can actually see blood coming out of yourself or someone else, it is external bleeding. Your veins are filled with blood and can be many different sizes – it all depends on where the vein is located in the body. Due to these different sizes, some wounds bleed more than others. This is where the three sorts of bleeding come in: capillary, venous, and arterial bleeding.
When you get hurt, it’s essential to figure out what type of bleeding you are experiencing of these three kinds. Afterward, you can pay more attention to the location of your injury and how to proceed in stopping the bleeding. Different places on the body require different remedies when they become injured. This article provides you with enough knowledge to be able to spot any dangerous symptoms related to the blood that you or any of your loved ones may experience throughout their lifetime.
10 Knowing the Three Types of Bleeding
As just mentioned, there are three types of bleeding that can occur. Capillary bleeding is the most common form of injury that involves blood. An example of capillary bleeding is when you are running and end up tripping on a rock. Your ankle twists while you fall and you end up on the ground. To try and break your fall, you put your hands out and then instantly feel a stinging pain in your palms. When you look at your hands, you notice tiny cuts all over with blood oozing out at a slow pace. This is capillary bleeding, where your blood clots and is able to stop itself in a short amount of time.
Another form of bleeding is known as venous bleeding. An easy example to explain this type of bleeding is when you are in the kitchen chopping up vegetables, then suddenly the knife slips and you slice your hand. Blood starts flowing quickly from your new cut. Your first response to this should be to apply pressure to the wound to stop the blood from coming out. When venomous bleeding like this happens, it means a vein has been damaged.
The third type of bleeding that can happen is arterial bleeding. This is the worst type of external bleeding that may occur. An instance that arterial bleeding can come about is if, for example, you are chopping wood with a new saw that you are trying out for the first time. You go to use the saw, and next thing you know is you’ve cut a piece of your arm, and blood begins shooting out. The blood doesn’t stop spurting out, and you begin to feel faint. This is when you need to call 9-1-1.
9 Treating Basic Cuts and Wounds
Whenever you accidentally cut yourself, you instantly hear your mom’s voice in the back of your head telling you to wash it right away. Well, as always, moms are never wrong! The second you notice yourself bleeding, you should act on it. Applying pressure, washing it, putting a topical ointment on it, then ending with a bandaid is the typical way to handle a situation with a small cut. Sometimes, this straightforward procedure isn’t enough. At this point, knowing home remedies that can help you control bleeding is a great idea. So, here are some:
Ice! This one may seem like a no brainer when it comes to pain, but people rarely think of putting ice of a bleeding wound. Applying ice to a bleeding wound helps it reduce the swelling that is likely to come about.
Another remarkable home remedy that can tame your bleeding is a tea bag. Putting a tea bag directly on a bleeding wound helps your blood clot faster, which makes the bleeding end quicker. It’s crucial that you use a tea bag with caffeine in it since it’s the tannins from the caffeine that go into the blood to help it clot.
Have you ever heard of witch hazel? Many people never have, but it’s a magical remedy to help you stop bleeding, so keep it around your house! The astringents found in witch hazel help keep skin tight and draws wounds back together, which is a quick fix when it comes to having small cuts.
8 Popped Blood Vessel in Eye
Have you ever looked in the mirror and noticed your eye having a red dot inside it? This is what happens when a blood vessel breaks inside your eye. This is more accurately referred to as a subjunctive hemorrhage. To explain this in more detail, WebMD says “The conjunctiva is the thin, moist, transparent membrane that covers the white part of the eye (called the sclera) and the inside of the eyelids. The conjunctiva is the outermost protective coating of the eyeball. The conjunctiva contains nerves and many small blood vessels. These blood vessels are usually barely visible but become larger and more visible if the eye is inflamed. These blood vessels are somewhat fragile, and their walls may break easily, resulting in a subconjunctival hemorrhage (bleeding under the conjunctiva). A subconjunctival hemorrhage appears as a bright red or dark red patch on the sclera.”
A popped blood vessel in your eye can happen for a few reasons. This can occur from something simple like sneezing or coughing, or something more obvious like vomiting. Vomiting is the most common reason for having subconjunctival bleeding in your eye because it causes a lot of strain on your entire face. It may also happen if you happen to rub your eye just a little too hard. Having an injury in your eye also makes a subconjunctival hemorrhage come about. Finally, a popped eye blood vessel may occur if you experience a severe eye infection or if you recently had eye surgery. They almost always go away on their own, so it isn’t much you can do when you noticed this in your eye.
7 Nosebleeds
Nosebleeds can come about for a number of reasons: dryness in the air, nervousness, and high blood pressure. Most times, a bloody nose is nothing to be concerned about. It happens extremely often to children, and most parents instantly freak out, but there typically is no reason to. When it comes to adults, nosebleeds can be a little more concerning. A nosebleed that has to do with hardening of the arteries or high blood pressure is something that needs to be paid attention to. Also, with these cases, the nosebleeds can be much more difficult to stop.
According to Healthline.com, there is an exact way to perform first aid when someone is experiencing a nosebleed. The procedure goes as follows “Have the person sit down and lean their head forward. This will reduce pressure in the nasal veins and slow the bleeding. It will also keep blood from flowing down into the stomach, which can cause nausea. If you’d like, use a nasal spray in the bleeding nostril while the person holds their head still. Have them push the bleeding nostril firmly against the septum (the dividing wall in the nose). If the person is unable to do this, put on latex gloves and hold the nose for them for five to 10 minutes. Once the nose stops bleeding, instruct the person not to blow their nose for several days. This could dislodge the clot and cause bleeding to begin again.”
6 Head Bleeds
As we all know, our brains are significant. It’s for this reason that head injuries can be hazardous, although many do not require medical attention. For most head injuries, they simply need the pressure to be added to the wound to reduce the bleeding, then be washed in a sink or shower. The only thing that differentiates a head wound from a regular scrap on your arm is the amount of blood that comes out. If you’ve ever experienced a head injury, you know that there is a lot of blood involved. Head wounds bleed so much because of the large number of blood vessels inside our heads, and because of the amount of oxygen, our brain needs to function. One-fifth of the blood that comes from our heart goes directly to our brain, so a lot is flowing around up there. This is why even the smallest cuts to the head can bleed so much.
When attempting to stop the bleeding from a head wound, it’s essential to apply pressure for 15 whole minutes, with no pauses. During this time and afterward, make sure to keep the wound as clean as possible. When treating a head injury, you need to watch the injured person for any signs of shock continually. If they seem to be experiencing any form of trauma, they need emergency care. Specific symptoms of shock may include the person going in and out of consciousness, saying they feel dizzy or weak, or being less alert than they usually are.
5 Coughing Up Blood
Healthline.com tells its readers, “Seeing blood when you cough can be alarming, whether it’s a large or small amount. Coughing up blood is nearly always a symptom of a disease. The seriousness of the condition depends on the amount of blood and the length of time the blood is being coughed up, but this symptom should never be ignored. The blood you cough up may come from your nose, throat, upper airways, or lungs. The medical term for coughing up blood is hemoptysis.” So, as you can tell from this, coughing up blood is nothing to joke around about. If this happens to you, you need to be prepared to know what to look for in the blood you cough up.
Any blood that comes from the respiratory tract is likely to come out in the form of bubbles. These aren’t the bubbles we all loved as a kid, though. These bubbles happen because of a mix between mucus and air within the lungs, and this bubbly blood can range from dark to bright red in color. Reasons for your body coughing up blood vary from an irritated throat to potential lung cancer. Other reasons for experiencing hemoptysis include asthma, throat infection, or bronchitis.
It’s important to remember that coughing up blood is different from bleeding from the mouth by a cut of some sort. A cut in your mouth is a common occurrence, so if that’s what’s happening to you, it’s nothing to stress over.
4 Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Gastrointestinal bleeding is any type of bleeding that occurs in your digestive tract, which in the body is the mouth all the way down to the rectum. If you happen to be losing a lot of blood in a short period of time, you may experience blood in your stool or vomiting blood. If your gastrointestinal bleeding is severe and continues for a long time, the loss of blood you are experiencing may result in iron-deficiency. Symptoms besides these could be a constant pain in your abdominals or random passing out.
“Bleeding is typically divided into two main types: upper gastrointestinal bleeding and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Causes of upper GI bleeds include peptic ulcer disease, esophageal varices due to liver cirrhosis and cancer, among others. Causes of lower GI bleeds include hemorrhoids, cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease, among others. Diagnosis typically begins with a medical history and physical examination, along with blood tests. A fecal occult blood test may detect small amounts of bleeding. Endoscopy of the lower and upper gastrointestinal tract may locate the area of bleeding. Medical imaging may be useful in cases that are not clear,” according to Wikipedia.
If treatment is required, it is possible that a blood transfusion may be needed. Another option can be antibiotics if you’re lucky. This is one of the hardest forms of bleeding to tract since many people fail to notice the initial symptoms, it is almost impossible to prevent. So, although no one wants to admit to doing it, paying attention to what your stool looks like may save your life!
3 Could You Have Hemophilia?
Hemophilia is an uncommon disorder where the person’s blood cannot clot as it should due to a decreased amount of blood-clotting proteins that the average person. People that suffer from hemophilia bleed for a much longer time than most whenever they get injured. Their bodies may be able to handle small cuts – these typically aren’t what a hemophiliac needs to worry about. The real concern is that people with hemophilia have a high chance of having deep bleeding internally. Too much bleeding in the inner workings of your body can affect your organs in a very nasty way, so severely that it can be life-threatening.
Not everyone with hemophilia experiences the same symptoms, so this is why the list of symptoms is long. Signs to look out for if you are concerned that you may have hemophilia include dark bruising often, excessive bleeding from wounds you cannot explain, high amounts of bleeding after receiving a vaccination, constant pain in throughout your body, blood in the toilet after you go to the bathroom, and random nosebleeds.
The simplest of cuts can cause a hemophiliac to have blood rush to their brain. When bleeding into the brain occurs, it is worth some severe concern – mainly because you may not realize it’s happening. Signs that you may be experiencing internal bleeding to the brain include seeing double, constant fatigue, seizures, or continuous painful headaches. There is a list of possible treatments for hemophilia, including physical therapy, but blood replacements seem to be the only way to slowly quick this disorder.
2 Could It Be Internal Bleeding?
Most of the bleeding that has been discussed in this article so far as forms of external bleeding. Now, let’s make our way to understanding what internal bleeding may entail. To start, a definition of internal bleeding is any form of bleeding that happens inside of you. Unlike external bleeding that can be spotted easily, internal bleeding is harder to notice with your eyes. This makes it more challenging to diagnose.
If you’re wondering how internal bleeding comes about, it is typically the aftermath of trauma or severe injury. Hemophiliacs, as mentioned before, are also more likely to experience internal bleeding than the average Joe. Internal bleeding can be just as dangerous, sometimes even more so, than external bleeding, so being able to recognize the symptoms of it is important. Signs to pay attention to include numbness on one side of your head, lousy coordination skills, experiencing difficulty reading and writing, pain in your abdomen or chest, or swelling around any of your body’s joints.
Healthline.com notes that “The presence of other underlying conditions may help doctors identify if you’re losing blood somewhere. For example, anemia is commonly associated with slow and chronic internal bleeding. It can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Some people with internal bleeding will also have low blood pressure because of constant blood loss. This is known as orthostatic hypotension. Common symptoms include feeling dizzy or light-headed when you stand.” So, the only way to stop internal bleeding is to seek medical attention and follow their instructions on what to do.
1 Knowing When to Call 9-1-1
We have just gone over a list of different places you may bleed from and how to handle any situation that comes your way regarding blood, but sometimes, the control is out of your hands, and you need to seek medical attention.
When it comes to simple cuts, ask yourself: could you need stitches? If the cut seems to go very deep, it is worth contacting a medical professional about it. If a nosebleed lasts longer than 20 minutes, then concern should have risen, and you should go see a doctor. It is not healthy for blood to continue flowing out of your nose this long, so it could signify a brain injury. When you experience a head injury, pay attention to how your head is feeling. Although the amount of blood that may come out is not necessarily a problem, how deep the cut is definitely is. If a head cut is deep enough that it pierces through the person’s skull, 9-1-1 should be contacted immediately.
When it comes to head injuries, never hesitate to call 9-1-1 the second the injured person seems to be experiencing any form of shock. If they look scared, weak, dizzy, or unresponsive, call the emergency. If you’ve been coughing up blood continuously, you should make an appointment with your doctor right away. It’s likely that the doctor takes an MRI of your neck and a blood sample. With this, they can see if there are any cancerous lumps in your respiratory tract or cancer cells in your blood.
In regard to internal bleeding, if you experience many of the possible symptoms like numbness, dizziness, passing out, or shortness of breath, in a very sudden amount of time, then you should seek medical help.
Conclusion
Making yourself aware of the three types of bleeding: capillary, venous, and arterial, is important so that you can know how to control any situation involving blood. No matter the size of your wound, you should pay attention to the blood that is coming out of it. Is it spurting out at a fast pace? Or is the blood coming out slowly? Questions like this are ones to ask yourself whenever you catch yourself bleeding. Our bodies are sacred things that need to be taken care of, so ignoring blood when you see it should be a crime!
Watch out for blood thinners like alcohol and Advil! Many people take aspirin when they are experience headaches or pain, and while this can save your life, too much of it can threaten it. Blood-thinning medications are made to help stop blood clots that can harm people, but they also cause you to bleed more when you face an injury, which is a danger in itself. Don’t be fooled; there are also natural blood thinners that can cause harm to your body, not just chemical ones. Ingredients that cause blood thinning include cayenne pepper, ginger, thyme, and paprika. When it comes to these, know that a little is great, but a lot may not be.
When our grandparents told us that “it’s better to be safe than sorry,” they were probably alluding to continually checking up on our own bodies and making sure they’re healthy, before it’s too late.
How to stop bleeding
From simple injuries to a cut off fingertip to a bullet wound with severe hemorrhaging, civilians with a little bit of bleeding control knowledge can have a big impact on survival chances in an emergency. That’s why the U.S. government has heavily promoted a “Stop The Bleed” campaign to raise awareness — including placing bleeding kits in public places — and teach more people the basics.
Well-aimed direct pressure is the simplest and best answer to almost every hemorrhage control (medics say ‘hemcon’) scenario. Using your hands, wound packing, and tourniquet use are just different forms of creating pressure.
Controlling bleeding is the required first step when treating a wound:
Like any survival skill, it’s important to practice before an emergency. During our in-person classes, we even try to simulate stress by having students sprint 200 yards to a mock patient so that they’re making decisions without a clear head. You can also try practicing in the cold, in the dark, with loud music in the background, and so on.
Use your head. Get professional help if you can.
The Prepared teaches survival medicine: what to do in emergencies when you can’t depend on normal help or supplies. How to make decisions, steps to take, gear to use… there’s a huge difference in the right answers between daily life and a survival situation.
You agree not to hold us responsible if you choose to do something stupid anyway.
Want more free guides from medical and survival experts delivered straight to your inbox?
Why you should trust us
Your three guides have 65 years of combined experience teaching or using these skills:
Act fast for severe bleeding
Major bleeding can cause someone to lose consciousness or die within minutes. That’s why tourniquets exist and why they are kept on the outside of gear (for rapid access).
The products and skills for severe hemorrhage control are different enough that we split them off from this guide. Check out the review of the best tourniquets and learn when and how to use a tourniquet.
If it’s wet and not yours, don’t touch it
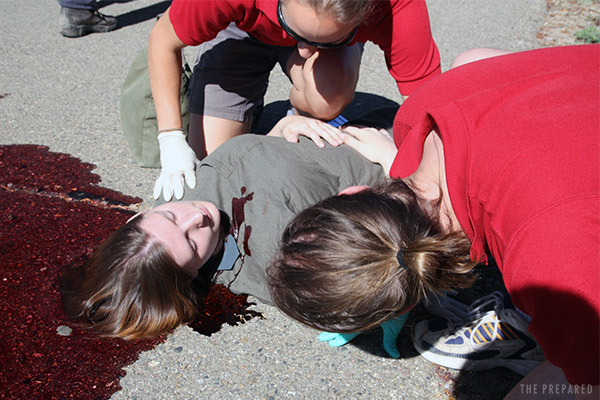

You’re probably someone who wants to take action in an emergency. Awesome, high five, we (and hopefully your patient) love you for that.
Although it may feel unnatural, a bloody injury is a good example of when you should pause a moment or three to be thoughtful and careful. In all but the most severe every-second-matters injuries, it’s worth taking a moment to protect yourself by putting on protective gear before exposure to other people’s fluids.
No one wants to pick up a serious illness because they didn’t put gloves on. But consider the patient, too — they might not have the ability to communicate or worry about giving you a disease they may have, or wonder what you might give them in the process.
A good kit has gloves. Use them.
Latex, nitrile, and vinyl gloves are common. Try to avoid latex because many people are allergic and they deteriorate over time.
Those thinner materials are easily torn in the kind of messy survival situations you might face outside of a hospital environment. Dishwashing gloves are useful because they’re tougher (e.g. less likely to rip from an exposed bone end) and you don’t need nimble finger dexterity for these first steps in hemorrhage control.
Mucous membranes, like the inside of your nostrils and corners of your eyes, are easy entrance points for contamination. So protect yourself with sunglasses, medical face shields, disposable or full-face respirator masks, or even a bandana (as a last resort).
How natural blood clotting works
The human body does a pretty decent job at repairing itself. That process kicks off with platelets, tiny disc-shaped cell fragments in the blood that lead the clotting process. Platelets make up around 1% of blood volume, just floating around waiting for a leak to plug.
Collagen is a protein in your skin and soft tissue (you sometimes hear of collagen in skin care advertisements) that normally doesn’t interact with the blood contained in vessels and veins.
An injury ruptures the walls between blood vessels and tissue, allowing the blood to flow over the newly-exposed collagen.
Platelets are attracted to and bind with collagen, using the collagen as an attachment point to build a sort of platelet blood-blocking dam across the wound. After a platelet has bonded, it changes shape from a flat disc to a sphere with little fibers to help catch other platelets.
Think of those morphing platelets like the Nova Corps in Guardians of the Galaxy, when they form up to blockade the Dark Aster:
Why pressure and elevation are key
The platelet dam is not impervious or super strong — especially while it’s forming.
That’s why adding pressure to the area or elevating above the heart aids with the natural clotting process. You make it easier and faster for the body to build that dam when it doesn’t have a flood of blood constantly screwing up the construction site.
Even in advanced situations where you’re using an absorbent material to pack a deep or hard-to-reach wound, the whole point is to create pressure when your fingers alone can’t do the job. You don’t pack a wound simply to absorb blood while waiting for the clot to form.
In 2010, the American Heart Association claimed that limb elevation was not an effective way to stop bleeding and may even be harmful. The AHA argued that there weren’t enough studies proving the effectiveness of elevation — but there weren’t any disproving it, either. They’ve since retracted, because recent studies have proven that elevation is appropriate and useful.
Stop the bleed with well-aimed direct pressure
It’s pretty simple: Find the source of bleeding and apply pressure as directly to that spot as possible. Then, if you can, elevate the wound above the heart while maintaining pressure.
Hold that pressure for 5-10 minutes. Resist the urge to sneak a peek — breaking the platelet barrier too soon can cause you to start over.
That’s all it will take to stop the bleeding in most wounds. Advanced techniques and products are all intended to help you create aimed pressure when it’s too hard to do with your hands.
How to use a pressure dressing
Consider a pressure dressing for simple wounds on the extremities, torso, or head. Pressure dressings are sometimes called “Israeli” dressings — an homage given by US troops to Bernard Bar-Natan, the Israeli Military medic who created the product.
Pressure dressings are an absorptive material combined with an elastic bandage and rigid “pressure bar” that makes it easier to focus pressure directly over the bleeding source.
You can think of Israeli dressings as a middle-ground combo between plain dressings and a tourniquet — although when used for the initial hemcon, they’ll likely need to be changed sooner than a separate dressing/bandage typically would.
There are variations between pressure dressing products, namely in how they create the focused pressure. Common pressure bars are half-moon shaped or “H” shaped, while some products use a pressure cup. The pictures below use a Recon Medical Elastic Bandage with a half-moon bar.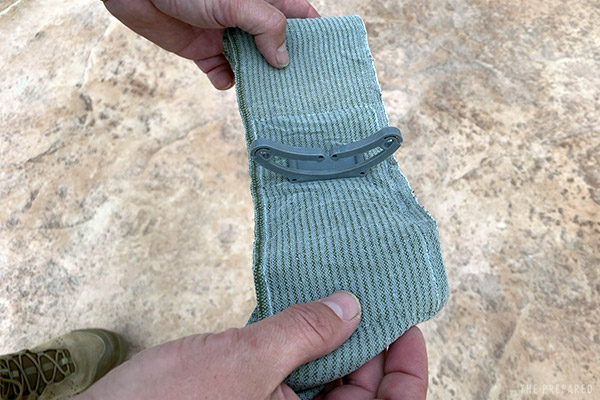 
Take the gauze out of its packaging. Place the dressing and pressure bar directly over the wound. Begin wrapping the elastic.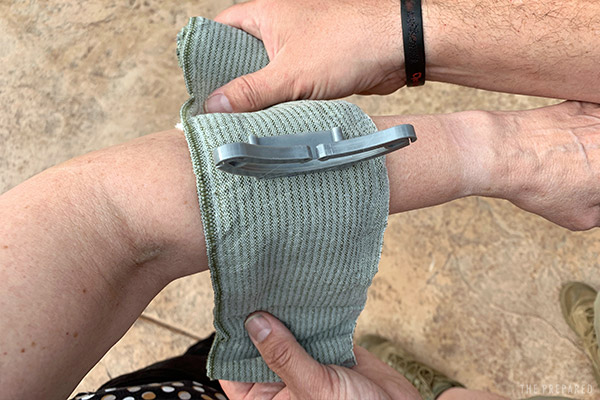 
When you get back around to the dressing, wind the elastic bandage around the pressure bar and double back to wrap in the opposite direction.
If you are using the OLAES Bandage or other products with a pressure cup, just go over the top and continue wrapping.
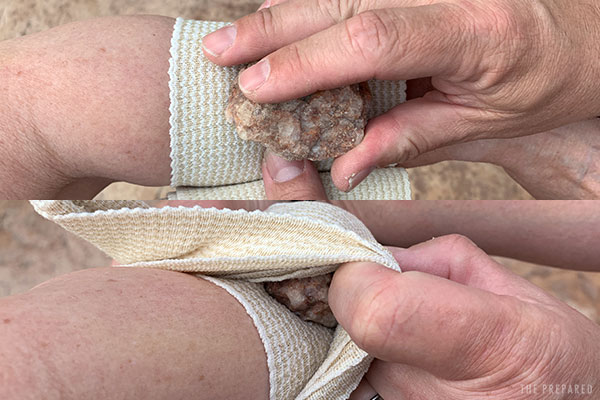
Tip: Don’t pull too tightly — the point isn’t to cut off blood flow to the whole area the way a tourniquet would. Check the patient’s fingers or toes afterwards for proper circulation.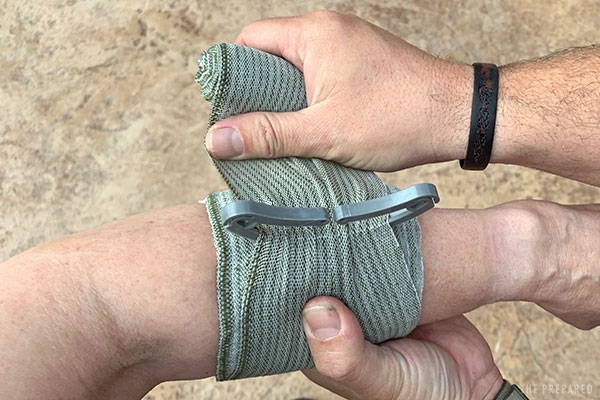 
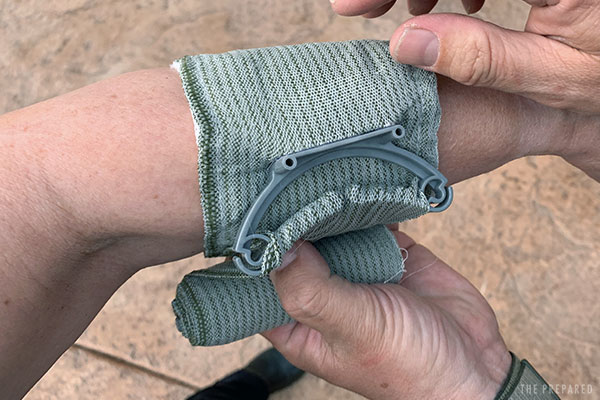

Create overlap on both sides of the dressing to maximize protection.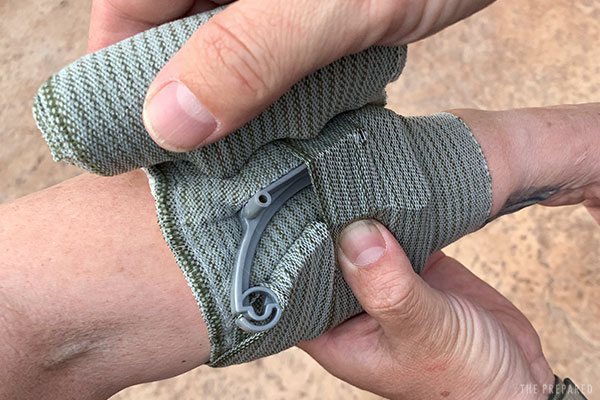 
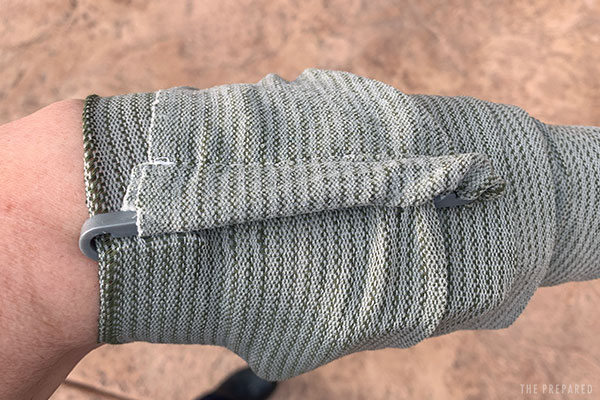

Tip: You can improvise an OLAES-style pressure dressing using gauze, an elastic bandage, and a small rock. Place the dressing against the wound like normal. Begin wrapping the elastic bandage. Part way through the wrap, place the rock directly over the wound. Finish the wrap, wedging the rock in between layers of the somewhat-tight bandaging.
How to pack a wound
There are places on the body — such as the armpit, groin, and neck junctions — that are just too difficult to create well-aimed direct pressure against. Or sometimes a wound is so deep that you can’t push hard enough on the surface to create pressure down at the point of severe hemorrhage.
Packing a wound is the process of building pressure by forcing gauze (or a similar material) into the wound.
You may have seen war movies where a medic asks someone nearby to stick their finger in a bleeding wound to create direct pressure. That’s one of the rare instances where survival advice shown in movies is correct.
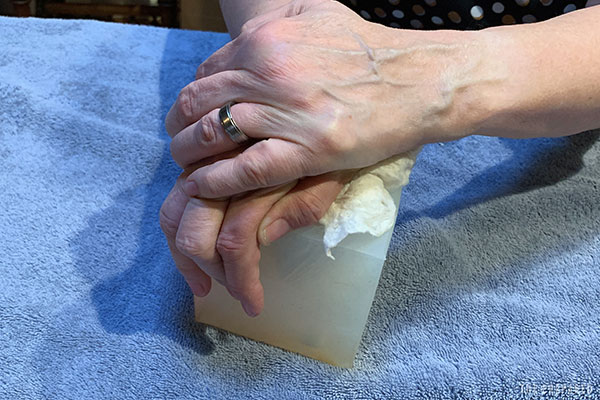
If it’s a serious bleed, stick your finger or thumb into the wound. Try to find the source of bleeding and push against it without making the wound worse.
Take the gauze out of its packaging. Start rolling one end of the gauze into a tight ball (sometimes called a speedball). That ball will be the first thing you push into the wound, so it should be a little smaller than the size of the wound but have enough heft to make the pushing easier.
Tip: If the gauze is rolled, you can poke the tightly-wound middle of the roll out with your fingers and use that as your starting point.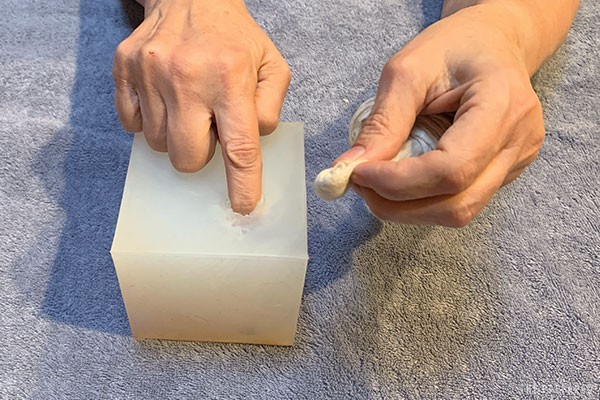 
Push the gauze ball into the wound channel alongside the finger you already have inside.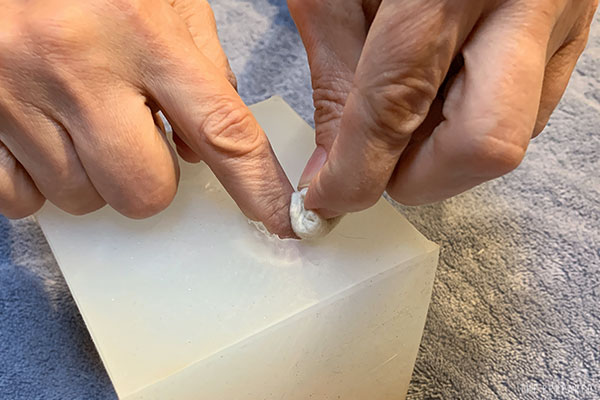 
Relax your finger just enough to swap places with the ball, immediately pushing the ball as deep and forcefully as needed.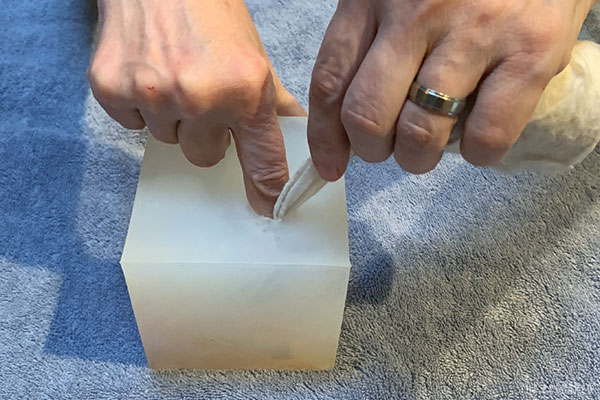 
Create another wad in the gauze near the wound entrance. Stuff it down. Repeat.
If you have enough material, eventually you’ll build the pack up until it reaches the surface. It’s then much easier to use your fingers to press down on the pack, transferring that pressure down onto the blood source for 10 minutes.
Wound packing sealants
It’s a neat concept, and we’re happy to see more innovation in this market. A recent (but limited) study concluded that, in the hands of civilians, the XSTAT was more effective than just gauze.
One of the challenges with a powdered hemostatic agent is deploying it where it is needed — the Celox-A solves this by using an applicator to deploy the Celox granules.
So you should still learn how to pack a wound with gauze and keep those basic materials on hand. Any of these injectable sealants are a nice-to-have bonus.
What about internal bleeding?
The short answer: If someone has internal bleeding in a bad survival scenario (no professional help, no grid, etc.), they’re probably going to die.
You just can’t create enough well-aimed direct pressure inside the belly without opening up the patient. Some studies have also shown that trying to create enough pressure on an organ from outside the body can further tear the wound and accelerate blood loss.
The exception would be when the internal bleeding isn’t so … internal. If someone has been torn open in such a way that you can get access to the source, then it might be worth applying pressure if all other hope seems lost.
How to stop a nosebleed
Your old school nurse may have taught you to hold the head back. This doesn’t do anything except potentially make things worse by draining blood through the throat into the stomach, which can lead to nausea.
Pinch both nostrils firmly against the septum, then lean forward. Adjust the pinch location up or down if there’s still bleeding after a minute or two.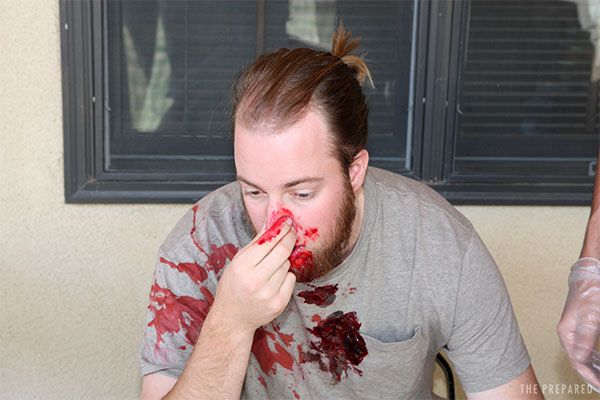 
Hold this pressure for at least ten minutes while breathing through the mouth. Once the bleeding has stopped, have the patient gently blow their nose to clear out excess clots.
Tip: If there have been several failed attempts to stop a nosebleed, have the patient blow their nose hard to clear existing clots, and then restart the pinch. The most likely cause for the failure was not holding pressure long enough.
Hemostatic gauze vs. regular gauze
Some products come with a hemostatic agent — chemicals that accelerate clotting — built into the gauze. All of the other steps are the same.
Research shows that hemostatic gauze doesn’t really add more value than plain gauze and well-aimed direct pressure. The exception is wound-packing scenarios that are in really tough spots where every little advantage helps.
But hemostatic gauzes are around 40 times more expensive than normal gauze. Plus you’re far more likely to find normal gauze when SHTF than a specialty product.
Pick up a few for your kit if you want the upgrade and have the budget — we carry some in our kits — but you should still practice with and rely on plain gauze.
What about blood stop powder?
We sometimes hear medics joke that the best way to use powdered hemostats is to dump them on the ground and forget you had them.
If you can even find these products anymore, they have a reputation for being difficult to apply correctly (even with two people) and causing significant damage to the surrounding tissues. Some of the side effects even require debriding or surgical removal in a hospital environment.
Products like Celox-A are a notable exception because they’ve addressed the “hard to apply” problem.
Can you use tampons for hemorrhage control?
Using a tampon to plug an injury (e.g. a bullet wound) is such an incorrect-but-still-popular “prepper hack” that it made our list of the worst survival myths.
Tampons are designed to absorb blood. They do that job well. You can even split tampons open and use them as extra gauze (or even fire-starting tinder) if you run out of proper materials.
Tampons and menstrual pads do not expand enough when soaked to apply pressure to a wound. Since bleeding is controlled through direct pressure, even in a bullet hole, a tampon is no more effective than simply putting in a few loose layers of gauze.
If you plug a bullet hole with a tampon, all you’re doing is creating an absorbent dam in the first few inches near the surface. Like a dam on a river, that will create a reservoir pool of blood. That’s not necessarily bad — but it’s definitely not helpful.
Sources and footnotes:
Application of Current Hemorrhage Control Techniques for Backcountry Care: Part One, Tourniquets and Hemorrhage Control Adjuncts. Brendon Drew, DO, CDR, MC; Brad L. Bennett, PhD, NREMT-P; Lanny Littlejohn, MD, CDR, MC. WILDERNESS & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE, 26, 236â245 (2015)
Comparison of hemorrhage control agents applied to lethal extremity arterial hemorrhages in swine. Acheson, E.M., Kheirabadi, B.S., Deguzman, R., Dick Jr, E.J. and Holcomb, J.B., 2005. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 59(4), pp.865-875.
Gauze vs XSTAT in wound packing for hemorrhage control. Kragh JF, Aden JK, Steinbaugh J, Bullard M, Dubick MA. The American journal of emergency medicine. 2015 Jul 1;33(7):974-6.
Wound Packing Essentials for EMTs and Paramedics. Taillac, Peter P., Bolleter, Scotty, Heightman, A.J. Apr 2017
Overview of Agents Used for Emergency Hemostasis. Khoshmohabat, H., Paydar, S., Kazemi, H. M., & Dalfardi, B. (2016). Trauma monthly, 21(1), e26023. doi:10.5812/traumamon.26023
How to Stop Rectal Bleeding
This article was co-authored by Dale Prokupek, MD. Dale Prokupek, MD is a board-certified Internist and Gastroenterologist who runs a private practice based in Los Angeles, California. Dr. Prokupek is also a staff physician at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and an associate clinical professor of medicine at the Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). Dr. Prokupek has over 30 years of medical experience and specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the liver, stomach, and colon, including chronic hepatitis C, colon cancer, hemorrhoids, anal condyloma, and digestive diseases related to chronic immune deficiency. He holds a BS in Zoology from the University of Wisconsin – Madison and an MD from the Medical College of Wisconsin. He completed an internal medicine residency at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and a gastroenterology fellowship at the UCLA Geffen School of Medicine.
There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 127,209 times.
While bleeding from the rectum or anus can be surprising and uncomfortable, it usually indicates a minor issue, like an anal fissure (tear) or hemorrhoids. It can also be a sign of a serious underlying condition, however. Schedule an appointment with your doctor right away if you experience unexplained rectal bleeding. If the rectal bleeding is severe, accompanied by painful stomach cramps, or lasts for several days, it may be a sign of colon cancer. Your doctor will be able to perform an abdominal exam that determines the cause and the severity of the rectal bleeding.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Rod-Brouhard-EMT-P_1000-85058e33388640c0a9cc5e20427cfe90.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Michael-Menna_1000-8152d12c2ee0452e86fbd22c6698e0f9.jpg)