How to use nmap
How to use nmap
Nmap — руководство для начинающих
Многие слышали и пользовались замечательной утилитой nmap. Ее любят и системные администраторы, и взломщики. Даже Голливуд знает про нее — в фильме «Матрица» при взломе используется nmap.
nmap — это аббревиатура от «Network Mapper», на русский язык наиболее корректно можно перевести как «сетевой картограф». Возможно, это не лучший вариант перевода на русский язык, но он довольно точно отображает суть — инструмент для исследования сети и проверки безопасности. Утилита кроссплатформенна, бесплатна, поддерживаются операционных системы Linux, Windows, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, Solaris, Mac OS X.
Рассмотрим использование утилиты в Debian. В стандартной поставке дистрибутива nmap отсутствует, установим его командой
# aptitude install nmap
Nmap умеет сканировать различными методами — например, UDP, TCP connect(), TCP SYN (полуоткрытое), FTP proxy (прорыв через ftp), Reverse-ident, ICMP (ping), FIN, ACK, SYN и NULL-сканирование. Выбор варианта сканирования зависит от указанных ключей, вызов nmap выглядит следующим образом:
Для опытов возьмем специальный хост для экспериментов, созданный самими разработчиками nmap — scanme.nmap.org. Выполним от root’а
Ключи сканирования задавать необязательно — в этом случае nmap проверит хост на наличие открытых портов и служб, которые слушают эти порты.
Запустим командой:
Через несколько секунд получим результат:
Interesting ports on scanme.nmap.org (74.207.244.221):
Not shown: 998 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
Ничего необычного, ssh на стандартном порту и http на 80. Nmap распознаёт следующие состояния портов: open, filtered, closed, или unfiltered. Open означает, что приложение на целевой машине готово для принятия пакетов на этот порт. Filtered означает, что брандмауэр, фильтр, или что-то другое в сети блокирует порт, так что Nmap не может определить, является ли порт открытым или закрытым. Closed — не связанны в данный момент ни с каким приложением, но могут быть открыты в любой момент. Unfiltered порты отвечают на запросы Nmap, но нельзя определить, являются ли они открытыми или закрытыми.
Хинт: Если во время сканирования нажать пробел — можно увидеть текущий прогресс сканирования и на сколько процентов он выполнен. Через несколько секунд получаем ответ, в котором пока что интересна строчка Device type:
Вообще, точную версию ядра средствами nmap определить невозможно, но примерную дату «свежести» и саму операционную систему определить можно. Можно просканировать сразу несколько хостов, для этого надо их перечислить через пробел:
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 5.3p1 Debian 3ubuntu7 (protocol 2.0)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.14 ((Ubuntu))
Service Info: OS: Linux
Прогресс налицо — мы узнали точные названия используемых служб и даже их версии, а заодно узнали точно, какая операционная система стоит на сервере. С расшифровкой никаких проблем не возникает, все вполне понятно.
Nmap выведет очень много информации, я не стану приводить пример. Сканирование может длится довольно долго, занимая несколько минут.
Сканирование проходит довольно быстро, так как по сути это обычный ping-тест, отвечает ли хост на ping. Следует учесть, что хост может не отвечать на ping из-за настроек фаерволла. Если нужный участок сети нельзя ограничить маской, можно указать диапазон адресов, с какого и по какой надо провести сканирование. Например, есть диапазон адресов с 192.168.1.2 до 192.168.1.5. Тогда выполним:
Ответ будет выглядеть так:
Host 192.168.1.2 is up (0.0023s latency)
Host 192.168.1.3 is up (0.0015s latency)
Host 192.168.1.4 is up (0.0018s latency)
Host 192.168.1.5 is up (0.0026s latency)
В моем случае все ip в данный момент были в сети.
Это далеко не все возможности nmap, но уместить их в рамках одной статьи несколько сложновато.
Если вам ближе GUI — есть замечательная утилита Zenmap — графическая оболочка для nmap, умеющая заодно и строить предполагаемую карту сети.
Хочу предупредить, что сканирование портов на удаленных машинах может нарушать закон.
UDPInflame уточнил, что сканирование портов все-таки не является противозаконным.
Documentation
The Nmap project tries to defy the stereotype of some open source software being poorly documented by providing a comprehensive set of documentation for installing and using Nmap. This page links to official Insecure.Org documentation, and generous contributions from other parties.
Nmap Reference Guide
The primary documentation for using Nmap is the Nmap Reference Guide. This is also the basis for the Nmap man page (nroff version of nmap.1). It is regularly updated for each release and is meant to serve as a quick-reference to virtually all Nmap command-line arguments, but you can learn even more about Nmap by reading it straight through. The 18 sections include Brief Options Summary, Firewall/IDS Evasion and Spoofing, Timing and Performance, Port Scanning Techniques, Usage Examples, and much more.
The original Nmap manpage has been translated into 15 languages. That is fantastic, as it makes Nmap more accessible around the world. The following languages are now available:
The links above go to the HTML guide. Nroff (man page format) and DocBook XML (source) versions of each man page translation can be found here. If you would like to update one of our existing translations or translate to a language not mentioned above, please read the instructions and FAQ and then mail our developers or open a pull request on Github. It is a lot of work, but the reward is that thousands of people may benefit from your translation every month.
Nmap Book

Other Insecure.Org Documentation
Installation is made easy by the detailed Nmap Installation Guide. This covers topics such as UNIX compilation and configure directives and Installing Nmap on Linux, Windows, Mac OS X, Free/Open/NetBSD, Solaris, Amiga, and HP-UX. It also covers Nmap removal in case you change your mind.
One of Nmap’s most exciting new features is the Nmap Scripting Engine, which extends Nmap’s functionality using the simple and efficient Lua programming language. Nmap includes about 50 valuable scripts for network discovery and vulnerability detection, and you can also write your own. We describe the system in depth (from simple usage instructions to writing your own scripts) in our NSE guide. We also have an NSE Documentation Portal which includes detailed documentation for every NSE script and library.
Fyodor regularly gives conference presentations covering advanced Nmap usage and new features. Audio, video, and/or slides for many of these are available on his presentations page.
Nmap Version Detection: Instead of using a simple nmap-services table lookup to determine a port’s likely purpose, Nmap will (if asked) interrogate that TCP or UDP port to determine what service is really listening. In many cases it can determine the application name and version number as well. Obstacles like SSL encryption and Sun RPC are no threat, as Nmap can connect using OpenSSL (if available) as well as utilizing Nmap’s RPC bruteforcer. IPv6 is also supported. Learn all about this great feature in our Version Detection Paper
Nmap now has an official cross-platform GUI named Zenmap. It is included in most of the packages on the Nmap download page. It is documented in the Zenmap User’s Guide. More information is available from the Zenmap site and Zenmap man page.
One of the coolest, yet still relatively obscure features of Nmap is the IPID Idle scan (-sI). Not only does this allow for a completely blind portscan (no packets sent to the target from your real IP), but it can even allow you to bypass packet filters in certain circumstances. We wrote a Idle scanning paper describing this technique as well as several other exploits based on predictable IPID sequence numbers. It includes real-life examples as well as a section on defending yourself from these techniques.
The most important changes (features, bugfixes, etc) in each Nmap version are described in its ChangeLog.
While it is now only of historical interest, Nmap was first released in a September 1, 1997 Phrack 51 Article titled The Art of Port Scanning
More Books
3rd Party Docs
Some of the best (and certainly most creative!) documentation has been contributed by Nmap users themselves. If you write an interesting or useful document about Nmap, please send the announcement to nmap-dev or directly to Fyodor.
James “Professor” Messer’s «Nmap Secrets» training course is no longer available, but he still has lots of Nmap-related content at ProfessorMesser.Com.
A detailed Nmap Tutorial was maintained between 2003 and 2006 by Andrew Bennieston (Stormhawk).
Mohamed Aly has created this single-page (PDF) Nmap Mindmap as a convenient reference to all of the major Nmap options. [2006]
Mark Wolfgang has written an excellent paper on advanced host discovery using Nmap. Here is the PDF paper [local copy] and associated source code. [2002]
Adrian Crenshaw has made a couple excellent video tutorials in Flash. Check out Volume 1: Basic Nmap Usage and Volume 2: Port Scan Boogaloo. [2005]
Long-time Nmap contributor Lamont Granquist wrote a clear and useful (if dated) guide to getting started with nmap. [1999]
Uh-oh! Security expert and Counter Hack author Ed Skoudis has discovered our secret partnership with Microsoft!
How To Use Nmap Security Scanner (Nmap Commands)
Nmap is a great security scanner. Many systems and network administrators use it for tasks such as network inventory, managing service upgrade schedules, and monitoring host or service uptime. In this article, I’ll guide you through how to use Nmap commands.
Nmap uses raw IP packets in novel ways to determine what hosts are available on the network, what services (application name and version) those hosts are offering, what operating systems (and OS versions) they are running, what type of packet filters/firewalls are in use, and dozens of other characteristics.
How To Install Nmap
Nmap should be installed by default on your system, but if it isn’t, you can install it with the package manager of your distro. Also, you can install the GUI for nmap: Zenmap.
Basic Nmap Scan
2. Scan a host name:# nmap www.google.com
3. Scan an ip and get more information:
Nmap Commands To Discover Your LAN
3. In my LAN the Bcast ip is: 192.168.100.255
4. Make an nmap scan to the LAN:
5. With this scan you can discover the hosts presents in your LAN.
Scanning multiple IP addresses With Nmap
2. Working with the same subnet:
3. Scanning an ip range:
4. Scanning an entire subnet:
5. Excluding hosts:
Working with Functional Options
You must use the “A” option to detect the target’s operating system:
Also, you can use the “O” option.
2. Checking if the target is protected by a firewall
You must use the “sA” option to detect the target’s firewall:
3. Discovering which devices are up
You must make a ping scan with the “sP” option:
4. Performing a fast scan
If you want a fast scan you can use the “F” option:
5. Showing host interfaces and routers
Use the “iflist” option:
Nmap Commands To Scan Ports
Nmap is able to recognize six port states:
1. open:
An application is actively accepting TCP connections, UDP datagrams or SCTP associations on this port.
2. closed:
A closed port is accessible (it receives and responds to Nmap probe packets), but there is no application listening on it.
3. filtered:
Nmap cannot determine whether the port is open because packet filtering prevents its probes from reaching the port.
4. unfiltered:
The unfiltered state means that a port is accessible, but Nmap is unable to determine whether it is open or closed.
5. open | filtered:
Nmap places ports in this state when it is unable to determine whether a port is open or filtered.
6. closed | filtered
This state is used when Nmap is unable to determine whether a port is closed or filtered. It is only used for the IP ID idle scan.
Port Scanning Techniques
] (idle scan)
Using Zenmap
This is a basic tutorial about Nmap, but this tool is very powerful, the number of things that you can do with Nmap is incredible. Also, you can find other powerful tools at Nmap’s website, and you can see the reference guide.
Nmap. Начало использования

Вы когда-нибудь интересовались откуда атакующий знает какие порты открыты в системе? Или как узнать, какие приложения запущены на сервере, не спрашивая об этом администратора? Вы можете сделать все это и даже больше вместе с небольшим инструментом под названием Nmap.
Что такое Nmap? Название Nmap это сокращение от “network mapper”, сам nmap это набор инструментов для сканирования сети. Он может быть использован для проверки безопасности, просто для определения сервисов запущенных на узле, для идентификации ОС и приложений, определения типа фаерволла используемого на сканируемом узле.
Nmap это знаменитый инструмент. Как только вы узнаете больше о Nmap, вы поймете, что он делает в эпизодах таких фильмов как Матрица Перезагрузка, Ультиматум Борна, Хоттабыч, и других.
В этом руководстве будут описаны основы использования Nmap и приведены некоторые примеры, которые вы сможете использовать.
Где взять Nmap?
Если Вы используете Linux, то можете найти пакеты Nmap в репозиториях для большинства дистрибутивов. Последний релиз Nmap вышел в начале 2010, поэтому самой свежей версии может не быть в текущих стабильных ветках. Найти исходники и некоторые бинарные сборки можно на странице загрузки.Там есть и windows версия.
Основы использования Nmap.
Синтаксис Nmap следующий:
nmap Опции_сканирования Цель_сканирования.
Допустим Вы хотите сканировать узел и узнать какая операционная система на нем работает. Чтобы сделать это выполните следующее:
Заметим что Nmap требует привилегий суперпользователя для запуска подобного типа сканирования. Процесс сканирования может занять около минуты, так что будьте терпеливы. Когда процесс закончится вы увидите что то похожее на это:
Starting Nmap 5.21 ( nmap.org ) at 2010-02-27 23:52 EST
Nmap scan report for 10.0.0.1
Host is up (0.0015s latency).
Not shown: 997 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
53/tcp open domain
5009/tcp open airport-admin
10000/tcp open snet-sensor-mgmt
MAC Address: 00:11:24:6B:43:E2 (Apple Computer)
Device type: WAP|printer
Running: Apple embedded, Canon embedded, Kyocera embedded, Xerox embedded
OS details: VxWorks: Apple AirPort Extreme v5.7 or AirPort Express v6.3; Canon imageRUNNER printer (5055, C3045, C3380, or C5185); Kyocera FS-4020DN printer; or Xerox Phaser 8860MFP printer
Network Distance: 1 hop
Как вы видите Nmap предоставляет множество информации. Здесь он отображает предположение об операционной системе, которая была запущена на узле. В данном случае выполнялось сканирование маршрутизатора Apple Airport Extrime. В качестве дополнительного бонуса Nmap сообщил, что устройство на расстоянии одного прыжка, а также MAC адрес устройства и производителя сетевой карты, открытые порты и сколько времени выполнялось сканирование.
Ниже приведены результаты другого сканирования, домашнего компьютера с запущенной Ubuntu 9.10:
Здесь мы видим, что система имеет сетевую карту HP, запущено Linux между версиями 2.6.19 и 2.6.31. Кстати, Вы не сможете явно идентифицировать дистрибутив, только версию Linux ядра.
Сканирование чужих узлов.
В примерах выше для сканирования были выбраны локальный маршрутизатор и одна из рабочих станций, потому что мы имели право на их сканирование. Однако, будет плохой идеей запуск множественного сканирования чужого узла, если вы их не контролируете или не имеете прав для сканирования. Для экспериментов Nmap имеет общедоступный тестовый сервер scanme.nmap.org который Вы можете использовать.
Многие администраторы не любят несанкционированного сканирования их серверов, так что лучшим вариантом будет ограничение сканирования узлов своей локальной сети или тех для которых у вас есть права на сканирование. Также в некоторых случаях вы можете нарушить договор с вашим провайдером, при использовании некоторых особо агрессивных методов сканирования Nmap, поэтому будьте осторожны.
Сканирование нескольких узлов.
Вы можете сканировать больше чем один узел за раз, используя nmap. Если вы производите сканирование по IP-адресу вы можете определить диапазон 10.0.0.1-6 или 10.0.0.0/24.Используя диапазон 10.0.0.1-6 будут сканироваться узлы от 10.0.0.1 до 10.0.0.6. Используя определение /24 будет сканироваться весь диапазон узлов от 10.0.0.0 до 10.0.0.255. Для примера, если нужно просканировать узлы от 10.0.0.1 до 10.0.0.42 и узнать какая ОС вероятно запущена используйте:
Если у вас есть некоторый список доменных имен вместо IP адресов, вы можете разделить их в командной строке, вот так:
Проверка открытых портов
Если вы запустите nmap вообще без опций и укажите какой то узел, то он будет сканировать порты и покажет все найденные открытые порты и сервисы запущенные на них. Например запустите:
nmap target.hostname.com
после чего он должен выдать что то похожее на это:
Interesting ports on target.hostname.com (10.0.0.88):
Not shown: 1711 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
3306/tcp open mysql
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.228 seconds
Сканирование запущенных сервисов
Если вы хотите узнать какой сервис возможно запущен попробуйте опцию –sV. Эта опция произведет более агрессивное сканирование и попытается выяснить какая версия сервисов запущена на данном узле, а также может помочь более точно определить какая ОС запущена. Для пример запустим nmap –sV на тестовый сервер и получим следующий ответ:
Starting Nmap 5.21 ( nmap.org ) at 2010-02-28 00:15 EST
Nmap scan report for test.host.net (XX.XXX.XXX.XX)
Host is up (0.090s latency).
Not shown: 965 closed ports, 33 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 4.7p1 Debian 8ubuntu1.2 (protocol 2.0)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.8 ((Ubuntu) PHP/5.2.4-2ubuntu5.10 with Suhosin-Patch)
Service Info: OS: Linux
Как вы видите, Nmap может проанализировать пакеты и определить версию запущенного приложений на SSH и HTTP портах. Здесь вы можете увидеть что опрашиваемая система это Ubuntu с Apache 2.2.8 и OpenSSH 4.7p1. Эта информация может быть полезна по ряду причин. Nmap сканирование может идентифицировать систему под управлением устаревших сервисов которые могут быть уязвимы для известных эксплойтов.
Кто в моей сети?
Не знаете сколько онлайн узлов находятся в вашей сети? Попробуйте использовать nmap –sP который запустит ping сканирование указанной сети. Для примера, nmap –sP 10.0.0.0/24 сканирует 256 узлов от 10.0.0.0 до 10.0.0.255 проверит доступны ли они и доложит об этом. Так же вы можете использовать диапазон, например:
nmap –sP 10.0.0.1-15
Zenmap
Наконец, если все эти радости командной строки не для вас, nmap имеет GUI который вы можете использовать для построения и выполнения команд. Называется Zenmap. Он позволит выбрать цель, запустить сканирование, отобразить результаты, а также сохранить их и сравнить с другими.
GUI Zenmap это хороший способ познакомиться с Nmap, но лучше знать как использовать Nmap в командной строке, если вы собираетесь работать с ним часто.
В будущем руководстве мы более глубоко познакомимся с Nmap и конкретными задачами которые вы сможете решить.
Данный пост это вольный перевод статьи Beginner’s Guide to Nmap. Спасибо за внимание.
Nmap Tutorial
Get introduced to the process of port scanning with this Nmap Tutorial and a series of more advanced tips.
With a basic understanding of networking (IP addresses and Service Ports), learn to run a port scanner, and understand what is happening under the hood.
Nmap is the world’s leading port scanner, and a popular part of our hosted security tools. Nmap, as an online port scanner, can scan your perimeter network devices and servers from an external perspective ie outside your firewall.
Getting started with Nmap
Windows or Linux?
Use the operating system that works for you. Nmap will run on a Windows system, however, it generally works better and is faster under Linux, so that would be my recommended platform. Plus, having experience with Linux based systems is a great way to get access to a wide selection of security tools.
The installation steps in this guide are for an Ubuntu Linux based system but could be applied, with minor changes, to other Linux flavors such as Fedora / Centos, or BSD based system.
Step 1: Operating System Installation
If you need to get a Linux system up and running, a Free virtual machine is Virtualbox. This is an easy to use virtual machine system, you could of course alternatively use VMware or Parallels.
Step 2: Ubuntu Installation
Download the latest Ubuntu iso from www.ubuntu.com, select the ISO as the boot media for your guest and start the virtual machine. Select the install option and Ubuntu will be installed onto the virtual hard disk on the machine.
Step 3: Nmap Installation from source
Ubuntu comes with Nmap in the repositories or software library, however this is not the one we want. In most cases, I suggest sticking with the software from the Software Center, but in this case, there are many benefits from running the latest version of Nmap.
On the download page https://nmap.org/download.html you will see the bzip2 version (you can get the stable or development).
To get the latest feature packed development version, start a terminal (type terminal in the menu of Ubuntu and it will show as an option):
Hopefully Internet access from your virtual machine is working, if it is you will soon have the latest in your home directory.
You may need to install g++ in order to compile. You should also install the libssl-dev package as this will enable the SSL testing NSE scripts to work.
Now unpack, compile and install. Use the standard configure and make commands when building software from source.
Run the nmap commmand to show available command line options if the installation has been successful.
You now have a list of the various options available. Start with the basics then move onto testing different scan options and NSE scripts. You have found the white rabbit, are you going to follow?
As you can see, there are a great many variations on port scanning that can be done with Nmap. Hit the book in the column to the right for an in-depth guide.
Nmap command example
This is a simple command for scanning your local network (class C or /24):
Zenmap for those who like to click
Start zenmap either from the command line or through the menu. This is the GUI interface to the Nmap scanner. It is solid and works, I prefer the command line as it allows you to script things, collect the output and have more understanding of what’s going on. One nice feature of the Zenmap scanner is the graphical map of the scanned networks, a bit of eye candy if nothing else.
Understanding Open, Closed and Filtered
Nmap has a variety of scan types. Understanding how the default and most common SYN scan works is a good place to start to examine how the scan works and interpreting the results.
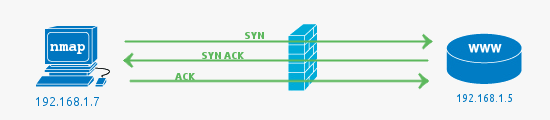
The 3 way TCP handshake
First, a bit of background, during communication with a TCP service, a single connection is established with the TCP 3 way handshake. This involves a SYN sent to an TCP open port that has a service bound to it, typical examples are HTTP (port 80), SMTP (port 25), POP3 (port 110) or SSH (port 22).
In all these examples a firewall could be a separate hardware device, or it could be a local software firewall on the host computer.
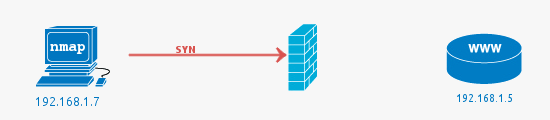
Filtered ports or when the Firewall drops a packet
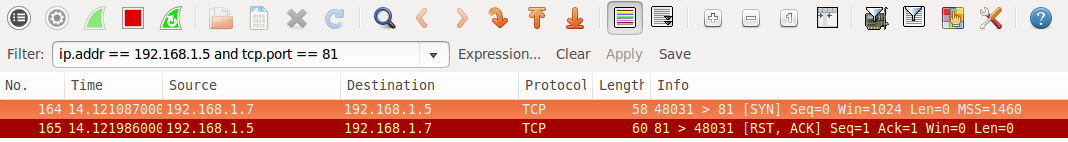
The job of a firewall is to protect a system from unwanted packets that could harm the system. In this simple example, the port scan is conducted against port 81, as there is no service running on this port, using a firewall to block access to it is best practice.
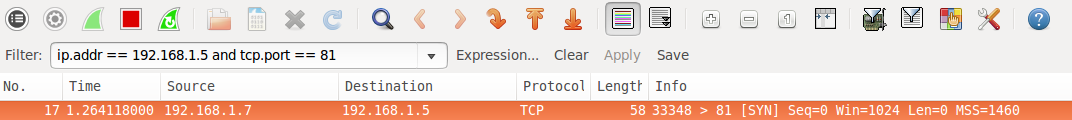
A filtered port result from Nmap indicates that the port has not responded at all. The SYN packet has simply been dropped by the firewall. See the following Wireshark packet capture that shows the initial packet with no response.
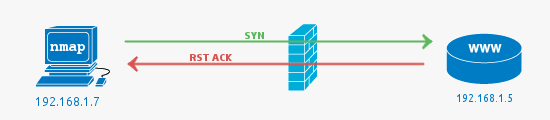
Closed ports or when the Firewall fails
In this case, closed ports most commonly indicate there is no service running on the port, but the firewall has allowed the connection to go through to the server. It can also mean no firewall is present at all.
Note that while we are discussing the most common scenarios, it is possible to configure a firewall to reject packets rather than drop. This would mean packets hitting the firewall would be seen as closed (the firewall is responding with RST ACK ).
Pictured below is a case where a firewall rule allows the packet on port 81 through even though there is no service listening on the port. This is most likely because the firewall is poorly configured.
anook2
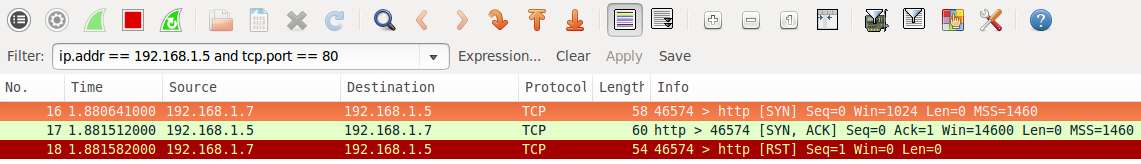
An Open Port (service) is found
Open Ports are usually what you are looking for when kicking off Nmap scans. The open service could be a publicly accessible service that is, by its nature, supposed to be accessible. It may be a back-end service that does not need to be publicly accessible, and therefore should be blocked by a firewall.
An interesting thing to notice in the wireshark capture is the RST packet sent after accepting the SYN ACK from the web server. The RST is sent by Nmap as the state of the port (open) has been determined by the SYN ACK if we were looking for further information such as the HTTP service version or to get the page, the RST would not be sent. A full connection would be established.
Hacking Nmap Video from Defcon 13
This video contains some interesting Nmap features, the presenter is Fyodor the creator of the Nmap port scanner.