How are the school years called in the united states
How are the school years called in the united states
Education in the USA — Образование в США. Текст на английском языке с переводом и аудио
На этой странице вы найдете текст на английском языке «Education in the USA» (Образование в США). Это одна из частых тем для топиков, сочинений, домашних работ по английскому языку. В тексте коротко описана образовательная система в США, в основном, школьная система. Вы узнаете, сколько классов в американских школах, сколько лет учатся в школах в США, какие есть варианты продолжения учебы после окончания школы. Текст дается с переводом и аудио.
Education in the USA – Образование в США. Текст на английском языке + аудио
Это вариант текста на тему «Образование в США» в формате «текст + аудио». Ниже вы найдете вариант с переводом.
Education in the USA
Пройдите тест на уровень английского:
The system of education in the United States is rather complicated. It is exposed to the constant changes of federal policies, adaptation to various social needs, and the emergence of new pedagogical methods.
In most schools, it is divided into three levels:
This 12-year system is called “K-12”. K-12 stands for the grades for students of various age groups from the kindergarten age (5 years old) to the 12th grade age (18 years old).
There are three types of schools in the United States: public, private, and home schools. Public schooling is financed by federal, state, and local authorities. Parents do not pay for their children’s education. Private schools have a right to choose their curriculum and establish their policies. This kind of education is not free of charge. Homeschooling addresses the needs of parents who do not want their children to attend regular schools for certain reasons. Among home school students are children with special needs and children whose parents support non-traditional methods of learning. There are also young athletes and celebrities whose tight schedule do not leave them enough time for going to school. About 3% of children are homeschooled in the USA.
The necessary standards of education in the United States are set by state governments. As a rule, the key requirement for American students is to pass obligatory standardized tests developed for the K-12 schooling system.
After high school, children have several options. First, they can choose a 4-year college or university program and get the education for the selected professional career. Second, children can choose a 2-year program in college and get prepared for their future career choice. Third, high school graduates can enter a vocational school and learn a trade to have an opportunity to be employed in a specific field of occupation such as design, baking or carpentry. Fourth, graduates of high schools can choose to serve in the US armed forces.
Fifth, if children are not ready to continue their education, they can have a gap year. Most kids prefer to spend this time exploring their life preferences and individual interests through active involvement in various jobs, internships, volunteering work, or traveling.
Текст на английском языке с переводом. Education in the USA – Образование в США
Это тот же самый текст об образовании в Соединенных Штатах, но с переводом каждого предложения, который поможет вам с незнакомыми словами и оборотами.
Education in the USA (4)
Образование в США (4)
Образование в Соединённых Штатах Америки обязательно для детей от 6 до 16 (или 18) лет. Оно подразумевает 12 лет учёбы в школе. Учебный год в Америке начинается в конце августа или в начале сентября, а заканчивается в конце июня или в начале июля. Учебный год состоит из трёх триместров или четырёх четвертей. Зимние, весенние и летние каникулы длятся 2—3 или 6—8 недель соответственно. Продолжительность учебного года и учебного дня варьируется в зависимости от штата. Дети учатся 5 дней в неделю и добираются до школы, как правило, на школьном автобусе.
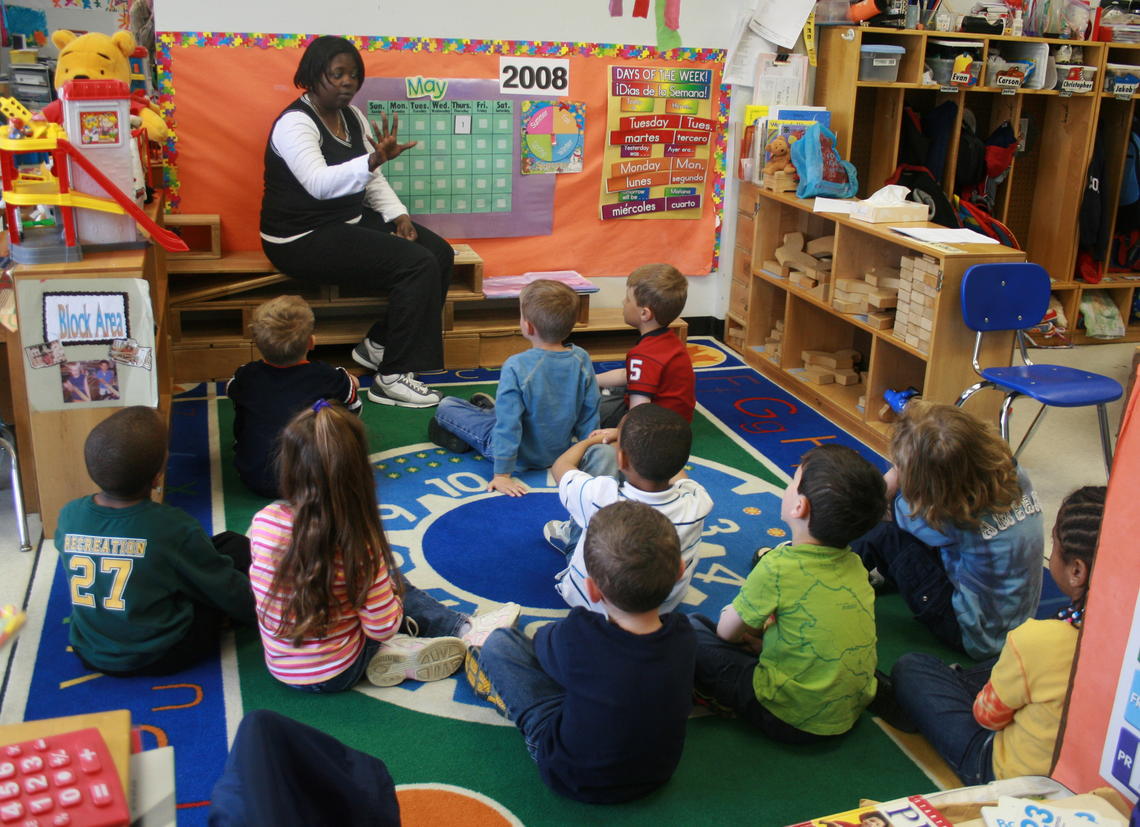
Американская система образования состоит из трёх основообразующих компонентов: начального, среднего и высшего образования. Помимо этого, в Америке существует понятие дошкольного образования. В возрасте 4—5 лет дети только начинают знакомиться с образовательным процессом в детском саду. Цель программы дошкольного обучения — методом игры подготовить детей к начальной школе, помочь им получить опыт общения. Когда им исполняется 6 лет, они поступают в 1-й класс начальной школы.
Учебная программа начальной школы включает в себя следующие предметы: английский язык, арифметика, география, история США, природоведение, физкультура, пение, рисование, трудовое обучение. В основном акцент ставится на обучении базовым навыкам — разговорной речи, чтению, письму и арифметике. Иногда дети изучают какие-либо иностранные языки и всемирную историю, а также такие предметы, как сексуальное образование, и уроки, посвященные изучению социальной роли наркотических препаратов. Главная цель начального образования — всестороннее интеллектуальное, социальное и физическое развитие ребёнка в возрасте от 5 до 12 или 15 лет.
Среднее образование начинается, когда учащиеся переходят в старшую школу, в 9-й класс; затем они продолжают обучение до 12-го класса. Расписание средней школы больше нацелено на обучение конкретным предметам, нежели общим знаниям. И хотя в расписании всегда имеется набор базовых предметов — английский язык, математика, естествознание, обществознание и физкультура, — ребятам предоставляется возможность изучать предметы по выбору, которые не являются обязательными для всех учащихся. После первых двух лет обучения они выбирают предметы в соответствии со своими профессиональными интересами. Такие предметы должны быть связаны с будущей работой учащихся либо с последующим обучением в университете или колледже. В каждой средней школе есть специальный учитель — советник по профессиональной ориентации. Он помогает учащимся определиться с выбором предметов, а также даёт советы, относящиеся к области социальных проблем. Курсы предметов на выбор различаются в зависимости от школы.
Учащиеся каждого класса старшей школы имеют свои особые имена: девятиклассники называются новичками, десятиклассники — второкурсниками, одиннадцатиклассники — студентами предпоследнего курса, а двенадцатиклассники — выпускниками.
По окончании старшей школы подавляющее число американцев продолжают обучение в высших учебных заведениях. В университетах молодые люди должны проучиться 4 года и сдать 4 зачёта, чтобы получить степень бакалавра. Для получения степени магистра нужно учиться ещё 2 года и заниматься научно-исследовательской работой. После этого студент может сделать ещё ряд необходимых работ, которые дадут ему возможность стать доктором наук.
1. At what age do American students start and finish their compulsory education?
2. How are the school years called in the United States?
3. The length of the school year varies among the states, doesn’t it?
4. What are the basic components of American education?
5. Do all children have to attend a nursery school?
6. When does elementary education start?
7. What is the main aim of elementary education?
8. The secondary school curriculum doesn’t imply a number of basic subjects, does it?
9. What are elective subjects?
10. Who is a guidance counselor?
compulsory — обязательный
to involve — включать
schooling — обучение в школе
to be divided into — делиться на
trimester — триместр
quarter — четверть
respectively — соответственно
to vary — варьироваться
to consist of — состоять из
elementary education — начальное образование
secondary education — среднее образование
higher education — высшее образование
notion — понятие
preschool education — дошкольное образование
to get acquainted with — знакомиться с
nursery school — детский сад
to aim — быть нацеленным
to acquire the experience of association — получить опыт общения
grade — класс
General History — всеобщая история
sex and drug education — сексуальное образование и уроки, посвященные изучению социальной роли наркотиков
skill — навык
goal — цель
curriculum — расписание, учебный план
specific — конкретный, определённый
Social Studies — обществознание
opportunity — возможность
elective subject — предметы по выбору
according to — в соответствии с
guidance counselor — советник по профессиональной ориентации
various — разнообразный
freshman — новичок
sophomore — студент второго курса колледжа или ученик 10-го класса средней школы
junior — студент предпоследнего курса колледжа или ученик 11-го класса средней школы
senior — студент последнего класса колледжа или ученик 12-го класса средней школы
majority — большинство
bachelor’s degree — степень бакалавра
master’s degree — степень магистра
to be engaged in — заниматься чем-либо
research work — научно-исследовательская работа
Education in the United States of America
Education in the United States of America is compulsory for children from the age of 6 till 16 (or 18). It involves 12 years of schooling. A school year starts at the end of August or at the beginning of September and ends in late June or early July. The whole school year is divided into three terms/trimesters or four quarters. American students have winter, spring and summer holidays which last 2 or 3 weeks and 6 or 8 weeks, respectively. The length of the school year varies among the states as well as the day length. Students go to school 5 days a week.
The American education system consists of 3 basic components: elementary, secondary and higher education. There is also such a notion as preschool education. At the age of 4 or 5 children just get acquainted with the formal education in a nursery school. The preschool education programme aims to prepare children for elementary school through playing and help them to acquire the experience of association. It lasts for one year. Then they go to the first grade (or grade 1).
Members of each grade in high school have special names: students in the ninth grade are called freshmen, tenth graders are called sophomores, eleventh graders are juniors and as for twelfth graders, they are seniors.
After graduating from high schools the majority of the Americans go on studying at higher education establishments. In universities they have to study for four years to get a bachelor’s degree. In order to get a master’s degree they must study two years more and, besides, be engaged in a research work.
Образование в США
Образование в Соединённых Штатах Америки обязательно для детей от 6 до 16 (или 18) лет. Оно подразумевает 12 лет учёбы в школе. Учебный год в Америке начинается в конце августа или в начале сентября, а заканчивается в конце июня или в начале июля. Учебный год состоит из трёх триместров или четырёх четвертей. Зимние, весенние и летние каникулы длятся 2-3 или 6-8 недель соответственно. Продолжительность учебного года и учебного дня варьируется в зависимости от штата. Дети учатся 5 дней в неделю и добираются до школы, как правило, на школьном автобусе.
По окончании старшей школы подавляющее число американцев продолжают обучение в высших учебных заведениях. В университетах молодые люди должны проучиться 4 года и сдать 4 зачёта, чтобы получить степень бакалавра. Для получения степени магистра нужно учиться ещё 2 года и заниматься научно-исследовательской работой. После этого студент может сделать ещё ряд необходимых работ, которые дадут ему возможность стать доктором наук.
Вопросы:
1. How are the school years called in the United States?
2. At what age do American students start and finish their compulsory education?
3. What are the basic components of American education?
4. The length of the school year varies among the states, doesn’t it?
5. When does elementary education start?
6. Do all children have to attend a nursery school?
7. The secondary school curriculum doesn’t imply a number of basic subjects, does it?
8. What is the main aim of elementary education?
9. Who is a guidance counselor?
10. What are elective subjects?
Сохранить эту страницу в социальной сети:
Англо-русский словарь онлайн 
5 тестов скорости!
Education system in the USA
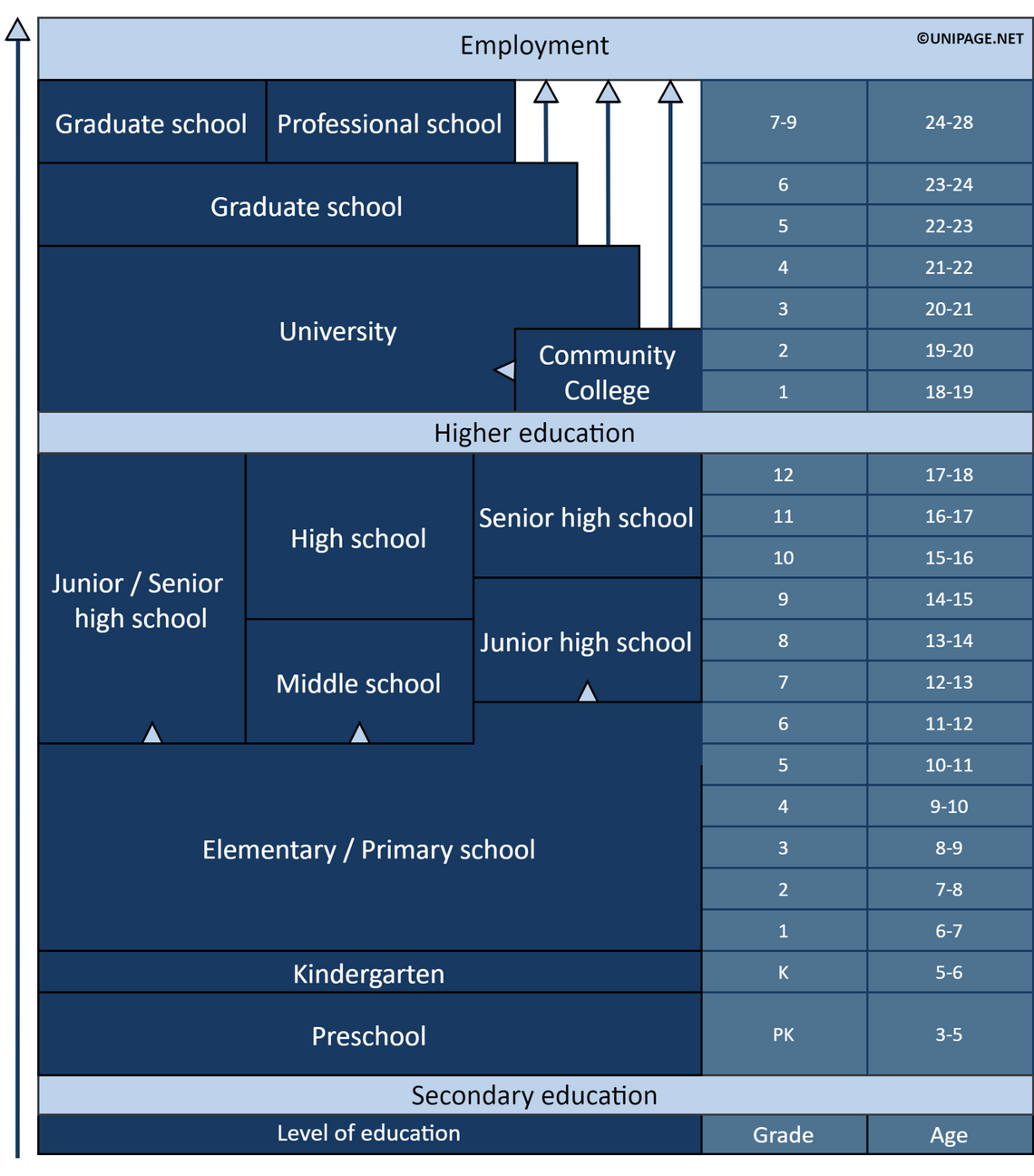
There are four stages in the US education system: preschool, primary, secondary, and higher education. The educational process at each of them is flexible, practice-oriented, and can flaunt an individual approach to students.
Guidance in the admission process
Our staff will walk you through the entire admission process: from choosing a university and preparing documents to enrollment and obtaining a visa. We are always in touch and ready to answer any questions. UniPage experts will always objectively assess your situation and suggest the most suitable university options.
| region | North America |
| Capital | Washington, D.C. |
| Language | English, Spanish |
| Currency | US Dollar |
| Population | 317,579,000 |
| Students | 21,000,000 |
| Foreigner students | 3.5% |
| Subject | |
|---|---|
| Arts and Humanities | 1 |
| Engineering and Technology | 1 |
| Life Sciences and Medicine | 1 |
| Natural Science | 1 |
| Social Sciences and Management | 1 |
| Mathematics | 1 |
| Physics | 1 |
| Chemistry | 1 |
| Computer Science | 1 |
| Economics & Business | 1 |
| Indicator | |
|---|---|
| Popularity rating in the world | 1 |
| Ranking of universities in the world | 1 |
| Academic Reputation | 1 |
| Employer Reputation | 1 |
| Quality of teaching | 1 |
| International Faculty | 2 |
| International Students | 1 |
| Citations per Faculty | 1 |
| Universities in top 100 | 37 |
| Universities in top 200 | 59 |
| Universities in top 500 | 109 |
| Universities in top 1000 | 195 |
| Universities in top 5000 | 1142 |
Features of education in the United States
Education system in the United States
Preschool education
Preschool classes are also very varied. The main goal is to help them socialize and prepare them for kindergarten. Children learn by playing. A lot of time is devoted to interaction with peers. A standard set of lessons in preschool can look like this:
From the age of five, children enter kindergarten and begin their journey through the K-12 system.
A class in an American preschool
Primary education
Kindergarten
Primary School
After kindergarten, children finally get to primary school (aka elementary school). It lasts from first to sixth grade. During this period, all subjects are taught by one teacher. The major subjects are English, Mathematics, Geography, History, and Natural Sciences. Well-funded schools employ individual teachers for the classes in Music, Art, or foreign languages. On average, children stay at school until 6-7 pm. They take extra hours or do their homework in the afterschool.
The grading system for the first two years is very simple:
Later the standard American school grades A, B, C, D, and F are gradually introduced, where A is «excellent» and F is “failure.” Already in elementary school, children pass their first standardized tests. They measure the academic progress of students and prepare them for the future university entrance exam, the SAT. There are no graduation exams in primary school.
A lesson in an American primary school
Secondary education
Middle school / Junior high school
Tests are carried out regularly. The final grade for the entire period of study in secondary school depends on them. There are no final exams here, it is enough to have «satisfactory» in all subjects to graduate.
Greenfield Central Junior high school
Senior high school
The final stage of secondary education is high school. Children from 14 years old go there. In America, there are mixed junior/senior high schools, where students spend six years until graduation. And there are also separate ones that are located in different buildings. High school lasts from grade 9 till 12. And this is the only opportunity for foreigners to attend a public school as an exchange student (only for one year). For the rest of the time, only private institutions are available to them. But even in public schools, foreign students must pay from 3,000 USD to 10,000 USD per year of study. Read more about admission to US schools in the article on secondary education.
All studies in high school are focused on entering a university: the students improve their GPA and prepare for the SAT/ACT. Compulsory subjects in high school:
In addition to the basic subjects, students can optionally take up Honors or Advanced Placements (AP). The former are students’ groups that study subjects on a more in-depth level, while the latter are university-level courses. There are a total of 33 disciplines in six scientific fields. There is even Japanese, Macroeconomics, and Mechanics [5] available. Upon completing a course, students take an oral or written exam. Excellent grades in AP subjects increase your chances of admission to a prestigious university.
Most likely in the near future, the importance of AP courses will grow significantly. In 2021, the College Board canceled the SAT Subject Test permanently. It used to help graduates demonstrate their knowledge in specific subjects, such as Physics or Chemistry. They were obligatory for admission to some specialties. Advanced Placements could be a great alternative to the SAT Subject Test.
Higher education
Vocational education
School graduates can get a quick vocational education in community colleges. Studying in one of them lasts two years. The workload is slightly lower than at universities, and a heavy emphasis is put on practical skills. In colleges, the student receives an associate degree and gets a job in the specialty.
Another option after community college is to transfer immediately to the third year of a university. To do this, you must have a GPA of 3.5 out of 4, while all grades in specialty subjects must be excellent. Foreigners are sometimes required to provide TOEFL and SAT certificates.
Studying at a university
There are three levels in the US higher education system:
The process of studying at US universities is flexible. Students make their own schedules, and the main focus is typically on seminars and discussions. Upon admission, applicants choose the main specialty, or ‘major,’ and then can add a minor. The latter can be a useful supplement to the main profession. For example, a major is in Engineering, and a minor is in Robotics. Alternatively, it may reflect the student’s personal interests: major — Biology, minor — French literature. Both options are natural for American universities.
Studying in the States costs 20,000-50,000 USD /year. Plus living expenses of about 10,000 USD /year. Fortunately, many US universities award scholarships and grants to students. Some of them, like the Ivy League, cover up to 100% of the tuition fees.
University of Virginia
Share to
UniPage guidance in the admission process
UniPage is an educational agency. We consult students and help them with admission to universities abroad, including the most renowned educational institutions such as Stanford, Sorbonne, and TUM.
We are experts in our field and know how to ensure that you enter the university that suits your goals, research interests and budget.
Education in The United States
School Term in the United States
Structure of the U.S. Education System
Early Childhood Education/Preschool
Pre-school programs usually occur in the year preceding school entry and sometimes the previous year as well, or around ages 3-5. The first year of pre-school education is often called pre-kindergarten or nursery school, while the second year is often called kindergarten or preschool. Just fewer than one million children currently enroll in the first year of pre-school education each year, and some 3.4 million enroll in the second year.
During the initial year of preschool education, children typically attend school for two to three days a week, usually for a period of 3-4 hours. In the second year, or in kindergarten, the instruction is a bit more rigorous and the time commitment is longer, with children attending school five days a week for 4-5 hours a day.
The 3-5 age range is considered a professional and research specialization for educators in the United States. Thus, U.S. instructors of early childhood education are generally very well-educated and highly trained, typically possessing a Bachelor degree or higher and a teaching certificate issued by the state in which they live and work. While the exact curriculum taught at preschools may vary from one state to the next, the goals of those curricula are typically very similar. Preschools aim to provide a developmental approach to learning, one emphasizing language and literacy, as well as physical, emotional and social development. Students are also introduced to basic concepts in the areas of math, science, social studies, music, movement and art. As a whole, these literacy-focused and problem solving programs provide teachers with all the tools they need to offer effective instruction—instruction built around the concept of cooperative learning within a carefully designed and supportive structure. To ensure the effectiveness of these programs, extensive training and support for teachers is not only offered, but integral to ongoing curriculum implementation.
Compulsory Education in the U.S. (Elementary School and Secondary School)
Texas school children Elementary or primary education in the United States typically begins at age six and represents the beginning of a student’s compulsory education. This stage of education lasts six years, beginning with grade one and culminating with grade 6 (age 12). The length of the school day for elementary-age children is 6-7 hours depending on the grade level and district, beginning at 7:30-8:30 AM and culminating at 2:00 to 3:00 PM.
Elementary education is offered free of charge at American public schools, although parents may be required to purchase certain school supplies and books. Parents not comfortable with the public school setting can instead opt to send their children to one of the thousands of private schools across the country, albeit for an expensive annual fee. These schools, which are mainly operated by churches and private companies, can usually offer smaller classroom sizes and are bound by the same academic standards that govern the public schools
Elementary schools in the United States provide instruction in the fundamental skills of reading, writing and mathematics, with each grade building on the year before. Students are also introduced to several other subjects throughout this six-year stage of education, including history and geography (taught together as social studies), crafts, music, science, art and physical education. Foreign languages, which formerly were taught solely at high schools, are now being introduced during the last few years of elementary school in some areas, although in the majority of cities, schools still do not offer any foreign language instruction. All schools, however, now have specialized programs for those students whose first language is something other than English. These programs, which stress English learning as part of the curriculum, prevent students from falling back on their studies due to barriers in language.
Instruction in elementary schools is guided by a national curriculum, set forth by the United States Secretary of Education, which prepares students for studies at the secondary school level. In addition to the regular curriculum, all U.S. elementary schools are also compelled to offer Special Education programs. These programs are designed for students with learning delays and other disabilities that affect their ability to learn at the same pace as other students. In addition, many elementary schools offer Gifted Education programs. These programs are designed to address the needs of students for whom the regular curriculum in one or more subjects is not challenging enough.
In elementary school, the instruction is led by one teacher and the classroom sizes range from 20-30 students. Regular elementary school teachers must, at minimum, possess a four-year Bachelor degree and a one-year, “multiple-subject” teaching credential. Special Education classrooms are generally led by a teacher and a teacher’s aide. The optimal class size for these programs is 15 or fewer students, with a maximum of 20 students. Special education teachers must have a Bachelor’s degree and a Special Education credential from an accredited university.
Secondary Education
Secondary education in the U.S. is also offered by both public and private schools. This stage of education is broken down into two distinct levels: middle or junior high school and high school. Middle school education generally spans two years (grades 7 and 8) and serves students who are 12-14 years of age. High school programs span four years (grades 9-12) for students ages 14-18. While only the initial two years of high school (or whenever a student reaches 16 years of age) are compulsory, most students in the United States complete the entire secondary school program and ultimately graduate from their high school. ThePensters custom writing service from the United States are the best place to get your high-school essays done.
The typical classroom size at American secondary schools is 25-35 students, and each classroom is led by a single teacher. Like primary schools, middle schools and high schools in the United States also offer Special Education classes (with a teacher and an adult assistant), as well as programs designed for gifted students. These courses, with names such as “Advanced Placement” or “Honors” classes, tend to have a much lower student to teacher ratio, typically topping out between 15 and 20 students per class. Exceptionally bright students can also take college-level courses during their final two years of high school.
The initial year of secondary school represents the first time in which students have multiple teachers for various subjects. National standards dictate that secondary school students must take and complete certain core courses for a prescribed number of years or terms as determined by each state. These core courses generally include English, mathematics, general science, health, physical education, foreign languages and social studies or social sciences, an area which may include American history, World History, Government, Geography, and Sociology or Social Problems.
Once students complete the middle school requirements, they are promoted to high school, where they enter as 9 graders. Public American high schools tend to be much larger than secondary schools in other countries, with campuses serving anywhere from between 1,500 to 4,000 students.
After the first two years of high school, students with no interest in pursuing an academic education at the college or university level can begin taking vocational classes in addition to the academic requirements mentioned above. These courses range from auto body and woodworking classes to computer-aided drafting and restaurant management. Collectively, these classes are designed to give students a head start by providing them with an opportunity to learn a marketable skill or trade.
Students who successfully complete their six-year secondary school requirements receive a high school diploma and are honored at a graduation ceremony. This diploma is the minimum requirement for pursuing a college or university education.
Tertiary Education in the United States
Junior Colleges (Community Colleges) and Private Vocational Institutions
Junior or community colleges offer an array of programs designed to help a wide variety of students meet their educational and career goals. Students who ultimately intend to pursue an academic degree at the college or university level can tackle the initial two years of that degree, also called the “general education requirements,” at a junior college and earn an Associate’s Degree in the process. Junior colleges allow underclassmen to take specific lower-level subject requirements and transfer the credits they earn to the college or university of their choice. Not only do these institutions represent an affordable option to a high-cost university, they allow students (with a less-than-stellar high school resume) to take and pass courses that will ultimately help them qualify for university admittance.
Although junior colleges are primarily known as academic institutions, they also offer scores of vocational pathways for students and an opportunity to earn a diploma or certification in a specific career field or trade. Like private vocational institutions, the programs they offer are designed for students seeking a much more rapid track through which to earn the credentials they need for their chosen career. Some of the specialized programs offered at junior colleges and private vocational institutions include:

Eligibility Requirements
Students who wish to earn a Bachelor, Master or Doctorate degree in the United States must first apply for admittance into one of the thousands of colleges and universities in the country, both public and private. Each institution sets its own policy for admission, but the minimum requirement at all U.S. institutions is a high school diploma. Other criterion that colleges and universities will look at prior to admittance includes:
Naturally, the eligibility requirements of the larger public colleges are not nearly as rigid as some of the more prestigious private universities, such as Harvard, Yale and Stanford, where only the brightest of students across the country are admitted each year.
Degree Structure
The degree structure at America’s colleges and universities is very similar to that of other North American and many European countries. It includes: