How do search engines work
How do search engines work
How Do Search Engines Work: 4 Important Functions
There is a very important communication platform between your target audience and your website: search engines. They enable users to find your website by searching for specific keywords, thus enabling the flow of visitors to you.
But how exactly does this process, which we always know “the last step” of, works very well? How exactly does your website is crawled, indexed, rendered, and ranked on certain keywords?
If you want to have information about SEO, if you want to strengthen the rankings of your website with strong SEO studies, you must first understand the working logic of Search Engines.
So let’s start with this detailed guide prepared by Screpy experts!
Try for free to boost your website traffic!
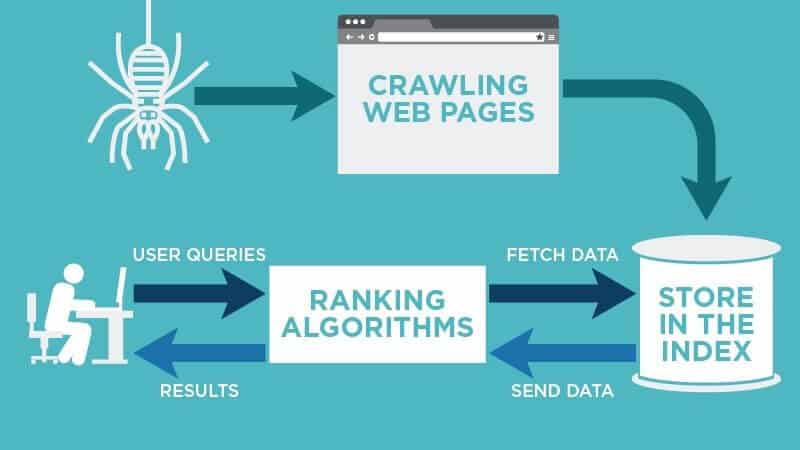
How does search engines work?
What Do Search Engines Do? 4 Function of One Actor!
A basic search engine performs 4 basic actions to develop a higher user experience (UX) by presenting the most powerful websites to its users.
What do search engines do?
These can be listed as follows:
Crawling
Digital software that provides web crawling, defined as robots, spiders, or bots, create a virtual experience by traveling between the links on your site (they actually jump from one page to another via links that bind them).
Through this experience, they will examine your website. Bots that navigate from one link on your website to another can learn about the user experience offered by a specific web page.
Indexing
The job of storing data on a web page is called indexing. A bot comes to your website and crawls it. Then the contents, links, and much more on this page are cataloged, which means they are indexed by the search engine. As you can imagine, this will require a very powerful computing resource.
Rendering
All content prepared to be published in the digital world on a web page is stored as HTML, CSS, and Javascript files. The browser’s task is to read and interpret these files by analyzing the relevant languages (the code languages). When these codes are converted into a web page, the browser interprets the files in front of the user. HTML or Javascript files with high load require a high loading process. In the modern era, it is recommended to save many links as HTML files.
Ranking
A search engine aims to show the users the result most relevant to the keyword they are searching for, thereby increasing the user experience. To do this, they rank the web pages in terms of the content they offer, their speed within the site, and other features that affect the user experience. This ranking shows how much more visible web pages are in related keywords than their competitors and directly affects visitor traffic. Results that offer the most relevant and successful performance are shown higher in search engines.
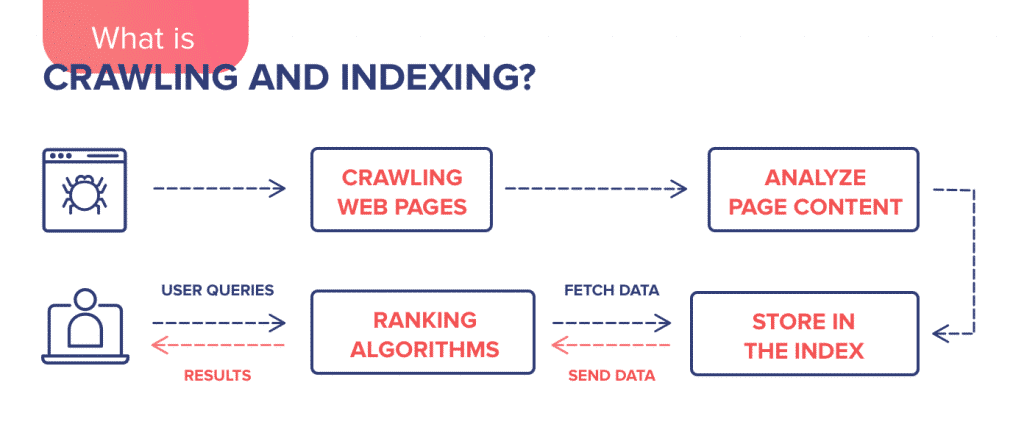
Are Search Engines Aware of Your Website?
If you want to appear in the SERP in related searches, you must first make sure that search engines can find your site. In addition to the pages that need to be crawled and indexed on a website, there may be pages that you do not want to be indexed. How will you know which pages search engines see and which pages don’t?
Crawling, indexing and ranking of a web page
There is no indexing without crawling, we got that now, right? So, pages that are not indexed by search engines are actually pages that give errors during crawling.
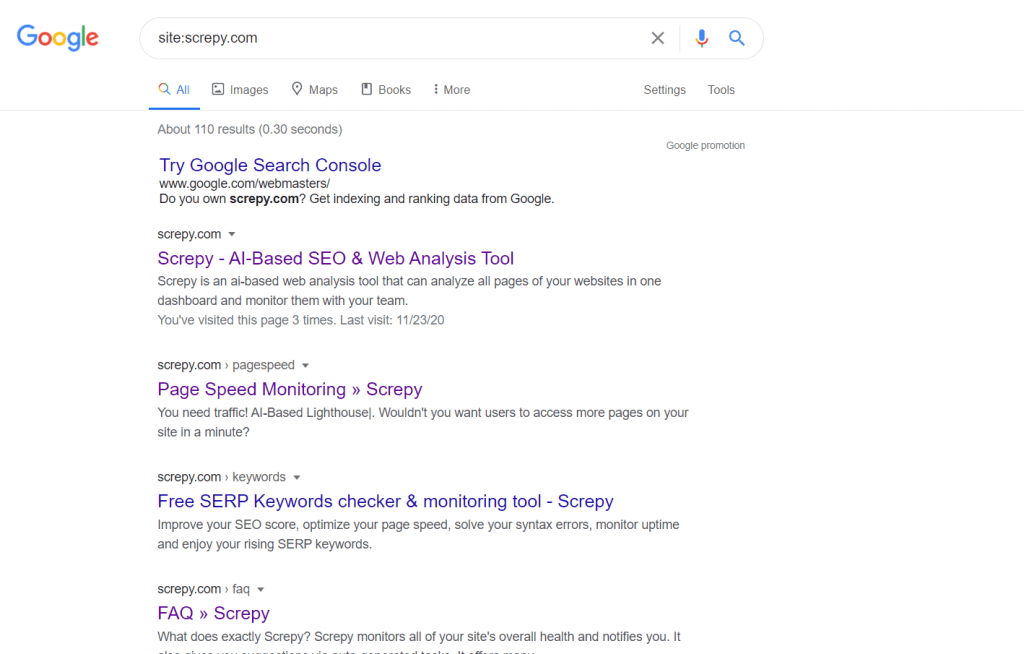
The best way to do a free test on this subject is to type “site:domainname.com” in the search engine and then click enter. The results you see are all pages on your site in the search engine. If there is no web page here, it means that Google (or whichever search engine you use) isn’t seeing it. In this case, it may make sense to examine the source code of this web page and see if the page has render-blocking features.
Checking for indexed web pages of a certain website
As you can see in the picture above, you can also use Google Search Console to analyze which of your pages are indexed and which of does aren’t.
Possible Reasons for Your Website Not Visible
So, if a page on your website is not visible, what are the reasons for this? Hey, detailed scans with Screpy can help you do code optimizations, which also called technical SEO. Because Screpy examines the source code of each of your web pages and alerts you to the problems. You can examine how to fix these warnings through tasks – and if you improve them, Screpy AI predicts what kind of score increase they will have.
Anyway, if your web pages are not indexed, you may be experiencing one of the following problems:
What About Robot.txt Files?
Not indexing any page on your site may be caused by robot.txt files. Errors in these files damage the crawling process and various problems occur. The main behavior of the Googlebots toward your website’s robot.txt files is as follows:
If Googlebots cannot find such a file on your site, your site will continue to be crawled. If there is such a file, the site will continue to be scanned unless otherwise stated. However, even though there is a robot.txt file, if there are problems with accessing this file and errors occur, Googlebots may stop crawling your site. This may cause many pages not to be indexed.
Googlebots crawling your web page
Why Does Crawling, Rendering and Indexing Matters?
In this content, we talked about four concepts in total: crawling, rendering, indexing, and finally ranking. In fact, the first three of these are of serious importance over the fourth. If you do the following, you can make Google crawl every page of your website and rank it at the top if you have enough quality content. This is the most important rule of SEO, which we call search engine optimization: Your website will be more visible and you will be visible to users before your competitors without having to spend a high budget for SEM. Your traffic and recognition will increase.
If Google comes across unnecessary code, low-quality pages, or errors with a lot of different codes during your website’s crawling process, it will think that the user experience you will offer is low and that you are not a high-quality website. This situation causes Google not to bring you to the position you want in the ranking even if it indexes you. So search rankings are about all of these, and much more than them!
How Do Search Engines Work?
Billions of searches take place on Google each day, but have you ever stopped to wonder how those useful algorithms work on search engines and how you can use them to your advantage?
On a basic level, search engines work by performing 3 basic functions:
Crawling: How Does A Search Engine Crawl The Web?
Google has its own main crawler called Googlebot. There are other search engine crawlers out there such as DuckDuckBot, YandexBot, and Slurp for Yahoo. Bing also has a web crawler called BingBot. These robots are what make it possible for your website to rank in SERPs or get on the top page of search engines. In fact, around 93% of all web traffic is thanks to a search engine.
These crawlers can visit web pages very quickly which allows Google’s algorithm to discover new websites, pages, and other content.
Crawlers also tend to visit popular websites that create new content more frequently than smaller unknown websites. Getting a link from a popular website could result in your content getting discovered more rapidly.
A great way to do this without a sales pitch is to use the broken link method. This method involves searching for broken links on a blog post or content page and suggesting to the webmaster to replace it with your own link. This can often result in a backlink which crawlers love!
Creating a sitemap also helps search engines crawl your site. A good sitemap will link to every page on your site.
Signing up for a Google Search Console account is a good step to take if you want to see more data on pages that Google has crawled. You can also see any crawling errors that may have occurred.
A few issues that might cause pages to not get crawled include poor navigation structure, redirect loops, and server errors.
In the past, it was popular to “submit” your site to search engines, but this is no longer needed as they have become much more advanced at detecting relevant results from new content that is published on the web. Your website needs to evolve and improve technical SEO with technology to compete with your competitors!
What is a Crawl Budget?
Now that you understand what crawlers are let’s go deeper and explain what a crawl budget is. Crawl budgets are also sometimes referred to as crawl space or crawl time. These terms are referred to as the number of pages search engines crawl onto a website within a timeframe.
So, these crawl budgets are assigned in a couple of different ways. These factors are based on host load and crawl demand.
Host loads are a factor because it’s basically just the website’s preference for how often a crawler accessed their page. This can also depend on often the host can handle crawling efforts.
Crawl demand is an important factor because it weighs whether or not a website is even worth crawling. These factors are based on popularity and how often the website or URLs are updated.
Crawl budgets aren’t just about pages, they have been used for any document that search engines crawl for. Such as JavaScript, CSS files, PDF files, and much more.
Let’s explain why crawl budgets are important and why you need to understand how they work, so you can incorporate that into a successful SEO strategy.
You need search engines to find as many of your indexable pages as possible. You also want them to do it as quickly as possible. When you create a new page and update already posted content, you want these search engines to find your information as fast as they can. The faster the crawlers can index the faster you can benefit from it.
How to Make Sure Your Website is Being Properly Crawled
If you aren’t sure if your website is being properly crawled by search engines, let’s take a look at what you can do to find out and make sure those little robot spiders are doing their job.
Here are the best ways to make sure your website is being crawled:
Creating a proper sitemap is vital for SEO purposes. A sitemap or XML (extensible markup language) is basically just a way to display information on a website.
They are a technical part of SEO which can make them a little intimidating but not overly complicated for a business owner who wants to learn.
You need a sitemap for Google so Googlebot can crawl your website, put it into their index, and then send its users to your website. Sitemaps just make it easier for Google to do that.
The next step is to review your sitemap, check it for optimization, as I stated above, there once was a time when you needed to submit your sitemap to Google. That is no longer needed as Google’s crawlers have evolved since then. Crawlers can now crawl your website without a submission.
You should also code your sitemap into your URL, by adding “/sitemap.xml” to it. By adding the sitemap file to your root folder, you will want to also add it to the robots.txt file as well. You can find this in the same area your root folders are in.
What this does is give crawlers the right directions to your website so it can index it, and share it with its users. Crawlers are vital to ranking, so it’s really important to make sure that your website doesn’t just have keywords, links, and up-to-date content. Your website needs to have an optimized website, and that includes the best methods to make sure search engine crawlers can’t reach your business content.
Earning backlinks and sharing your content on social media is also a great way to earn rankings in SEO and it also shows crawlers that your content is important to other websites giving you a boost in traffic and leads.
Indexing: How Does A Search Engine Read and Store Website Information?
When crawlers reach pages, they collect data and store the information in an index. You may have heard of metatags and metadata, these web crawlers are what collects that information from a webpage where it’s stored in its search engine’s index and then used when a user’s search request for that information is received. It is then displayed on a search engine results page for any given user.
By default, search engines will crawl and try to index every page on your site that they can find.
However, if you have pages you don’t want web searchers to be able to find through search engines, like private member-only pages, then using Robots Meta Tags will help.
A great tip for keeping a page private from crawlers is to exclude pages that aren’t useful like tag and category pages in WordPress.
If you’re wasting crawl budget, then you’re allowing important parts of your website to be left undiscovered. Which isn’t an effective method for your SEO rankings. If crawlers don’t know about pages, then they can’t crawl and index them for users.
Ranking: How Does A Search Engine Rank Websites?
There are two main factors that influence Search Engines rankings:
Off-page factors are factors that help improve a website’s rank outside of the business itself. This type of content is displayed on social media or guest blogs. It can also be considered as backlinks and other off-page related content such as articles linking back to a landing page.
These algorithms assign scores to various ranking factors and then rank relevant pages with the best scores from highest to lowest. RankBrain is also considered a major ranking factor when considering search engines and how they actually work.
Search engine algorithms also change over time in an effort to improve search results. Keep in mind that the goal of search engines is to provide quality content so that their users are satisfied with search results and keep using their search engine.
How Do Search Engines Work Wrap-Up
Search engines are a vital part of everyday life. Whether you’re a business trying to improve your SEO ranking or if you’re simply trying to find the best sushi restaurant near you.
Search engines and modern technology make it easy to find the best and most accurate and relevant information available.
If you’re feeling froggy, how about jumping into our next section and finding out what factors do search engines use to determine what content ranks at the top?
We discuss the top-ranking factors in the next chapter!
Talk Strategy With An Expert
Find out how SEO can work for you. Get expert advice on the right strategy for your business!
How Do Search Engines Work & Why You Should Care
Learn what search engines do and how they work. Easy step-by-step tutorial with a video for beginners.

If you are a developer, designer, small business owner, marketing professional, website owner, or thinking of creating a personal blog or website for your business, then you need to understand how search engines work.
Having a clear understanding of how search works, can help you create a website that search engines can understand, and this has a number of added benefits.
It’s the first step you need to take before even dealing with Search Engine Optimization (SEO) or any other SEM (Search Engine Marketing) tasks.
In this guide, you’ll learn the three main processes (crawling, indexing, and ranking) that search engines follow to find, organize, and present information to users.
What does a Search Engine Do?
Have you ever wondered how many times per day you use Google or any other search engine to search the web?
Is it 5 times, 10 times or even sometimes more? Did you know that Google alone handles more than 2 trillion searches per year?
The numbers are huge. Search engines have become part of our daily life. We use them as a learning tool, a shopping tool, for fun and leisure but also for business.
It’s not an exaggeration to say that we reached a point that we depend on search engines for almost anything we do.
And the reason this is happening is very simple. We know that search engines and in particular, Google has answers to all our questions and queries.
What happens though when you type a query and click search? How do search engines work internally and how do they decide what to show in the search results and in what order?
Watch the video tutorial to learn how do search engines work.
How Do Search Engines Work
Search engines are complex computer programs.
Before they even allow you to type a query and search the web, they have to do a lot of preparation work so that when you click “Search”, you are presented with a set of precise and quality results that answer your question or query.
What does ‘preparation work’ includes? Three main stages. The first stage is the process of discovering the information, the second stage is organizing the information, and the third stage is ranking.
This is generally known in the Internet World as Crawling, Indexing, and ranking.
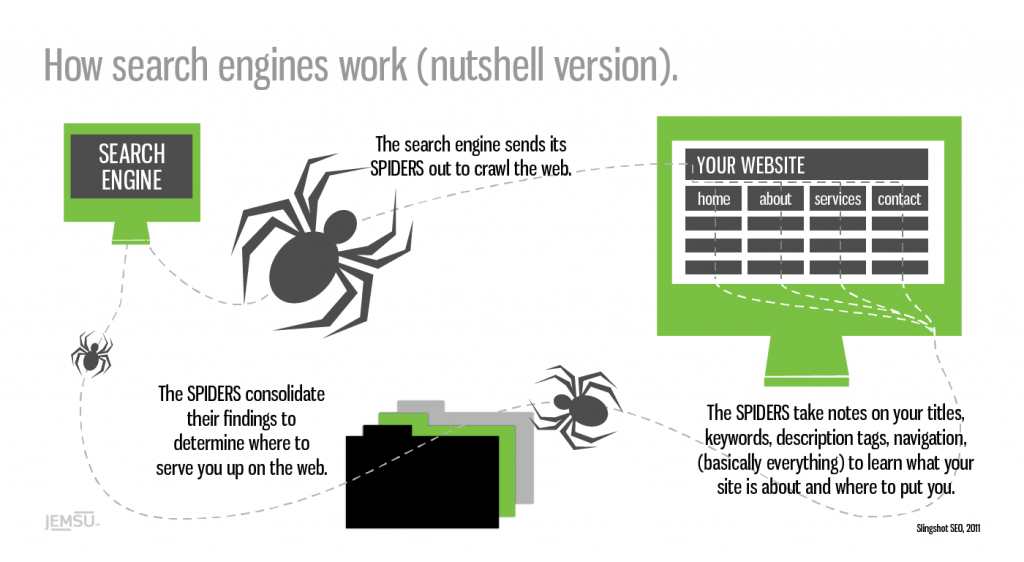
Step 1: Crawling
Search engines have a number of computer programs called web crawlers (thus the word Crawling), that are responsible for finding information that is publicly available on the Internet.
To simplify a complicated process, it’s enough for you to know that the job of these software crawlers (also known as search engine spiders), is to scan the Internet and find the servers (also known as webservers) hosting websites.
They create a list of all the webservers to crawl, the number of websites hosted by each server and then start work.
They visit each website and by using different techniques, they try to find out how many pages they have, whether it is text content, images, videos or any other format (CSS, HTML, javascript, etc).
When visiting a website, besides taking note of the number of pages they also follow any links (either pointing to pages within the site or to external websites), and thus they discover more and more pages.
They do this continuously and they also keep track of changes made to a website so that they know when new pages are added or deleted, when links are updated, etc.
If you take into account that there are more than 130 trillion individual pages on the Internet today and on average thousands of new pages are published on a daily basis, you can imagine that this is a lot of work.
Why care about the crawling process?
Your first concern when optimizing your website for search engines is to ensure that they can access it correctly otherwise if they cannot ‘read’ your website, you shouldn’t expect much in terms of high rankings or search engine traffic.
As explained above, crawlers have a lot of work to do and you should try and make their job easier.
There are a number of things to do to make sure that crawlers can discover and access your website in the fastest possible way without problems.
Step 2: Indexing
Crawling alone is not enough to build a search engine.
Information identified by the crawlers needs to be organized, sorted and stored so that it can be processed by the search engine algorithms before made available to the end-user.
This process is called Indexing.
Search engines don’t store all the information found on a page in their index but they keep things like: when it was created/updated, title and description of the page, type of content, associated keywords, incoming and outgoing links and a lot of other parameters that are needed by their algorithms.
Google likes to describe its index like the back of a book (a really big book).
Why care about the indexing process?
It’s very simple, if your website is not in their index, it will not appear for any searches.
This also implies that the more pages you have in the search engine indexes, the more are your chances of appearing in the search results when someone types a query.
Notice that I mentioned the word ‘appear in the search results’, which means in any position and not necessarily on the top positions or pages.
In order to appear in the first 5 positions of the SERPs (search engine results pages), you have to optimize your website for search engines using a process called Search Engine Optimization or SEO in short.
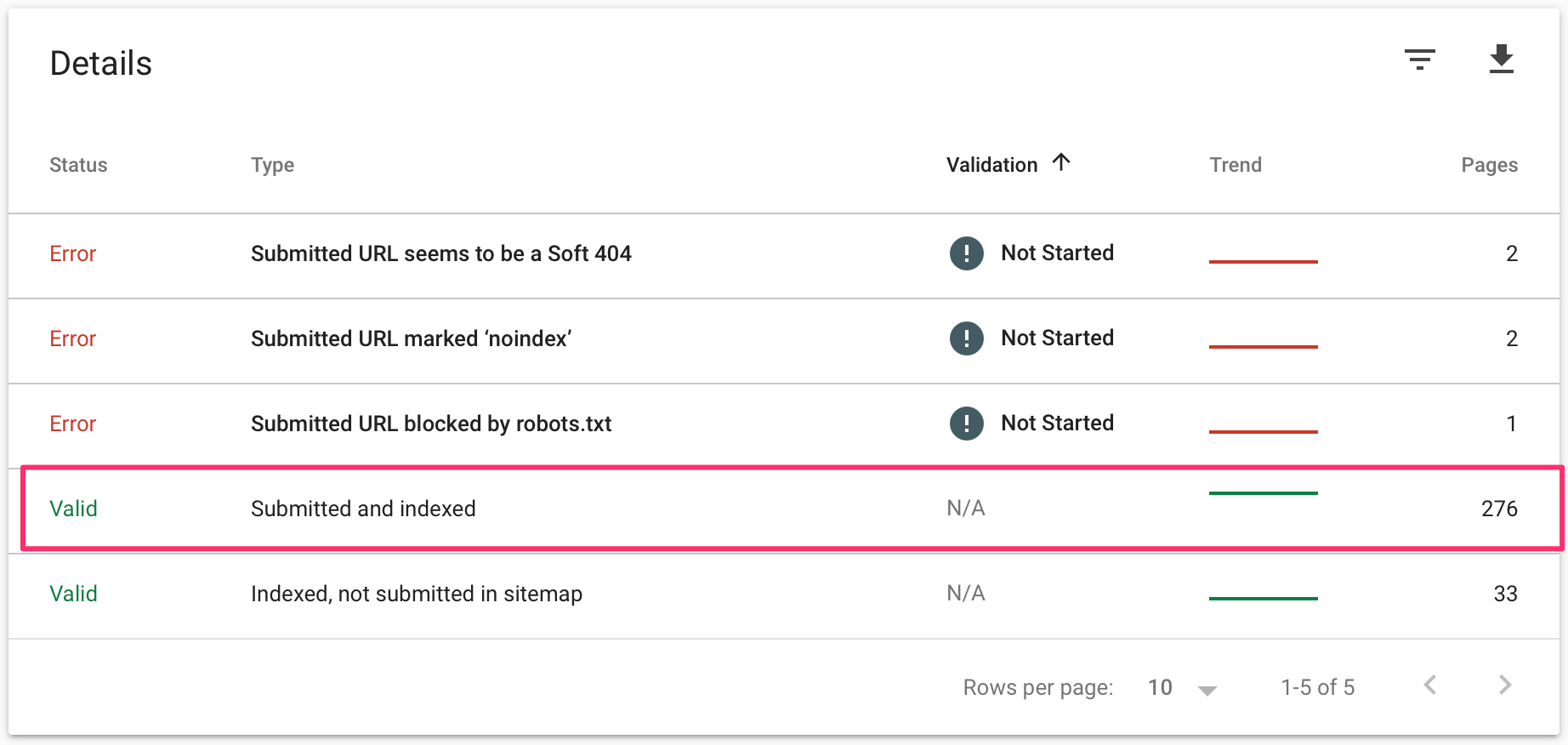
How to find how many pages of your website are included in the Google index?
There are two ways to do that.
Open Google and use the site operator followed by your domain name. For example site:reliablesoft.net. You will find out how many pages related to the particular domain are included in the Google Index.
The second way is to create a free Google Search Console account and add your website.
Then look at the Coverage report and in particular the VALID AND INDEXED pages.
Step 3: Ranking
Search Engine Ranking Algorithms
The third and final step in the process is for search engines to decide which pages to show in the SERPS and in what order when someone types a query.
This is achieved through the use of search engine ranking algorithms.
In simple terms, these are pieces of software that have a number of rules that analyze what the user is looking for and what information to return.
These rules and decisions are made based on what information is available in their index.
How do search engine algorithms work?
Over the years search engine ranking algorithms have evolved and became really complex.
At the beginning (think 2001) it was as simple as matching the user’s query with the title of the page but this is no longer the case.
Google’s ranking algorithm takes into account more than 255 rules before making a decision and nobody knows for sure what these rules are.
And this includes Larry Page and Sergey Brin (Google’s founders), who created the original algorithm.
Things have changed a lot and now machine learning and computer programs are responsible for making decisions based on a number of parameters that are outside the boundaries of the content found on a web page.
To make it easier to understand, here is a simplified process of how search engines ranking factors work:
Step 1: Analyze User Query
The first step is for search engines to understand what kind of information the user is looking for.
To do that, they analyze the user’s query (search terms) by breaking it down into a number of meaningful keywords.
A keyword is a word that has a specific meaning and purpose.
For example, when you type “How to make a chocolate cake”, search engines know from the words how-to that you are looking for instructions on how to make a chocolate cake and thus the returned results will contain cooking websites with recipes.
If you search for “Buy refurbished ….”, they know from the words buy and refurbished that you are looking to buy something and the returned results will include eCommerce websites and online shops.
Machine learning has helped them associate related keywords together. For example, they know that the meaning of this query “how to change a light bulb” is the same as this “how to replace a light bulb”.

They are also clever enough to interpret spelling mistakes, understand plurals and in general extract the meaning of a query from natural language (either written or verbal in case of Voice search).
Step 2: Finding matching pages
The second step is to look into their index and decide which pages can provide the best answer for a given query.
This is a very important stage in the whole process for both search engines and web owners.
Search engines need to return the best possible results in the fastest possible way so that they keep their users happy and web owners want their websites to be picked up so that they get traffic and visits.
This is also the stage where good SEO techniques can influence the decision made by the algorithms.
To give you an idea of how matching works, these are the most important factors:
Title and content relevancy – how relevant is the title and content of the page with the user query.
Type of content – if the user is asking for images, the returned results will contain images and not text.
Quality of the content – content needs to be thorough, useful and informative, unbiased, and cover both sites of a story.
Quality of the website – The overall quality of a website matters. Google will not show pages from websites that don’t meet their quality standards.
Date of publication – For news-related queries, Google wants to show the latest results so the date of publication is also taken into account.
The popularity of a page – This doesn’t have to do with how much traffic a website has but how other websites perceive the particular page.
A page that has a lot of references (backlinks), from other websites is considered to be more popular than other pages with no links and thus has more chances in getting picked up by the algorithms. This process is also known as Off-Page SEO.
Language of the page – Users are served pages in their language and it’s not always English.
Webpage Speed – Websites that load fast (think 2-3 seconds) have a small advantage compared to websites that are slow to load.
Device Type – Users searching on mobile are served mobile-friendly pages.
Location – Users searching for results in their area i.e. “Italian restaurants in Ohio” will be shown results related to their location.
That’s just the tip of the iceberg. As mentioned before, Google uses more than 255 factors in their algorithms to ensure that its users are happy with the results they get.
Why care how search engine ranking algorithms work?
In order to get traffic from search engines, your website needs to appear in the top positions on the first page of the results.
It is statistically proven that the majority of users click one of the top 5 results (both desktop and mobile).
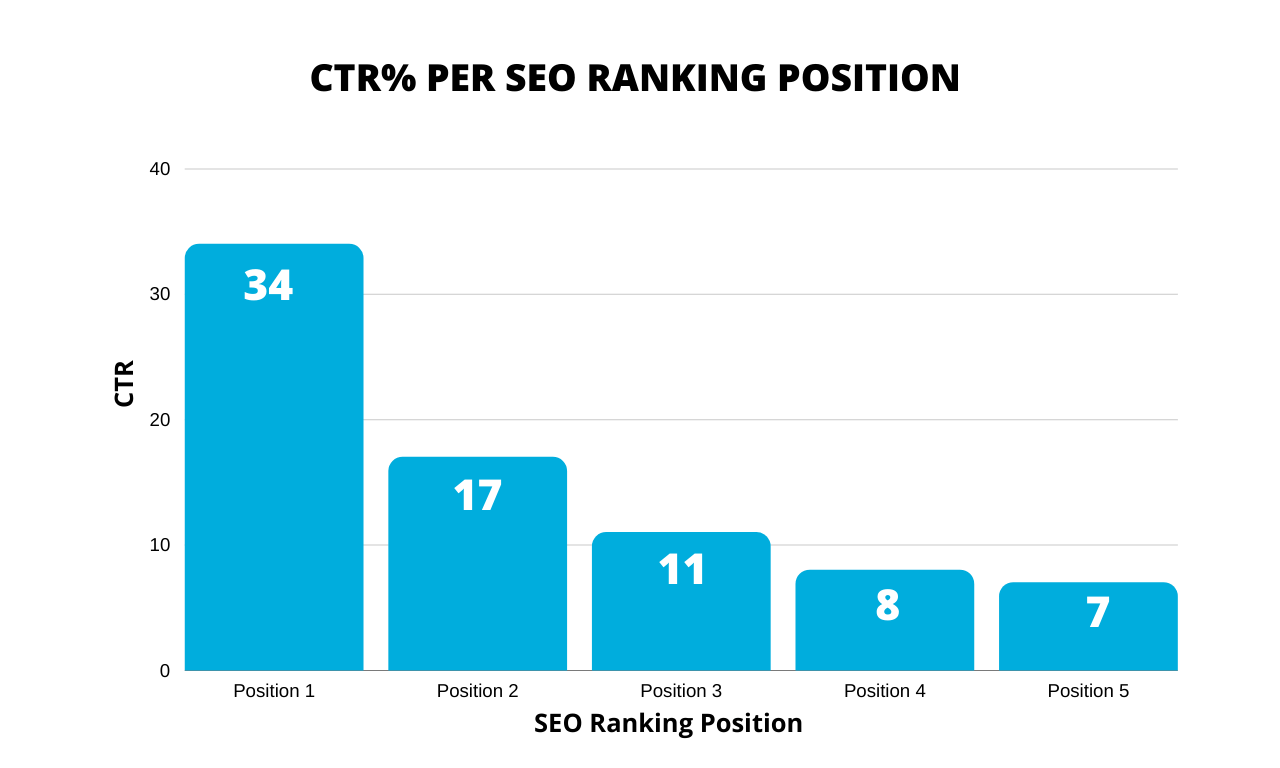
Appearing on the second or third page of the results will not get you any traffic at all.
Traffic is just one of the benefits of SEO, once you get to the top positions for keywords that make sense for your business, the added benefits are much more.
Knowing how search engines work can help you adjust your website and increase your rankings and traffic.
Conclusion
Search engines have become very complex computer programs. Their interface may be simple but the way they work and make decisions is far from simple.
The process starts with crawling and indexing. During this phase, the search engine crawlers gather as much information as possible for all the websites that are publicly available on the Internet.
They discover, process, sort, and store this information in a format that can be used by search engine algorithms to make a decision and return the best possible results back to the user.
The amount of data they have to digest is enormous and the process is completely automated. Human intervention is only done in the process of designing the rules to be used by the various algorithms but even this step is gradually being replaced by computers through the help of artificial intelligence.
As a webmaster, your job is to make their crawling and indexing job easier by creating websites that have a simple and straightforward structure.
Once they can “read” your website without issues, you then need to ensure that you give them the right signals to help their search ranking algorithms, pick your website when a user types a relevant query (that’s SEO).
Getting a tiny share of the overall search engine traffic is enough to build a successful online business.
Alex Chris is a digital marketing consultant, author, and instructor. He has more than 18 years of practical experience with SEO and digital marketing. Alex holds an MSc Degree in eCommerce and has consulted with Fortune 500 companies in different industries. He blogs regularly about SEO and Digital marketing, and his work has been referenced by leading marketing websites. Connect with Alex on Twitter and LinkedIn.
How Do Search Engines Work In 2022? What You Need To Know
Updated on Aug 09, 2022
Search engines work by simply crawling billions of pages using the web crawlers they have developed. These are commonly referred to as search engine spiders or bots. A search engines spider then navigates the web by following links on a new web page it discovers to find new pages and so forth.

But understanding how search engines work is paramount!
Why?
Because you need to know how the system works in order to try and leverage it!
You can’t fix a car’s engine problem without knowing what’s going on under the hood…
… and the same rules apply for all search engines.
But, you don’t need to know everything about search engine algorithms either.
I’m going to take you through how search engines work step by step. Let’s start with the search engine essentials to lay the foundation for a successful SEO career.
What Will I Learn?
How Google Works & How They Rank Your Page
Google’s search engine works around these two main functions:
Crawling and Indexing
We will be looking at these in more detail in a moment.
Search engines use their own search algorithms, so if you appear in the top positions in the search engine results page for one search engine this doesn’t necessarily mean you will for all search engines.
Some place a heavy focus on content quality, others user experience and others link building. Understanding what the search engine wants is critical to your success in the SERPs. We’ll look closer at this shortly. But for now, understand that:
Google is the pioneer of many techniques you will see in this guide.
As you can see Google dominates the search engine world. But how does the search engine we all know and love function?
It’s actually pretty simple and happens in a 2 stage process-
On a basic level, think of it like someone creating a huge library of books.
The only difference between a library and Google – is that Google has billions of books.
What Is Crawling?
When you enter a search query in the search engine, you might assume that Google hunts through the entire world wide web in that moment.
What’s really happening is that the search engine web crawler has compiled a huge database of pages and you are searching that database, NOT the entire world wide web.
The database is made up of pre-approved websites that Google has checked over and deemed safe for its users. So you won’t find anything dodgy from the ‘dark web’ for your search query when using Google.
Why does Google do this?
- It can access this database reliably It provides a quicker and more user-friendly experience It allows Google to add its own “tags” to these pages and provide relevant results
These web crawlers have 2x jobs-
- Find new web pages to index Scrape information about each web page
But how do they find websites, get access and recover that information? Well, it’s not actually as complex as you might think…
How Does A Crawler Work?
All websites are part of a network called the World Wide Web which is basically like a huge spider web spread all over the world.
The only difference is the world wide web is held together by links (also known as hyperlinks or backlinks).
And search engine crawlers (or spiders) use these links to travel around the web and discover new content!
Once web crawlers find a new page, they start reading all of the content and code of the page.
In the ideal world, we want the code to be as easy as possible for Google to interpret and understand. Which is where a website owner will perform SEO (search engine optimization).
The crawling process isn’t human-manned and each web crawler works autonomously (using machine learning from the search engine algorithm) to decide whether pages they find should be added to the Google index or not.
For example:
Crawlers know that sites where you can buy guns and drugs shouldn’t be added to their database.
But once a web crawler has decided that a page should be added to the database, it’s time for a site to enter the second stage of the process – indexing.
What Is Indexing?
Once a website has been crawled, it’s time to for it to be added to the database.
Indexing is where a search engine files away what’s been found and “tags” it.
(It’s a little more complex than that, but tagging works for now).
Think of it in terms of the library example I gave earlier:
If a box of assorted books is dropped off at a library, they will be organised, tagged and placed into their relevant sections-
- Crime Fantasy Reference Biographies
Let’s say you’re interested in learning French verbs.
You might go along to Google and enter the search query “French verb list”.
The search engine will search its database for the pages that match that search term:
(in a matter of seconds)
(Note: To complete more specific research, you can also exclude words from Google search to find exactly what you want quickly).
There is a range of factors that determine why those pages show up in that order.
These factors vary depending on the search engine you’re using for example Amazon’s ranking factors are very different to Google’s (more on that later).
First, just understand that the “indexing” process is fluid and as websites grow/add new content/delete new content – it will be re-crawled and re-indexed to provide relevant results for the search queries.
You can get your web page indexed quicker by submitting your XML sitemap to Google Search Console.
Why Do Some Pages Show Up Higher Than Others?
As I briefly mentioned earlier, search engines (also called search platforms) work on an algorithm that determines the order the pages appear.
That’s a series of equations that are based on different factors that help the computer decide where each piece of content should rank.
With Google, the simplest way I can explain it is through the concept of voting. In its very basic essence, the more “votes” a website has – the higher it ranks.
Let me explain it in more detail with a live example. If you wanted to learn how to make money through Fiverr, it’s likely you would enter a search query like this in Google-
And you’ll find is that lots of web pages show up. But there is one at the top.
That means of all the pages that relate to that topic, my site has the “most votes”
But how do websites get these “votes”?
Well… “Votes” are otherwise known as backlinks (or external links) meaning that when one website links to another website, they are essentially “voting” for it.
For example Niche Pursuits voted for my article when they linked to it-
But that’s not the only vote/backlink that page has.
It also has votes/backlinks from 83 other websites-
And for the most part it’s these votes/backlinks that are driving the number #1 position in the search engine rankings.
BUT!
It’s not quite as simple as that because not all “votes/backlinks” are created equal. The bigger the site and the more well known it is, the more weight their “vote” carries.
If you were to get a link from a big media outlet like The New York Times or The Guardian, it would carry significantly more weight than a link for a brand new unestablished blog.
I’ll show you how all of these pieces together later. But for now:
Remember that in general the more “votes” a page has, the better and that not all “votes” are created equal.
Stuck in the Google sandbox period? Read my guide to learn how to get out of Google sandbox as quickly as possible.
How Other Search Engines Work And How They Differ

Many “web” search engines use (like Bing) similar search engine algorithms.
They will crawl and index web pages to use in their search results.
BUT they each have different ranking factors to consider which I will talk about in a minute.
Because there are also other types of search engines you should be aware of like-
How Search Engines Work: Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking
The Beginner’s Guide to SEO
Previous
How Search Engines Work: Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking
As we mentioned in Chapter 1, search engines are answer machines. They exist to discover, understand, and organize the internet’s content in order to offer the most relevant results to the questions searchers are asking.
In order to show up in search results, your content needs to first be visible to search engines. It’s arguably the most important piece of the SEO puzzle: If your site can’t be found, there’s no way you’ll ever show up in the SERPs (Search Engine Results Page).
How do search engines work?
Search engines work through three primary functions:
What is search engine crawling?
Crawling is the discovery process in which search engines send out a team of robots (known as crawlers or spiders) to find new and updated content. Content can vary — it could be a webpage, an image, a video, a PDF, etc. — but regardless of the format, content is discovered by links.
What’s that word mean?
Googlebot starts out by fetching a few web pages, and then follows the links on those webpages to find new URLs. By hopping along this path of links, the crawler is able to find new content and add it to their index called Caffeine — a massive database of discovered URLs — to later be retrieved when a searcher is seeking information that the content on that URL is a good match for.
What is a search engine index?
Search engines process and store information they find in an index, a huge database of all the content they’ve discovered and deem good enough to serve up to searchers.
Search engine ranking
When someone performs a search, search engines scour their index for highly relevant content and then orders that content in the hopes of solving the searcher’s query. This ordering of search results by relevance is known as ranking. In general, you can assume that the higher a website is ranked, the more relevant the search engine believes that site is to the query.
It’s possible to block search engine crawlers from part or all of your site, or instruct search engines to avoid storing certain pages in their index. While there can be reasons for doing this, if you want your content found by searchers, you have to first make sure it’s accessible to crawlers and is indexable. Otherwise, it’s as good as invisible.
By the end of this chapter, you’ll have the context you need to work with the search engine, rather than against it!
In SEO, not all search engines are equal
Crawling: Can search engines find your pages?
As you’ve just learned, making sure your site gets crawled and indexed is a prerequisite to showing up in the SERPs. If you already have a website, it might be a good idea to start off by seeing how many of your pages are in the index. This will yield some great insights into whether Google is crawling and finding all the pages you want it to, and none that you don’t.
One way to check your indexed pages is «site:yourdomain.com», an advanced search operator. Head to Google and type «site:yourdomain.com» into the search bar. This will return results Google has in its index for the site specified:
The number of results Google displays (see “About XX results” above) isn’t exact, but it does give you a solid idea of which pages are indexed on your site and how they are currently showing up in search results.
For more accurate results, monitor and use the Index Coverage report in Google Search Console. You can sign up for a free Google Search Console account if you don’t currently have one. With this tool, you can submit sitemaps for your site and monitor how many submitted pages have actually been added to Google’s index, among other things.
If you’re not showing up anywhere in the search results, there are a few possible reasons why:
Tell search engines how to crawl your site
If you used Google Search Console or the “site:domain.com” advanced search operator and found that some of your important pages are missing from the index and/or some of your unimportant pages have been mistakenly indexed, there are some optimizations you can implement to better direct Googlebot how you want your web content crawled. Telling search engines how to crawl your site can give you better control of what ends up in the index.
See which pages Google can crawl with Moz Pro
Moz Pro can identify issues with your site’s crawlability, from critical crawler issues that block Google to content issues that impact rankings. Take a free trial and start fixing issues today:
Most people think about making sure Google can find their important pages, but it’s easy to forget that there are likely pages you don’t want Googlebot to find. These might include things like old URLs that have thin content, duplicate URLs (such as sort-and-filter parameters for e-commerce), special promo code pages, staging or test pages, and so on.
To direct Googlebot away from certain pages and sections of your site, use robots.txt.
Robots.txt
Robots.txt files are located in the root directory of websites (ex. yourdomain.com/robots.txt) and suggest which parts of your site search engines should and shouldn’t crawl, as well as the speed at which they crawl your site, via specific robots.txt directives.
How Googlebot treats robots.txt files
Optimize for crawl budget!
Not all web robots follow robots.txt. People with bad intentions (e.g., e-mail address scrapers) build bots that don’t follow this protocol. In fact, some bad actors use robots.txt files to find where you’ve located your private content. Although it might seem logical to block crawlers from private pages such as login and administration pages so that they don’t show up in the index, placing the location of those URLs in a publicly accessible robots.txt file also means that people with malicious intent can more easily find them. It’s better to NoIndex these pages and gate them behind a login form rather than place them in your robots.txt file.
You can read more details about this in the robots.txt portion of our Learning Center.
Defining URL parameters in GSC
Some sites (most common with e-commerce) make the same content available on multiple different URLs by appending certain parameters to URLs. If you’ve ever shopped online, you’ve likely narrowed down your search via filters. For example, you may search for “shoes” on Amazon, and then refine your search by size, color, and style. Each time you refine, the URL changes slightly:
How does Google know which version of the URL to serve to searchers? Google does a pretty good job at figuring out the representative URL on its own, but you can use the URL Parameters feature in Google Search Console to tell Google exactly how you want them to treat your pages. If you use this feature to tell Googlebot “crawl no URLs with ____ parameter,” then you’re essentially asking to hide this content from Googlebot, which could result in the removal of those pages from search results. That’s what you want if those parameters create duplicate pages, but not ideal if you want those pages to be indexed.
Can crawlers find all your important content?
Now that you know some tactics for ensuring search engine crawlers stay away from your unimportant content, let’s learn about the optimizations that can help Googlebot find your important pages.
Sometimes a search engine will be able to find parts of your site by crawling, but other pages or sections might be obscured for one reason or another. It’s important to make sure that search engines are able to discover all the content you want indexed, and not just your homepage.
Ask yourself this: Can the bot crawl through your website, and not just to it?
Is your content hidden behind login forms?
If you require users to log in, fill out forms, or answer surveys before accessing certain content, search engines won’t see those protected pages. A crawler is definitely not going to log in.
Are you relying on search forms?
Robots cannot use search forms. Some individuals believe that if they place a search box on their site, search engines will be able to find everything that their visitors search for.
Is text hidden within non-text content?
Non-text media forms (images, video, GIFs, etc.) should not be used to display text that you wish to be indexed. While search engines are getting better at recognizing images, there’s no guarantee they will be able to read and understand it just yet. It’s always best to add text within the markup of your webpage.
Can search engines follow your site navigation?
Just as a crawler needs to discover your site via links from other sites, it needs a path of links on your own site to guide it from page to page. If you’ve got a page you want search engines to find but it isn’t linked to from any other pages, it’s as good as invisible. Many sites make the critical mistake of structuring their navigation in ways that are inaccessible to search engines, hindering their ability to get listed in search results.
Common navigation mistakes that can keep crawlers from seeing all of your site:
This is why it’s essential that your website has a clear navigation and helpful URL folder structures.
Do you have clean information architecture?
Information architecture is the practice of organizing and labeling content on a website to improve efficiency and findability for users. The best information architecture is intuitive, meaning that users shouldn’t have to think very hard to flow through your website or to find something.
Are you utilizing sitemaps?
A sitemap is just what it sounds like: a list of URLs on your site that crawlers can use to discover and index your content. One of the easiest ways to ensure Google is finding your highest priority pages is to create a file that meets Google’s standards and submit it through Google Search Console. While submitting a sitemap doesn’t replace the need for good site navigation, it can certainly help crawlers follow a path to all of your important pages.
If your site doesn’t have any other sites linking to it, you still might be able to get it indexed by submitting your XML sitemap in Google Search Console. There’s no guarantee they’ll include a submitted URL in their index, but it’s worth a try!
Are crawlers getting errors when they try to access your URLs?
Before you can do anything meaningful with the crawl error report, it’s important to understand server errors and «not found» errors.
4xx Codes: When search engine crawlers can’t access your content due to a client error
4xx errors are client errors, meaning the requested URL contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled. One of the most common 4xx errors is the “404 – not found” error. These might occur because of a URL typo, deleted page, or broken redirect, just to name a few examples. When search engines hit a 404, they can’t access the URL. When users hit a 404, they can get frustrated and leave.
5xx Codes: When search engine crawlers can’t access your content due to a server error
5xx errors are server errors, meaning the server the web page is located on failed to fulfill the searcher or search engine’s request to access the page. In Google Search Console’s “Crawl Error” report, there is a tab dedicated to these errors. These typically happen because the request for the URL timed out, so Googlebot abandoned the request. View Google’s documentation to learn more about fixing server connectivity issues.
Thankfully, there is a way to tell both searchers and search engines that your page has moved — the 301 (permanent) redirect.
Create custom 404 pages!
Say you move a page from example.com/young-dogs/ to example.com/puppies/. Search engines and users need a bridge to cross from the old URL to the new. That bridge is a 301 redirect.
| When you do implement a 301: | When you don’t implement a 301: | |
|---|---|---|
| Link Equity | Transfers link equity from the page’s old location to the new URL. | Without a 301, the authority from the previous URL is not passed on to the new version of the URL. |
| Indexing | Helps Google find and index the new version of the page. | The presence of 404 errors on your site alone don’t harm search performance, but letting ranking / trafficked pages 404 can result in them falling out of the index, with rankings and traffic going with them — yikes! |
| User Experience | Ensures users find the page they’re looking for. | Allowing your visitors to click on dead links will take them to error pages instead of the intended page, which can be frustrating. |
The 301 status code itself means that the page has permanently moved to a new location, so avoid redirecting URLs to irrelevant pages — URLs where the old URL’s content doesn’t actually live. If a page is ranking for a query and you 301 it to a URL with different content, it might drop in rank position because the content that made it relevant to that particular query isn’t there anymore. 301s are powerful — move URLs responsibly!
You also have the option of 302 redirecting a page, but this should be reserved for temporary moves and in cases where passing link equity isn’t as big of a concern. 302s are kind of like a road detour. You’re temporarily siphoning traffic through a certain route, but it won’t be like that forever.
Watch out for redirect chains!
Once you’ve ensured your site is optimized for crawlability, the next order of business is to make sure it can be indexed.
Indexing: How do search engines interpret and store your pages?
Once you’ve ensured your site has been crawled, the next order of business is to make sure it can be indexed. That’s right — just because your site can be discovered and crawled by a search engine doesn’t necessarily mean that it will be stored in their index. In the previous section on crawling, we discussed how search engines discover your web pages. The index is where your discovered pages are stored. After a crawler finds a page, the search engine renders it just like a browser would. In the process of doing so, the search engine analyzes that page’s contents. All of that information is stored in its index.
Read on to learn about how indexing works and how you can make sure your site makes it into this all-important database.
Can I see how a Googlebot crawler sees my pages?
Yes, the cached version of your page will reflect a snapshot of the last time Googlebot crawled it.
Google crawls and caches web pages at different frequencies. More established, well-known sites that post frequently like https://www.nytimes.com will be crawled more frequently than the much-less-famous website for Roger the Mozbot’s side hustle, http://www.rogerlovescupcakes. (if only it were real…)
You can view what your cached version of a page looks like by clicking the drop-down arrow next to the URL in the SERP and choosing «Cached»:
You can also view the text-only version of your site to determine if your important content is being crawled and cached effectively.
Are pages ever removed from the index?
Yes, pages can be removed from the index! Some of the main reasons why a URL might be removed include:
If you believe that a page on your website that was previously in Google’s index is no longer showing up, you can use the URL Inspection tool to learn the status of the page, or use Fetch as Google which has a «Request Indexing» feature to submit individual URLs to the index. (Bonus: GSC’s “fetch” tool also has a “render” option that allows you to see if there are any issues with how Google is interpreting your page).
Tell search engines how to index your site
Robots meta directives
Meta directives (or «meta tags») are instructions you can give to search engines regarding how you want your web page to be treated.
You can tell search engine crawlers things like «do not index this page in search results» or «don’t pass any link equity to any on-page links». These instructions are executed via Robots Meta Tags in the of your HTML pages (most commonly used) or via the X-Robots-Tag in the HTTP header.
Robots meta tag
The robots meta tag can be used within the of the HTML of your webpage. It can exclude all or specific search engines. The following are the most common meta directives, along with what situations you might apply them in.
index/noindex tells the engines whether the page should be crawled and kept in a search engines’ index for retrieval. If you opt to use «noindex,» you’re communicating to crawlers that you want the page excluded from search results. By default, search engines assume they can index all pages, so using the «index» value is unnecessary.
follow/nofollow tells search engines whether links on the page should be followed or nofollowed. “Follow” results in bots following the links on your page and passing link equity through to those URLs. Or, if you elect to employ «nofollow,» the search engines will not follow or pass any link equity through to the links on the page. By default, all pages are assumed to have the «follow» attribute.
noarchive is used to restrict search engines from saving a cached copy of the page. By default, the engines will maintain visible copies of all pages they have indexed, accessible to searchers through the cached link in the search results.
Here’s an example of a meta robots noindex, nofollow tag:
This example excludes all search engines from indexing the page and from following any on-page links. If you want to exclude multiple crawlers, like googlebot and bing for example, it’s okay to use multiple robot exclusion tags.
Meta directives affect indexing, not crawling
X-Robots-Tag
The x-robots tag is used within the HTTP header of your URL, providing more flexibility and functionality than meta tags if you want to block search engines at scale because you can use regular expressions, block non-HTML files, and apply sitewide noindex tags.
For example, you could easily exclude entire folders or file types (like moz.com/no-bake/old-recipes-to-noindex):
Or specific file types (like PDFs):
For more information on Meta Robot Tags, explore Google’s Robots Meta Tag Specifications.
WordPress tip:
Understanding the different ways you can influence crawling and indexing will help you avoid the common pitfalls that can prevent your important pages from getting found.
Ranking: How do search engines rank URLs?
How do search engines ensure that when someone types a query into the search bar, they get relevant results in return? That process is known as ranking, or the ordering of search results by most relevant to least relevant to a particular query.
To determine relevance, search engines use algorithms, a process or formula by which stored information is retrieved and ordered in meaningful ways. These algorithms have gone through many changes over the years in order to improve the quality of search results. Google, for example, makes algorithm adjustments every day — some of these updates are minor quality tweaks, whereas others are core/broad algorithm updates deployed to tackle a specific issue, like Penguin to tackle link spam. Check out our Google Algorithm Change History for a list of both confirmed and unconfirmed Google updates going back to the year 2000.
Why does the algorithm change so often? Is Google just trying to keep us on our toes? While Google doesn’t always reveal specifics as to why they do what they do, we do know that Google’s aim when making algorithm adjustments is to improve overall search quality. That’s why, in response to algorithm update questions, Google will answer with something along the lines of: «We’re making quality updates all the time.» This indicates that, if your site suffered after an algorithm adjustment, compare it against Google’s Quality Guidelines or Search Quality Rater Guidelines, both are very telling in terms of what search engines want.
What do search engines want?
Search engines have always wanted the same thing: to provide useful answers to searcher’s questions in the most helpful formats. If that’s true, then why does it appear that SEO is different now than in years past?
Think about it in terms of someone learning a new language.
At first, their understanding of the language is very rudimentary — “See Spot Run.” Over time, their understanding starts to deepen, and they learn semantics — the meaning behind language and the relationship between words and phrases. Eventually, with enough practice, the student knows the language well enough to even understand nuance, and is able to provide answers to even vague or incomplete questions.
When search engines were just beginning to learn our language, it was much easier to game the system by using tricks and tactics that actually go against quality guidelines. Take keyword stuffing, for example. If you wanted to rank for a particular keyword like “funny jokes,” you might add the words “funny jokes” a bunch of times onto your page, and make it bold, in hopes of boosting your ranking for that term:
Welcome to funny jokes! We tell the funniest jokes in the world. Funny jokes are fun and crazy. Your funny joke awaits. Sit back and read funny jokes because funny jokes can make you happy and funnier. Some funny favorite funny jokes.
This tactic made for terrible user experiences, and instead of laughing at funny jokes, people were bombarded by annoying, hard-to-read text. It may have worked in the past, but this is never what search engines wanted.