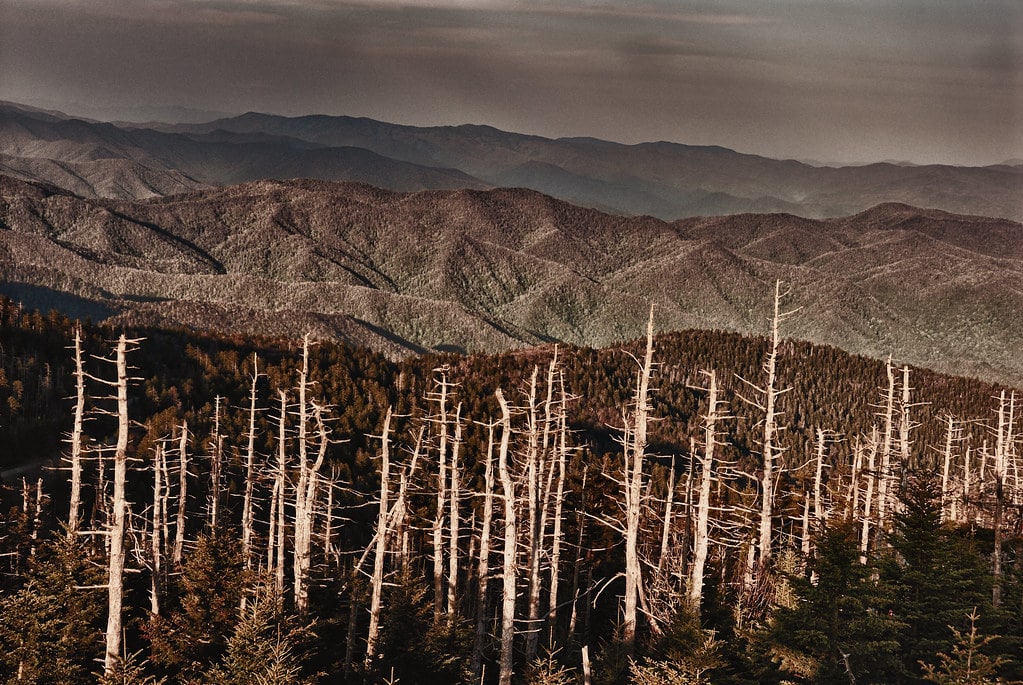
How does acid rain affect our environment
How does acid rain affect our environment
Acid rain: Causes, effects and solutions
How acid rain affects nearly everything it touches, and what we can do about it.
Acid rain, or acid deposition, is a broad term that includes any form of precipitation that contains acidic components, such as sulfuric acid or nitric acid. The precipitation is not necessarily wet or liquid; the definition includes dust, gases, rain, snow, fog and hail. The type of acid rain that contains water is called wet deposition. Acid rain formed with dust or gases is called dry deposition.
The precipitation is not necessarily wet or liquid; the definition includes dust, gasses, rain, snow, fog and hail. The type of acid rain that contains water is called wet deposition. Acid rain formed with dust or gasses is called dry deposition.
Causes of acid rain
In the 1950s, scientists in the United States started studying the phenomenon, and in the 1960s and early 1970s, acid rain became recognized as a regional environmental issue that affected Western Europe and eastern North America.
Though manmade pollutants are currently affecting most acidic precipitation, natural disasters can be a factor as well. For example, volcanoes can cause acid rain by blasting pollutants into the air. These pollutants can be carried around the world in jet streams and turned into acid rain far from the volcano. After an asteroid supposedly wiped out the dinosaurs 65.5 million years ago, sulfur trioxide was blasted into the air. When it hit the air, it turned into sulfuric acid, generating a downpour of acid rain.
Even before that, over 4 billion years ago, it is suspected that the air may have had 10,000 times as much carbon dioxide as today. Geologists from the University of Wisconsin-Madison backed up this theory by studying rocks and publishing the results in a 2008 issue of the journal Earth and Planetary Science Letters. «At [those levels of carbon dioxide], you would have had vicious acid rain and intense greenhouse [effects]. That is a condition that will dissolve rocks,» said study team member John Valley.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) released into the air by fossil-fuel power plants, vehicles and oil refineries are the biggest cause of acid rain today, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (opens in new tab) (EPA). Two thirds of sulfur dioxide and one fourth of nitrogen oxide found in the atmosphere come from electric power generators.
A chemical reaction happens when sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides mix with water, oxygen and other chemicals in the air. They then become sulfuric and nitric acids that mix with precipitation and fall to the ground. Precipitation is considered acidic when its pH level is about 5.2 or below. The normal pH of rain is around 5.6.
Environmental affects of acid rain
Acid rain affects nearly everything. Plants, soil, trees, buildings and even statues can be transformed by the precipitation.
Acid rain has been found to be very hard on trees. It weakens them by washing away the protective film on leaves, and it stunts growth. A United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA (opens in new tab) ) study showed that acid rain is particularly hard on trees.
«By providing the only preserved soil in the world collected before the acid rain era, the Russians helped our international team track tree growth for the first time with changes in soil from acid rain,» said Greg Lawrence, a U.S. Geological Survey scientist. «We’ve known that acid rain acidifies surface waters, but this is the first time we’ve been able to compare and track tree growth in forests that include soil changes due to acid rain.»
It can additionally deteriorate limestone and marble buildings and monuments, like gravestones.
Solutions and prevention
There are several solutions to stopping human-caused acid rain. Regulating the emissions coming from vehicles and buildings is an important step, according to the EPA. This can be done by restricting the use of fossil fuels and focusing on more renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power.
Also, each person can do their part by reducing their vehicle use. Using public transportation, walking, riding a bike or carpooling is a good start, according to the EPA. People can also reduce their use of electricity, which is widely created with fossil fuels, or switch to a solar plan. Many electricity companies offer solar packages to their customers that require no installation and low costs.
Additional resources
Effects of Acid Rain
The Effects of Acid Rain on Ecosystems
An ecosystem is a community of plants, animals and other organisms along with their environment including the air, water and soil. Everything in an ecosystem is connected. If something harms one part of an ecosystem – one species of plant or animal, the soil or the water – it can have an impact on everything else.
Effects of Acid Rain on Fish and Wildlife
The ecological effects of acid rain are most clearly seen in aquatic environments, such as streams, lakes, and marshes where it can be harmful to fish and other wildlife. As it flows through the soil, acidic rain water can leach aluminum from soil clay particles and then flow into streams and lakes. The more acid that is introduced to the ecosystem, the more aluminum is released.
Some types of plants and animals are able to tolerate acidic waters and moderate amounts of aluminum. Others, however, are acid-sensitive and will be lost as the pH declines. Generally, the young of most species are more sensitive to environmental conditions than adults. At pH 5, most fish eggs cannot hatch. At lower pH levels, some adult fish die. Some acidic lakes have no fish. Even if a species of fish or animal can tolerate moderately acidic water, the animals or plants it eats might not. For example, frogs have a critical pH around 4, but the mayflies they eat are more sensitive and may not survive pH below 5.5.
Effects of Acid Rain on Plants and Trees
Dead or dying trees are a common sight in areas effected by acid rain. Acid rain leaches aluminum from the soil. That aluminum may be harmful to plants as well as animals. Acid rain also removes minerals and nutrients from the soil that trees need to grow.
At high elevations, acidic fog and clouds might strip nutrients from trees’ foliage, leaving them with brown or dead leaves and needles. The trees are then less able to absorb sunlight, which makes them weak and less able to withstand freezing temperatures.
Buffering Capacity
Many forests, streams, and lakes that experience acid rain don’t suffer effects because the soil in those areas can buffer the acid rain by neutralizing the acidity in the rainwater flowing through it. This capacity depends on the thickness and composition of the soil and the type of bedrock underneath it. In areas such as mountainous parts of the Northeast United States, the soil is thin and lacks the ability to adequately neutralize the acid in the rain water. As a result, these areas are particularly vulnerable and the acid and aluminum can accumulate in the soil, streams, or lakes.
Episodic Acidification
Melting snow and heavy rain downpours can result in what is known as episodic acidification. Lakes that do not normally have a high level of acidity may temporarily experience effects of acid rain when the melting snow or downpour brings greater amounts of acidic deposition and the soil can’t buffer it. This short duration of higher acidity (i.e., lower pH) can result in a short-term stress on the ecosystem where a variety of organisms or species may be injured or killed.
Nitrogen Pollution
It’s not just the acidity of acid rain that can cause problems. Acid rain also contains nitrogen, and this can have an impact on some ecosystems. For example, nitrogen pollution in our coastal waters is partially responsible for declining fish and shellfish populations in some areas. In addition to agriculture and wastewater, much of the nitrogen produced by human activity that reaches coastal waters comes from the atmosphere.
Effects of Acid Rain on Materials
Not all acidic deposition is wet. Sometimes dust particles can become acidic as well, and this is called dry deposition. When acid rain and dry acidic particles fall to earth, the nitric and sulfuric acid that make the particles acidic can land on statues, buildings, and other manmade structures, and damage their surfaces. The acidic particles corrode metal and cause paint and stone to deteriorate more quickly. They also dirty the surfaces of buildings and other structures such as monuments.
The consequences of this damage can be costly:
Other Effects of SO2 and NOX
Visibility
In the atmosphere, SO2 and NOX gases can be transformed into sulfate and nitrate particles, while some NOX can also react with other pollutants to form ozone. These particles and ozone make the air hazy and difficult to see through. This affects our enjoyment of national parks that we visit for the scenic view such as Shenandoah and the Great Smoky Mountains.
Human Health
Walking in acid rain, or even swimming in a lake affected by acid rain, is no more dangerous to humans than walking in normal rain or swimming in non-acidic lakes. However, when the pollutants that cause acid rain —SO2 and NOX, as well as sulfate and nitrate particles— are in the air, they can be harmful to humans.
SO2 and NOX react in the atmosphere to form fine sulfate and nitrate particles that people can inhale into their lungs. Many scientific studies have shown a relationship between these particles and effects on heart function, such as heart attacks resulting in death for people with increased heart disease risk, and effects on lung function, such as breathing difficulties for people with asthma.
Learn more about:
In addition, NO X emissions also contribute to ground level ozone, which is also harmful to human health.
Acid rain, explained
The fossil fuels that humans burn for energy can come back to haunt us as acid rain.
What is Acid Rain?
Acid rain describes any form of precipitation that contains high levels of nitric and sulfuric acids. It can also occur in the form of snow, fog, and tiny bits of dry material that settle to Earth. Normal rain is slightly acidic, with a pH of 5.6, while acid rain generally has a pH between 4.2 and 4.4.
Causes of acid rain
Rotting vegetation and erupting volcanoes release some chemicals that can cause acid rain, but most acid rain is a product of human activities. The biggest sources are coal-burning power plants, factories, and automobiles.
When humans burn fossil fuels, sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) are released into the atmosphere. Those air pollutants react with water, oxygen, and other substances to form airborne sulfuric and nitric acid. Winds may spread these acidic compounds through the atmosphere and over hundreds of miles. When acid rain reaches Earth, it flows across the surface in runoff water, enters water systems, and sinks into the soil.
A virtual tree graveyard of Norway spruce in Poland bears the scars of acid rain. Caused when rain droplets absorb air pollution like sulfur and nitrogen oxides, acid rain weakens trees by dissolving nutrients in the soil before plants can use them.
Effects of acid rain
Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are not primary greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming, one of the main effects of climate change; in fact, sulfur dioxide has a cooling effect on the atmosphere. But nitrogen oxides contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a major pollutant that can be harmful to people. Both gases cause environmental and health concerns because they can spread easily via air pollution and acid rain.
Acid rain has many ecological effects, especially on lakes, streams, wetlands, and other aquatic environments. Acid rain makes such waters more acidic, which results in more aluminum absorption from soil, which is carried into lakes and streams. That combination makes waters toxic to crayfish, clams, fish, and other aquatic animals. (Learn more about the effects of water pollution.)
Some species can tolerate acidic waters better than others. However, in an interconnected ecosystem, what affects some species eventually affects many more throughout the food chain, including non-aquatic species such as birds.
Acid rain and fog also damage forests, especially those at higher elevations. The acid deposits rob the soil of essential nutrients such as calcium and cause aluminum to be released in the soil, which makes it hard for trees to take up water. Trees’ leaves and needles are also harmed by acids.
How Does Acid Rain Affect the Environment
Damage caused by acid rain has been well-documented leading to it being labelled as an environmental hazard. So, how does acid rain affect the environment? Here we examine how it alters Earth’s natural processes, and consider the types of damages to the living world that can occur as a result of these changes.
Acid rain can be defined as precipitation that is abnormally acidic due to it containing dissolved pollutants, which make it capable of causing great environmental harm. Typical rain will have a pH of around 5.5 whereas the pH of acid rain is much lower at around 4.0 due to it containing dissolved sulphur dioxide or nitrogen oxides, which are acidic pollutants.
How Does Acid Rain Affect the Atmosphere
We believe in Compassionate Humanity
We believe in One Planet Thriving
We love our Home
The majority of the emissions of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides come from human activities such as burning of fossil fuels or vehicle exhaust fumes. However, a small fraction of emissions exist from natural processes such as decaying vegetation and volcanic activity.
These emissions of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide diffuse into the atmosphere and dissolve in water droplets in clouds forming sulphuric acid and nitric acid respectfully. Clouds containing these acidic droplets can then be transported by winds before precipitation occurs, creating acid rain through a process known as wet deposition. Alternatively, some of the pollutant particles may not become dissolved in cloud water to form acid rain so instead return to Earth’s surface through dry deposition.
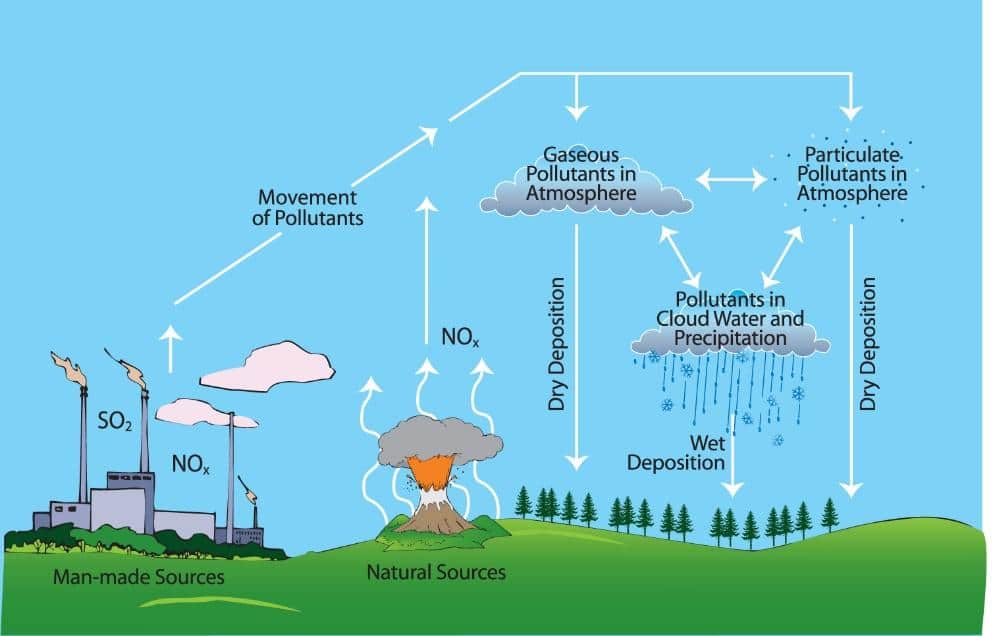
How Does Acid Rain Affect the Water Cycle
After being released from clouds as precipitation, acid rain reaches the Earth’s surface and a large fraction of it is transported to rivers and lakes through surface runoff or by groundwater flow. Here it mixes with the existing water and increases the acidity of the water body with this drop in pH being particularly dramatic when large volumes of rainfall enter a relatively small water body.
In addition to rainfall, acid rain can also be deposited from the atmosphere as acid snow when temperatures are cold enough. This form of acid deposition can be particularly devastating to the natural environment as it will accumulate on the ground before suddenly melting to release a large volume of acidic water into the surrounding landscape.
If you enjoyed learning how does acid rain affect the environment, you might also like: What are the Biggest Causes and Effects of Air Pollution?
How Does Acid Rain Affect Soil and Rock
Land surfaces that are made up of limestone rock are vulnerable to erosion from acid rain as the calcium carbonate in limestone reacts to the acidity, producing calcium sulphate or calcium nitrate which are both soluble products. The reaction releases carbon dioxide gases as well. Water will eventually transport the soluble products into river systems where the concentration of it may be high enough to cause damage to aquatic life. Additionally, carbon dioxide released from the reaction will enter the atmosphere where it will contribute to and exacerbate global warming.
The decrease in pH caused by the acid rain also impacts the concentration of different heavy metals that are present in the surrounding water. For example, a more acidic environment allows aluminium to be more readily released from the soil into the surrounding water whereas calcium becomes less readily available, so its concentration in the water is lower. The increase in concentration of some heavy metals in the water may make it toxic to sensitive aquatic organisms and equally, the reduction of some metals that may be crucial to an organism’s survival could have damaging effects on the ecosystem.
How Does Acid Rain Affect Plant Growth and Ecosystems
Living organisms suffer directly from acid rain falling in their habitat with species living in confined aquatic environments being particularly vulnerable as they cannot migrate to less acidic waters. Whilst some species have a high tolerance to acidic conditions, others cannot survive even very small changes in pH. For example, the increased acidity in several lochs in Galloway, Scotland in the 1900s led to the local extinction of several of the local fish populations.
The waxy outer layer of plant leaves can also become damaged by acid rain and the inability to photosynthesise efficiently makes the plant weak with an increased chance of mortality. The initial loss of key species in an ecosystem due to their high sensitivity to acid rain can result in the subsequent loss of further species who were dependent on the key species for their own survival, and this may result in the collapse of entire ecosystems.
Simulation of leaf damage that can be caused by acid rain. Source: Verónica et al. (2020)
How Does Acid Rain Affect Human Health
Acid rain and the pollutant particles of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide that it is formed from have been linked to human health problems including asthma, heart disease and eye irritation. In addition to forming acid rain, nitrogen oxides are also known to be involved in a reaction which creates tropospheric ozone which is known to cause respiratory problems in humans.
In answering the question on how does acid rain affect the environment, one will discover a whole host of environmental problems and impacts on humans. To prevent further damage from acid rain, it is important that we identify the main sources of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide pollution and cut these emissions to meet higher air quality standards. Cutting emissions from these polluting sectors such as electric utilities and vehicles requires cleaner technologies to be used which can scrub out the pollutant gases and prevent them from causing environmental damage.
22 Causes, Effects & Solutions for Acid Rain
“I have acid rain in my head and it’s killing the flowers in my heart.”
Acid Rain: Causes, Effects & Solutions
Acid rain can be defined as rain or any other kind of precipitation that is unusually acidic, which means that it has higher levels of hydrogen and thus a lower pH-score.
It is caused by emissions of nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide, which react with water molecules in the atmosphere and produce acid rain.
Acid rain has harmful effects on the environment, especially on aquatic animals and plants. It has also shown damaging effects on freshwaters, soils and insects.
Please enable JavaScript
Moreover, also humans are adversely affected since acid rain causes corrosion of steel structures (e.g. bridges) and the weathering of statues and stone buildings.
Acid rain can also have a negative impact on human health.
Audio Lesson
Scientific Definition
“Acid rain” is defined as a mixture of wet and dry acidic components.
Distilled water has a neutral pH of 7 (once carbon dioxide is removed). Liquids with pH greater than 7 are alkaline, and those with a pH of less than 7 are acidic.
Unpolluted rain has an acidic pH between 5 and 5.5, the pH of acid rain is usually around 4.0.
The difference seems not to be that great.
However, a drop from 5 to 4 on the pH-scale means that acid rain is 10-times more acid than normal rain.
Forms of Acid Rain
Acid rain can manifest in two forms, wet and dry deposition.
Wet deposition occurs when any form of precipitation like snow, rain, etc. removes acids from the atmosphere and delivers them to the surface of the earth.
This can be the result of the precipitation removing acids either in or below clouds or from the deposition of acids formed in raindrops.
Wet removal of both aerosols and gases both plays an important role in wet deposition.
Dry deposition occurs when gases and particles stick to the ground, plants or other surfaces.
Causes for Acid Rain
Natural Causes
The main source that naturally contributes to acid rain are emissions from volcanoes.
The emission of gases from volcanoes leads to an increase in the acidity level of rain, impacting the surrounding vegetation, wildlife and also humans in an adverse manner.
However, there are several other causes of acid rain, including gases produced by biological processes that occur in wetlands, oceans and on land.
This includes wildfires, lightning strikes and decaying vegetation.
Human activity
Apart from natural causes, human behavior plays a major role in the contribution to acid rain.
Sulfur and nitrogen are produced in big amounts in the process of generating electricity, for motor vehicles, for (animal) agriculture and in factories.
Acid rain does not only affect local areas, but also affects large surrounding regions.
Through winds and other weather conditions, acid rain is spread across whole countries and even across borders.
When the acid rain hits the ground, it reaches lakes, rivers and the groundwater.
Electricity generation
The generation of electricity through the use of coal and the resulting gaseous contamination is one of the biggest contributing factors for the emergence of acid rain.
Coal still is the most important substance when it comes to electricity production worldwide.
Especially since the industrial revolution period has happened, the demand for energy increased dramatically.
Another trend in our current century is the development of artificial intelligence and machine learning, which will lead to even more electricity demand in the future since in many jobs, machines will replace humans.
However, in the coal combustion process related to the production of electricity, large amounts of sulfur oxides enter the air, which reacts with water molecules in the atmosphere, eventually resulting in acid rain.
Vehicles
Especially high amounts of gases that lead to acid rain are also caused by the automotive industry and the resulting extensive number of cars and the corresponding traffic.
In our daily life, almost everyone owns one or even more cars.
The use of cars is considered the standard means of transportation of our society right now.
Even for small distances, people often use cars instead of just walking or using a bicycle.
This behavior leads to excessive traffic and therefore to an excessive amount of harmful gases that are emitted into the atmosphere.
These gases eventually return to the earth in the form of acid rain.
The phenomenon of acid rain is especially severe in areas that have a high population density compared to rural areas since the number of inhabitants usually positively correlates with the number of cars and therefore leads to more emissions and eventually to more acid rain.
Agriculture
Agriculture also plays an important role as a factor for acid rain.
On the one hand, farmers often use excessive amounts of fertilizers and pesticides in order to maximize their crop yields.
However, these substances can contain substances like nitrogen compounds which can eventually result in acid rain.
On the other hand, for the purpose of meat production, there is a vast number of farm animals worldwide which emit large quantities of harmful gases like methane, resulting in both in acid rain and also contributing to the global warming problem.
Industrial processes and consumption levels
In many industrial processes, harmful substances like nitrogen oxides or sulfur dioxides are released into the air.
Since our society always wants to have the newest clothes, technological items, cars and so on, our consumption levels exploded compared to 100 years ago.
Although we are able to afford many material things that our ancestors could not even have dreamed of, this consumption behavior also has a serious downside.
Higher levels of consumption also imply a higher level of air pollution, including the pollution with substances that cause acid rain.
Thus, industrial processes as a consequence of our high consumption levels play a major role in the acid rain debate.
Effects of Acid Rain
Effects on aquatic environments
When acid rain comes to the ground, it impacts all forms of water systems, including lakes, rivers and oceans.
Also, the groundwater system is eventually affected by acid rain. This leads to an overall drop in pH-levels in the entire water system.
If the pH level is below a certain threshold, it can harm or even kill a significant amount of water animals and plants.
Moreover, a low pH-score also diminishes the reproduction rate of water animals, since it can destroy fish eggs.
In the long run, acid rain can even lead to the extinction of certain water animals.
Effects on animals and plants
There is also an adverse effect of acid rain on many animals and plants.
Animals and plants need certain living conditions in order to survive.
If these living conditions are altered, they may be forced to move to other areas.
Acid rain leads to a change in these living conditions since it makes the soil more acid.
A higher level of acidity in the soil leads to a change in the growth behavior of plants.
Many plants need a stable pH-level in order to grow.
If the pH-level changes due to acid rain, the plants may no longer be able to grow.
Animals that eat these plants lose some of their natural food sources which may lead to a decrease in animal populations.
Effects on forests
Acid rain can also have harmful effects on forests and the associated vegetation.
Forests, like many plants, need a certain pH-level to grow in an optimal way.
If acidity levels are altered due to acid rain, trees may no longer be able to grow.
Moreover, the trees and the corresponding ecosystem are more vulnerable to insect destruction, diseases, and damages caused by extreme weather.
Thus, acid rain can have severe impacts on our forests and on the corresponding environmental system.
Effects on global warming
Since acid rain can lead to a degradation of forests, it can also indirectly contribute to the global warming problem.
Since trees are a natural storage space for CO2, dying forests are no longer able to store this harmful greenhouse gas.
If forests are dying off, they release the stored CO2 into the atmosphere and therefore contribute to the global warming issue.
Effects on soil
Due to the change in pH-levels of soil through acid rain, several processes of the soil are adversely affected.
This includes chemical composition, microorganisms and biological activities.
Microorganisms that are not able to adapt to the acidic conditions will simply die off which in turn has negative consequences for other processes building on microorganism activities.
Moreover, nutrients and minerals in the soil may be withdrawn from the soil.
Effects on vegetation cover
The negative effects of acid rain on vegetation cover are not at all surprising.
The vegetation cover is the first layer when the rain hits the ground.
Thus, the acidity can directly affect and harm this surface.
Especially affected are forests in high altitudes since they, in addition to rain, are also affected by clouds and fogs.
The effects on vegetation cover and thus on the related vegetation can be dramatic since the vegetation usually reacts quite sensitive to changes in pH-levels.
Forest and other plants may eventually die off because of the increased acidity levels.
Effects on buildings
Acid rain can be quite damaging to buildings.
In fact, especially for limestone buildings, acid rain is quite a problem since it can react with minerals and could lead to corrosion of the buildings.
Eventually, these building types will even decay from acid rain if no measures are taken against this process.
Effects on health
Acid rain can have adverse effects both on human as well as on environmental health.
Although there is no direct impact from acid rain on human health since it is too dilute to cause serious problems, one of the indirect causes of acid rain is that gases like nitrogen oxide or sulfur dioxide and certain derivatives can impact the visual visibility and thus cause traffic accidents.
Moreover, not acid rain but gaseous particles like nitrogen or sulfur can cause heart and lung problems.
Solutions to the Acid Rain Problem
Optimize fossil energy processes
Since a large fraction of our electricity supply comes from fossil fuels like gas, coal and oil, great amounts of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are produced which heavily contributes to acid rain.
While burning fuel mainly accounts for nitrogen emissions, burning coal is the main contributor to the emission of sulfur dioxide.
However, modern technology can mitigate this problem dramatically.
There are processes that can reduce gas emission by up to 95%.
Thus, there should be a great focus on research, including the use of artificial intelligence, in order to further reduce sulfur and nitrogen emissions in the future.
Transition to renewable energies
Another supplementary solution is the transition from fossil to renewable energies for the generation of electricity.
Some examples are geothermal, wind, solar or hydropower energy sources.
By abandoning the usage of coal, oil and gas, the nitrogen and sulfur emissions could be greatly reduced.
In order to accomplish a full transition to renewable energies, much effort should be put into research and development for renewable energy sources.
There should also be subsidies for companies that really make an impact on the transition process to renewable energies.
Confine the use of fertilizers and pesticides
Since the excessive use of pesticides and fertilizers lead to pollution with nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxides which in turn lead to acid rain, a reduction in the use of these substances may also mitigate the acid rain problem to a certain extent.
We have to make sure that farmers understand the problem of excessive fertilizer use and that they are also willing to change their practices to a more environmental-friendly and sustainable farming behavior.
Restoring environments
Damages caused by acid rain can often be fixed.
For example, there is a process called limed where lime is put in large amounts in rivers or lakes, thus increasing pH-levels.
However, this is associated with high costs and has to be executed repeatedly in order to sustain the pH-level at a moderate level.
Moreover, this is just a try to fight the symptoms.
Fighting the sources of nitrate and sulfur gases should be the primary effort in order to mitigate the acid rain problem.
Save energy
Everyone who is consuming energy should be aware that he contributes to the acid rain problem.
Thus, in order to mitigate this problem, we should save energy whenever possible.
There are so many possibilities to save energy in our daily lives.
This could include turning off lights when not needed or using public transport or even bicycles instead of cars.
Another measure would be not to use an elevator and walk instead if possible in your physical condition.
Thus, people can make their contribution in their daily lives to mitigate the acid rain problem.
Reduce consumption levels
Since the industrial revolution has taken place, our consumption levels skyrocketed.
Due to the use of machines and the resulting mass production, material goods became quite cheap and affordable for many people.
This may sound great at a first glance. However, our excessive consumption behavior also causes severe issues, also contributing to the acid rain problem.
Since for the production of material goods, large amounts of energy and resource have to be processed, also many harmful gases are released into the air, including nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide.
These substances are known to cause acid rain.
Moreover, also in our food production processes, elements that contribute to acid rain are produced.
Especially in the production process of meat, the livestock emits many harmful gases which contribute to global warming and also to acid rain.
Since our meat consumption levels are quite high at the moment, we also contribute to the acid rain issue through our meat consumption.
A reduction in meat consumption as well as a reduction in the consumption of material goods would therefore mitigate the acid rain issue to a certain extent.
Government regulations
As an additional step, governments and municipalities should support renewable energies and punish fossil energy use.
Thus, firms have a bigger financial incentive to enhance the process for the transition from fossil to renewable energies.
This will eventually lead to a reduction in the acid rain problem.
Moreover, not only industries but also private people should be rewarded if they behave in an ecologically senseful manner.
For example, governments could subsidize the price for public transport in order to give people an incentive to switch from using their car to using a train and thus save energy and stop pollution
Education
Another point related to the „convince others“ solution is the education of people.
This education has to start at an early stage in elementary school.
People have to grow up with a sense of what they are doing and how they are harming and also saving the environment.
When people learn this at an early stage, the likelihood that they also pay attention to their environmental behavior when they are adults increases drastically.
However, we also have to educate adults since many of them are not aware or don’t care about how their actions affect the acid rain problem.
We have to make sure that adults understand that their behavior has major influence on the life quality of their children in the future.
If people understand this, they are much more likely to save electricity and thus to contribute to a sustainable ecological future.
Convince others
Individual actions are a first part of solving the acid rain problem, but through convincing others to overthink their actions and raise their awareness regarding their energy consumption, an impact can be made in a much bigger way.
Convincing others to reduce energy consumption can lead to a state in which these convinced people convince other people and so on.
In the end, you can create a large circle of convinced people which can make a real impact on the consumption of energy.
Conclusion
Acid rain can be caused either by natural events or by human behavior.
Human behavior plays a much bigger role in the production of acid rain than natural events.
Acid rain can be a significant contributor to environmental decay.
Since it is spread broadly all over the globe through winds, clouds and fog, it impacts the whole ecological system in an adverse manner.
Water animals and plants can die if the pH-level is getting too low and the acidity therefore too high. Forests can suffer since they are also quite sensitives to changes in the pH-level.
Also, the vegetation cover and the soil can be harmed in a dramatic way.
In order to mitigate the issue of acid rain, on the one hand, we have to optimize the current production processes of oil, gas and coal.
On the other hand, we have to transit to renewable resources for the production of electricity in order to further reduce the emission of sulfur and nitrogen gases which cause acid rain.
From acid rain-affected areas can be partly restored by using lime to increase pH-levels.
However, this process is costly and has to be repeated.
To fight the cause, not only the symptoms of acid rain, we have to also make changes in our daily life behavior.
Our consumption of electricity is a major cause of the emergence of acid rain.
We have to decrease our energy demands in order to fight this issue on an individual level.
Moreover, convincing others to save energy is a powerful weapon against acid rain.
We have to make sure that people understand the problem and that they can pay their share by consuming less energy.
Through all these measures, the acid rain issue can be mitigated in an effective way and thus the environment can be protected against this acid enemy.
Sources
About the author
My name is Andreas and my mission is to educate people of all ages about our environmental problems and how everyone can make a contribution to mitigate these issues.
As I went to university and got my Master’s degree in Economics, I did plenty of research in the field of Development Economics.
After finishing university, I traveled around the world. From this time on, I wanted to make a contribution to ensure a livable future for the next generations in every part of our beautiful planet.
Wanna make a contribution to save our environment? Share it!




