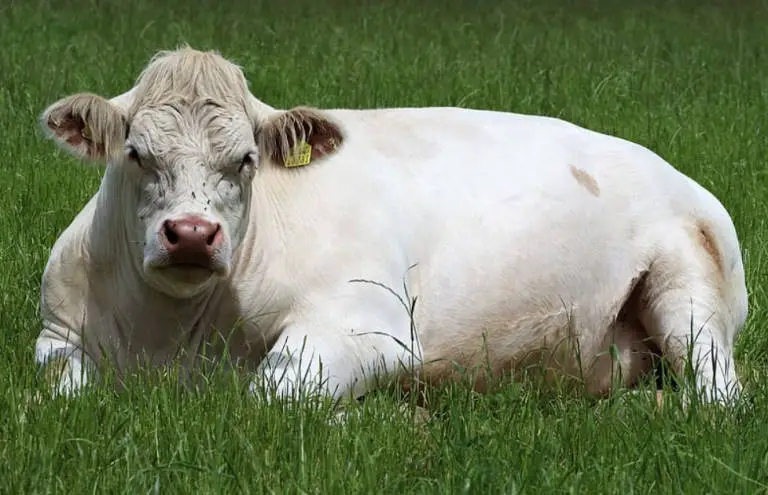
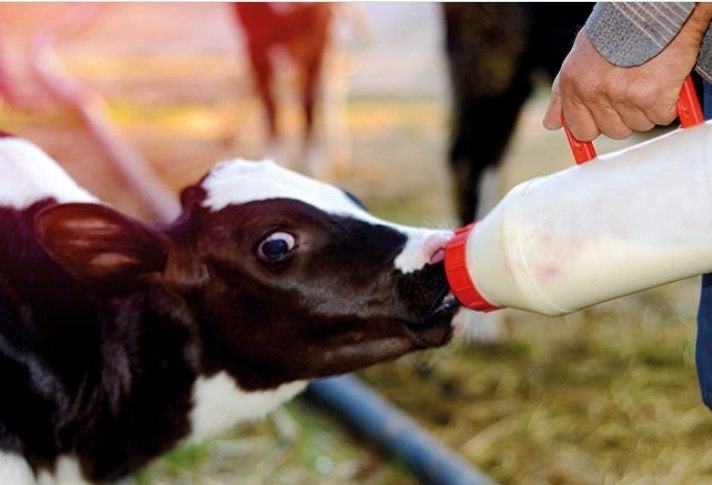
How long do cows live
How long do cows live
Cow Lifespan: How Long Do Cows Live?
Cows have a natural lifespan of 15 to 20 years. However, their lives, like those of other farm animals, are significantly shortened by the meat and dairy industries. Here, we’ll explore the subject of how long cows live and how this differs from non-consumption cows.
How Long Do Cows Live?
Absent farming needs, cows have a typical lifespan of 15 to 20 years. That lifespan could even understate their longevity. Guinness World Records lists the oldest cow as 48 years and nine months old.
Long-lived cattle can be found around the world. However, the dozens of millions of cattle being slaughtered each year mean that they rarely get to live out their full lives.
Dairy Cow Lifespan
At six years of age, or when it is no longer able to produce milk, dairy cows are often killed for meat. Dairy farmers put cows’ bodies through extreme strain, rendering them unable to stand or move in some situations. Because of this degradation, dairy cows’ meat is commonly used in lower-priced meat products such as ground beef.
The dairy and beef industries are inseparable, even though the two industries are unrelated. Dairy cows produced 21% of the commercially sold meat in the United States in 2018. Some cows are slain on dairy farms, not to be sold for human consumption.
Beef Cow Lifespan
Beef cattle live to around 2 to 3 years of age before they are slaughtered. Cattle from six months to one year are put to feedlots to be matured to market weight. Large feedlots produce 80-85% of the country’s cattle.
Some advocate slaughtering cows for meat at an older age. However, the argument poses severe ethical issues. For example, while delaying slaughter may lessen infanticide, it may also prolong factory farm suffering.
Calves Lifespan
Gender affects a calf’s longevity in agriculture. In the dairy sector, they sell female calves that can’t produce enough milk to be raised for meat. Many male calves are killed as soon as they are born because the firm deems them unprofitable. Others are “matured” to make veal or beef.
At three days old, calves can be taken from their mothers and placed in small hutches or cages known as “veal crates,” where they are kept in isolation. In turn, this slows muscle growth and yields the gray, delicate meat that veal producers seek. They are typically killed at 16 to 18 weeks. Calves are butchered in the United States at a rate of 700,000 per year.
Do Cows Make Good Pets?
Angusmclellan – Public Domain
Cows can make great pets! Oftentimes, people think of cows as animals that are used for meat and milk production on farms. Cows have more personality than most people realize, and many people maintain cows for their companionship.
Cows can be extremely affectionate and eager to meet new people. Even cows who have been abused in the past, time and patience can heal wounds and help them trust again. Cows are incredibly clever, emotional, and affectionate. It is common for cows to display their affection in a dog-like manner, such as following you around and licking your face, as well as allowing you to pet them.
How to Help Your Cow Live Longer
Because of their size and strength, cows require a lot of resources to survive, such as land, a place to hide from the rain, and food. Also, cows are far more sanitary than you may expect. Clean water, a well-maintained environment, and good grooming are all things that they need.
However, for those who have the resources, time, and patience to raise a simple and happy cow, here are some tips to help them live longer!
Ample Housing and Space
A single cow or calf doesn’t need expensive housing. You’ll be fine if you can build a simple box stall. Remember that cows prefer to graze and roam. You can’t have a cow as a pet if you live in the city or have a little yard. A couple of acres of fenced-in territory for the cow to wander, jump, play, and graze is essential. You must also maintain a sturdy fence. You don’t want to spend time chasing a cow around the neighborhood!
Lots of Clean Water
A cow can drink up to thirty gallons of water every day! This number rises in the summer and when a female is nursing. Plus, cows avoid dirty, frigid, or unclean water. You can’t keep a cow if you can’t supply clean, lukewarm water every day. If you own a property with a clean pond, this might suffice.
Plenty of Food to Graze
A cow’s stomach has four separate sections, so they spend most of their time consuming, regurgitating, and chewing grass all day. Cows still require hay and cow feed, even if they have plenty of grass to graze on. Store grains and hay in a clean, dry place free of dirt. Never give them rotting hay or grain.
Regular Grooming
Cows attract a lot of flies. Flies like to lay eggs in excrement, and cows have plenty of that around. Because flies also feed on their blood, they might spread diseases like anaplasmosis, a blood illness that can cause miscarriages and death in cattle. To keep these pests off your pets, you’ll need fly sprays and insecticides.
Cows’ hoofs also need trimming every few months. Dirty stalls can cause foot rot and other bacterial illnesses. This is a process that is best left to a professional farrier. A farrier is an expert in equine hoof care. A competent farrier should have all the tools needed to confine and trim cow hooves safely. A cow chute is also excellent for all cow care needs. This helps to alleviate stress and keep your cattle relaxed while you work on them.
How Long Do Cows Live on Your Homestead [Beef and Dairy 101]
Posted on Last updated: August 2, 2022
Outdoor Happens is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Click to learn more
All creatures who are born eventually die. There is no exception to the rule. The only variation lies in the time each species gets to walk on Earth. But – what about cows? How long do cows live naturally? Is there a difference between how long dairy cows live and beef cows? We’re about to answer all your questions about the average cattle lifespan.
You may be a farmer, wondering how long you will enjoy the company of your cows. Other homesteaders wonder about cow lifespans, too. Or – you might be a regular dairy consumer, sipping a glass of delicious milk and being curious if the milk’s creator was still alive. And for how long would she be?
You may also be interested in animal welfare. And confused by a variety of numbers you come across when you inquire about the average cow lifespan. Or, you may get a question from your child.
In any case, we have all wondered at some point – how long do cows live?
Table of contents
How Long Do Cows Live?
It depends! The mean lifespan of a domestic cow is 20 years, with sources mentioning averages from 15 to 22 years. (Some even say 30).
The two-decade lifespan is the natural life expectancy of a cow. In reality, beef and dairy cows usually get slaughtered or culled before they reach the bovine old age.
One question leads to another! And by now, you may be wondering the following. Why do these nerdy homesteaders need an entire article for a question that gets answered with just one figure?
There is a good – and practical – reason for that. Cow or cattle lifespans are not that simple. As pointed out above, there is a distinction between how long cows live naturally and how long cows live in various settings. Cow lifespans differ widely on homesteads and for industrial milk production. And beef production. Additionally, there is a slight variation across breeds.
Let’s break the cattle lifespan down into more detail – here is an overview of cow lifespans depending on their use on a farm or in the industry.
(We believe the short lifespan of bull calves is controversial. And terrible! We think the premature culling of bull calves is a crying shame. For humanity – and for animal dignity.)
How Long Do Cows Live Naturally in the Wild?
Domestic cows do not live in the wild – and if left in the wild to their own devices, they probably wouldn’t live very long and comfortable lives.
On the other hand, it is interesting to note the lifespan of wild bovine cousins.
We could also argue that the average life span of wild bovines is the same or longer than their domesticated cousins. Wild cows get subjected to natural selection that favors the most resilient genetic material.
But human farmers select for traits such as muscle mass and milk production. They disregard the cow’s vitality and fitness in the process.
That is why farmers who prefer holistic or regenerative farming, with animals roaming freely as much as possible, often choose old, primitive cow breeds. They are closer to the original resilient animals.
What Was the Oldest Cow in History?
The oldest cow in history and the holder of the Guinness record was a cow named Bertha from Ireland. In tune with the last paragraph of the previous section, she belonged to the ancient Irish Droimeann breed and got calved on St. Patrick’s Day in 1944.
After living a life of productivity, fame, and charity work, Bertha died on New Year’s eve of 1993, just three months before her 49th birthday. That means that she lived more than double what she was supposed to!
Besides the lifespan record, Bertha holds more honors – she is the cow who birthed the most calves over her lifetime. This legendary cow became a momma cow 39 times, helping save her ancient breed from extinction! It would be interesting to study if her offspring inherited her long-lived genes.
(Bertha is another reason we say the average cow’s lifespan is tough to define with certainty. There are a ton of variables! Including the cow’s environment, diet, genetics, health, and cattle breed. And luck!)
Do Dairy Cows Get Slaughtered for Meat?
Yes! Many people are surprised upon discovering that dairy cattle get slaughtered for meat. Just like beef industry cows! Contrary to popular belief of farming-naive individuals, dairy cows and beef cows end up on the same human plates. Around 21 percent of beef in the US comes from milk cows who have passed their prime. The figure is even higher in the UK, with 40% of cow beef coming from the dairy industry.
How Long Do Dairy Cows Live?
The dairy cows in large farms have their first calf at about two years old. The cows remain at their maximum production for three to four additional years. After that, they get culled or slaughtered. The cows could also get sold to smaller farms and homesteads, depending on their overall health.
Add these two figures, and you’ll get that the average lifespan of a dairy industry cow is five to six years.
Of course, many small scale-farmers take a different approach and carefully watch their cow’s productivity and health to know if and when it’s time to cull.
According to our best research, a small-scale production cow can stay highly productive until nine years old. But many family-scale farmers treat their cows as family members and have them live out their natural lifespan. If the animal’s health is fine and the cost of keeping them alive is bearable, there is no reason to cull them prematurely. As for productivity obsession, most families do not need large volumes of milk every day.
However, there are situations when farmers regret not culling their old cows after watching them suffer a health decline and poor death. All in all – each case is different.
How Long Do Beef Cows Live?
Meat is the main reason for raising beef cattle – meaning that as soon as they reach the desired weight? They get sent to slaughter. Slaughter happens when they are between one and two years old. And usually at 18 months. Meaning the beef steer’s lifetime is no longer than two years.
The figures above go for grain-fed beef. Grass-fed animals may take a bit longer to finish because they consume fewer calories per meal. Thus, their lifetime is usually around three years.
Things are mildly different with beef cows, especially those in ranchland cow-calf systems. These cows get to live in large herds, usually breeding naturally. Although they can live up to 20 years, their fertility substantially drops after age 12, so most (commercial) farmers decide to cull them at this point.
What’s the Average Lifespan We Can Expect from Our Cows on the Homestead?
Some ranchers will look at resources and studies and conclude that they have to end an animal’s life at a certain age. But the answer isn’t so clear-cut!
Each cow’s health, fertility, and milk production varies individually. Unless the animal is sick from a transmittable disease, there is no obligation to cull it at any particular age. Or at all! Each farmer needs to track their animal’s well-being and performance and make decisions based on their data rather than general rules.
I always suggest keeping your cows alive and well until it becomes evident that they cannot fulfill your family’s needs or that their health has declined to the point of no return.
If you take care of your cows well and if the cows come from good genetic stock, you can expect them to live for about 20 years.
Cow Lifespan Across Breeds
Cow lifespans vary across different breeds. But are these differences so significant?
Let’s find out by looking at some of the most famous cow breeds.
How Long Do Angus Cows Live?
The average lifespan is tricky to pin down with certainty. Being a beef breed that rarely reaches the end of its natural life, the lifespan of Angus cattle is arguably unmeasured, believe it or not! Some sources claim that the lifespan is up to 15 years, with most animals slaughtered at five to six years. Other sources say that the functional lifetime of Angus bulls (in South Australia) is around 2.3 years.
How Long Do Jersey Cows Live?
Jersey cows are known for their longevity. If well-cared for, it is not rare for a Jersey to reach 25 years old. The oldest known jersey cow lived in a sanctuary in the UK and died at the age of 37.
How Long Do Mini Cows Live?
Of all the cow breeds, one could say that the mini cows have the best luck when it comes to (literally) living life to the fullest. Kept predominantly as small farm cows, family, or even pet cows, they get culled less frequently before their natural death, which could happen after 18 or more years. (Except for beef minis that only get to live for two years).
Another reason for the longer lifespan of mini cows is that they eat only one-third of the food that a standard cow needs, meaning that even when their productivity starts to go down, it doesn’t cost as much to keep them alive.
Which Cow Breeds Live the Longest?
According to our best research, the Jersey cow and the Droimeann are among the longest-living cow breeds. However, they’re probably not the only cow breeds capable of living long lives. But due to many individuals failing to reach old age, we feel the available data on the average cow lifespan is tremendously inadequate.
However, as a general rule, older (primitive) and lighter breeds have longer lifespans.
Cow Lifespan FAQs
Figuring out the average cow’s lifespan is trickier than most farmers think! We penned the following list of questions and answers to help you brainstorm cow lifespans anyway. We hope it helps!
The natural lifespan of a domestic cow is about 20 years. However, since millions of cattle get slaughtered yearly in the US alone – much of the data regarding the average cow lifespan is confusing. Big time!
Of course, some cows will get to live beyond the average for their species – especially if well-cared-for. Take Big Bertha as an example! Big Bertha was the oldest-known cow we could find. Bertha lived from 1944 to 1993 and died when she was 48 years and nine months. Bertha belonged to the old Irish Droimeann breed.
Industry dairy cows are usually slaughtered at five to six years old because it is the most economical solution for declining productivity in an industrial setting. Dairy cows on family farms can live for longer – it depends on the farmer’s needs, the cow’s productivity, the cost of keeping them alive, and their health and quality of life.
Depending on their health, dairy cows are either slain for meat or culled at the end of their days. A substantial portion of beef on the market comes from dairy cows. On the other hand, farmers can buy aged milk cows that have passed their prime but can still satisfy the milk needs of an average family, thereby increasing their lifespan.
Beef steers raised for meat live for up to two years until they gain enough weight for slaughter. On the other hand, mothers of these animals – the beef cows – live for 10 to 12 years and sometimes even longer if kept in a cow-calf system.
Conclusion
The answer to the question of cow lifespan goes in two directions – the first query is the natural life expectancy of a cow. The second question is how long the animal is allowed to live in different settings.
The animal’s purpose on the farm, its breed, genetics, overall health, and the farmer’s motivations and preference all influence how long a cow or a bull will stick around.
In this article, you learned that cow lifespan varies. Big time!
Whatever a particular cow’s lifespan ends up to be? It is of the uttermost importance for the animal to receive high-quality care and remain in good health over its lifetime. Although humans love numbers, the quality of life is often more important than quantity.
So – if you have a cow or are a rancher? You can help increase the cow’s life expectancy. And – please treat your cow like a king (or queen) while they are alive!
What about you? What is the average cow lifespan on your farm or homestead?
We’d love to hear your feedback!
Thanks so much for reading.
And – have a great day!
Author
How Long Do Cows Live?
Cows can live many years in their natural environment. But in agriculture, the lifespan of domesticated cows has to be shortened to meet their meat and milk production expectancy.
Have you ever asked yourself: how long do cows live in each living environment?
Table of Contents
*This post may have affiliate links, which means I may receive commissions if you choose to purchase through links I provide (at no extra cost to you). As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases. Please read my disclaimer for additional details.
How Long Do Cows Live In The Wild?
In the wild, cows are long-lived animals. They can live for about 15 to 20 years or even more.
However, cows and bulls are not permitted to live their whole lives naturally when fed on commercial farms. Instead, they are raised on a farm with a budget of hundreds of millions for meat, milk, and leather.
What About Domesticated Cows?
How long do dairy cows live?
The average dairy cow lifespan is from 6 to 7 years, much shorter than wild cows.
This short lifespan of dairy cows results from the overexploitation of the dairy industry. The dairy industry pushes their milk production until they can’t stand or walk.
As long as their milk production drops, they are sent to slaughters for meat. Due to this exploitation, the meat of dairy cows has a lower price than the meat of ground beef.
After finishing their starter food period at 6 months old, dairy cows are switched to a protein-rich diet, aiming to gain 1 pound of weight per day. When they reach 1 to 2 years old, they start giving birth and continue producing milk 10 months later.
A female cow can produce from 6 to 10 gallons of milk per day in her peak production. To maintain milk production for 10 months of the year, they are required to have one calf annually. In some large farms worldwide, mother cows are artificially inseminated after three months of giving birth to shorten their idling time.
Unlike in dairy farms, where most pregnancies happen via artificial insemination, over 90% of mattings and pregnancies in beef farms happen naturally. However, due to their unhealthy lifestyle, mating bulls and female cows used for artificial pregnancy often have injuries or suffer from serious health problems, like hoof injuries or arthritis.
While new female calves will become the next generation of dairy cows, male calves will be sent to beef farms.
There is a close connection between the dairy and beef industries. In 2018, 21% of beef sold in the U.S was sent from dairy farms. Some cows with Down syndrome are killed on the farm since their meat can’t be reused for commercial beef production.
How long do beef cows live?
Steers, bulls, or cattle raised for meat can only live until their age at slaughter, about 2 to 3 years.
Their short life results from the market’s high demand for beef. Extreme commercial consumption is the main reason for their short life. While farms of 1,000 cattle heads only make up 5% of feedlots in the U.S, they can meet 80-85% of beef production demand for this country.
Calves started being fed with grains and corn from 6 months old to 1 year old until they reached their market weight.
The daily diet and age of beef cows significantly affect their meat quality. According to Modern Farmer magazine, the meat of grass-fed, 5-year-old cows has a more pleasant beefy flavor than that of a younger one with a commercial grain-fed diet. Additionally, their digestive system is not designed to consume such a high amount of grains and starch.
Studs or bulls are usually the next generation of beef cows and are often raised for meat or dairy production. These cows often stay in their herd for approximately 5 years. After retiring at the age of 5, these male cows are used for beef production in the slaughterhouse.
Bulls can start their breeding period at 12 months old and remain active until they are 10 to 12 years old. These cows are kept active on commercial farms as long as they are available for breeding or until the herd is full of its offspring. Farmers should also take care of these studs to prevent their possible temperament and health issues.
How long do calves live?
The lifespan of a calf in agriculture depends on whether the animal is female or male.
Female calves are raised mainly for milk, while some of them are raised for meat. When they can’t produce milk (around 6 years old), they are sent to slaughter for beef production.
On the other hand, male calves are raised mainly for beef or veal consumption. Except for the unprofitable ones who will be killed soon after birth and those who are grain-fed for meat, others are kept in veal crates (or small hutches/pens) to limit their physical movement and muscle development. At 16 to 18 weeks old, they will be killed for veal which is a gray, tender type of meat.
How Long Do Cows Live As Pets?
There are some fluffy miniature cows you can own as pets. This cow type is two times smaller than regular-sized cows. However, if they are fed and cared properly, they can fulfill their natural life expectancy of 17 to 18 years or more.
You can see mini cows in many areas worldwide. They are more loving and gentle than domestic cows. The Australian Lowline, the smallest and original pet cow breed, has a height of 100-100cm and a weight of 323 – 400 kilograms, depending on its gender.

Up till now, there have been 9 active mini cow breeds around the world. However, this number has been raised to 18, according to an American breeder Richard Gradwohl. Some of them are original breeds, while others have been selectively developed recently.
Caring tips to increase the lifespan of pet cows
Below are some valuable tips to expand the lifespan of your miniature cow:
FAQs
1. Can cows live for 100 years?
Up till now, there has been no cow that can live for 100 years. The oldest cow in the world is Big Bertha (1944-1993). This Dremon cow is owned by Jerome O’Leary in Ireland, and it has lived until it reached 48 years and 9 months.
2. What diseases affect cows?
Some common diseases are found in cows, namely foot/mouth disease, mad cow disease, bluetongue, bovine tuberculosis, botulism, brucellosis, bovine viral diarrhea, and Johne’s disease.
3. Do cows die because of old age?
Domestic cattle don’t usually die because of old age. They are sent to slaughterhouses when they have reached their market weight. Some others are killed on farms before that if they won’t be profitable for the farms or can’t be used for human consumption.
Some cows well raised and fed in sanctuaries or pets can live longer and die of old age.
4. What to do if a cow naturally dies?
When a cow naturally dies because of disease, injury, or old age, farmers should report his death to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). You can scan for rendering service in your area on USDA’s website and contact it to send his body for proper disposal.
5. How are farm cows slaughtered?
Throat-cutting is the most common way to kill cows in slaughterhouses. According to the Humane Slaughter Act of 1958 (amended in 2002), cows and other livestock must be wholly unconscious or sedated by electronarcosis or stunning before slaughter to minimize their suffering.
Final Words
Many criteria affect a cow’s lifespan, including genetics, living environment, nutrition/daily diet, weather, and overall physical health.
After knowing how long cows live, you understand that although wild cows have to deal with harsh weather elements, they have a happier and longer life with good health than those who are raised in commercial dairy or beef farms.
How Long Do Domesticated Cows Live? Cows Lifespan According to Use
The average cow naturally lives for between 15-20 years, although they can live for longer! However, a cow’s actual lifespan will depend on its purpose. Beef cows and dairy cows, for example, have very different life lengths.
How long do domesticated cows live? In the wild, cows generally live until 26 years, on average, and assuming no predators get them. Domesticated cows live between 18-22 years, but few cows die of old age. Beef cattle either live until 1-2 years, when many beef cattle are butchered for the market, or between 5-6 years, when cows and breeding bulls are culled. Most dairy cows live for around six. Cattle are generally culled or butchered when their productivity declines to maintain the profitability of the farm. Miniature cows are generally raised as both pets and for production and have an average lifespan of about 18 years.
It may sound simple, but within each industry, gender, and purpose, the time that cattle are kept depends on various factors. Let’s dive into those.
Beef Cow Lifespan In the United States
Meat or beef cows typically live for 1.5-2 years in the United States. Beef cattle are weaned from their mother’s milk at 4-6 months of age. Male calves that will be raised for meat and not breeding will be castrated at 3-4 weeks old. Female calves, or heifers, will be bred at around 15 months old to produce the next generation of meat cows.
After weaning, beef cattle will be either grass or grain-fed until they weigh 1000-1200 pounds. When they reach their target weight at 18-24 months of age, the cows are considered “finished” and sent to the slaughterhouse. There all animals should be killed humanely under the Humane Methods of Slaughter Act. Whilst the majority of their bodies are used for meat. Other parts are used for the production of leather as well.
Dairy Cow Lifespan
Dairy cows have an average lifespan of six years. Dairy cattle are weaned off their mother’s milk at 4-8 weeks of age. Then they are fed starter grain up until 6 months old. At that point, they are moved on to an adult diet of protein-rich feeds. Dairy farmers aim to have their cows gaining over one pound of weight per day. At this point, and they should have their first calf between 1 and 2 years of age. Like humans, female cows are pregnant for around nine months.
When mothers have their first calf, they will start producing milk. Mothers produce milk for 10 months after giving birth. In peak production they can produce 6 – 10 gallons of milk per day. From then on, they should be having one calf per year.
Female calves born on dairy farms will be the next generation of dairy cows. Some male calves will be sold into beef farms.
Female cows are generally fertile until 8-10 years of age. However, their milk production generally slows down after their third calf. Because of this, dairy cows are typically sold to families or sent to the slaughterhouse at around 6 years old. A “lower production” cow may give 3.5 gallons of milk a day, instead of 4, and can make a perfect dairy cow for a family.
Diseases that affect a cow’s ability to reproduce and/or produce good quality milk, such as the bovine viral diarrhea virus, can also cause dairy farmers to retire a cow early.
Bull Lifespan
Studs or bulls used for breeding typically remain in the herd for 5 years. They are usually the calves of beef cows and are used for breeding more cows for beef and dairy production. Bulls become fertile at 12 months old and can remain in action until they are 10-12 years old.
In dairy farming, most pregnancies occur through artificial insemination. Mating bulls and those used for artificial insemination both tend to suffer injuries and develop health conditions due to their lifestyle that stops them from being able to breed well. Hoof injuries and arthritis are common ailments for breeding cows.
On average, stud cows are retired aged 5. They are usually sent to the slaughterhouse for beef production. The general advice from farmers is to keep a stud active as long as they are fit to breed or until the herd is full of his daughters! Farmers should keep their studs in good conditions to prevent health and temperament problems.
Miniature Cow Lifespan
Miniature cows are about half the size of regular cows and have a similar natural lifespan of around 17-18 years. Unlike regular-sized cows, most mini cows tend to fulfill their natural lifespan. That’s because 80% of these cuties are kept as pets, and those that aren’t are farmed on a much smaller scale.
Miniature cows are found in various parts of the world and have a sweeter temperament than regular-sized cows. The smallest and original breed is the Australian Lowline, which stands between 100 – 110 cm tall and weighs between 323 – 400 kilograms, depending on the gender of the cow.
There are currently nine recognized active breeds of miniature cow, although American breeder Richard Gradwohl claims to have developed eighteen more. Some are traditional breeds, while others have been selectively bred more recently.
Miniature cows were originally the unexpected result of a scientific experiment. However, because of their size, they are a popular choice for small-scale farms. They are less expensive to keep as they require less feed and space to live.
All that said, they still produce a lot of goods! Mini cows used for dairy can produce 1-2 gallons of milk per day, depending on the breed. They also make good quality meat and are easier to handle and breed due to their temperament. They produce less methane gas, too, which is a plus for environmentally-minded farmers.
Miniature cows tend to have longer lives than regular-sized cows, and not just because most of them are kept as pets. Miniature meat and dairy cows are farmed on a much smaller scale, with less demand, and the commercial approach is not always necessary. Whilst they don’t live to their full life expectancy, they tend to get a lot closer to it than regular-sized farm cows.
Frequently Asked Questions
What diseases affect cattle?
Diseases that can affect cows include bluetongue, botulism, bovine tuberculosis, bovine viral diarrhea, brucellosis, mad cow disease, foot and mouth disease, and Johne’s disease.
To minimize the chances of illness, all of the cows kept on a farm should be vaccinated against common diseases and kept clean. Cows that die naturally or have to be euthanized due to disease should not be used for beef production, as their meat could be contaminated and unsafe for human consumption.
Do miniature cows have any health problems?
Miniature cows are generally very healthy and don’t face many issues that miniatures of other breeds face.
The one condition they are more likely to inherit is Chondrodysplasia, commonly referred to as the bulldog gene or dwarfism, which manifests as a physical malformation. It is typically passed on genetically but can be a result of environmental factors.
The recessive gene causes the nose to appear pushed inwards, much like a bulldog, increasing the likelihood of respiratory issues. It can also cause abortion and stillbirth in females.
The Dexter breed is the most common breed known to carry the condition. Both parents must carry the gene to produce a calf with the condition. However, there is still only a 25% chance of passing it on, and it is a relatively rare condition.
It’s also easy to test for the gene. Vets can perform a test via a blood sample, and tests can determine whether a cow or calf carries the gene. We strongly encourage any budding buyers of a miniature cow to test for the gene before purchasing.
How are farm cows killed?
The most common way slaughterhouses kill cows is by throat-cutting. Under the Humane Slaughter Act of 1958, amended in 2002, all livestock animals sent to the slaughterhouse must be completely sedated and unable to feel pain before being killed. This is to minimize the suffering and pain felt by the animals. Electronarcosis or stunning is the most common method of sedation for cows.
What happens if a cow dies naturally?
If a livestock cow dies from natural causes such as disease, old age, or injury, farmers should report it to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). To dispose of the body, you can contact a local rendering service, a list of which can be found on the USDA’s website. Alternatively, yo
Conclusion
To find learn more about when to cull and how long to keep older cattle in your herd, check out Determining How Long To Keep Older Cattle In Your Herd and A Bulls Ability To Breed Cows: Ratio Timing and Strategy.
Hi readers! I’m Laura, I have an animal-related degree and plenty of hands-on experience. I am passionate about animal welfare and want to arm you all with plenty of helpful info to keep your animals happy & healthy.
Recent Posts
One of the first animals to ever be domesticated by humans, the humble sheep has held an essential place in the history of livestock farming for thousands of years. With more than 200 unique breeds.
Having a sick pig can be stressful and traumatic, especially when trying to find the cause of its symptoms. When my pig started vomiting uncontrollably, I knew that this was an acute symptom. Pigs.
About Us
We are passionate about farm animals. Collectively, we own horses, donkeys, chickens, ducks, pigs, alpacas, cows, and other animals! We have years of experience. Best Farm Animals is the ultimate resource for learning everything you need to know about your farm animals.
How Long do Cows Live?
Have you ever wondered how long cows live; if so you come to the right place. It’s said that life is short but maybe it’s only a matter of perspective.
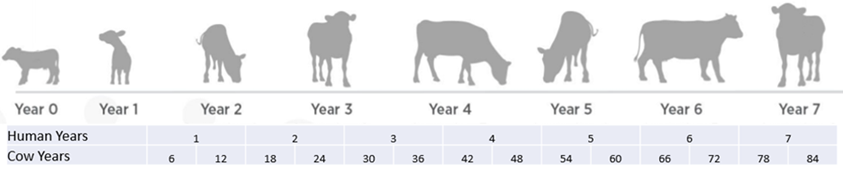
In Cow Years
Cows mature at a different pace than humans do. It’s like they’re living on a different timeline- you know, the whole dog years concept. An easy way to extrapolate the cows’ age in human years would be to look at when a cow reaches puberty. It takes people about 12 years to reach puberty, while it only takes a cow 1 year to reach puberty. This timeline puts things into better context:
Living on different timelines – Cow years are different from people years
When a cow reaches seven or eight she definitely begins showing signs of aging. Old age is a cruel friend affecting all species.
How many Years does the average Cow live?
The average Dairy cow will live 5 to 7 years. This number depends on different factors:
Some factors that affect a cows age:
The Oldest Cow
Interestingly, the oldest known cow was Big Bertha who lived to be 48 years old living from 1945-1993. She also held the record for most babies, having 39 calves.
What was the secret to Big Bertha’s longevity? Her owner fed her whiskey to steady her nerves when she was around people- maybe it helped to reduce her stress levels.
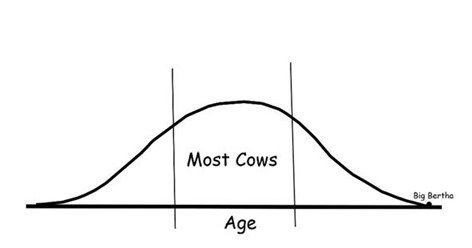
Her story is a fascinating example of bovine achievement. To say that most cows can accomplish living that long would be a mistake though, Big Bertha was an exception rather than the rule, an outlier.
The average age of cows would be represented on a bell curve
Cows can live 18-20 years or even 48 years, but it’s not normal or average. People can live to 120 but it’s not the norm.
The average age of cows can be depicted in a bell curve format. Outliers do not predict the average but are represented on the extremities of the curve.
Knowing the maximum age cows can live is fascinating, it represents possibilities.
Breeding Healthier Cows
Longevity in dairy cows has actually improved tremendously in the past 20 years. Instead of breeding for only milk production, dairy farmers are focused on breeding healthier, longer lasting cows by selecting males with better health and longevity traits. Genes really do make a difference in how long a cow will live.
Genomics, (genetic testing) is helping to bring positive change to cows’ lives.
With genomic testing, we know more about a cow’s DNA than any time in history. As more and more cows are tested, we can know which cows have the best genes for longevity- which cows will live longer. In knowing which cows have a predisposition for longevity, breeders can mate cows to bulls with good genes to help breed cows more cows can have these good traits. It is helping to speed genetic progress which helps all dairy cows as a whole.
A lot of genetic progress has been made to help improve a cow’s longevity and quality of life.
Before genetic testing, a cow’s traits used to be determined by visual appearance and data collection on mothers and daughters (which took years to get accurate data). Now a cow’s genetic traits can be determined by genomic testing which gives trait data including longevity and health. Accurate data in a short time.

(Left) Compare the cow from 1935 to the modern-day cow (Right), you can see the amount of genetic progress.
The modern cow, on the right, is stronger and more balanced which contributes to a longer life. The modern cow has a wider chest, is deeper in heart girth, stronger in her backbone, walks on a more correct set of feet and legs and is much stronger in her udder attachments. All these physical traits play a role in a cow’s longevity and quality of life
The Natural Life of a Cow
But what would the cow’s age be if she lived her life naturally in the wild? Compared to cows at the farm, a cow living in the wild would not necessarily be happier or live longer.
A good example would be deer- it is hard to measure what a cows age would be in the wild but we can assume shorter. Deer, for example, living wild and free have shorter lives:
“The life span of a whitetail deer can be from 6 to 14 years in captivity. In the wild, the majority of deer don’t make it to that age because of disease, hunting and automobile collisions. The average life span for wild whitetail deer is 4½ years (Lopez et al 2003). Males have an average life span of 2.9 years and females have an average life span of 6½ years (Lopez et al 2003).”
Life in the wild is not easy. Elements- wind, rain, snow, dry weather- food availability, and predators are just some of the major things animals in the wild have to deal with.
Cows wouldn’t have easier lives in the wild – most likely they would be more stressed- and their lifespan would not necessarily be longer than a cow’s life on a farm.