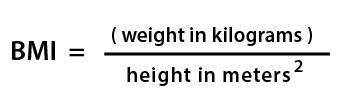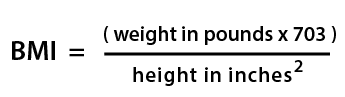How to calculate bmi
How to calculate bmi
Body mass index is a measure of body fat and is commonly used within the health industry to determine whether your weight is healthy. BMI applies to both adult men and women and is the calculation of body weight in relation to height. This article delves into the BMI formula and demonstrates how you can use it to calculate your own BMI.
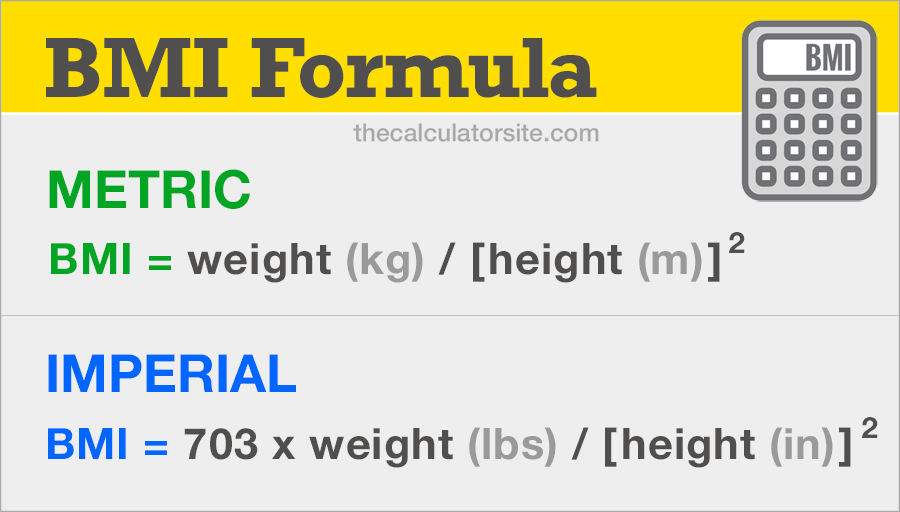
The first formula we’ve listed is the metric BMI formula, using kilograms and meters. The second one is the imperial BMI formula, which uses units of pounds and inches. Converters are available for kilos to stone, kilos to pounds and ounces and pounds, should you need them.
Metric BMI Formula
BMI = weight (kg) / [height (m) ] 2
Imperial BMI Formula
BMI = 703 × weight (lbs) / [height (in) ] 2
Let’s go through a couple of examples to demonstrate how these formulae work.
Using the BMI formula (metric units)
These simple steps will help you work out your BMI:
Example using formula
For an adult with height of 180 cm and weight of 75 kg. Our first step needs to be to convert the height into meters (British spelling: metres). As there are 100cm in a meter, we divide our figure by 100. This gives us 1.8m.
Let’s plug those figures into our formula:
BMI = 75 ÷ (1.8 × 1.8)
This gives us a BMI figure of 23.15.
Using the imperial BMI formula
Simple steps to work out your imperial BMI:
Example using formula
For an adult with height of 5ft 11 inches and weight of 155 pounds (lbs). Step one is to convert the height into inches only. There are 12 inches in a foot, so we simply multiply the 5ft by 12 and then add the 11 inches. This gives us a total of 71 inches.
Let’s plug those figures into our formula:
BMI = 703 × (155 ÷ (71 × 71))
We do the multiplication inside the brackets first:
BMI = 703 × (155 ÷ 5041)
BMI = 703 × 0.030747867
This gives us a BMI figure of 21.62.
Of course, should you not wish to calculate BMI manually with the formula, you can use my popular BMI calculator or the interactive BMI formula below.
Interactive BMI formula
Use the interactive BMI formula calculator below to demonstrate the formula and resulting BMI calculation for your chosen weight and height figures. Options for both metric and imperial units are available.
Please note that this calculator requires JavaScript to be enabled in your browser.
Metric BMI Formula
Note that the results given by the Interactive BMI Formula should be used only as a guide and should not replace medical advice.
BMI Categorization
The BMI statistical categories below are based on BMI scores and apply to adults of age 20 years and upwards. The World Health Organisation (WHO) regards a healthy adult BMI to be between 18.5 and 25.
| BMI | BMI Category |
|---|---|
| Less than 15 | Very severely underweight |
| Between 15 and 16 | Severely underweight |
| Between 16 and 18.5 | Underweight |
| Between 18.5 and 25 | Normal (healthy weight) |
| Between 25 and 30 | Overweight |
| Between 30 and 35 | Moderately obese |
| Between 35 and 40 | Severely obese |
| Over 40 | Very severely obese |
BMI chart
For a full chart of BMI values, customised for your own height and weight, see my interactive BMI chart.
The BMI formula remains controversial
We can’t feature an article about the BMI formula without touching upon some of the controversies surrounding it.
It is a common argument that the results the BMI formula provides are too general and do not consider the gender, build, age or ethnicity of a person. For example, professional athletes are often considered overweight or obese when using BMI measurements due to their muscle content, which weighs more than fat.
Similarly, as people age their bone density decreases. So, although they may seem to have a weight within the normal BMI range, their measurement actually needs to be scaled-down to reflect this. In a study published in the Journal of Economics in 2008, John Cawley, professor at Cornell University, was able to demonstrate that, relative to percent body fat, BMI appears to misclassify substantial fractions of individuals as obese or non-obese. You can read more about his research in this HealthyDebate article published in 2016.
Alternatives to BMI do exist for those who consider BMI an inaccurate measurement tool.
It goes without saying that you should always speak to a Doctor or health professional for advice and guidance if you are concerned about your weight.
Please rate this article below. If you have any feedback on it, please contact me.
The BMI Formula
Imperial Formula
Metric Formula
In this article I will show you how to calculate your BMI and how to find your weight category. BMI is a measurement which determines which weight category a person belongs to. Depending on their height and weight, a person can belong to one of the following weight categories:
If your math is a little rusty, that’s ok. Calculating BMI is straight forward, the formula is easy to compute and I will provide step by step examples.
In fact, the simplicity of this formula was part of the reason for its success (and also it’s main criticism).
It was developed by Belgium Statistician Adolphe Quetelet approximately 150 years ago. This was before the era of electronic calculators; any formula used to indicate weight status needed to be easy for physicians to manually calculate.
Only the height and weight values of a person are needed in the equation.
How To Calculate BMI
Metric Method
The metric formula accepts height measurements in meters and weight in kilograms. If you know your height in centimeters only, simply divide the number of centimeters by 100 convert it to meters.
For example, a person who is 183cms tall is 1.83m tall (183cm / 100 = 1.83m).
Using the metric formula is even easier than the imperial method as it’s a two step process
The resulting number is your BMI. Compare this BMI value with the weight status table below.
Example:
Paul weighs 150kgs and is 1.8m tall. He wants to know if he is overweight.
1. First we multiply Paul’s height by itself: 1.8 x 1.8 = 3.24 ²
Next we divide Paul’s weight by his height in meters ² just calculated: 150 / 3.24 = 46.3
Paul’s BMI is 46.3
We compare this value to the weight categories listed on the BMI table and find that he is obese.
Imperial (US) Method
The imperial formula accepts height measurements in inches and weight in pounds. It’s popular in the US where the imperial system is mostly used. Many people know their height in feet and inches, but not in inches only.
If this applies to you, we need to convert your height into inches so we can use it in the equation. There are 12 inches in a foot, so multiply your number of feet by 12 and add them to the number of extra inches.
For example, if your height is 5 feet 10 inches, multiply 5 by 12 (which gives 60″) and add them to the extra 10 inches (which gives 70″).
Now we have the right measurements we can use them in the formula.
There are three simple steps for computing BMI with imperial values:
The resulting number is your BMI. Compare this BMI value with the weight status table below.
Example:
Jane weighs 150lbs and is 5 feet 4 inches tall. She wants to know if she is overweight.
Jane’s height in inches is (5 * 12) + 4 = 64″
1. Using the first part of the formula we multiply her weight by 703. 150 * 703 = 105450
2. Using the second part of the formula we multiply Jane’s height by itself. 64 x 64 = 4096
3. Finally we divide the first figure by the second. 105450 / 4096 = 25.74
Jane’s BMI is 25.74
We compare this value to the weight categories listed on the BMI table and find that she is overweight.
BMI Weight Status Categories
The weight status categories opposite, are those currently used by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). They are suitable for adults who have stopped growing.
For children and teens who are still growing, the CDC base the weight categories on a BMI percentile. A child’s weight status is based on where their BMI value lies compared to children of a similar age.
Limitations Of The BMI Formula
There’s no question that the body mass index calculation has been useful for some physicians.
However, since it’s creation many have stated that this method of calculating BMI is not fit for purpose.
BMI does not take into account other factors which may affect a persons height or weight:
Please consult your doctor if you are concerned about your health.
Terms Of Use
BMI Calculator
Result
The Body Mass Index (BMI) Calculator can be used to calculate BMI value and corresponding weight status while taking age into consideration. Use the «Metric Units» tab for the International System of Units or the «Other Units» tab to convert units into either US or metric units. Note that the calculator also computes the Ponderal Index in addition to BMI, both of which are discussed below in detail.
BMI introduction
BMI is a measurement of a person’s leanness or corpulence based on their height and weight, and is intended to quantify tissue mass. It is widely used as a general indicator of whether a person has a healthy body weight for their height. Specifically, the value obtained from the calculation of BMI is used to categorize whether a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese depending on what range the value falls between. These ranges of BMI vary based on factors such as region and age, and are sometimes further divided into subcategories such as severely underweight or very severely obese. Being overweight or underweight can have significant health effects, so while BMI is an imperfect measure of healthy body weight, it is a useful indicator of whether any additional testing or action is required. Refer to the table below to see the different categories based on BMI that are used by the calculator.
BMI table for adults
This is the World Health Organization’s (WHO) recommended body weight based on BMI values for adults. It is used for both men and women, age 20 or older.
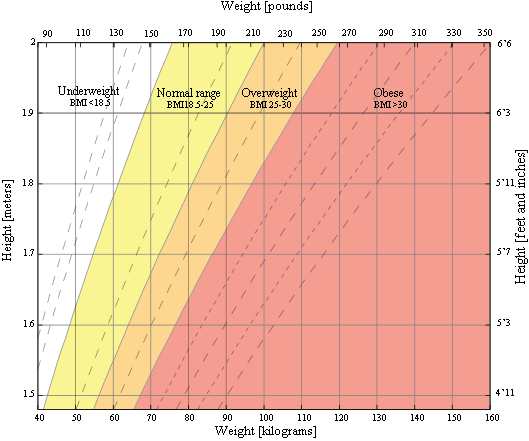
BMI chart for adults
This is a graph of BMI categories based on the World Health Organization data. The dashed lines represent subdivisions within a major categorization.
BMI table for children and teens, age 2-20
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends BMI categorization for children and teens between age 2 and 20.
| Category | Percentile Range |
| Underweight | 95% |
BMI chart for children and teens, age 2-20
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) BMI-for-age percentiles growth charts.
Risks associated with being overweight
Being overweight increases the risk of a number of serious diseases and health conditions. Below is a list of said risks, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
Risks associated with being underweight
Being underweight has its own associated risks, listed below:
In some cases, being underweight can be a sign of some underlying condition or disease such as anorexia nervosa, which has its own risks. Consult your doctor if you think you or someone you know is underweight, particularly if the reason for being underweight does not seem obvious.
Limitations of BMI
Although BMI is a widely used and useful indicator of healthy body weight, it does have its limitations. BMI is only an estimate that cannot take body composition into account. Due to a wide variety of body types as well as distribution of muscle, bone mass, and fat, BMI should be considered along with other measurements rather than being used as the sole method for determining a person’s healthy body weight.
In children and adolescents:
The same factors that limit the efficacy of BMI for adults can also apply to children and adolescents. Additionally, height and level of sexual maturation can influence BMI and body fat among children. BMI is a better indicator of excess body fat for obese children than it is for overweight children, whose BMI could be a result of increased levels of either fat or fat-free mass (all body components except for fat, which includes water, organs, muscle, etc.). In thin children, the difference in BMI can also be due to fat-free mass.
That being said, BMI is fairly indicative of body fat for 90-95% of the population, and can effectively be used along with other measures to help determine an individual’s healthy body weight.
BMI formula
Below are the equations used for calculating BMI in the International System of Units (SI) and the US customary system (USC) using a 5’10», 160-pound individual as an example:
| BMI = 703 × |
| = 703 × |
| = 22.96 |
|
| BMI = |
| = |
| = | 22.90 |
| ||||||||
Ponderal Index
The Ponderal Index (PI) is similar to BMI in that it measures the leanness or corpulence of a person based on their height and weight. The main difference between the PI and BMI is the cubing rather than squaring of the height in the formula (provided below). While BMI can be a useful tool when considering large populations, it is not reliable for determining leanness or corpulence in individuals. Although the PI suffers from similar considerations, the PI is more reliable for use with very tall or short individuals, while BMI tends to record uncharacteristically high or low body fat levels for those on the extreme ends of the height and weight spectrum. Below is the equation for computing the PI of an individual using USC, again using a 5’10», 160-pound individual as an example:
Calculate BMI
BMI calculator 
BMI table
What is BMI?
How to calculate Body Mass Index
BMI formula
BMI calculation example
Example: A person is 175 cm tall and has a weight of 70 kg.
How to calculate BMI with imperial units: feet
To use pounds (lb) and feet (ft) instead of kilograms (kg) and meters (m), use the same fomula, but multiply the weight by 4.88.
BMI formula for pounds and feet
BMI calculation example (feet)
Example: A person is 5’6″ tall and has a weight of 160 lb.
Why the factor 4.88?
1 lb = 0.45359237 kg
Where w is the weight in pounds, and h is the height in feet.
How to calculate BMI with imperial units: inches
To use pounds (lb) and inches (in) instead of kilograms (kg) and meters (m), multiply the weight by 703.
BMI formula for pounds and inches
BMI calculation example (inches)
Example: A person is 5’6″ tall and has a weight of 100 lb.
5′ 6″ = (5*12) + 6 = 60 + 6 = 66″
Why the factor 703?
1 lb = 0.45359237 kg
Where w is the weight in pounds, and h is the height in inches.
BMI Prime
BMI Prime formula
The formula to calculate BMI Prime is very simple:
BMI Prime formula for Asian body types
Since the upper limit for normal weight is often lower for Asian body types, the formula for BMI Prime looks like this:
How to lose weight?
In theory it is simple to lose weight. Use more energy than you take in (eat).
However, in practice it is not so simple as it may sound, since it requires a lot of self control and hard work. But do not give up! If you really put your mind to it, you can do it. A good start could be to have a nice walk for at least 30-60 minutes every day. If you think it is boring, you could listen to music or audio books while walking, or walk with a friend.
If you start working out more than you are used to, you should consult your doctor first.
BMI Calculator – Check Your Body Mass Index For Women & Men
It is an excellent tool to measure a person’s leanness or fatness as per height and weight. It widely describes whether your are in healthy zone or need to lose or gain weight. BMI ranges may vary based on your exercise regime. More you gain weight more will be the BMI but it does not mean that you are obese it can be because of high muscle mass also.
Results
Based on the height and weight entered, your BMI is indicating your weight is in the Category for adults. For your height,a normal weight range would be from to
What Is Body Mass Index?
BMI is Body Mass Index a parameter to assess nutritional status as per height and weight. It is a ratio between weight in kilograms and height in square meters (1).
BMI chart Adults
Standard BMI ranges and nutritional status as per WHO
| BMI | Weight Status |
|---|---|
| Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal weight |
| 25.0–29.9 | Pre-obesity |
| 30.0–34.9 | Obesity class I |
| 35.0–39.9 | Obesity class II |
| Above 40 | Obesity class III |
BMI chart Kids
BMI for age percentile is basically designed to assess growth pattern of children and teenage
| Weight Status Category | Percentile Range |
|---|---|
| Underweight | Less than the 5th percentile |
| Normal or Healthy Weight | 5th percentile to less than the 85th percentile |
| Overweight | 85th to less than the 95th percentile |
| Obese | Equal to or greater than the 95th percentile |
How to calculate body mass index?
In Metric Scale
Step 1: Measure your weight in kg preferably in an empty stomach to get actual weight.
Step 2: Measure height by Stadiometer and convert it to meter by dividing it by 100.
In Imperial Scale
Step 1: Measure weight in pounds by digital weighing machine.
Step 2: Multiply height in inches inself.
Step 3: Divide weight and height, results should be multiplied by 703.
BMI = Weight (kg) ÷ Height 2 (meter 2 )
Imperial BMI Formula:
BMI = Weight (lb) ÷ height 2 (in 2 ) × 703
Risks of being overweight?
Overweight or severely obesity increases the risk of many diseases as per Postgraduate Medicine review studies :
Risks for being underweight?
Being underweight multiple risks are associated with it:
Limitations of BMI
BMI is not an accurate measure when it comes to analyse body fat
What is a healthy BMI for women?
BMI varies as per age, height and weight. It is invariable in respect to gender. Though women have more fat mass compared to men but it does not affect BMI and no scientific evidence mentioned specific BMI for women.
Sources
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best BMI for a senior woman?
A BMI between 25-27 is ideal for older women. However, the number may vary from person to person depending on their height and age.
How do I calculate my BMI in pounds?
BMI= (weight in pounds / (height in pounds) squared) X 703 (conversion factor)
Divide your weight (in pounds) by the squared amount of your height (in pounds). Then multiply that amount by 703 (the conversion factor). This will give you your BMI value in pounds.
Embed Code
To embed this on to your site just copy and paste the below code