How to calculate roe
How to calculate roe
How to Calculate Return on Equity (ROE)
Return on equity (ROE) is a ratio that provides investors with insight into how efficiently a company (or more specifically, its management team) is handling the money that shareholders have contributed to it. In other words, return on equity measures the profitability of a corporation in relation to stockholders’ equity. The higher the ROE, the more efficient a company’s management is at generating income and growth from its equity financing.
ROE is often used to compare a company to its competitors and the overall market. The formula is especially beneficial when comparing firms of the same industry since it tends to give accurate indications of which companies are operating with greater financial efficiency and for the evaluation of nearly any company with primarily tangible rather than intangible assets.
Key Takeaways
Return On Equity (ROE)
Formula and Calculation of Return on Equity (ROE)
The basic formula for calculating ROE is:
The net income is the bottom-line profit—before common-stock dividends are paid—reported on a firm’s income statement. Free cash flow (FCF) is another form of profitability and can be used instead of net income.
Shareholder equity is assets minus liabilities on a firm’s balance sheet and is the accounting value that’s left for shareholders should a company settle its liabilities with its reported assets.
Note that ROE is not to be confused with the return on total assets (ROTA). While it is also a profitability metric, ROTA is calculated by taking a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) and dividing it by the company’s total assets.
ROE can also be calculated at different periods to compare its change in value over time. By comparing the change in ROE’s growth rate from year to year or quarter to quarter, for example, investors can track changes in management’s performance.
Putting It All Together
The ROE of the entire stock market as measured by the S&P 500 was 6.95% in the fourth quarter of 2020, as reported by CSI Market. A first, critical component of deciding how to invest involves comparing certain industrial sectors to the overall market.
For example, a look at ROE figures categorized by industry might show the stocks of the railroad sector performing very well compared to the market as a whole, with an ROE value of 18.55%, while the general utilities and retail sales sectors had ROEs of 5.96% and 22.16%, respectively. This could indicate that railroad companies have been a steady growth industry and have provided excellent returns to investors.
P&G’s ROE was below the average ROE for the consumer goods sector of 14.14% at that time. In other words, for every dollar of shareholders’ equity, P&G generated 8.4 cents in profit.
Not All ROEs Are the Same
Measuring a company’s ROE performance against that of its sector is only one comparison.
For example, in the fourth quarter of 2020, Bank of America Corporation (BAC) had an ROE of 8.4%. According to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), the average ROE for the banking industry during the same period was 6.88%. In other words, Bank of America outperformed the industry.
In addition, the FDIC calculations deal with all banks, including commercial, consumer, and community banks. The ROE for commercial banks was 6.38% in the fourth quarter of 2020. Since Bank of America is, in part, a commercial lender, its ROE was above that of other commercial banks.
In short, it’s not only important to compare the ROE of a company to the industry average but also to similar companies within that industry.
In evaluating companies, some investors use other measurements too, such as return on capital employed (ROCE) and return on operating capital (ROOC). Investors often use ROCE instead of the standard ROE when judging the longevity of a company. Generally speaking, both are more useful indicators for capital-intensive businesses, such as utilities or manufacturing.
When Shareholder Equity Is Negative
There can be circumstances when a company’s equity is negative. This usually occurs when a company has incurred losses for a period of time and has had to borrow money to continue staying in business. In this case, liabilities will be greater than assets.
If one were to calculate return on equity in this scenario when profits are positive, they would arrive at a negative ROE; however, this number would not be telling the entire story. It could indicate that a company is actually not making any profits, running at a loss because if a company was operating at a loss and had positive shareholder equity, the ROE would also be negative.
In a situation when ROE is negative because of negative shareholder equity, the higher the negative ROE, the better. This is so because it would mean profits are that much higher, indicating possible long-term financial viability for the company.
ROE will always tell a different story depending on the financials, such as if equity changes because of share buybacks or income is small or negative due to a one-time write-off. Understanding the components is critical.
What Does Return on Equity Tell You?
ROE tells you how efficiently a company can generate profits. Generally the higher the ROE the better, but it is best to look at companies within the same industry or sector with one another in order to make comparisons.
What Is the Average ROE for U.S. Stocks?
The S&P 500 had an average ROE in 2021 of 21.88%. Of course, different industry groups will have ROEs that are typically higher or lower than this average.
How Do You Calculate ROE Using DuPont Analysis?
ROE can be alternatively calculated using DuPont analysis. There are two such versions, one decomposing ROE with three steps and the second with five:
The Bottom Line
Return on equity (ROE) is an important financial metric that investors can use to determine how efficient management is at utilizing equity financing provided by shareholders. It compares the net income to the equity of the firm. The higher the number, the better, but it is always important to measure apples to apples, meaning companies that operate in the same industry, as each industry has different characteristics that will alter their profits and use of financing.
As with all investment analysis, ROE is just one metric highlighting only a portion of a firm’s financials. It is critical to utilize a variety of financial metrics to get a full understanding of a company’s financial health before investing.
How is the Return on Equity (ROE) Ratio Calculated?
Contents
In this article, we’ll talk about the Return on Equity (ROE) ratio, as one of the key indicators of investment returns that helps to assess the financial stability and investment attractiveness of different companies.
What is the ROE for?
The Return on Equity (ROE) is a ratio that assesses the effectiveness of the funds invested by companies’ shareholders. To be precise, the ROE is the company’s annual profit after taxes, fees, and other statutory expenses, divided by the cost of all the funds invested by its founders and shareholders without borrowed money.
As a rule, investors have a preference for companies and firms with a higher ROE. However, profit and income in different sectors of the economy vary considerably. For example, the indicator may differ even within the same sector if a company decides to pay out dividends instead of keeping profits as available cash assets.
It’s important to assess the ROE ratio in real-time mode, for a particular period of time (for example, 5 years). Investors usually calculate the ROE at the beginning and the end of their investment period, to be able to determine the real changes in profitability. Through this method, they can assess the dynamics of growth, and compare the performance results with those of other companies.
A stable and eventually growing ROE ratio is attractive to investors. If a chosen company has a high ROE, this means it’s reliable and can produce stable income because it knows how to wisely employ its capital to increase performance and profits. On the other hand, a declining ROE could indicate that the company’s management makes wrong decisions by re-investing money into non-profitable assets.
The ROE normal value
The ROE ratio shows shareholders how successful the company has been with their invested funds, namely how much net profit was generated by each unit of the owned capital. To sum up:
On average, the ROE normal value in advanced economies is about 10-12%. In countries with higher inflation, the indicator should be higher too – about 20-30%. To assess investment attractiveness, one can compare the ROE ratio of the chosen company with investments in such instruments as bonds or deposits. The higher the ROE ratio, the more attractive the company is for investors.
For example, a company with an ROE ratio that’s double the bank’s deposit rate will be very interesting for investors. When investing, Warren Buffett pays a great deal of attention to this ratio. In his opinion, a company with a high ROE and a small loan debt has excellent investment prospects.
Formula to calculate the ROE
There are two methods for calculating the ROE ratio: the conventional way using total results, and the DuPont analysis.
Calculation of total results
In this case, the ROE is calculated as the ratio between the company’s net profit and the average equity of the shareholders:
ROE = Net income of the company / Average equity of the shareholders *100%
The DuPont formula
The calculation using the DuPont formula allows to analyse the ROE ratio as well. By means of additional variables, we can analyse the exact factors that influence the indicator to change:
ROE = Net Profit Margin * AT * EM *100%, where:
As a result, the DuPont formula shows three factors that influence the ROE ratio:
The purpose of using the DuPont analysis here is not only for the calculation of the ROE ratio, but also for estimating the possible impact of the above-mentioned factors on its value. It helps to determine the cause of the issues encountered, and take the appropriate steps to eliminate them.
Example of the ROE ratio calculation
ROE = 100,000 / 50,000 * 5 * 100% = 40%
This is a high ROE ratio, which indicates that the company is actively developing. For a more detailed estimate, it is advisable to analyse the average ROE dynamics over 3-5 years – this will provide a fair insight into the company’s prospects.
However, it is to be noted that even if the ROE is growing, a company’s profit is not necessarily always paid out to investors. If the company decides to keep its profits without paying out dividends, the shareholders may still receive their profit indirectly, thanks to the rise of the company’s share price.
Closing thoughts
The ROE ratio helps to assess the financial performance and investment attractiveness of any given company. As a rule, the ROE is used for comparing the performance of different companies within the same sector. Changes in the ROE ratio dynamics are constantly analysed by both company managers and investors, for the purpose of estimating a company’s profits and sustainability.
Material is prepared by
Victor G.
Trades on financial markets since 2004. Victor has developed his own approach to analysing assets, which he shares with RoboMarkets Blog readers.
What is return on equity? How to calculate ROE to evaluate a company’s profitability
Twitter LinkedIn icon The word «in».
LinkedIn Fliboard icon A stylized letter F.
Flipboard Facebook Icon The letter F.
Email Link icon An image of a chain link. It symobilizes a website link url.
The key to value investing is developing a knack for spotting undervalued companies. The value investor is looking for hidden gems — companies with solid management, good financial performance, and relatively low stock price.
Uncovering value stocks requires careful analysis of a company’s fundamentals, but some metrics help you separate the wheat from the chaff quickly. Return on equity (ROE) is one of them — it tells you how well a company generates profit from invested cash.
What is return on equity (ROE)?
Return on equity (ROE) is a financial ratio that tells you how much net income a company generates per dollar of invested capital. This percentage is key because it helps investors understand how efficiently a firm uses its capital to generate profit.
Understanding how ROE works
ROE is a useful metric for evaluating investment returns of a company within a particular industry. Investors can use ROE to compare a company’s ROE against industry average to get a better sense of how well that company is doing in comparison to its competitors.
A higher ROE signals that a company efficiently uses its shareholder’s equity to generate income. Low ROE means that the company earns relatively little compared to its shareholder’s equity.
What percentage is considered a «good» ROE?
It depends. In some industries, firms have more assets — and higher incomes — than in others, so ROE varies widely by sector. For example, data published by New York University puts the average ROE for online retail companies at 27.05%. But it’s only 2.93% in the advertising industry. Savvy investors look for companies with ROEs that are above the average among its industry peers.
An upward trend in ROE is also a good sign. «While a company’s absolute ROE is important, the change in ROE over time — and what drove the change — may be even more relevant,» says JP Tremblay, teaching professor of finance in the Daniels College of Business at the University of Denver.
ROE can also be used to help estimate a company’s growth rates — the rate at which a company can grow without having to borrow additional money.
How to calculate ROE
To calculate ROE, divide a company’s net annual income by its shareholders’ equity. Multiply the result by 100 to get a percentage.
Net income: This is a company’s income after deducting expenses. A company’s annual net income is reported on its income statement
Shareholder’s equity: This is the claim shareholders have on a company’s assets, after its debts are paid. Shareholder’s equity is reported on the balance sheet.
Example of ROE
That means that its annual net income is about 22.7% of its shareholders’ equity.
How to calculate ROE in Excel
To calculate ROE in excel, input a company’s annual net income in cell A2. Then input the value of their shareholders’ equity in cell B2. In cell C2, enter the formula: =A2/B2*100. The resulting figure will be the ROE expressed as a percentage.
ROE can be negative. But that doesn’t necessarily mean the company has a negative cash flow. Dr. Robert R. Johnson, professor of finance at Creighton University’s Heider College of Business, notes, «companies that are losing money on an accrual accounting basis may have a negative ROE but a positive cash flow.» Negative ROE isn’t necessarily bad, but it warrants further investigation.
The DuPont Formula
One way to obtain further insight from ROE is by breaking it down into components using a framework called the DuPont analysis. This more advanced analysis decomposes ROE into three ratios, helping analysts understand how a company achieved its ROE, its strengths, and opportunities for improvement.
Increasing any of these ratios increases ROE. «Two firms can have the same ROE and get there in completely different ways,» says Johnson.
Other uses for ROE
An unusual or extremely high ROE can prompt an analyst to do more research.
ROE vs. return on assets vs. return on invested capital
ROE tells investors how much income a company generates from a dollar of shareholder’s equity. It has some similarities to other profitability metrics like return on assets or return on invested capital, but it is calculated differently.
Return on assets (ROA) tells you how much of a company’s profit is being driven by fixed investments like property and equipment. The formula for ROA is almost the same as ROE, but it uses total assets in the denominator whereas ROE uses shareholders’ equity.
Return on invested capital (ROIC) also measures profitability relative to investment, but it adds a little more complexity: It tells you how much in net income (after paying dividends) a company generates from all its capital — both debt and equity. ROIC is calculated using net income less dividends in the numerator and the sum of a company’s debt and equity in the denominator.
Each of these metrics is used to evaluate and compare companies based on how efficiently their management uses their financial resources to generate profit, but each takes a different angle.
Limitations of ROE
While it’s one of the most important financial indicators to stock investors, ROE doesn’t always tell the whole story.
For example, it can be misleadingly low for new companies, where there’s a large need for capital when income may not be very high. Similarly, some factors, like taking on excess debt, can inflate a company’s ROE while adding significant risk.
Another limitation of ROE is that it can be intentionally distorted using accounting loopholes. Inflated earnings or assets hidden off the balance sheet can boost ROE and make a company look more profitable than it really is.
Because of these limitations, the diligent investor should undergo a full analysis of a company’s financial performance using ROE as one of several metrics.
The financial takeaway
ROE is one of the most important financial ratios for the stock investor hunting good value companies. It’s a straightforward and handy indication of how well a firm is able to generate revenue from the money invested in it. High and stable ROE is generally better, but the absolute number should be considered in the context of the industry. It’s also a good sign if ROE increases over time.
Use ROE to sift through potential stocks and find the companies that turn invested capital into profit fairly efficiently. That’ll give you a short list of candidates on which to conduct more detailed analysis.
ROE: как рассчитать коэффициент рентабельности капитала и зачем он инвесторам
Чтобы правильно оценить экономическое положение компании, используют специальные коэффициенты — мультипликаторы. Коэффициент рентабельности собственного капитала (ROE) считается одним из основных. Как его посчитать — в статье.
Показатель ROE позволяет дать общее представление об эффективности бизнеса, а также сравнить компании из одной отрасли друг с другом и выбрать наиболее перспективную для инвестирования.
Что показывает ROE
Коэффициент рентабельности собственного капитала показывает, сколько чистой прибыли компания зарабатывает на 1 рубль собственных средств. Этот коэффициент свидетельствует о том, насколько эффективно собственники используют средства, вложенные ими в бизнес. Показатель позволяет инвесторам быстро проанализировать компанию, сравнить ее с аналогичными в отрасли и выбрать ту, что наиболее привлекательна для инвестиций.
Например, средний ROE в определенном секторе экономики равен 15%. В таком случае акции компании, ROE которой равен 10%, будут мало привлекательны для инвесторов. Но если ROE компании составит 25%, инвесторы будут активнее приобретать ценные бумаги этого эмитента в свой портфель.
Также коэффициент ROE показывает доходность, на которую инвестор может рассчитывать при приобретении ценных бумаг по цене, равной или примерно равной балансовой стоимости компании. Такой доход может быть выражен в дивидендах, а также в росте цены акций компании.
Классическая формула расчета ROE
Базово коэффициент ROE ― это годовая прибыль компании за вычетом всех налогов, сборов и прочих обязательных расходов, поделенная на стоимость всех вложенных в компанию средств учредителей. В расчет не включаются заемные средства.
Классическая формула для расчета ROE выглядит следующим образом:
Можно рассчитать ROE, исходя из суммы первоначально вложенных средств. Например, два предпринимателя решили заняться производством мебели. Один из них внес в уставный капитал компании станки стоимостью 10 млн рублей, а другой — помещение для цеха, которое стоит 20 млн рублей. Таким образом, собственный капитал компании при ее создании был равен 30 млн рублей. За первый год работы предприятие заработало 6 млн рублей чистой прибыли, то есть на каждый рубль, вложенный собственниками, они получили 20 копеек прибыли: 6 / 30 = 0,20. Или, другими словами, ROE компании за первый год работы был равен 20%.
Но собственный капитал компании в процессе работы постоянно меняется — например, собственники компании могут делать дополнительные вклады или пополнять его за счет нераспределенной прибыли. Поэтому для более точного расчета можно взять средний показатель за период и рассчитать ROE как отношение чистой прибыли за период к среднему собственному капиталу компании.
Допустим, компания получила в 2021 году 50 млн рублей чистой прибыли. На начало года ее собственный капитал составлял 380 млн рублей, а к концу года — уже 420 млн рублей.
ROE = 50 / ((380 + 420) / 2) = 50 / 400 = 12,5%
ROE по формуле Дюпона: что она показывает и зачем она нужна
Показатель ROE позволяет оценить деятельность компании в целом. Но его расчет по классической формуле не дает возможности понять, почему компания работает именно с такой эффективностью. Определить, какие факторы влияют на ROE, позволяет формула Дюпона, которая получила свое название благодаря американской компании DuPont, впервые исследовавшей этот показатель в 20-х годах XX века.
Формула Дюпона позволяет «разложить» показатель ROE на три составные части: рентабельность продаж, оборачиваемость активов и финансовый рычаг.
Соотношение чистой прибыли и выручки говорит об эффективности использования компанией своих ресурсов. Чем оно выше, тем лучше.
Соотношение выручки и активов говорит о том, что средства компании более интенсивно «крутятся» в процессе работы и быстрее приносят прибыль. Например, мебельная фабрика купила материалы, произвела из них мебель, отгрузила ее в магазин, затем получила выручку и вновь купила материалы. Чем быстрее происходят все эти процессы, тем больше прибыли можно заработать при тех же вложенных средствах.
Соотношение активов к собственному капиталу показывает, насколько эффективно компания использует финансовый рычаг. С одной стороны, предприятие может работать вообще без заемных средств, но это ограничивает возможности для развития бизнеса. Но если привлеченных ресурсов в балансе будет слишком много, это грозит компании финансовыми проблемами, вплоть до банкротства. Нормативная величина финансового рычага составляет не более 2. Это означает, что заемные средства в общем случае должны составлять не более половины от активов баланса.
Расчет по формуле Дюпона лучше делать за два или несколько периодов. Тогда будет понятно, какие из факторов и в какой степени повлияли на изменение ROE.
Наилучшая ситуация с точки зрения инвестора — рост ROE за счет повышения рентабельности и (или) коэффициента оборачиваемости активов. Это говорит о том, что компания эффективно использует свои средства и получает высокую доходность.
Если же ROE растет за счет финансового рычага, то есть из-за увеличения доли заемных средств в балансе предприятия, это повышает риски инвесторов. В следующих периодах ситуация на рынке может измениться в худшую сторону. Если упадет выручка, то при большом финансовом рычаге компании может быть сложно рассчитаться с кредиторами, и ей может даже грозить банкротство.
Как анализировать ROE предпринимателю и инвестору
Для предпринимателя один из вариантов анализа коэффициента ROE — сравнение его с доходностью по вложениям с низким риском, например по банковским вкладам или ОФЗ. ROE позволяет понять, стоит ли начинать свой бизнес или проще открыть вклад или купить облигации.
Например, предприниматель рассчитал, что ROE его компании составит 7%. Доходность же выпуска облигаций Банка ГПБ серии БО–17 может составить 10,03%. Значит, вложив в бизнес 1 млн рублей, за год он получит 70 000 рублей, а облигации могут принести более 100 000 рублей. При этом предпринимателю не придется тратить время и нервы на управление компанией.
Вложения в любой бизнес (даже самый надежный) — это очень рискованная операция. Может ухудшиться общая ситуация на рынке, могут появиться новые конкуренты, невыгодные для компании изменения законодательства и тому подобное. Поэтому потенциальный доход должен компенсировать риски предпринимателя.
Инвестору, как и предпринимателю, показатель ROE позволяет оценить состояние дел компании в динамике. Чтобы составить объективное представление об эффективности бизнеса, данных за один год недостаточно. Результаты конкретного года (как положительные, так и отрицательные) могут быть обусловлены случайными факторами, которые в дальнейшем не будут действовать.
Также мультипликатор ROE позволяет сравнить эмитента с компаниями-конкурентами или со средними показателями по отрасли. Это поможет понять, как рассмотренная компания выглядит на фоне своих «коллег» по бизнесу и отрасли в целом.
Преимущества и недостатки анализа компании с помощью ROE
Коэффициент ROE просто считать, а понять его экономический смысл достаточно легко. Этим показатель удобен для любого инвестора. В том числе им могут пользоваться и новички, даже если они не обладают глубокими познаниями в экономике. ROE позволяет быстро провести первичный анализ и отобрать компании для дальнейшего изучения.
Допустим, инвестор рассматривает три компании, которые производят мебель, со следующими показателями ROE: ООО «Мечта» — 15,5%, ООО «Полюс» — 5,6%, ООО «Старт» — 18,7%. Согласно мультипликатору, «Мечту» и «Старт» стоит проанализировать детальнее, а вот компанию «Полюс» вряд ли стоит рассматривать в качестве объекта для инвестиций. На сегодня такую и даже более высокую доходность можно получить, просто разместив средства на банковском вкладе.
Но у анализа по коэффициенту ROE есть и минусы. Собственный капитал компании может быть незначительным или вообще отрицательным, и тогда ROE не даст объективной информации о состоянии бизнеса. Такая ситуация возникает, например, если компания несколько лет работала в убыток, а потом получила прибыль. Убыток, который накапливался на балансе, уменьшал собственные средства предприятия. Поэтому любая полученная после «убыточных» лет прибыль, даже небольшая, даст возможность показать высокий ROE. Кроме того, чистая прибыль, на которой основан расчет ROE, может существенно колебаться от года к году. Избежать ошибок в таких случаях поможет анализ деятельности компании за несколько отчетных периодов.
Высокий ROE еще не говорит о том, что инвестор может рассчитывать на такие же дивиденды. Поэтому, чтобы объективно оценить свои перспективы, нужно изучить дивидендную политику компании за последние годы и подробнее изучить отчетность эмитента. Что она показывает — в статье Анализ компании: о чем говорит финансовая отчетность.
Кратко
Читайте также
Общество с ограниченной ответственностью «ГПБ Инвестиции» осуществляет деятельность на основании лицензии профессионального участника рынка ценных бумаг на осуществление брокерской деятельности N045-14007-100000, выданной Банком России 25.01.2017, а так же лицензии на осуществление дилерской деятельности N045-14084-010000, лицензии на осуществление деятельности по управлению ценными бумагами N045-14085-001000 и лицензии на осуществление депозитарной деятельности N045-14086-000100, выданных Банком России 08.04.2020.ООО «ГПБ Инвестиции» не гарантирует доход, на который рассчитывает инвестор, при условии использования предоставленной информации для принятия инвестиционных решений. Представленная информация не является индивидуальной инвестиционной рекомендацией. Во всех случаях решение о выборе финансового инструмента либо совершении операции принимается инвестором самостоятельно. ООО «ГПБ Инвестиции» не несёт ответственности за возможные убытки инвестора в случае совершения операций либо инвестирования в финансовые инструменты, упомянутые в представленной информации.
С целью оптимизации работы нашего веб-сайта и его постоянного обновления ООО «ГПБ Инвестиции» используют Cookies (куки-файлы), а также сервис Яндекс.Метрика для статистического анализа данных о посещениях настоящего веб-сайта. Продолжая использовать наш веб-сайт, вы соглашаетесь на использование куки-файлов, указанного сервиса и на обработку своих персональных данных в соответствии с «Политикой конфиденциальности» в отношении обработки персональных данных на сайте, а также с реализуемыми ООО «ГПБ Инвестиции» требованиями к защите персональных данных обрабатываемых на нашем сайте. Куки-файлы — это небольшие файлы, которые сохраняются на жестком диске вашего устройства. Они облегчают навигацию и делают посещение сайта более удобным. Если вы не хотите использовать куки-файлы, измените настройки браузера.
Условия обслуживания могут быть изменены брокером в одностороннем порядке в любое время в соответствии с условиями регламента брокерского обслуживания. Клиент обязан самостоятельно обращаться на сайт брокера за сведениями об изменениях, произведенных в регламенте брокерского обслуживания и несет все риски в полном объеме, связанные с неполучением или несвоевременным получением сведений в результате неисполнения или ненадлежащего исполнения указанной обязанности.
What Is a Good ROE (Return on Equity) and Why Is It Warren Buffett’s Most Important Number?
I often get asked by users of our stock research tool: what is a good ROE? And why should I care?
A consistent return on equity (ROE) of 20% or higher is considered a good ROE.
However, there are some caveats, which I’ll dive into shortly.
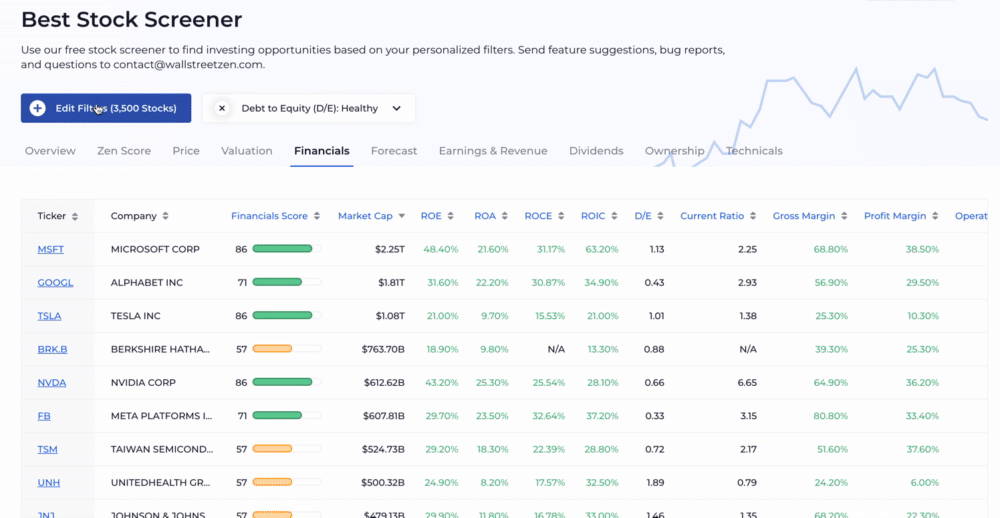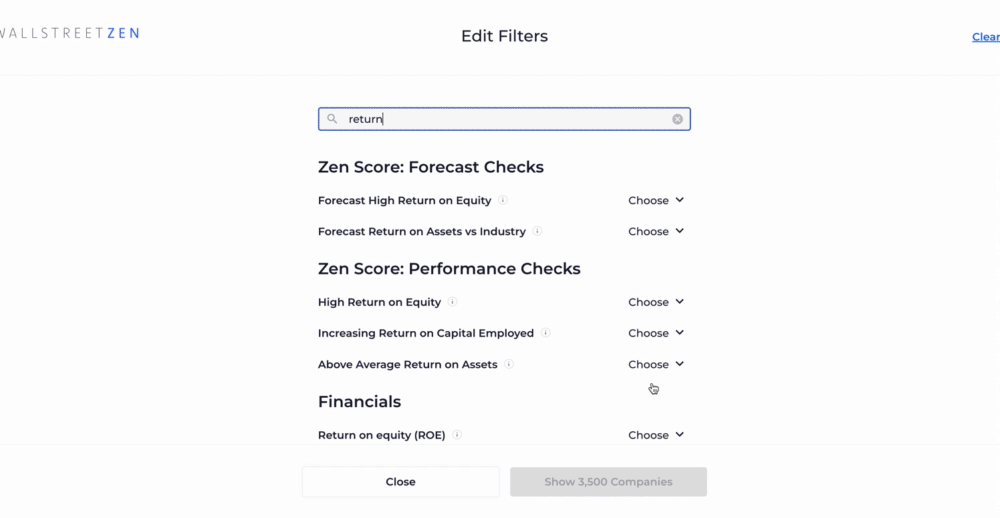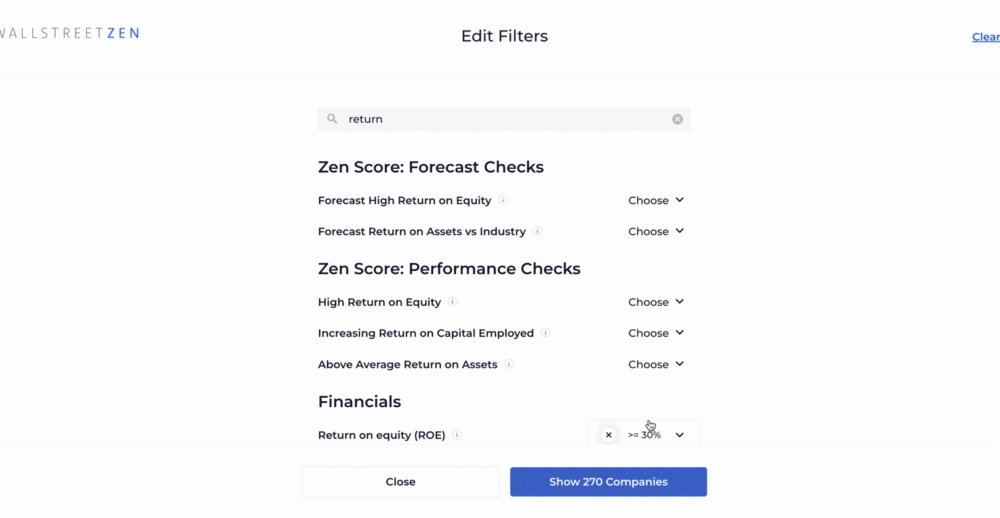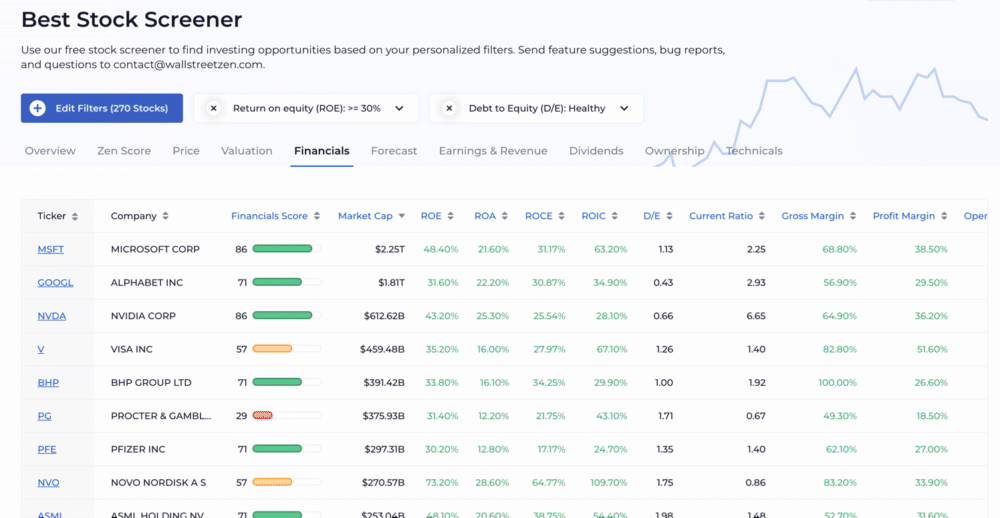
Return on equity is so important that it’s one of the 38 fundamental due diligence checks that we run on stocks, to calculate our Zen Score.
Check out the video below to learn more about how WallStreetZen makes it easy to quickly check if a stock has good return on equity, alongside 38 other fundamental due diligence checks. 👇
You can sign up here to start a 14-day trial and see for yourself how WallStreetZen makes data-informed investing easier for part-time investors like you and me.
Anyways, shameless plug over. Back to return on equity!
In this article, you’ll learn:
Why should you care whether a stock has a good ROE?
In his famous letters to Berkshire Hathaway shareholders, Warren Buffett has consistently emphasized the importance of return on equity (ROE).
It’s the most important numbers he looks at when evaluating a company.
Why is it important to him? In his own words:
“If you earn high enough returns on equity and you can keep employing more of that equity at the same rate — that’s also difficult to do — you know, the world compounds very fast.”
A big part of Warren’s genius is his ability to identify stable, predictable businesses with long histories of producing above average returns on equity.
Identifying and holding these companies with exceptional returns is how Warren has managed to slowly and steadily become the most successful investor of all time.
Let’s take a closer look at return on equity and how you can use it in your own stock analysis.
How To Calculate ROE
This is the ROE formula:
Net income / Shareholder Equity
Great, but what does this actually mean?
What is ROE (return on equity)?
Return on equity (ROE) is a measure of the company’s ability to generate profits for shareholders.
This is not the same as your “return” on investment based on stock price.
The stock price reflects your return based on what the market thinks about the value of the company, while the return on equity actually measures the performance of the company directly.
If a company’s stock price tumbles but its ROE stays constant, or even grows – it can potentially be a sign the company is undervalued.
ROE is important because it directly tracks the profits generated by the company on your shares.
It’s right there in the name:
A high return on equity (20%+), generated consistently for many years – is often the sign of an exceptional company run by a great manager, operating a great business with an economic moat.
Successful companies have to constantly be looking at new ways to reinvest earnings profitably.
If they don’t increase earnings proportionally to their equity, ROE will go down.
So a company that has a consistent, or even growing RoE over many years – is a company where management is consistently finding effective ways to generate more profit on the earnings they generate.
It’s the sign of a good, long-term manager in a business with a durable competitive advantage.
So what is a good return on equity ratio?
What is a good ROE?
A return on equity (ROE) of 20+% is considered good, 30% ROE is considered exceptional.
You can use WallStreetZen’s stock screener to find companies with good ROE, or even exceptional ROE.
In his 1987 letter to Berkshire Hathaway shareholders, Warren quoted a study by Fortune magazine where Fortune looked at 1000 of the largest stocks in the US and found that:
Only 6 of the 1000 companies averaged over 30% ROE over the previous decade (1977-1986)
If you go to Wall Street Zen, you can see we have a due diligence check to see if the company’s ROE is over 20%.
This quickly tells you if a company is highly efficient at transforming shareholder equity into returns.
Average ROE by Industry
ROE is not only useful for assessing the profitability of individual companies, but it’s useful for assessing industries as well.
You can use WallStreetZen to see the average ROE of any stock market sector, or stock market industry.
Pros and Cons Of Return on Equity (ROE)
Return on equity (ROE) may be one of Warren Buffett’s most important financial ratios, but that doesn’t mean it’s perfect.
You should never use a single financial ratio to decide whether to buy or sell a stock. This rule applies to ROE as well.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of ROE helps you use it correctly as a tool in evaluating stocks.
Pros of ROE
Here are some of the reasons return on equity is a good metric to look at.
ROE surfaces quality companies with good management
A high RoE does not mean that much if looked at as a snapshot in time.
You need to see consistently high ROE over many years to be able to use it as a gauge of management’s performance.
Exceptionally well managed companies demonstrate a high ROE, year over year, decade over decade. A good ROE is a sign of strong capital allocation, effective use of leverage, and an economic moat.
A manager can improve ROE by generating more profit with fewer assets, increasing profit margin, or effectively using leverage – all of which get captured in the ROE metric.
As a company generates earnings, those earnings are retained in the company and it increases shareholder equity. Thus it actually gets more difficult for mediocre companies to sustain ROE over time.
Keeping ROE steady or even increasing over many years is no small feat, and those companies that can achieve this are exceptionally well run companies able to consistently find opportunities to generate shareholder wealth.
ROE gives us a consistent way to compare companies
Out of all the profitability ratios, ROE most directly measures shareholder returns. While earnings can vary across sectors and industries, ROE makes it easy to directly compare earnings across sectors.
💡 On WallStreetZen, you can quickly see the average ROE across stock market sectors.
ROE helps us quickly screen out companies that are not generating returns for us, the shareholders.
Cons of ROE
While we’ve looked at some of the advantages of using ROE, let’s dive into some of the disadvantages:
Debt can heavily skew ROE
ROE can be artificially inflated by the use of debt.
This is because shareholder equity (ROE’s denominator) and debt are connected.
If you increase debt, equity decreases. And if the denominator decreases, the ROE formula produces a higher ROE.
Because equity = assets – liabilities, a company can actually increase ROE simply by taking on more debt!
That’s why it’s important to watch ROE over many years – a company that increases ROE by taking on debt may inflate ROE in the short term, but if it cannot effectively generate return from that debt, in the long term its ROE will suffer.
This is also why it’s important to look at metrics holistically – in this case, looking at debt to equity (D/E) and the company’s balance sheet alongside ROE can also help investors identify cases where high use of leverage is inflating ROE.
If you’re screening for high ROE companies, you may want to screen out companies with high D/E as well.
👉 Here is a link to a screener where you can screen for companies with high ROE, AND a reasonable Debt to equity ratio.
Another way you can quickly sanity check the RoE number is by looking at Return on Assets – which doesn’t include debt in the denominator – if you see a company with a good ROE but poor ROA, might be another sign company is drowning in debt.
ROE Is Not Effective For Growth Companies
Like all ratios that rely on earnings (P/E most famously), ROE cannot effectively measure loss-making companies. This rules out most growth companies.
Generally, ROE is better for evaluating stable, mature companies.
ROE is Subject to Earnings Manipulation
Earnings can be misleading. Whether intentionally or unintentionally, companies can paint a better picture by using accounting tricks to paint a rosier picture.
This is again why it’s important to analyze ROE over many years, and also combine quantitative indicators with a qualitative analysis of the business.
Past earnings is not a sign of future earnings.
How to Use ROE In Your Stock Analysis
Profitability ratios like ROE are a great way to screen for well-managed companies that are producing returns for you, the shareholder!
While there are some downsides to the ratio, like with all financial ratios, they are not magic – they are tools you can use to better understand a company.
And while ROE is a great metric for assessing a company’s efficiency at generating profits based on shareholder’s equity, if this efficiency is already baked into the price – the stock may not necessarily be good value.
A high ROE may help you identify a quality company, but you need to look at valuation metrics to determine whether or not it is at a fair price.
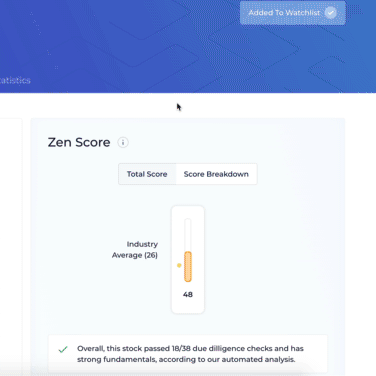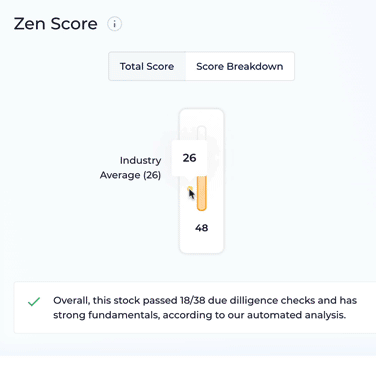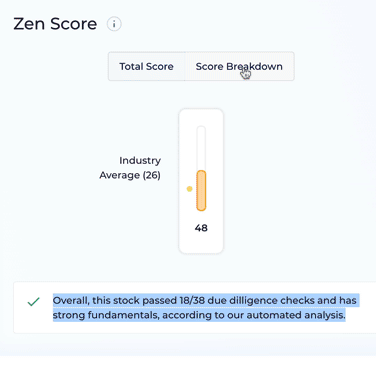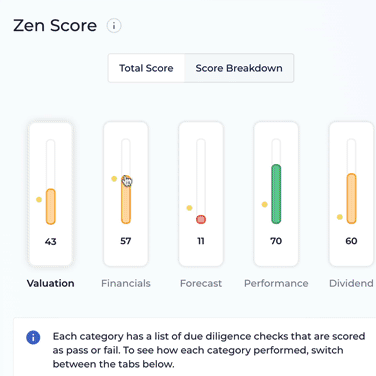
Here at WallStreetZen, we created Zen Score to try to make it as easy as possible for you to do fundamental analysis across all important aspects of a stock, so you can focus your time and energy on understanding the companies you invest in, rather than hunting for data and messing around with spreadsheets.
💡 Click here to sign up for a 14-day trial today, and see how WallStreetZen makes data-informed investing easier for part-time investors like you and me.
Interested in getting high-quality stocks picks delivered straight to your inbox? Read this review of the best investment newsletters 2022.
About the author
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cfa_candidate_guide__ryan_fuhrmann-5bfc2622c9e77c005142f4ca.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/JamesHeadshot-PeggyJames-9f712f1197374a9b824289fe0d5ec842.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TimothyLi-picture1-4fb5c746f503451bacfee414a08f5c1f.jpg)