How to calculate roi
How to calculate roi
Return on Investment (ROI)
Investopedia / Lara Antal
What Is Return on Investment (ROI)?
Return on investment (ROI) is a performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency or profitability of an investment or compare the efficiency of a number of different investments. ROI tries to directly measure the amount of return on a particular investment, relative to the investment’s cost.
To calculate ROI, the benefit (or return) of an investment is divided by the cost of the investment. The result is expressed as a percentage or a ratio.
Key Takeaways
How To Calculate Return On Investment (ROI)
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)
The return on investment (ROI) formula is as follows:
«Current Value of Investment” refers to the proceeds obtained from the sale of the investment of interest. Because ROI is measured as a percentage, it can be easily compared with returns from other investments, allowing one to measure a variety of types of investments against one another.
Understanding ROI
ROI is a popular metric because of its versatility and simplicity. Essentially, ROI can be used as a rudimentary gauge of an investment’s profitability. This could be the ROI on a stock investment, the ROI a company expects on expanding a factory, or the ROI generated in a real estate transaction.
The calculation itself is not too complicated, and it is relatively easy to interpret for its wide range of applications. If an investment’s ROI is net positive, it is probably worthwhile. But if other opportunities with higher ROIs are available, these signals can help investors eliminate or select the best options. Likewise, investors should avoid negative ROIs, which imply a net loss.
Limitations of ROI
Examples like Jo’s (above) reveal some limitations of using ROI, particularly when comparing investments. While the ROI of Jo’s second investment was twice that of the first investment, the time between Jo’s purchase and the sale was one year for the first investment but three years for the second.
Jo could adjust the ROI of the multi-year investment accordingly. Since the total ROI was 40%, to obtain the average annual ROI, Jo could divide 40% by 3 to yield 13.33% annualized. With this adjustment, it appears that although Jo’s second investment earned more profit, the first investment was actually the more efficient choice.
ROI can be used in conjunction with the rate of return (RoR), which takes into account a project’s time frame. One may also use net present value (NPV), which accounts for differences in the value of money over time, due to inflation. The application of NPV when calculating the RoR is often called the real rate of return.
Developments in ROI
Recently, certain investors and businesses have taken an interest in the development of new forms of ROIs, called «social return on investment,» or SROI. SROI was initially developed in the late 1990s and takes into account broader impacts of projects using extra-financial value (i.e., social and environmental metrics not currently reflected in conventional financial accounts).
SROI helps understand the value proposition of certain environmental social and governance (ESG) criteria used in socially responsible investing (SRI) practices. For instance, a company may decide to recycle water in its factories and replace its lighting with all LED bulbs. These undertakings have an immediate cost that may negatively impact traditional ROI—however, the net benefit to society and the environment could lead to a positive SROI.
There are several other new variations of ROIs that have been developed for particular purposes. Social media statistics ROI pinpoints the effectiveness of social media campaigns—for example how many clicks or likes are generated for a unit of effort. Similarly, marketing statistics ROI tries to identify the return attributable to advertising or marketing campaigns.
So-called learning ROI relates to the amount of information learned and retained as a return on education or skills training. As the world progresses and the economy changes, several other niche forms of ROI are sure to be developed in the future.
What Is ROI in Simple Terms?
Basically, return on investment (ROI) tells you how much money you’ve made (or lost) an investment or project after accounting for its cost.
How Do You Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)?
What Is a Good ROI?
What qualifies as a “good” ROI will depend on factors such as the risk tolerance of the investor and the time required for the investment to generate a return. All else being equal, investors who are more risk-averse will likely accept lower ROIs in exchange for taking less risk. Likewise, investments that take longer to pay off will generally require a higher ROI in order to be attractive to investors.
What Industries Have the Highest ROI?
Historically, the average ROI for the S&P 500 has been about 10% per year. Within that, though, there can be considerable variation depending on the industry. For instance, during 2020, many technology companies generated annual returns well above this 10% threshold. Meanwhile, companies in other industries, such as energy companies and utilities, generated much lower ROIs and in some cases faced losses year-over-year. Over time, it is normal for the average ROI of an industry to shift due to factors such as increased competition, technological changes, and shifts in consumer preferences.
How To Calculate ROI? Return on Investment Calculation
May 24, 2019 By Hitesh Bhasin Tagged With: Finance
Business has its own rules and regulations along with its terms and conditions. It is imperative that an entrepreneur learns about all its facets so that he can clear his concept and increase his understanding of the matter.
Remember knowledge is crucial to gain success and it is the understanding of the facts along with information that will help a person in achieving the desired triumph in life. Human beings are always on the look-out for opportunities so that they can create wealth for future use.
This is possible via investing in different options so that you can diversify your portfolio. This will increase your profits as you are minimizing your risks. The goal of investments is making money hence people try to pursue those prospects that could offer the best return.
How will you know whether your choice or option is the best one? You cannot make any random decision that will depend on luck and circumstances. At such times return on investment or ROI can come to your aid and help you in arriving at viable estimates effectively.
Table of Contents
What is Return on Investment or ROI?
Return on investment is commonly known as ROI. It is actually a financial metric that helps to measure the profitability factor from an investment. It is calculated as a ratio of gain relative to the cost.
Simply said, If you invested 10 rs in an investment, and you got back 15 rs, what was your return on investment? It was 50% or 5 Rs.
ROI is a powerful tool that can evaluate return from an individual investment as well as make comparisons from various investments in your portfolio. In most cases, it is expressed as a percentage and only sometimes as a ratio.
In simple terms ROI tells us about the financial advantages that you have received from your investment by letting you know what you are getting back if compared to what you put in as an investment.
ROI is used in business as well as several areas of finance. Remember that a person’s goal is a maximum return on minimum investment so that he can have the desired ROI. High ROI denotes favourable gains against cost and the purpose of an ROI metric is to measure rates of return per period on invested money in order to determine whether the venture is fruitful or not.
Simply put it is an indicator that will help you in prioritizing your investment portfolio effectively.
Determining ROI in percentages?
Are you interested in learning the proper method of calculating ROI? The goal of an investor is to achieve higher ROI. Try to measure ROI on all investments so that you can spend maximum time on activities that can generate the best possible results for you.
The best way to do so is by comparing the losses and gains over a considerable time period in terms of percentage of your initial investment. Suppose you have gained Rs 24000 on investment and the figure looks good by itself.
But how much was the actual investment is the question that needs to be addressed. If the investment was six lakhs then you have earned only 4% whereas if the investment was one lakh then your investment is simply 24% which is great. In order to determine the actual value, you need to convert it in terms of percentage as it will help you in getting a clear picture.
To figure the total percentages for the entire investment period first calculate the total returns by including any dividends if paid in the interim. Now subtract your investment from the total return to know about the actual profit or loss.
Later divide it by the initial investment and again multiply it by 100 to convert it in percentage. Suppose you invested 100000 in shares and after selling you received 140000.
In between you have received dividends amounting to 10000 so your actual returns are 140000 + 10000= 150000. First, subtract 100000 from 150000 to know your actual gain and that is = 50000. Now divide it by the investment that is 50000/100000 = ½. To calculate in terms of percentage multiply it by 100 that is = 1/2 * 100 = 50%.
Remember the percentage helps you in determining and comparing rates so that you can know which investment is proving beneficial for you.
What is the formula of return on investment or ROI
ROI is measured as the net income divided by the capital cost. Remember the higher your ratio is the benefits earned will automatically increase. Let me tell you that the calculation is straightforward and you can arrive at the result by either of the methods.
The first formula –
The second formula –
Important points to remember
How to calculate ROI with examples?
ROI calculations are very simple and an individual just has to follow the set directions to come up with the answer. Remember positive or negative ROI is an indicator that can help you to make suitable adjustments. It can be applied in case of real estate, stocks and even employees.
Ravi wants to calculate his ROI for his investment in a real estate operation. He has invested till date Rs, 50000 and he has earned Rs 60000.
His ROI thus is 20% and it has been a profitable venture for him.
Benefits of ROI formula
According to a recently conducted survey, more than 77% of the people responded favorably for the use of ROI metric. According to them, it has proved a blessing in several circumstances as it has helped an individual in determining actual facts about their investment.
Calculating ROI can make it clear what is working for you and what is not. Now you can make changes accordingly so that you can generate higher ROI and improve your prospects.
1) Universally understood and accepted
Return on investment or ROI has been accepted as the set formula for determining the return on your investment. It is a universally understood concept and if you tell people that your ROI is this and this, people generally will understand that you have used the conversation metric to know the answer.
2) Easy and simple to use
The return on investment metric is very easy to use and hence is used very frequently to determine the actual ROI. You just need to know the investment and return amount and voila you have your answer.
Limitations of the ROI formula
No doubt the ROI formula is very easy to use and is generally accepted but nothing comes without some negative aspects and so is the case with this formula. It is imperative that you know about its limitations beforehand so that you can work accordingly.
1) Disregards time
Higher ROI figures do not signify that it will always be the better option in terms of investment. Suppose you have invested in two schemes and both have an ROI of 40% does that mean that both are equally beneficial.
The first yielded the returns in two years whereas the second in four years. It is obvious that the first scheme that completed in two years is better than the one that yielded results in four years. Time is a great Factor but the actual ROI equation disregards time hence keep in mind about this limitation while calculating ROI.
2) Does not consider the risk factor
The higher the return the greater is the risk on that investment. An investor who is targeting higher returns will have to take greater risks compared to the one who does not want to take risks and is happy playing safe.
Business and investments are always subjected to risk but ROI does not consider and take into account the risk factor. If one considers only the ROI without determining the risk you cannot actually understand whether the investment will yield better results or not in the long-term.
3) Susceptible to manipulation
If an individual wants to show higher ROI he can easily manipulate the formula to his advantage. He can ignore additional costs that have occurred during the time period to remain in the black.
Conclusion
It is the ROI that helps to determine actual gain or return that has been possible through the investment. It is a powerful metric that can rank and evaluate investment alternatives very effectively.
As the positives supersede the negatives by a great margin people have been using this metric a great deal for calculating ROI successfully.
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI is a straightforward measure of the gain or loss from an investment
Return on investment (ROI) is the key measure of the profit derived from any investment. It is a ratio that compares the gain or loss from an investment relative to its cost. It is useful in evaluating the current or potential return on an investment, whether you are evaluating your stock portfolio’s performance, considering a business investment, or deciding whether to undertake a new project.
In business analysis, ROI and other cash flow measures—such as internal rate of return (IRR) and net present value (NPV)—are key metrics that are used to evaluate and rank the attractiveness of a number of different investment alternatives.
Although ROI is a ratio, it is typically expressed as a percentage rather than as a ratio.
Key Takeaways
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI can be calculated using either of two methods.
Interpreting ROI
When interpreting ROI calculations, it’s important to keep a few things in mind. First, ROI is typically expressed as a percentage because it is intuitively easier to understand than a ratio. Second, the ROI calculation includes the net return in the numerator because returns from an investment can be either positive or negative.
When ROI calculations yield a positive figure, it means that net returns are in the black (because total returns exceed total costs). But when ROI calculations yield a negative figure, it means that the net return is in the red because total costs exceed total returns.
Finally, to calculate ROI with the highest degree of accuracy, total returns and total costs should be considered. For an apples-to-apples comparison between competing investments, annualized ROI should be considered.
The ROI formula can be deceptively simple. It depends on an accurate accounting of costs. That’s easy in the case of stock shares, for example. But it is more complicated in other cases, such as calculating the ROI of a business project that is under consideration.
ROI Example
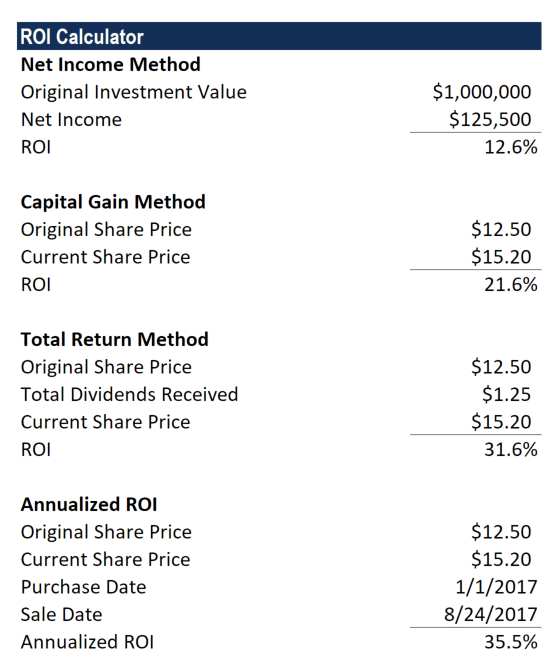
The ROI for this investor can be calculated as follows:
Here is a step-by-step analysis of the calculation:
If you further dissect the ROI into its component parts, it is revealed that 23.75% came from capital gains and 5% came from dividends. This distinction is important because capital gains and dividends are taxed at different rates.
A positive ROI means that net returns are positive because total returns are greater than any associated costs. A negative ROI indicates that the total costs are greater than the returns.
An Alternative ROI Calculation
Annualized ROI helps account for a key omission in standard ROI—namely, how long an investment was held.
Annualized ROI
The annualized ROI calculation provides a solution for one of the key limitations of the basic ROI calculation. The basic ROI calculation does not take into account the length of time that an investment is held, also referred to as the holding period. The formula for calculating annualized ROI is as follows:
Assume a hypothetical investment that generated an ROI of 50% over five years. The simple annual average ROI of 10%–which was obtained by dividing ROI by the holding period of five years–is only a rough approximation of annualized ROI. This is because it ignores the effects of compounding, which can make a significant difference over time. The longer the time period, the bigger the difference between the approximate annual average ROI, which is calculated by dividing the ROI by the holding period in this scenario, and annualized ROI.
From the formula above,
This calculation can also be used for holding periods of less than a year by converting the holding period to a fraction of a year.
Assume an investment that generated an ROI of 10% over six months.
In the equation above, the numeral 0.5 years is equivalent to six months.
Comparing Investments and Annualized ROI
Annualized ROI is especially useful when comparing returns between various investments or evaluating different investments.
Assume that an investment in stock X generated an ROI of 50% over five years, while an investment in stock Y returned 30% over three years. You can determine what the better investment was in terms of ROI by using this equation:
According to this calculation, stock Y had a superior ROI compared to stock X.
Combining Leverage With ROI
Leverage can magnify ROI if the investment generates gains. By the same token, leverage can amplify losses if the investment proves to be a losing investment.
The calculation must also account for the cost of buying on margin. In this example, the margin loan carried an interest rate of 9%.
Here is the calculation for ROI in this scenario:
The Problem of Unequal Cash Flows
When evaluating a business proposal, it’s possible that you will be contending with unequal cash flows. In this scenario, ROI may fluctuate from one year to the next.
This type of ROI calculation is more complicated because it involves using the internal rate of return (IRR) function in a spreadsheet or calculator.
The investment will generate cash flows over the next five years; this is shown in the Cash Inflow row. The row called Net Cash Flow sums up the cash outflow and cash inflow for each year.
Investopedia / Sabrina Jiang
Using the IRR function, the calculated ROI is 8.64%.
Investopedia / Sabrina Jiang
In this case, the IRR is now only 5.00%.
The substantial difference in the IRR between these two scenarios—despite the initial investment and total net cash flows being the same in both cases—has to do with the timing of the cash inflows. In the first case, substantially larger cash inflows are received in the first four years. Considering the time value of money, these larger inflows in the earlier years have a positive impact on IRR.
Advantages of ROI
The biggest benefit of ROI is that it is a relatively uncomplicated metric. It is easy to calculate and intuitively easy to understand.
Due to its simplicity, ROI has become a standard, universal measure of profitability. As a measurement, it is not likely to be misunderstood or misinterpreted because it has the same connotations in every context.
Disadvantages of ROI
There are some disadvantages to the ROI measurement. First, it does not take into account the holding period of an investment, which can be an issue when comparing investment alternatives.
For example, assume investment X generates an ROI of 25%, while investment Y produces an ROI of 15%. One cannot assume that X is the superior investment unless the time frame of each investment is also known. It’s possible that the 25% ROI from investment X was generated over a period of five years, while the 15% ROI from investment Y was generated in only one year.
Calculating annualized ROI can overcome this hurdle when comparing investment choices.
No Risk Adjustment
A second disadvantage of ROI is that it does not adjust for risk.
Investment returns have a direct correlation with risk: the higher the potential returns, the greater the possible risk. This can be observed firsthand in the stock market, where small-cap stocks are likely to have higher returns than large-cap stocks but also are likely to have significantly greater risks.
An investor who is targeting a portfolio return of 12%, for example, would have to assume a substantially higher degree of risk than an investor whose goal is a return of 4%. If that investor hones in on the ROI number without also evaluating the associated risk, the eventual outcome may be very different from the expected result.
Some Costs May Be Omitted
ROI figures can be inflated if all possible costs are not included in the calculation. This can happen deliberately or inadvertently.
For example, in evaluating the ROI on a piece of real estate, all associated expenses should be considered. These include mortgage interest, property taxes, and insurance. They also include maintenance costs, which can be unpredictable.
These expenses can subtract from the expected ROI. Without including all of them in the calculation, the ROI figure may be grossly overstated.
Some Issues May Be Ignored
Finally, like many profitability metrics, ROI considers only financial gains when evaluating the returns on an investment. It does not consider ancillary benefits, such as social or environmental costs.
A relatively new ROI metric, known as social return on investment (SROI), helps to quantify some of these benefits for investors.
How to Calculate ROI in Excel
What Is ROI?
Return on investment, or ROI, is a straightforward measurement of the bottom line. How much profit (or loss) did an investment make after considering its costs?
ROI is used for a wide range of business and investing decisions. It can be used to calculate the actual returns on an investment, to project the potential return on a new investment, or to compare the potential returns on a number of investment alternatives.
For example, if a business owner is considering expanding into a new product line, the ROI formula can be used to chart out its costs and estimate its potential returns. If an entrepreneur is evaluating a new project, an ROI calculation can help determine if the likely return is worth the expense. If an investor is evaluating past or future stock purchases, the ROI formula is a quick indicator of real or potential stock performance.
How Is Return on Investment (ROI) Used?
ROI is a straightforward method of calculating the return on an investment. It can be used to measure profit or loss on a current investment or to evaluate the potential profit or loss of an investment that you are considering making.
Keep in mind that ROI omits a key factor: the length of time that it took to earn that profit (or make that loss). Obviously, a stock that makes a 10% return in one year is preferable to a stock that makes a 10% return in four years.
For this reason, the formula for annualized return on investment may be a better choice than the basic formula for return on investment. (Both are shown above.)
How Do You Calculate ROI for Real Estate?
The return on investment (ROI) formula remains the same whether you’re evaluating the performance of a single stock or considering the potential profit of a real estate investment. (See formula above.)
Some investments are more complicated to evaluate than others, though, particularly when it comes to costs. A ROI on a real estate investment must include all of the potential costs that may be involved, including such matters as maintenance, repairs, insurance, and lost rental income.
The Bottom Line
Return on investment (ROI) is a simple and intuitive metric of the profitability of an investment. There are some limitations to this metric, including the facts that it does not consider the holding period of an investment and is not adjusted for risk. Despite these limitations, ROI is a key metric used by business analysts to evaluate and rank investment alternatives.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/jason_mugshot__jason_fernando-5bfc261946e0fb00260a1cea.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/mansaPicture_08T-Copy-JuliusMansa-127908fd255745b5886a16fced0cdb7b.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SuzannesHeadshot-3dcd99dc3f2e405e8bd37271894491ac.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():gifv()/returnoninvestment_final2-ba1e17c451154f6792b07ddf008bd826.jpg)






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/andy__andrew_beattie-5bfc262946e0fb005143d642.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/JamesHeadshot-PeggyJames-9f712f1197374a9b824289fe0d5ec842.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2G8T0126-BW-5a525a4d8c434885b365bee7b3807f60.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_A_Guide_to_Calculating_Return_on_Investment_ROI_Aug_2020-01-82c5e4327e174fab8b2905ea7220417d.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_A_Guide_to_Calculating_Return_on_Investment_ROI_Aug_2020-02-221fa416eaef4e88bcdfd36dd9553bdd.jpg)