How to delete file ubuntu
How to delete file ubuntu
How to Delete a File in Ubuntu
If you are a new Ubuntu user and don’t know how to delete a file or multiple files in Ubuntu using the command line or via the GUI, we will cover in this article all details about how to remove or delete a file in Ubuntu. It is important to note that you need certain writable permissions to delete a file in the Ubuntu Linux system.
Methods to Remove or Delete Files in Ubuntu
Using the following two different methods, you can delete or remove a file in the Ubuntu Linux system:
Important Note: You must be extra careful before deleting a file from your Ubuntu system. Once the file is deleted from the system, it would be hard to recover its content.
Method 1: Delete or Remove a File in Ubuntu Using Terminal
Using this method, you can remove a file using the command line application ‘Terminal’. Two Linux commands are available to delete or remove a file in Ubuntu distribution. First is the ‘Unlink’ command but, you can delete only a single file using this command.
The other most popular is the ‘rm’ command shortly used for “remove”, which is used to delete a file in the Ubuntu Linux system. Using the ‘rm’ command, you can delete multiple files at once from your Ubuntu system.
How to Use the Unlink Command to Delete a File?
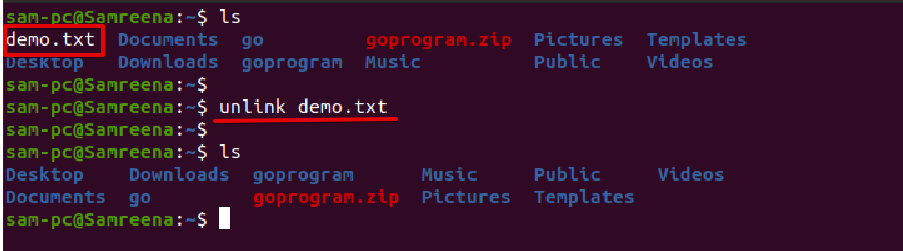
To delete or remove a file using the unlink command, type the unlink command followed by the name of the file which you want to delete. The syntax of the unlink command is mentioned below:
Example
For example, we want to remove a text file with the name ‘demo.txt’ from the Ubuntu system. Using the above ‘unlink’ command, you can easily delete this file from your system as follows:
Delete or Remove a File Using the rm Command
Using the rm command, you can delete single or multiple files in the Ubuntu system. To delete a file using the ‘rm’ command, use the following syntax:
Example
For example, we want to remove a text file from the system ‘Downloads’. To do this task, use the rm command followed by the file path as follows:
If you delete a write-protected file from the Ubuntu system, the prompt displays on the terminal screen for confirmation, enter ‘y’ and then press the ‘Enter’ key. Otherwise, the file will be deleted from your system without displaying any confirmation prompt.
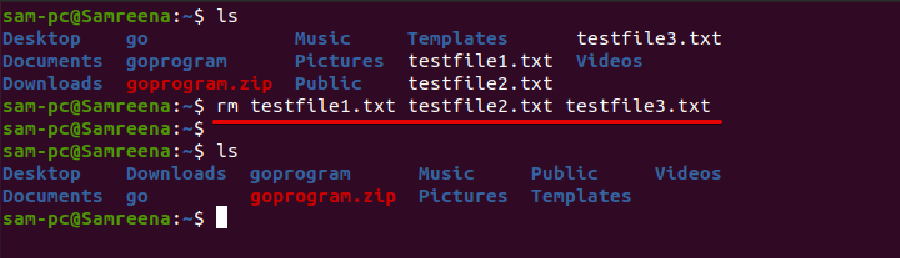
Delete multiple files using the rm command
You can also delete multiple files from the Ubuntu system using the ‘rm’ command. To remove multiple files, you must have certain write permissions on the files. To remove or delete multiple files from your system, use the ‘rm’ command and specify the file names which will be separated by a space as follows:
Delete multiple similar files using the wildcard (*)
You can also remove the multiple match file in the current directory using the regular expansions or wildcard(*).
Options with rm Command
The following options can use along with the rm command:
How to Use rm Command Options?
We discussed a few examples here related to ‘rm’ command options, which are given below:
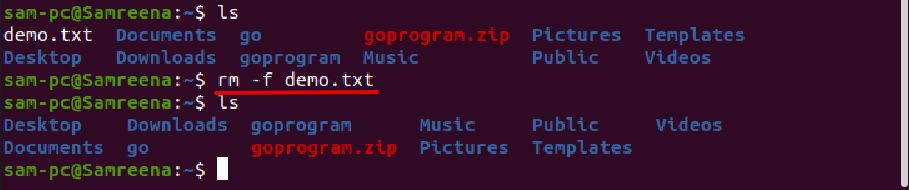
Type the ‘rm’ command followed by the option ‘-i’ that each time confirms before deleting a file:
If you delete a file without displaying a user confirmation prompt, even if the files are write-protected then, use the ‘rm’ command followed by the option ‘-f’.
You can also combine rm command options for deleting a file. For example, to delete all matched files from the current directory without prompt a verbose. Use the ‘rm’ command and also mention the ‘-fv’ option as follows:
Method 2: Delete a File Using the Graphical User Interface
To delete a file using the GUI, you should have writable permissions on the file and you must be logged in as a root user on your Ubuntu system. By following few simple steps, you can easily delete a file or multiple files from the Ubuntu system:
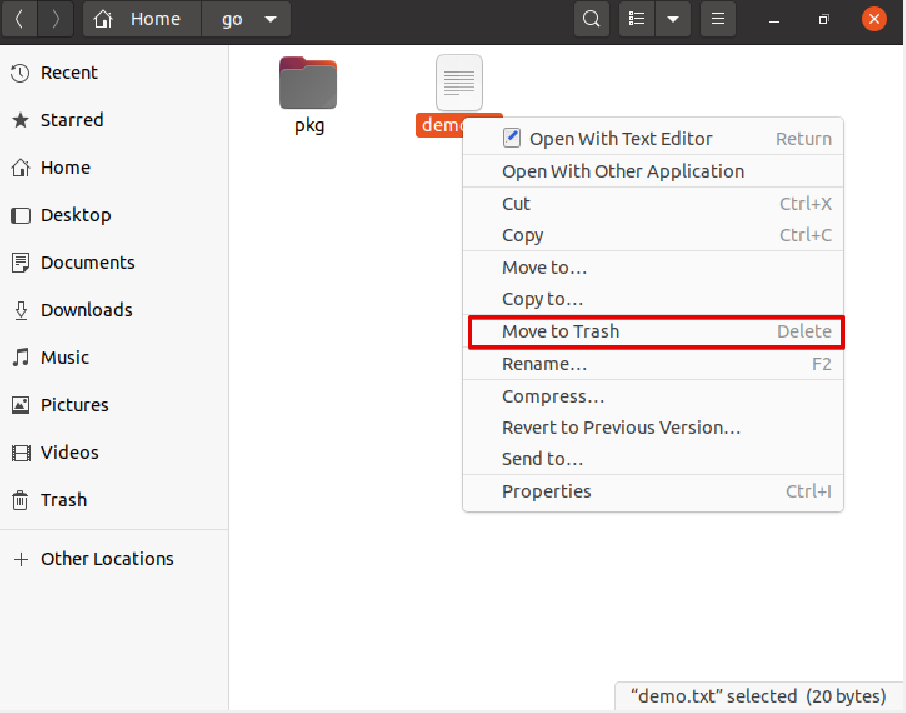
Go into the Ubuntu file system and right-click on a file that you want to delete from your system.
To delete the selected file, choose ‘move to trash’ from the displayed dropdown list.
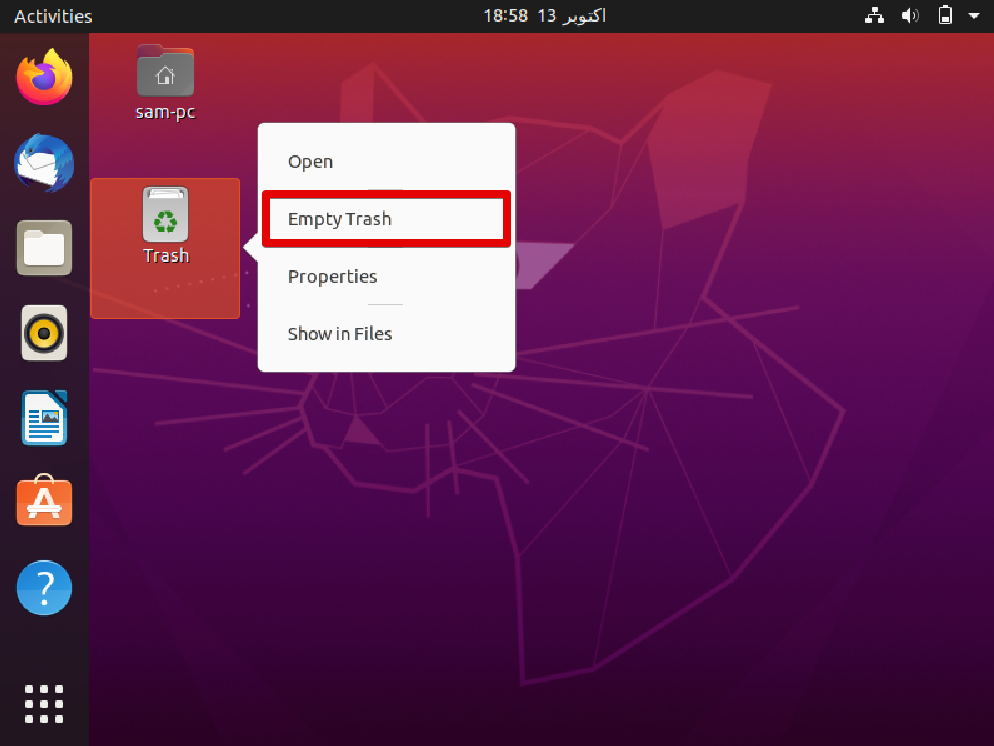
To permanently remove from the ‘Trash’ folder, right-click on the Trash and then choose the ‘empty trash’.
Conclusion
We learned how to delete files in the Ubuntu Linux system. Moreover, we have also seen some files we cannot delete using GUI but these type of files you can delete via the command line by executing commands as a root user.
About the author
Samreena Aslam
Samreena Aslam holds a master’s degree in Software Engineering. Currently, she’s working as a Freelancer & Technical writer. She’s a Linux enthusiast and has written various articles on Computer programming, different Linux flavors including Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and Mint.
How To Delete File In Linux?
Deleting files in Linux can be sometimes tricky. We have a tool named rm which is the shortcut for the word remove. In this tutorial, we will look at how to remove or delete a file in Linux with different examples and ways.
rm Command Syntax
rm command syntax is the same as the most the Linux command. We can provide options before specifying the file and directories we cant to operate or delete.
rm Command Help
Delete Single File with rm Command
We will start with simple steps just deleting a single file. We will just specify the file name we want to delete. In order to remove the file successfully, we should have privileges to modify a file. For example, if we try to remove the file owned by root with a regular user we will get an error and would not delete the file. In this example, we will delete the file named foo.txt
Delete Multiple Files with rm Command
We have the ability to delete multiple files in a single rm command. We will just put file names we want to delete by separating them with space. In this example, we will delete file names foo.txt and bar.txt but we can add more if we need it.
Delete Files According To Their Extensions/Types with rm Command
We can also specify names like deleting all files which name starts with pof like below.
Delete Files Recursively
Delete File with Prompt Before Every Removal
Print Verbose Output About Delete Operation
Delete empty Directories or Folders with rmdir Command
In some cases, we need to delete empty folders. rm without options will not work in this case as we can see this in the following screenshot. We case use rmdir command to remove an empty directory or folder.
Read File Names From Text File For Delete or Removal
Another interesting use case for rm command is providing file or directory names from a list like a text file. We will use xargs command to-read the list and redirect to the rm command.
Delete Files By Reading Their Names From A File/List
Delete Files By Finding them with find Command
find is a very useful command which is used to find files and folders. find command also provides some options like running commands on the search results. We can also remove or delete files found by the find command. In this example, we will delete files that are older than 3 days.
How to remove files on Ubuntu
There are two types of files; Program files and Data files. Program files contain software instructions which can be executable, Data files contain simple information. Files can be distinguished by file extensions like pdf files will have “.pdf” and text files “.txt” extensions. We can save, move, update or delete files in the system.
In this Article we will discuss how to remove/delete unnecessary files or files from the system to free up storage using Ubuntu Linux commands. Follow the steps to successfully remove the file from the system.
Removing files on Ubuntu using rm command
The rm command is used to delete files from the system at a time.
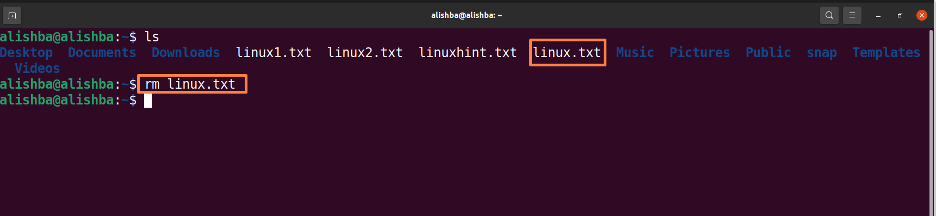
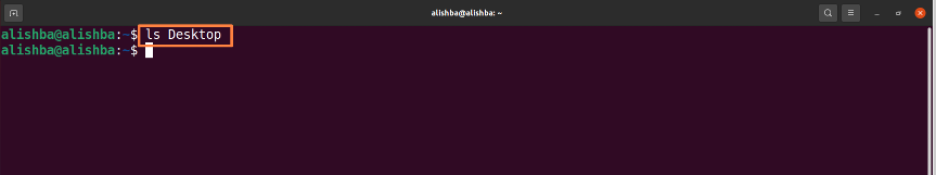
Removing a file using rm command: Run the below mentioned command to remove “linux.txt” file from current directory:
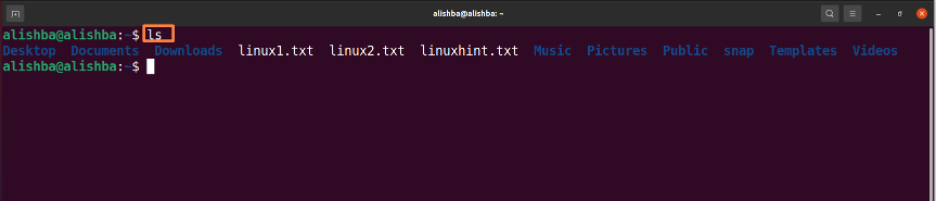
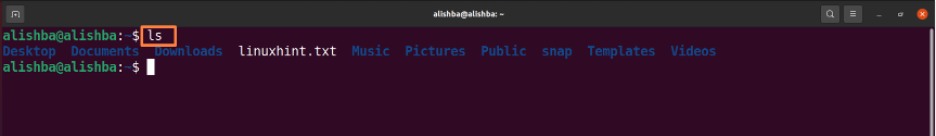
The “ls” command is used to list all files of current directory to check whether the file to be removed exist or not:
Now run the below mentioned command to check that whether file is removed by displaying all files of current directory:
Now from the above image we can see “linux.txt” no longer exists in the current directory.
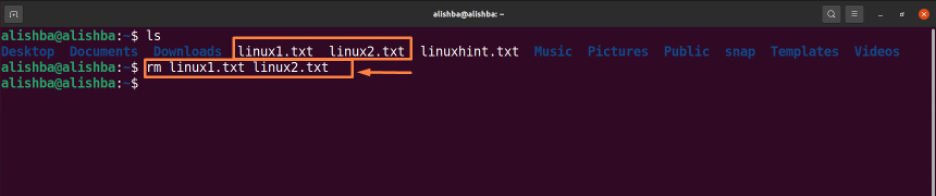
Removing multiple files at a time: Run the below mentioned command to delete “linux1.txt” and “linux2.txt” from current directory:
Change filenames ”linux1.txt, linux2.txt” according to your requirement. The “ls” command is used to list all files of current directory to check whether the files to be removed exist or not
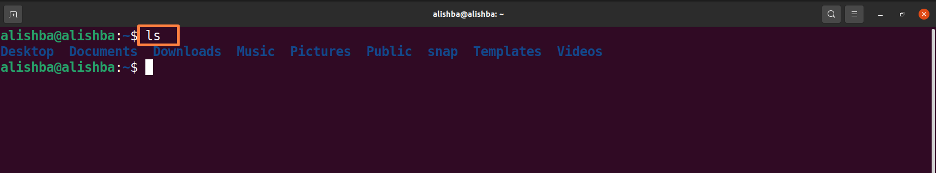
Now run the below mentioned command to check that whether file is removed or not by displaying all files of current directory:
We can see “linux1.txt, linux2.txt” no longer exist in the current directory.
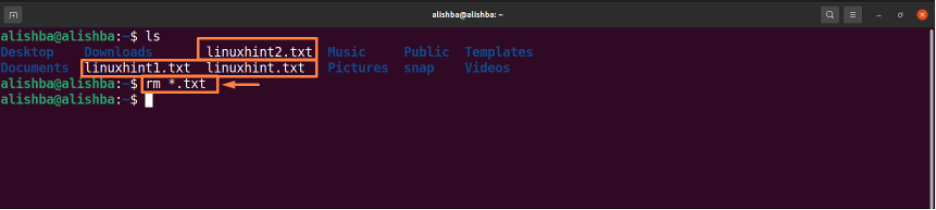
Removing all files of same type : To remove all similar type use a wildcard (*) and standard expansions. Run the below mentioned command to remove all “.txt” files from current directory:
The “ls” command is used to list all files of the current directory to check whether the files to be removed exist or not.
Now run the below mentioned command to check that whether file is removed by displaying all files of current directory:
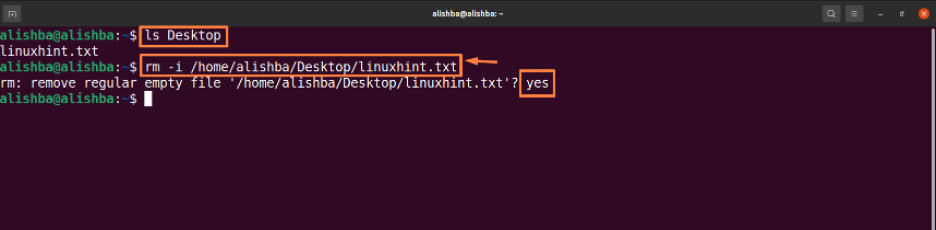
Provide the path of the file to remove the file which is not in the current directory. The “ls” command is used to list all files of the desktop directory to check whether the files to be removed exist or not. You have to enter “yes” to confirm deletion of the file.
Now run the below mentioned command to check that whether file is removed by displaying all files of current directory:
Removing files on Ubuntu using unlink command
The unlink command is also used to delete one file at a time.
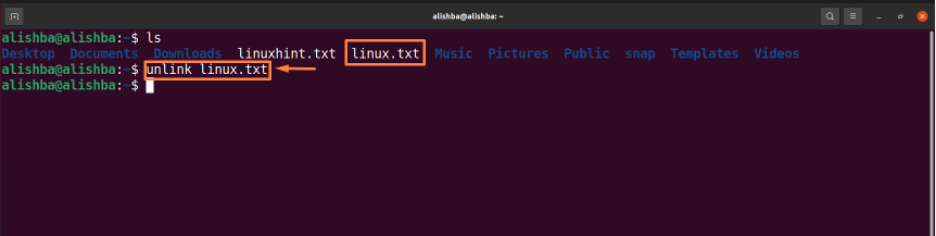
Removing file from current directory : Run the below mentioned command to remove “linux.txt” file from current directory:
The “ls” command is used to list all files of the desktop directory to check whether the files to be removed exist or not.
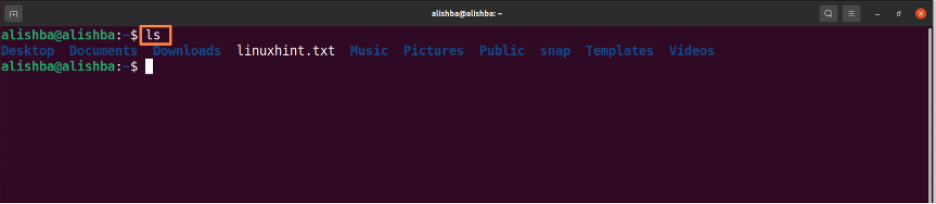
Now run the below mentioned command to check that whether file is removed by displaying all files of current directory:
Removing files on Ubuntu through GUI
If you are beginner and don’t know to use Command Line properly then you can also delete files using GUI method as shown below:
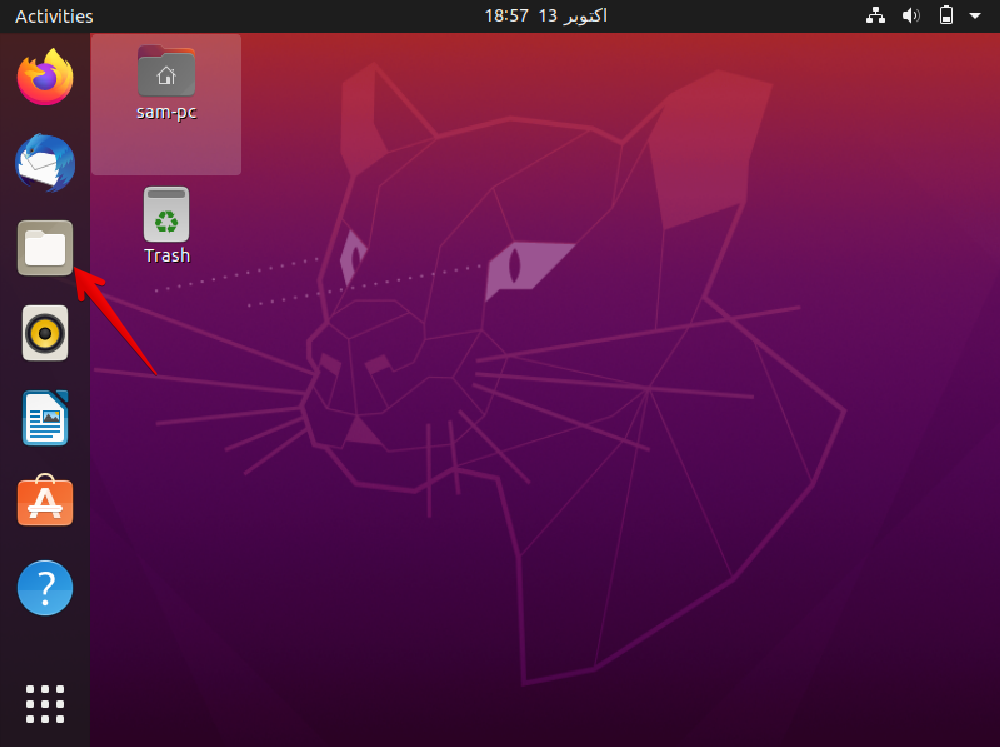
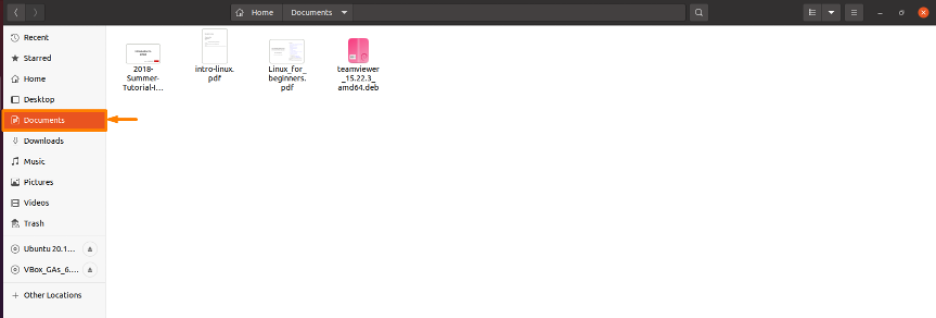
Step 1: Open File location
First open the directory or folder in which your file (which you want to delete) is present, as my file is in “Documents” folder so I will open “Documents” folder:
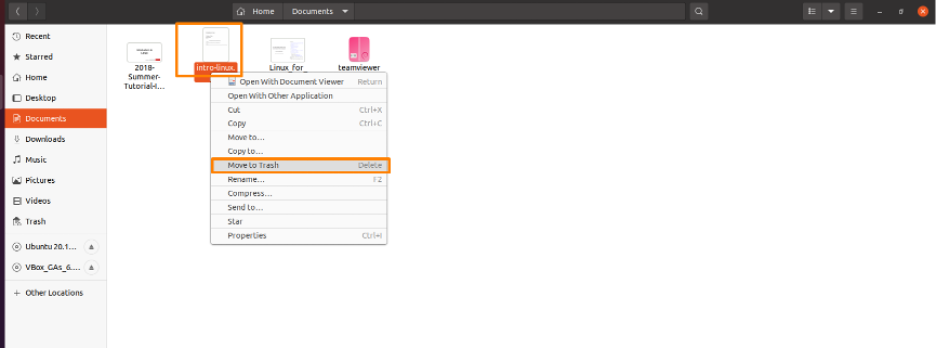
Step 2: Delete the file
Now to delete the specific file, right click on that file and a drop down list will appear, choose “Move to trash” option from list and your file will be deleted, I am deleting “intro-linux.pdf” file from my Documents folder:
And file will no longer present in folder as shown below:
Conclusion
About the author
Alishba Iftikhar
I am currently an undergraduate student in my 1st year. I am an internee author with Linuxhint and loved learning the art of technical content writing from senior authors. I am looking forward to opting my career as a full time Linux writer after I graduate.
How to Remove (Delete) a File or Directory in Linux
Home » SysAdmin » How to Remove (Delete) a File or Directory in Linux
How do I delete a file in Linux using the command line option? How can I remove a Linux directory?
Deleting files and directories is a necessary task when working with Linux. In this guide, learn how to remove files and directories from the command line in Linux using the RM Command.
Note: If you feel that a directory is misplaced and you do not want to remove it, try moving it to a different place. To learn how, visit our post How to Move Directories in Linux.
How To Remove or Delete Linux Files
The rm command deletes files in a Linux. The command unlinks the data from the file name, allowing the user to overwrite on that particular storage space.
To delete a single file, entering the following in the command line:
The rm command can be used to delete more than one file at a time:
Wildcards can be used with this command.
This method is also used to delete all files that contain a string of characters:
This will erase any file that has the word sample in the name.
The system will search the current directory for the file you want to remove.
To delete a file in a different directory, either switch to that directory first:
Or you can specify the file location in a single command directly:
Note: Once the rm command has deleted a file, you will not be able to access it. The only way to retrieve a file would be to restore it from a backup (if one is available).
rm Command Options
You can adjust the way the rm command works by adding options. An option is a hyphen, followed by one or more letters that stand for commands.
If you’re deleting multiple files, add a confirmation prompt. Use the –i option to use an interactive dialog:
Confirm the deletion of files by typing ‘yes’ or ‘no.’
To display the progress of the deletion with the v or verbose command:
The output confirms that the file test.txt has been successfully removed.
To force the removal of a file that’s write-protected, use the –f option:
To use sudo privileges for a file that says Access denied and delete it:
How to Delete a Directory in Linux
A linux directory (or folder) can be empty, or it can contain files. To remove a directory in Linux, use one of the following two commands:
Remove Directory Linux with rm Command
To remove a directory (and everything inside of it) use the –r option as in the command:
This will prompt you for confirmation before deleting.
To remove a directory without confirmation:
Also, you can delete more than one directory or folder at a time:
Remove Directories in Linux with rmdir Command
Remember, the rmdir command is used only when deleting empty folders and directories in Linux. If a specified directory is not empty, the output displays an error.
The basic syntax used for removing empty Linux folders/directories is:
Additionally, you can delete multiple empty directories at once by typing:
If the command finds content in one of the listed directories, it will skip it and move on to the next one.
Note: To permanently delete a file in Linux by overwriting it, use the shred command.
With this tutorial, deleting files and directories in Linux was made easy. The rm and rmdir commands are flexible with many options available.
Ubuntu Documentation
Why use the terminal?
«Under Linux there are GUIs (graphical user interfaces), where you can point and click and drag, and hopefully get work done without first reading lots of documentation. The traditional Unix environment is a CLI (command line interface), where you type commands to tell the computer what to do. That is faster and more powerful, but requires finding out what the commands are.»
— from man intro(1)
This page gives an introduction to using the command-line interface terminal, from now on abbreviated to the terminal. There are many varieties of Linux, but almost all of them use similar commands that can be entered from the terminal.
There are also many graphical user interfaces (GUIs), but each of them works differently and there is little standardization between them. Experienced users who work with many different Linux distributions therefore find it easier to learn commands that can be used in all varieties of Ubuntu and, indeed, in other Linux distributions as well.
For the novice, commands can appear daunting:
However, it is important to note that even experienced users often cut and paste commands (from a guide or manual) into the terminal; they do not memorize them.
Starting a terminal
In Unity
Unity is the default desktop environment used as of 11.04. Where systems are not ready for Unity they revert to GNOME which is also used in previous releases such as Ubuntu 10.04 LTS (Lucid), see next sub-section.
Keyboard Shortcut: Ctrl + Alt + T
In GNOME
GNOME is the classic desktop environment for Ubuntu 11.04 (Natty) and is the default desktop environment in earlier releases, such as Ubuntu 10.04 LTS (Lucid).
Keyboard Shortcut: Ctrl + Alt + T
In Xfce (Xubuntu)
Keyboard Shortcut: Super + T
Keyboard Shortcut: Ctrl + Alt + T
In KDE (Kubuntu)
In LXDE (Lubuntu)
Keyboard Shortcut: Ctrl + Alt + T
Commands
sudo: Executing Commands with Administrative Privileges
The sudo command executes a command with administrative privileges (root-user administrative level), which is necessary, for example, when working with directories or files not owned by your user account. When using sudo you will be prompted for your password. Only users with administrative privileges are allowed to use sudo.
File & Directory Commands
) symbol stands for your home directory. If you are user, then the tilde (
) stands for /home/user
pwd: The pwd command will allow you to know in which directory you’re located (pwd stands for «print working directory»). Example: «pwd» in the Desktop directory will show «
/Desktop». Note that the GNOME Terminal also displays this information in the title bar of its window. A useful gnemonic is «present working directory.»
ls: The ls command will show you (‘list’) the files in your current directory. Used with certain options, you can see sizes of files, when files were made, and permissions of files. Example: «ls
« will show you the files that are in your home directory.
cd: The cd command will allow you to change directories. When you open a terminal you will be in your home directory. To move around the file system you will use cd. Examples:
To navigate into the root directory, use «cd /»
To navigate to your home directory, use «cd» or «cd
To navigate through multiple levels of directory at once, specify the full directory path that you want to go to. For example, use, «cd /var/www» to go directly to the /www subdirectory of /var/. As another example, «cd
/Desktop» will move you to the Desktop subdirectory inside your home directory.
mv: The mv command will move a file to a different location or will rename a file. Examples are as follows: «mv file foo» will rename the file «file» to «foo». «mv foo
‘ in place of the home directory.
Note that if you are using mv with sudo you can use the
shortcut, because the terminal expands the
will refer to the root account’s home directory, not your own.
rm: Use this command to remove or delete a file in your directory.
mkdir: The mkdir command will allow you to create directories. Example: «mkdir music» will create a directory called «music».
Here is an example of when it would be necessary to execute a command with administrative privileges. Let’s suppose that another user has accidentally moved one of your documents from your Documents directory to the root directory. Normally, to move the document back, you would type mv /mydoc.odt
/Documents/mydoc.odt, but by default you are not allowed to modify files outside your home directory. To get around this, you would type sudo mv /mydoc.odt
/Documents/mydoc.odt. This will successfully move the document back to its correct location, provided that you have administrative privileges.
Running a File Within a Directory
So you’ve decided to run a file using the command-line? Well. there’s a command for that too!
./filename.extension
System Information Commands
du: The du command displays the disk usage for a directory. It can either display the space used for all subdirectories or the total for the directory you run it on. Example:
In the above example -s means «Summary» and -h means «Human Readable».
top: The top (‘table of processes’) command displays information on your Linux system, running processes and system resources, including CPU, RAM & swap usage and total number of tasks being run. To exit top, press «q».
ip addr reports on your system’s network interfaces.
Adding A New User
The «adduser newuser» command will create a new general user called «newuser» on your system, and to assign a password for the newuser account use «passwd newuser».
Options
«Man» and getting help
Nearly every command and application in Linux will have a man (manual) file, so finding them is as simple as typing «man «command»» to bring up a longer manual entry for the specified command. For example, «man mv» will bring up the mv (move) manual.
Move up and down the man file with the arrow keys, and quit back to the command prompt with «q».
«man man» will bring up the manual entry for the man command, which is a good place to start!
There are also info pages, which are generally more in-depth than man pages. Try «info info» for the introduction to info pages.
Some software developers prefer info to man (for instance, GNU developers), so if you find a very widely used command or app that doesn’t have a man page, it’s worth checking for an info page.
Searching the manual pages
If you aren’t sure which command or application you need to use, you can try searching the manual pages. Each manual page has a name and a short description.
To search the names for enter:
To search the names or descriptions for enter:
Other Useful Things
Prettier Manual Pages
Users who have Konqueror installed will be pleased to find they can read and search man pages in a web browser context, prettified with their chosen desktop fonts and a little colour, by visiting man:/command in Konqueror’s address bar. Some people might find this lightens the load if there’s lots of documentation to read/search.
Pasting in commands
Often, you will be referred to instructions that require commands to be pasted into the terminal. You might be wondering why the text you’ve copied from a web page using Ctrl + C won’t paste in with ctrl+V. Surely you don’t have to type in all those nasty commands and filenames? Relax. ctrl+shift+V pastes into a GNOME terminal; you can also do middle button click on your mouse (both buttons simultaneously on a two-button mouse) or right click and select Paste from the menu. However, if you want to avoid the mouse and yet paste it, use «Shift + Insert», to paste the command. If you have to copy it from another terminal / webpage, you can use «Ctrl + Insert» to copy.
Save on typing
Up Arrow or Ctrl + P
Scrolls through the commands you’ve entered previously.
Down Arrow or Ctrl + N
Takes you back to a more recent command.
Enter
When you have the command you want.
tab
A very useful feature. It autocompletes any commands or filenames, if there’s only one option, or else gives you a list of options.
Ctrl + R
Searches for commands you’ve already typed. When you have entered a very long, complex command and need to repeat it, using this key combination and then typing a portion of the command will search through your command history. When you find it, simply press Enter.
History
The history command shows a very long list of commands that you have typed. Each command is displayed next to a number. You can type !x to execute a previously typed command from the list (replace the X with a number). If you history output is too long, then use history | less for a scrollable list.
Example: you ran history and found you want to use command 1967. Simply enter
Change the text
The mouse won’t work. Use the left/right arrow keys to move around the line.
Ctrl + A or Home
Moves the cursor to the start of a line.
Ctrl+ E or End
Moves the cursor to the end of a line.
Esc + B
Moves to the beginning of the previous or current word.
Ctrl + K
Deletes from the current cursor position to the end of the line.
Ctrl + U
Deletes from the start of the line to the current cursor position.
Ctrl + W
Deletes the word before the cursor.
Alt + B
Goes back one word at a time.
Alt + F
Moves forward one word at a time.
Alt + C
Capitalizes letter where cursor is and moves to end of word.
More ways to run a terminal
You can set your own keyboard shortcut to run a terminal. See KeyboardShortcuts for details of keyboard shortcuts.
An extremely handy tool :: Incremental history searching
In terminal enter:
Then copy paste and save:
From now on, and many agree this is the most useful terminal tool, it saves you a lot of writing/memorizing.
All you need to do to find a previous command is to enter say the first two or three letters and upward arrow will take you there quickly:
All I need to do is enter:
And hit upward arrow command will soon appear.
How to create upsidedown and/or reverse text with your terminal
If you wish or need to ever flip text upside down [vertical flip] «uʍop ǝpısdn ʇxǝʇ dıʃɟ» or/and create reverse text here is a terminal way to achieve this.
Copy/paste and save the following as flip.pl in your home folder (thanks to Lars Noodén for script).
Then to set it up:
Then open terminal and enter:
Write what you want and hit return
If you want to reverse back to front, write your text in a text editor and save as mytext to the home folder.
Copy and paste the result, tluser eht etsap dna ypoc.
And of course you can combine both for truly cryptic results, ɔodʎ ɐup dɐsʇǝ ʇɥǝ ɹǝsnʃʇ
More Information
Within the Community Help Wiki:
Detailed tutorials on the Linux command line:
UsingTheTerminal (последним исправлял пользователь clissold345 2016-07-02 09:16:41)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details
You can contribute to this wiki, see Wiki Guide for details