How to get ssl certificate
How to get ssl certificate
Security is essential for any website to provide security, build the trust of visitors, and for better ranking.
It’s necessary for the transactional or membership-based site to encrypt the sensitive data from a client to a server.
Improve your Website Security with SSL/TLS Certificate.
HTTPS would also boost the search engine ranking, so you may consider having this for your blog as well.
The following acronyms are used below.
If you are looking for shared hosting that provides a free SSL certificate, you may try SiteGround. If you are wondering why SiteGround then, the following are some of the features.
Now, let’s take a look at the following to get a certificate.
ZeroSSL
You can get your SSL certificate in just a few minutes with ZeroSSL. You start by entering the required details, go through the quick verification process, and BOOM, there’s your SSL certificate ready.
The generated SSL certificate is 100% free to use and lasts for 90 days, after which you can renew again and again at no cost.
Don’t want to renew the certificate manually?
No problem, you can use ZeroSSL Certbot to automate the renewal. Cool, isn’t it?
ZeroSSL is a certificate authority, so certs are issued by them. You can manage all your certs with their easy-to-use dashboard. You get up to 3 certificates for FREE. However, if you need more, you can go for a paid plan which offers unlimited certificates with many other premium features.
They also offer a custom solution, so talk to them if you have a business requirement to issue certificates for your clients.
Let’s Encrypt
Let’s Encrypt is a collaborative project with Linux Foundation and a new certificate authority sponsored by Mozilla, Akamai, SiteGround, Cisco, Facebook, etc., which offers an SSL/TLS Certificate free.
This is great to save costs to get it implemented in a non-production environment.
It’s automated, which means you don’t have to spend time creating CSR and send it to the CA authority to get it signed. It all happens in the background on your web servers.
Let’s Encrypt has issued more than one billion certificates so far. Check out the guides to implement Let’s Encrypt in Apache HTTP or Nginx.
SSL For Free
SSL For Free uses Let’s Encrypt ACME server by using domain validation to provide you a certificate. It’s 100% free, and certs are issued within minutes.
SSL.com offers free SSL at zero cost for 90 days. This is a good fit if you are looking to play around to understand how SSL works or some short-term projects.
Get your free SSL cert issued in minutes with the highest strength and bit encryption. All the main browsers recognize SSL.com issued certificates.
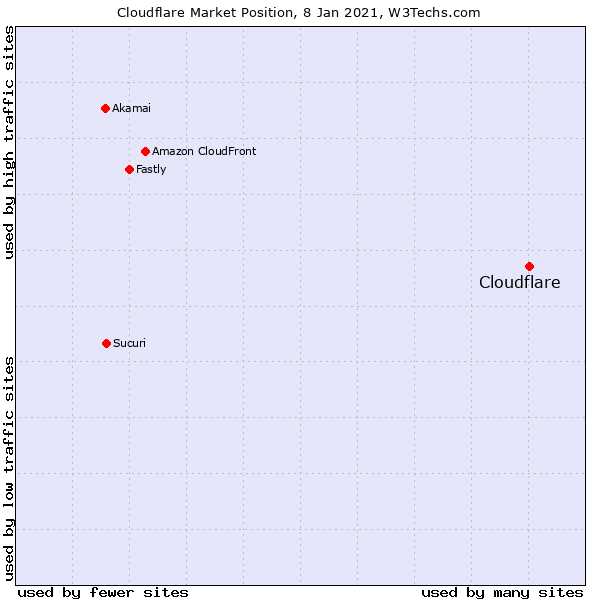
Cloudflare
Cloudflare is CDN & Security Company. They make your website faster and secure—Cloudflare power many popular sites, including Reddit, yelp, Mozilla, StackOverflow, etc.
Recently, Cloudflare announced universal SSL is free for all users. That’s right, even if you are in the free plan. If you are using Cloud Flare and SSL is not yet activated, then here is how you can do it quickly.
It may take a few seconds to go live. You can verify by accessing your website with HTTPS.
Cloudflare’s FREE SSL certificate is also offered by many hosting providers who integrate tightly with Cloudflare to offer CDN and web security. One such example is Kinsta for premium WordPress hosting.
30 Days Free
You may also obtain 30 days of the free trial from the following certificate providers.
I hope the above helps you in getting free SSL for your website/blog. But if you are looking to buy a premium certificate for enterprise business, you can check out the SSL Store.
How to Install an SSL Certificate
Last updated on: June 22nd, 2022
How to Install an SSL Certificate
With an SSL certificate, your website can use the HTTPS protocol to securely transfer information from point A to B. This is crucial when transferring sensitive information like credit card data on checkout pages and personally identifiable information (PII) on login and contact forms.
In addition to security benefits, websites with SSL encryption get better rankings on Google and improved performance through the use of HTTP/2. It’s also important to understand that SSL does not protect your website — rather, it protects the data that is sent through your website.
This guide is designed to show beginners and intermediate users how to deploy a free SSL certificate from Let’s Encrypt on their self-hosted websites.
Step 1
Gather Requirements
It is now easier than ever to use HTTPS on your website. Beginners should start by having a conversation with their hosting company about the options they offer.
There are a few easy ways to add SSL to your website:
Regardless of the type of certificate you choose, the encryption and level of security is the same.
Get Help With SSL & Security
Want to have an SSL certificate and website security? We’ve got you covered.
1.1 – Types of SSL Certificates
Some visitors recognize the additional authenticity and trust offered extended validation (EV) and organization validated (OV) certificates due to their rigorous validation process.
There are three types of certificates to be familiar with:
Domain Validated (DV)
DV certificates only need the certificate authority to verify that the user requesting the certificate owns and administers the domain. Visitors will see a lock icon in their address bar, but no specific information about the owner.
Organization Validated (OV)
OV certificates require a certificate authority to confirm the business making the request is registered and legitimate. When visitors click the green lock icon in their browser, the business name is listed.
Extended Validation (EV)
EV certificates require even more documentation for the certificate authority to validate the organization. Visitors will see the name of the business inside the address bar (in addition to clicking the lock icon); however, most updated browsers no longer display the EV visual indicator.
1.2 – Commercial vs. Free SSL Certificates
It’s important to understand the difference between commercial and free certificates.
Commercial (paid) SSL certificates
These are a decent option for many website owners. Paying a certificate authority (or your hosting company) will often give you the benefits of technical support. The encryption level is the same as with free SSL certificates. The key differentiator will come in the level of support you get with your certificate.
Free SSL certificates
These are being spearheaded by the Let’s Encrypt initiative – an open collaboration between a number of global organizations focused on making SSL certificates accessible to all website owners.
Many hosts offer specific instructions on how to deploy free SSL certificates. Check with your host’s support channels and articles for more information before following this guide.
1.3 – SSL in the Cloud
You can also get the benefits of SSL certificates through cloud providers, such as content delivery networks (CDNs) and website application firewalls (WAFs) solutions like the one from Sucuri, who offer it at no additional charge.
These services are a proxy between the visitor and your website. By changing your domain records to point to their servers, they can cache your content to make your website faster and filter out malicious traffic. This also means that the browser recognizes which server IPs are connected to your domain, allowing for the use of DV certificates.
These providers can also work with your own SSL certificate. If you are a Sucuri customer, you can contact our technical support team for information and assistance.
If you are implementing an SSL certificate through your host, you may want to skip ahead to Step 3: Important Final Steps.
1.4 – Getting a Free SSL Certificate
The following guide works best if you have a dedicated IP for your site (through a VPS or dedicated server). If you’re on a shared platform, talk to your host about deploying Let’s Encrypt; a number of hosts have automated the process of deploying a free SSL for shared hosting accounts. It is possible to use server name indication (SNI) with one server IP address and generate certificates for all sites on the server.
The rest of this guide will assume you have full access and control of your web server.
You will need the following information about your server:
SSH Access Through cPanel
You can contact your host to obtain any missing information.
Step 2
Generate Certificate
Now that you have all the required information, you can connect to your server and install a tool that will generate an SSL certificate.
From your computer, you need a way to log into your server and send SSH commands. If you are on a Mac, you can use Terminal (built-in application) and on Windows you can download PuTTY. Some hosts also offer a web interface for running commands on your server.
The instructions will vary depending on your server software and system. Some systems do not support Certbot, but you can find a list of other reputable clients that should work with your server environment.
2.1 – Overview of Steps
Here is a quick overview of how you can get a free SSL certificate from Let’s Encrypt using the Certbot tool.
Overview of steps to use Certbot:
The following images and animations illustrate the entire process for a server using Apache on Ubuntu 16.04.
Sucuri Customers
Manually removing malicious code from your website files can be extremely hazardous to the health of your website. Never perform any actions without a backup. If you’re unsure, please seek assistance from a professional.
2.2 – Install Certbot Client
Using the instructions provided for your server, install any dependencies and the Certbot tool. The following images are an example of what you can expect.
Get Instructions for Your Server from the Certbot Website
Connect to Your Server Over SSH (GIF)
Install Dependencies (if required) (GIF)
Install Certbot (GIF)
If you are getting permission errors, check with your host to ensure your user has permissions to run administrative commands (i.e. sudo).
2.3 – Generate SSL Certificate
Continuing with the same set of instructions, the Get Started section will provide the commands needed to create the SSL certificate for your website. The following images are an example of what you can expect.
Run Certbot (GIF)
Agree to the Terms
Make a Secure Backup
After generating the certificate the Important Notes shows the location of your Certbot configuration directory. This contains your account credentials, certificate, and private keys.
You should navigate to this location on your server and download a backup. If you aren’t sure how to do this, you can follow our post on how to make backups over the command line.
2.4 – Automate Renewal
Now you have an active SSL certificate on your site! Your certificate will expire, however. Let’s Encrypt certificates are only valid for 90 days. You can automate this process so you don’t have to remember to manually renew the certificate.
It’s recommended to set the cron or systemd job to renew the certificate twice a day. Before you begin, note the location of your Certbot configuration directory from the previous step.
Set Up SSL Certificate Renewal via Cron Job
To schedule the cron job that renews the SSL certificate:
Some server configurations may need to run additional commands to load the new certs.
You can view the full documentation on Certbot renewals for more information.
These charitable organizations are working to help make the internet a safer place for everyone. While these tools are free, you can donate to help support both Let’s Encrypt and Certbot.
We’ve outlined instructions below for how to manually install a certificate (free or paid) using a hosting control panel such as Plesk or cPanel
How to install via the Plesk control panel:
Your certificate signing request displays in the CSR section.
How to upload your certificate:
How to activate your certificate:
How to generate a CSR:
How to install the certificate:
A Beginner’s Guide to SSL: What It is & Why It Makes Your Website More Secure
Maybe you noticed that extra «s» when you were browsing websites that require giving over sensitive information, like when you were paying bills online.
But where’d that extra «s» come from, and what does it mean?
To put it simply, the extra «s» means your connection to that website is secure and encrypted; any data you enter is safely shared with that website. The technology that powers that little «s» is called SSL, which stands for “Secure Sockets Layer.”
As a consumer, you always want to see https:// when visiting any site you trust with your essential information. As a marketer, you’ll want to make sure you have an SSL or two for your audience.
Let’s talk about why SSL is a big deal.
What is an SSL certificate?
SSL certificates are a small data files that cryptographically establish an encrypted link between a web server and a browser. This link ensures that all data passed between the web server and browser remain private.
When you land on a page with a form to fill in and submit, the information you enter can be intercepted by a hacker on an unsecure website.
This information could be anything from details on a bank transaction to an email enter to register for an offer. In hacker lingo, this «interception» is often referred to as a «man-in-the-middle attack.»
Wondering how attacks happen? Here’s one of the most common ways: A hacker places a small, undetected listening program on the server hosting a website. That program waits in the background until a visitor starts typing information on the website, and it will activate to start capturing the information and then send it back to the hacker.
A little scary, right?
But when you visit a website that’s encrypted with SSL, your browser will form a connection with the web server, look at the SSL certificate, then bind your browser and the server. This binding connection is secure to ensure no one besides you and the website can see or access what you type.
This connection happens instantly, and in fact, some suggest it’s faster than connecting to an unsecure website. You simply have to visit a website with SSL, and voila — your connection will automatically be secured.
An SSL is security technology. It’s a protocol for servers and web browsers that makes sure that data passed between the two are private. This is done using an encrypted link that connects the server and browser.
SSL certificates are categorized by the level of validation and encryption provided OR the number of domains or subdomains under the certificate.
There are three types of certificates you can earn depending on the SSL you obtain. Let’s talk about them in more detail.
Types Of Certificates
The umbrellas that SSL certificates fall under are encryption and validation, and domain number. They each have three classifications, and can be applied for on the SSL website. Certificates are processed by a Certificate Authority (CA), which is software designed specifically for running and granting these certificates.
For encryption and validation certificates, there are domain, organization, and extended validation. For certificates defined by the domain number, the types are single, multidomain, and wildcard.
Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificate
This certificate shows the padlock, HTTPS, business name, and business country in the address bar to diminish being mistaken for a spam website.
Extended Validation (SV) SSL are the most expensive SSLs to obtain, but they are valuable in showing the legitimacy of your domain from the address bar. To set up an EV SSL, you must prove that you are authorized to own the domain you’re submitting. This ensures users that you are legally collecting the data needed to execute certain actions — such as a credit card number for an online transaction.
An EV SSL certificate can be obtained by any business, and it should be a priority especially for those that need identity assurance. For instance, if your website processes web payments or collects data, you’d want to get this certificate.
Organization Validated (OV SSL) Certificate
This certificate verifies that your organization and domain validation are real. Organization Validated (OV) SSL certificates offer a medium level of encryption and are obtained in two steps. First, the CA would verify who owns the domain and if the organization is operating legally.
On the browser, users would see a small green padlock with the company’s name following. Use this type of certificate if you don’t have the financial resources for an EV SSL but still want to offer a moderate level of encryption.
Domain Validation (DV) Certificate
The Domain Validation (DV) certificate offers a low level of encryption shown as a green padlock next to the URL in the address bar. This is the quickest validation you can receive, and you’ll only need a few company documents to apply.
This verification happens when you add a DNS to the CA. For this certificate, the CA will review the right of the applicant to own the domain being submitted. (Note: DVs don’t secure subdomains, just the domain itself).
Unlike the EV SSL, the CA won’t vet any identity data, so you won’t know who is receiving your encrypted information. But if you’re part of a business that can’t afford a higher-level SSL, a DV gets the job done.
Wildcard SSL Certificates
Wildcard SSL Certificates are in the «domain and subdomain number» category. Wildcard SSLs ensure that if you buy a certificate for one domain, you can use that same certificate for subdomains.
For example, if you bought a Wildcard for example.com, it could be applied to mail.example.com and blog.example.com. An option like this is cheaper than obtaining multiple SSL certificates for a number or domain.
Unified Communications (UCC) SSL Certificate
Also known as Multi-domain SSL certificates, Unified Communications certificates (UCCs) allow multiple domain names to be on the same certificate. UCCs were created to bridge communication between a single server and browser but have since expanded to include multiple domain names by the same owner.
A UCC in the address bar shows a padlock to display verification. They can also be considered an EV SSL if they are configured to show that green text, padlock, and home country. The only difference is the number of domain names associated with this certificate.
Multi-domain SSL certificates cover up to 100 domain names. If you need to alter the names in any way, you can do that with the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) option. Some examples of Multi-domain names you can use are: www.domain.co.uk, www.domain.com, mail.example.com, and checkout.example.com.
Single Domain SSL Certificate
A Single Domain SSL protects one domain. The thing to remember about this certificate is that you can’t use it to protect subdomains or a completely different domain.
For example, if you purchase this certificate for example.com, you can’t use it for blog.example.com or 2ndexample.com.
How can I get an SSL certificate for my website?
The first step is to determine what type of certificate you need. For example, if hosting content on multiple platforms (on separate domains/subdomains) it may mean that you need different SSL certificates.
For most, a standard SSL certificate will cover your content. But for companies in a regulated industry — such as finance or insurance — it may be worth talking with your I.T. team to ensure you’re meeting the specific SSL certificate requirements set within your industry.
The costs of SSL certificates vary, but you can get a free certificate or pay per month to obtain a custom certificate. On the free side — Let’s Encrypt offers certificates at no cost, but I would strongly recommend that you have someone knowledgeable about the DNS and technical setup of your website to help. These certificates will also expire every 90 days, so make sure they stay up to date. Some CMS platforms like HubSpot’s free CMS will offer a free SSL to help get your website security started.
One of the other key considerations is the validity period of a certification. Most standard SSL certificates that you purchase are available for one to two years by default, but if you’re looking for longer-term options, consider more advanced certificates that offer longer time periods.
Is SSL good for SEO?
Yes. While the primary purpose of SSL is securing information between the visitor and your website, there are benefits for SEO as well. According to Google Webmaster Trends Analysts, SSL is part of Google’s search ranking algorithm.
In addition, let’s say two websites are similar in the content provided but one has SSL enabled and the other doesn’t. That first website may receive a slight rank boost because it’s encrypted. As a result, there is a clear SEO benefit to enabling SSL on your website and across your pages.
How can I tell if my website has SSL?
When you visit a website with SSL, there are a few distinct differences that display within the browser. Click here for a free SSL checker tool.
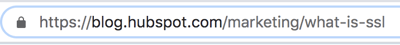
1. The URL says «https://» and not «http://».
The URL should look something like the screenshot below. Remember, an SSL-encrypted website will always have that «s» that stands for «secure.» Additionally, that text can show up green and follows a green padlock (another indicator, explained below).
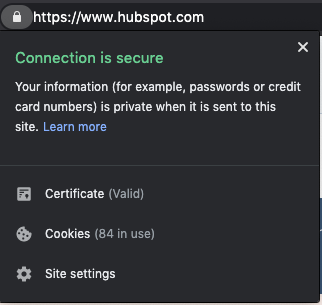
2. You’ll see a padlock icon in the URL bar.
The padlock will show up on the left- or right-hand side of the URL bar, depending on your browser. For example, on Chrome and Safari, it’ll be on the left. You can click on the padlock to read more information about the website and the company that provided the certificate.
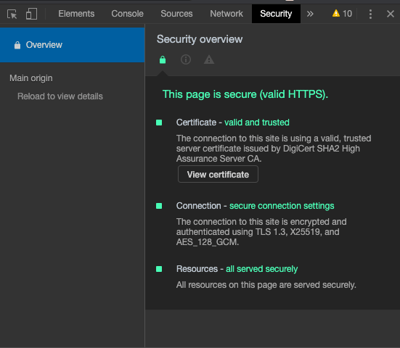
 3. The certificate is valid.
3. The certificate is valid.
Even if a website has the https:// and a padlock, the certificate could still be expired — meaning your connection wouldn’t be secure. In most cases, a site that displays as https will be secure but, if you encounter a site that asks for a lot of personal information, it may be worth double-checking to be sure the certificate is valid.
The next time you visit a website, check its encryption status. I love knowing that by clicking a little padlock, I can see if my data is secure. On the flip side, if you are a part of a business that doesn’t have SSL certificates, make them a part of your next goal set, so you can protect your customers’ data and privacy.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in June 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.


Originally published Jun 18, 2020 3:00:00 PM, updated June 14 2022
Как получить ssl сертификат бесплатно и зачем он нужен
В этой статье расскажу, как получить SSL сертификат бесплатно — подобрала для вас четыре сервиса, которые выдают такие сертификаты, и подскажу еще один не самый очевидный способ. Заодно разберемся, какие вообще бывают сертификаты, зачем они нужны и подойдет ли бесплатный вариант вашему бизнесу.
Что такое SSL сертификат
Вы наверняка замечали, что у сайтов в начале адреса стоит либо http://, либо https://. Буква s во втором варианте означает наличие у сайта SSL сертификата — это подтверждение, что пользователь и сайт будут обмениваться данными в зашифрованном виде. В этом случае данные все равно можно перехватить, но без ключа из сертификата их будет невозможно расшифровать. Вместо информации по кредитке воришка получит хаотичный набор данных.
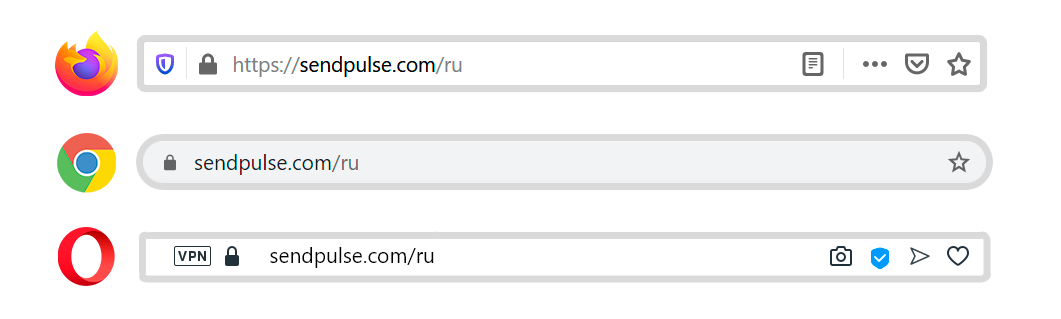
Наличие SSL сертификата можно понять по значку замка в адресной строке:
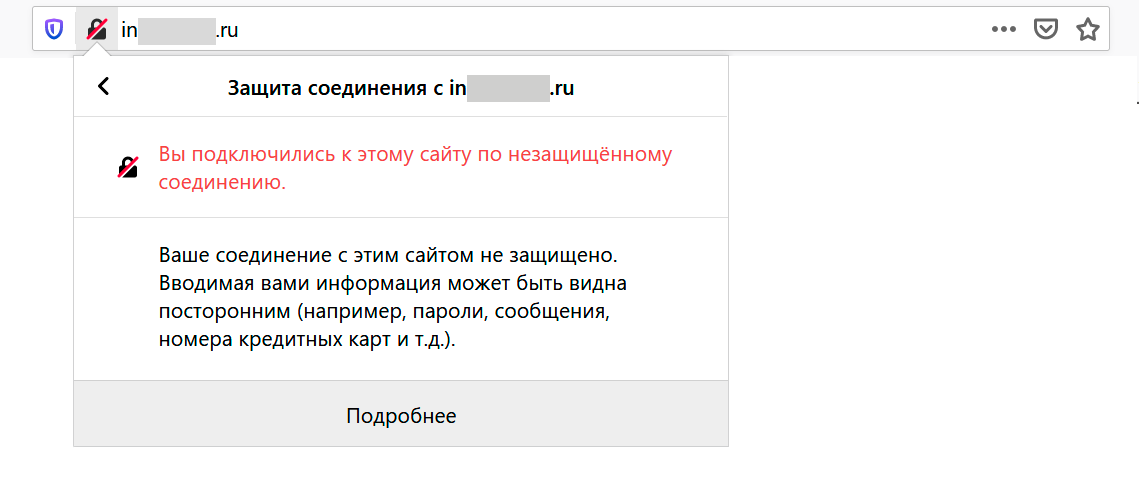
Если сертификата нет, браузеры предупреждают об опасности сайта: что злоумышленники могут перехватить данные, которые пользователи оставляют на сайте, например, адрес почты или номер банковской карты. Это может выглядеть как зачеркнутый замочек:
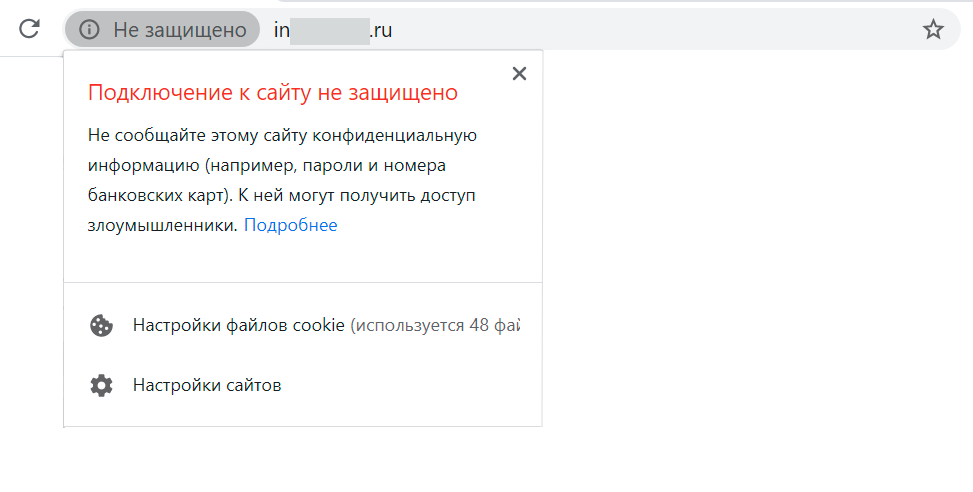
Или текстовое предупреждение:
Простой, но мощный конструктор лендингов
Создайте мобильный лендинг, интернет-магазин или мультиссылку для Instagram и продвигайте ее через чат-боты в мессенджерах, email и SMS — все это на одной платформе!
Для чего нужен SSL сертификат
Во-первых, SSL сертификат поможет защитить ваших пользователей от мошенников. Какие варианты обмана могут быть:
Во-вторых, пользователь будет спокоен — он увидит значок замка и будет чувствовать себя в безопасности.
В-третьих, получение SSL сертификата положительно скажется на ранжировании сайта поисковиками. Это знак, что вы заботитесь о безопасности пользователей, и повод для системы разместить вас повыше в выдаче.
Какие бывают SSL сертификаты
Есть разные виды SSL сертификатов. Они могут отличаться по количеству доменов и субдоменов, для которых они могут использоваться. Например, мультидоменные сертификаты могут защищать два, три или пять доменов. Сертификат с опцией wildcard распространяется на все субдомены указанного в сертификате домена.
Также сертификаты различаются по тому, как именно сайт будет проверяться. Тут есть три варианта:
И, наконец, есть несколько доверенных центров, которые выпускают сертификаты — например, Thawte, Sectigo, Geotrust, GlobalSign и другие. Их продукты отличаются уровнем защиты и различными дополнительными функциями.
Кому подойдет бесплатный SSLсертификат
В большинстве случаев бесплатно вы можете получить только SSL сертификат низшего уровня, то есть с подтверждением домена — DV. Это значит, что вариант с бесплатным SSL сертификатом подойдет только для небольших сайтов, которые не просят у пользователя «опасных» данных вроде номера кредитки. Например, это:
Для интернет-магазинов и прочих сайтов, которые запрашивают у пользователя финансовые и/или деликатные личные данные, лучше получать SSL сертификаты следующих уровней.
Где получить SSL сертификат бесплатно
Нашла для вас пять способов получить SSl сертификат без затрат.
Let’s Encrypt
Эта некоммерческая организация выдает бесплатные SSL DV сертификаты со сроком жизни три месяца. Можно получить wildcard-сертификат.
Free SSL Space
Еще одна некоммерческая организация, которая также выдает 90-дневные DV сертификаты. Отличается от Let’s Encrypt совместимостью: как заявляет компания, их сертификаты поддерживаются на 99,99% устройств. Нет опции wildcard.
ZeroSSL
У этого сервиса есть бесплатный тариф — DV сертификат на 90 дней. Как и Free SSL, заявляют о 99,99% совместимости с серверами, браузерами и устройствами, однако на бесплатном тарифе не поддерживается wildcard.
CloudFlare
Этот сервис защищает сайты от DDoS-атак — моментов, когда злоумышленники пытаются перегрузить ваш сайт множеством одновременных запросов, а также ускоряет загрузку. Бесплатный SSL сертификат — приятное дополнение к сервису. CloudFlare предлагает получить SSL сертификат бесплатно и на неопределенный срок на базовом тарифе, который предназначен для личных некоммерческих сайтов.
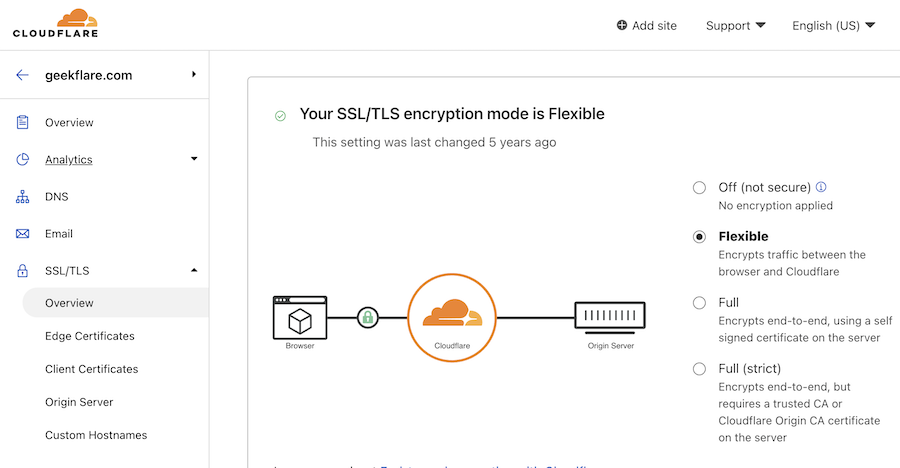
У бесплатного SSL от CloudFlare есть одно «но». Загрузка сайта ускоряется благодаря тому, что сервис кеширует ваш сайт на свои серверы и контент попадает пользователю с них. Общение происходит по цепочке «пользователь — серверы CloudFlare — ваш сервер», и SSL зашифрует только первую связь. На ваш сервер данные будут идти уже открыто. Впрочем, это уже решает самые распространенные проблемы безопасности вроде использования общественного Wi-Fi.
У хостинг-провайдера или регистратора доменных имен
Это условно-бесплатный способ получить SSL сертификат. Если вы только собираетесь заводить сайт или ищете новый хостинг — рассмотрите предложения, где бонусом идет сертификат.
Как получить SSL сертификат бесплатно и зачем он нужен: что стоит запомнить
SSL сертификат — это инструмент, который переключает ваш сайт в защищенный режим https. Благодаря ему все данные, которыми вы обмениваетесь с пользователями, будут надежно зашифрованы, а ключ к расшифровке будет только у вас.
Благодаря SSL сертификату:
Сертификаты бывают трех уровней:
Бесплатный SSL сертификат уровня DV выдают несколько сервисов:
Также можно обзавестись SSL в качестве бонуса, когда вы покупаете услуги хостинг-провайдера или доменное имя.
Обеспечьте безопасность своим клиентам и себе! Обзаведитесь SSL сертификатом, чтобы никто не украл данные пользователей, а для безопасных рассылок через email, SMS, push, Viber и чат-боты используйте SendPulse.
Рассказываю, как делать по-настоящему крутые email рассылки. Помогаю найти баланс между заботой о клиенте и успешными продажами.
How to Get an SSL Certificate [+10 Best Free SSLs]
How do you protect your users, prospects, and customers as they browse your website? And your company, along the way? The answer is a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate.
An SSL certificate keeps your customers’ sensitive information secure as they visit pages, read posts, submit interest forms, and purchase products. In this post, you’ll learn everything you need to know about SSL certificates and the best SSLs you can get for any budget.
What Is an SSL?
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a security protocol that creates an encrypted link between a web server and a web browser. It ensures that all transferred data remains confidential. You may have noticed the lock icon next to the URL in your address bar. That means the site is protected by SSL.
Why get an SSL certificate?
Your website is more than just a digital billboard — it’s a data highway between your business and your visitors. Anytime a visitor accesses your website, data, like their IP address, gets transferred from one server to another before it reaches its destination. Your visitors expect your company to keep that data secure. Without a secure connection, the data they share with you is at risk of falling into the wrong hands — compromising their privacy — which could mean steep consequences for your business.
In short, your site should have SSL, especially if you process financial transactions. This added layer of security will protect you from data breaches, and it gives visitors a good reason to trust you with sensitive information. Not to mention, SSL improves your ranking in search results.
More of a visual learner? Check out this quick video on what SSL is and why you need it:
Ready to dive a little deeper? Let’s do it.
How SSL Certificates Work
SSL certificates can be a bit complicated to understand with all the technical jargon and acronyms. To give you a simple but accurate overview of how SSL certificates work, let’s imagine our friend Michelle is visiting her favorite website, hubspot.com.
Verification
Initially, Michelle opens her laptop and types “hubspot.com” into her web browser, Google Chrome. While Google Chrome is loading the site, Michelle’s computer receives HubSpot’s SSL certificate through a public key and verifies it with the certificate authority.
Handshake
Michelle’s computer and HubSpot’s server come to an agreement that everything looks legitimate, and the two computers form a connection which is called a handshake.
Encryption
From here, Michelle’s computer and the hubspot.com server decide on the type of encryption they’ll use to securely transmit data back and forth. What makes this connection secure is the coding and decoding of information while it is in transit between the computer and the server. The timeframe where security attacks are prone to happen is when the data is moving from one place to the next, so scrambling the information in an encrypted language, or private key, keeps everything secure until it gets where it needs to be.
Authentication
Once the data is decrypted by Michelle’s computer by the private key, a lock icon appears next to the website’s name in the browser’s search bar.
Michelle is free to browse hubspot.com knowing that any data she shares is safe and won’t be intercepted by malicious hackers.
How much is an SSL?
The cost of your SSL can range from free to hundreds of dollars, depending on the level of security you require. Here are the types of SSLs, ranging from least secure to most secure (and, generally, lowest to highest in price):
The type of SSL you choose depends on what types of actions you expect users to take on your site. SSL certificates can be expensive if you don’t know where to look or what you’re buying.
Once you choose the type of certificate you require, you can then shop around for Certificate Authorities that offer SSLs at that level. After, you’ll install the certificate on your website.
Here’s how to get an SSL certificate from start to finish:
How to Get an SSL Certificate
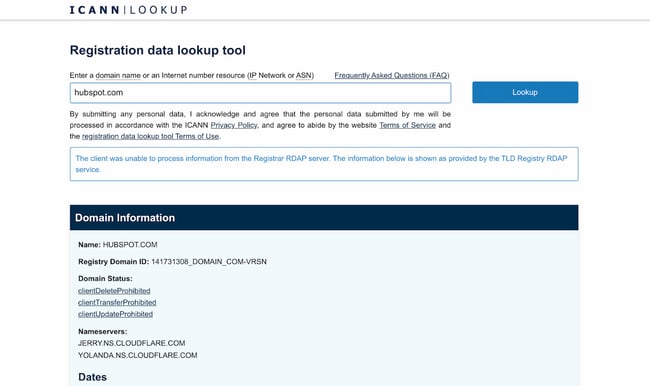
1. Verify your website’s information through ICANN Lookup.
Before you apply for an SSL certificate, you must ensure your ICANN Lookup record is updated and matches what you’re submitting to the Certificate Authority. Access the ICANN lookup tool and look at your name server, your registrar information, and your authoritative servers.
2. Generate the Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
Before you can find a certificate authority, you first have to generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR). You can do so through your server, through your cPanel, or through an online CSR generator.
Option 1: Server
If you have access to your server, you can generate a CSR yourself. Find your server’s specific instructions here. This option is recommended for advanced users and web developers.
Option 2: cPanel
If you have access to your cPanel through your hosting provider, you can also generate a CSR using its tools. First, access your cPanel via your hosting provider. For Bluehost, your cPanel is located under “Advanced.”
Scroll down to a section titled “Security.” Click the “SSL/TSL” option.
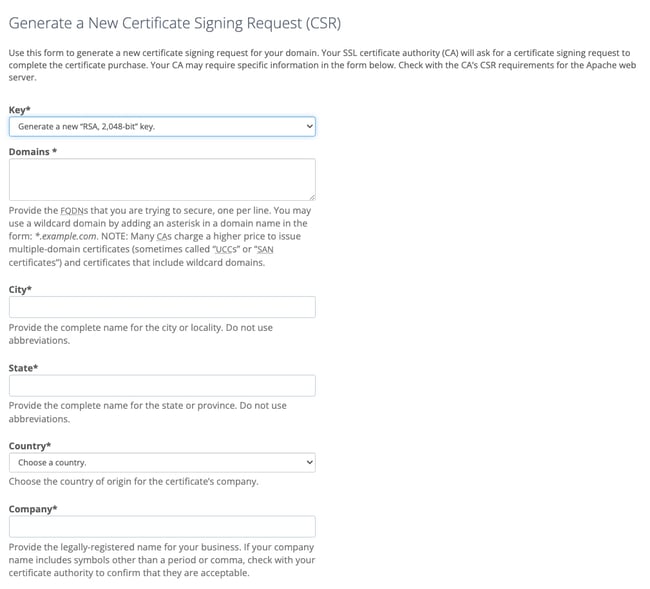
From there, you should find an option to generate a CSR. In Bluehost, this option is located on the right-hand sidebar.
After you click it, you’ll be taken to a form that asks for your domain, city, state, country, and company.
Done! Your CSR has been generated.
Option 3: Online CSR Generator
Lastly, you can bypass any complicated steps and simply use an online CSR generator for free. Some of your options include:
We recommend using this as a last resort because it’s not connected to your server, hosting service, or cPanel.
If you’re not sure how to move forward, you can reach out to your hosting company for support, and they’ll give you instructions specific to your website. They can advise you on the type of CSR certificate you should request.
3. Submit your CSR to the Certificate authority to validate your domain.
When you buy an SSL certificate from a certificate authority, you’ll be required to submit your CSR. Be sure to have it on hand when you’re completing the sign-up process for your SSL certificate.
4. Install the certificate on your website.
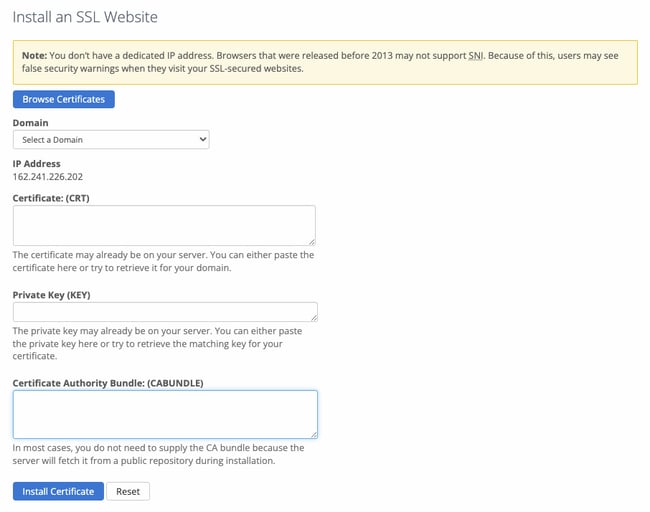
Lastly, install the certificate on your website. The best way to do so is through cPanel. Under “Security,” click “SSL/TLS.” Then click “Manage SSL sites.”
There, you’ll be able to upload a new certificate to your chosen domain.
If you purchased an SSL via your hosting provider, the certificate may already be automatically installed on your site, so you may not need to manually do it.
Ready to dive into the best services that you can use to get an SSL?
Best Free and Low-Cost SSL Certificate Authorities
If you require a lower level of encryption for a blog or business site that doesn’t transfer sensitive financial information, the following authority will get the job done:
1. HubSpot
If you have content hosted on HubSpot’s CMS, you can secure your content and lead data with a free standard SSL. Because we know you’re busy, HubSpot takes care of renewal for you. Your SSL certificate will automatically renew 30 days before it expires.
2. Let’s Encrypt
Let’s Encrypt was created by the Linux Foundation, and the project was sponsored by Mozilla, Site Ground, Cisco, Facebook, Akamai, and other top tech companies. It offers DV SSL certificates (no OV or EV here) free of cost, but you should be aware that these certificates are only valid for three months at a time and should be renewed every sixty days at the earliest. Why? The company has a firm stance on automatic certificate renewals to achieve their long term goal of moving the web from HTTP to HTTPS.
Price: Always free for three months at a time. Then you must renew, for free, for another three months.
 3. Comodo
3. Comodo
Comodo offers 90-day free trials for SSL certificates, and they’re recognized by all major browsers. You can cover up to 100 domains with a single certificate.
It’s specially designed for MS Exchange and Office servers. Comodo offers unlimited server licenses with priority phone support. And, most importantly, Comodo is certified as a Best Seller of SSL certificates.
4. Cloudflare
Cloudflare is known for their products that make websites faster and more secure. It’s a CDN and security company that’s used by many popular sites, including Reddit, Mozilla, and Stack Overflow. Cloud Flare blocks millions of attacks every day and provides 24/7 support.
5. SSL For Free
SSL For Free is a nonprofit certificate authority, and it works on all major browsers. Similar to Let’s Encrypt and other SSL certificate authorities, SSL For Free offers certificates that are valid for three months at a time.
Price: Always free for three months at a time. Then you must renew, for free, for another three months.
6. GoDaddy
You’ve heard of GoDaddy — with over 60 million domains, it’s the world’s #1 name registrar. If you have an open-source project, GoDaddy will provide you with a free SSL certificate that’s valid for a year.
7. GeoTrust
GeoTrust offers a full range of DV, OV, and EV SSL certificates, and automated domain name validation is included with each one. They’re known for having easy installation and speedy issuance of certificates and being compatible with leading desktop and mobile browsers.
8. GoGetSSL
GoGetSSL is another public SSL certificate provider. It gives you a 90-day free trial for SSL certificates, and it only takes about five minutes to get your domain validated (no callback or face-to-face verification required). Their certificates are compatible with all major browsers, such as Chrome, Firefox, Opera, and Safari.
9. Instant SSL
Instant SSL is another option that deserves your attention. Their free certificates are good for 90 days, and they work on all major browsers. Unlimited server licensing, 24/7 support, and unlimited re-issuance are among the features included in their SSL certificate options.
10. Basic SSL
Basic SSL also offers a 90-day trial before you make a purchase. With a quick and simple validation process, you can focus on other aspects of your website while Basic SSL takes care of the certificate for you.
Price: Free for 90 days
Protect your customer’s experience on your website.
Browsing the web has its risks, but it doesn’t have to when users visit your site. With an SSL certificate from a reputable company, your website can safely and securely handle data transfers between your customers and your business. With a visible lock icon in the search bar, your site visitors know they can trust your business. In the end, this creates a better user experience, increases your website’s ranking in search results, and ultimately helps your business operate to industry security standards.
This blog post was originally published May 2020 and was updated for comprehensiveness.
Originally published Dec 15, 2021 7:00:00 AM, updated June 14 2022














 3. The certificate is valid.
3. The certificate is valid.






 3. Comodo
3. Comodo