How to get token github
How to get token github
Getting started with the REST API
In this article
Learn the foundations for using the REST API, starting with authentication and some endpoint examples.
Let’s walk through core API concepts as we tackle some everyday use cases.
Most applications will use an existing wrapper library in the language of your choice, but it’s important to familiarize yourself with the underlying API HTTP methods first.
There’s no easier way to kick the tires than through cURL. If you are using an alternative client, note that you are required to send a valid User Agent header in your request.
Let’s start by testing our setup. Open up a command prompt and enter the following command:
The response will be a random selection from our design philosophies.
Any headers beginning with X- are custom headers, and are not included in the HTTP spec. For example, take note of the X-RateLimit-Limit and X-RateLimit-Remaining headers. This pair of headers indicate how many requests a client can make in a rolling time period (typically an hour) and how many of those requests the client has already spent.
Unauthenticated clients can make 60 requests per hour. To get more requests per hour, we’ll need to authenticate. In fact, doing anything interesting with the GitHub API requires authentication.
Using personal access tokens
The easiest and best way to authenticate with the GitHub API is by using Basic Authentication via OAuth tokens. OAuth tokens include personal access tokens.
When prompted, you can enter your OAuth token, but we recommend you set up a variable for it:
When authenticating, you should see your rate limit bumped to 5,000 requests an hour, as indicated in the X-RateLimit-Limit header. In addition to providing more calls per hour, authentication enables you to read and write private information using the API.
To help keep your information secure, we highly recommend setting an expiration for your personal access tokens.
API requests using an expiring personal access token will return that token’s expiration date via the GitHub-Authentication-Token-Expiration header. You can use the header in your scripts to provide a warning message when the token is close to its expiration date.
Get your own user profile
When properly authenticated, you can take advantage of the permissions associated with your account on GitHub.com. For example, try getting your own user profile:
This time, in addition to the same set of public information we retrieved for @defunkt earlier, you should also see the non-public information for your user profile. For example, you’ll see a plan object in the response which gives details about the GitHub plan for the account.
Using OAuth tokens for apps
Apps that need to read or write private information using the API on behalf of another user should use OAuth.
OAuth uses tokens. Tokens provide two big features:
Tokens should be created via a web flow. An application sends users to GitHub to log in. GitHub then presents a dialog indicating the name of the app, as well as the level of access the app has once it’s authorized by the user. After a user authorizes access, GitHub redirects the user back to the application:
Treat OAuth tokens like passwords! Don’t share them with other users or store them in insecure places. The tokens in these examples are fake and the names have been changed to protect the innocent.
Now that we’ve got the hang of making authenticated calls, let’s move along to the Repositories API.
Almost any meaningful use of the GitHub API will involve some level of Repository information. We can GET repository details in the same way we fetched user details earlier:
The information returned from these calls will depend on which scopes our token has when we authenticate:
As the docs indicate, these methods take a type parameter that can filter the repositories returned based on what type of access the user has for the repository. In this way, we can fetch only directly-owned repositories, organization repositories, or repositories the user collaborates on via a team.
In this example, we grab only those repositories that octocat owns, not the ones on which she collaborates. Note the quoted URL above. Depending on your shell setup, cURL sometimes requires a quoted URL or else it ignores the query string.
Create a repository
Fetching information for existing repositories is a common use case, but the GitHub API supports creating new repositories as well. To create a repository, we need to POST some JSON containing the details and configuration options.
Next, let’s fetch our newly created repository:
Oh noes! Where did it go? Since we created the repository as private, we need to authenticate in order to see it. If you’re a grizzled HTTP user, you might expect a 403 instead. Since we don’t want to leak information about private repositories, the GitHub API returns a 404 in this case, as if to say «we can neither confirm nor deny the existence of this repository.»
The UI for Issues on GitHub aims to provide ‘just enough’ workflow while staying out of your way. With the GitHub Issues API, you can pull data out or create issues from other tools to create a workflow that works for your team.
Just like github.com, the API provides a few methods to view issues for the authenticated user. To see all your issues, call GET /issues :
A project the size of Rails has thousands of issues. We’ll need to paginate, making multiple API calls to get the data. Let’s repeat that last call, this time taking note of the response headers:
The Link header provides a way for a response to link to external resources, in this case additional pages of data. Since our call found more than thirty issues (the default page size), the API tells us where we can find the next page and the last page of results.
Creating an issue
Now that we’ve seen how to paginate lists of issues, let’s create an issue from the API.
To create an issue, we need to be authenticated, so we’ll pass an OAuth token in the header. Also, we’ll pass the title, body, and labels in the JSON body to the /issues path underneath the repository in which we want to create the issue:
The response gives us a couple of pointers to the newly created issue, both in the Location response header and the url field of the JSON response.
A big part of being a good API citizen is respecting rate limits by caching information that hasn’t changed. The API supports conditional requests and helps you do the right thing. Consider the first call we made to get defunkt’s profile:
In addition to the JSON body, take note of the HTTP status code of 200 and the ETag header. The ETag is a fingerprint of the response. If we pass that on subsequent calls, we can tell the API to give us the resource again, only if it has changed:
The 304 status indicates that the resource hasn’t changed since the last time we asked for it and the response will contain no body. As a bonus, 304 responses don’t count against your rate limit.
Now you know the basics of the GitHub API!
Keep learning with the next API guide Basics of Authentication!
Help us make these docs great!
All GitHub docs are open source. See something that’s wrong or unclear? Submit a pull request.
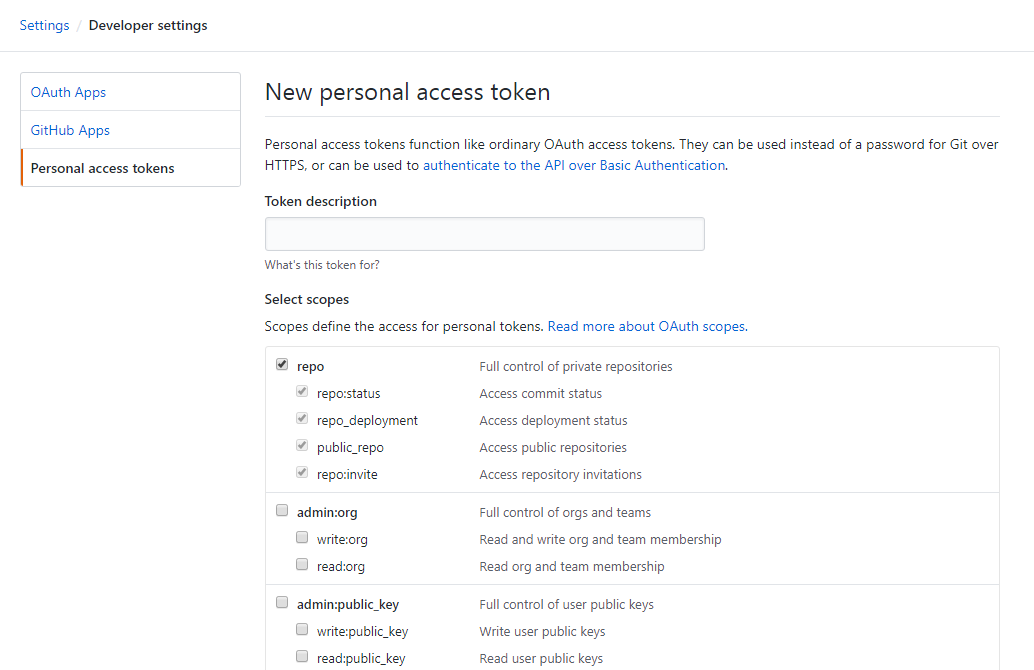
Personal Access Tokens are the easiest way to authenticate requests as a GitHub user. You can create a new Personal Access Token at https://github.com/settings/tokens/new.
Set the note to something memorable. The scopes are pretty self-explanatory, only select what you are sure you will need. The public_repo scope is what you’ll need in most cases, e.g. to retrieve, create or update all things related to repositories.
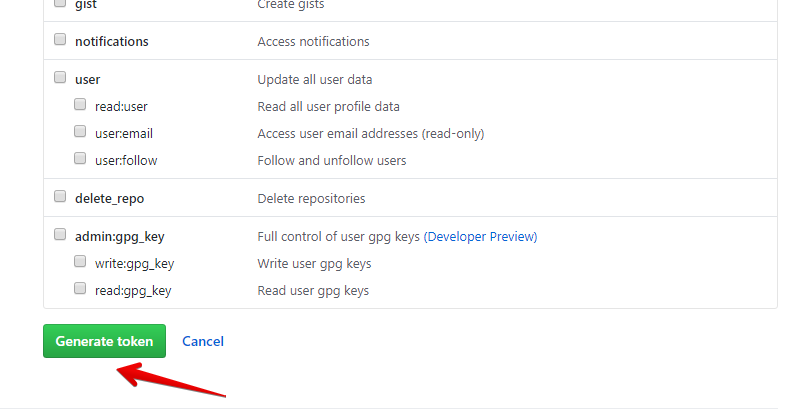
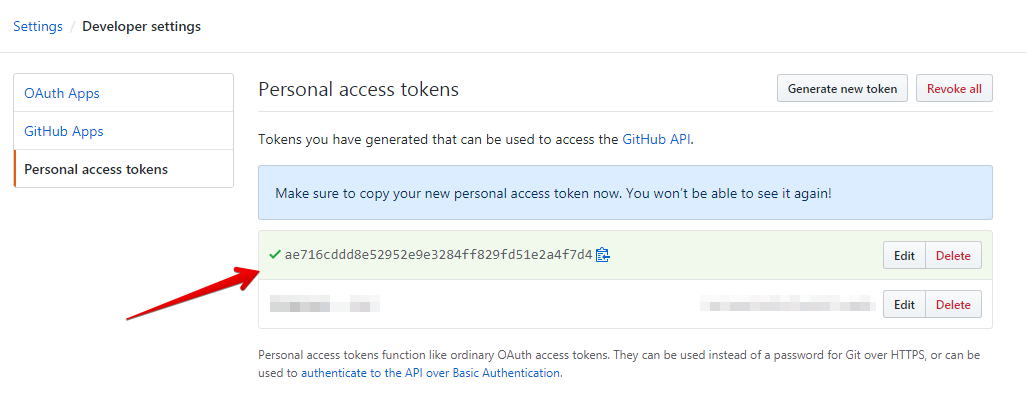
The next screen will show you the token. Make sure to copy it somewhere safe as it won’t be shown again.
You can now use that token, for example to retrieve the latest release of octokit/core.js using curl from your terminal
Exit fullscreen mode
Or using fetch in a browser or node-fetch in Node.js
Exit fullscreen mode
Using the JavaScript Octokit
Authenticating using a personal access token is straight forward, so it’s already built into https://github.com/octokit/core.js and all libraries that are built upon it.
Sending the above request would look like this in the browser
Exit fullscreen mode
And like this in Node.js
Exit fullscreen mode
Handling errors
If the token is invalid, the server will respond with a 401 status and a «bad credentials» message
Exit fullscreen mode
If the token does not have the required scopes, the server will respond with a 403 status and an explanatory message
Exit fullscreen mode
New scopes cannot be added to existing tokens, you will have to create a new token with the required scopes selected to address 403 errors.
Limitations
Personal Access Tokens work great for personal usage. But if you plan to create a service or a CLI application that integrate with GitHub, there are better options that don’t require the user to manually create and maintain tokens. I will write about all of them in the remaining posts of this series.
Personal Access Tokens can be used in GitHub Actions if you want the script to act as your user account. Next week I’ll talk about authenticating scripts run by GitHub Actions, and how to utilize the special GITHUB_TOKEN secret as a simpler alternative to using Personal Access Tokens for most cases.
Using Personal Access Tokens with GIT and GitHub
Recently I was alerted by GitHub that I should stop using a username/password when using the GIT command line utility. Instead of a password, I should be using a Personal Access Token that is more flexible and easier to secure. This is a brief walk-through of how to setup and use these tokens.
NOTE: In this document I am assuming you already have a GitHub account and are somewhat familiar with the GIT command line utility. This information is based on the document published at https://docs.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/creating-a-personal-access-token
Get Token
The first step in using tokens is to generate a token from the GitHub website. Note that it would be best practice to use different tokens for different computers/systems/services/tasks so that they can be easily managed.
To generate a token:
Configure local GIT
Once we have a token, we need to configure the local GIT client with a username and email address. On a Linux machine, use the following commands to configure this, replacing the values in the brackets with your username and email.
Clone from GitHub
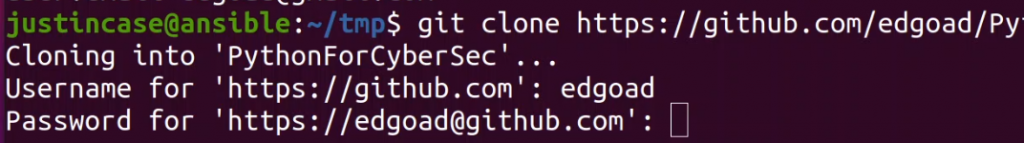
Once GIT is configured, we can begin using it to access GitHub. In this example I perform a git clone command to copy a repository to the local computer. When prompted for the username and password, enter your GitHub username and the previously generated token as the password.
Configure Credential Caching
Lastly, to ensure the local computer remembers the token, we can enable caching of the credentials. This configures the computer to remember the complex token so that we dont have too.
If needed, you can later clear the token from the local computer by running
Создание токена персонального доступа для командной строки
Вы можете создать токен доступа и использовать его вместо пароля при выполнении операций Git через HTTPS с Git в командной строке или API.
Для аутентификации в GitHub требуется токен персонального доступа в следующих ситуациях:
Создание токена
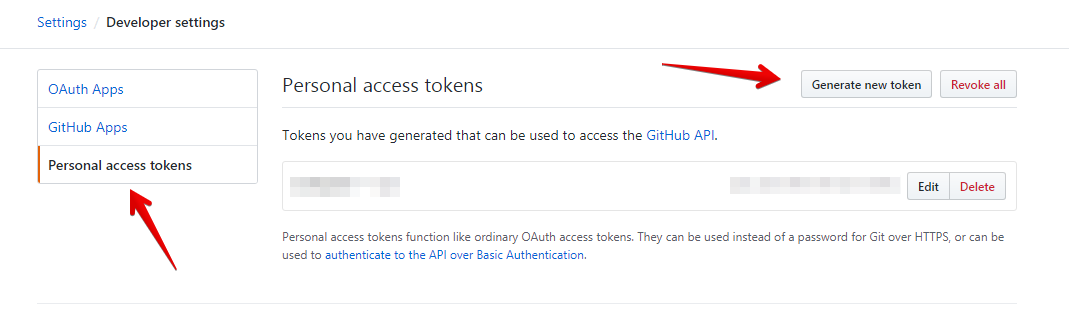
3) В левой боковой панели нажмите «Developer settings»
4) В левой боковой панели нажмите «Personal access tokens» и затем чтобы создать новый токен нажмите «Generate new token»
5) Задайте маркеру описание и выберите область действия или разрешения, которые нужно предоставить этому токену. Чтобы использовать маркер для доступа к репозиториям из командной строки, выберите repo.
6) Нажмите «Generate token», чтобы создать токен.
7) Скопируйте полученный токен в буфер обмена для следующего использования.
Использование токена в командной строке
Теперь, с помощью токена, вы можете ввести его вместо пароля при выполнении операций Git через HTTPS.
Например, в командной строке вы должны ввести следующее:
Create a GitHub Personal Access Token example
Community driven content discussing all aspects of software development from DevOps to design patterns.
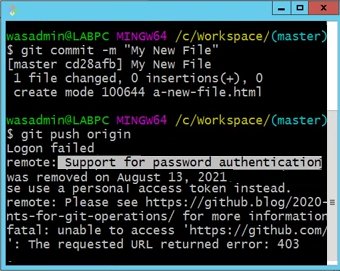
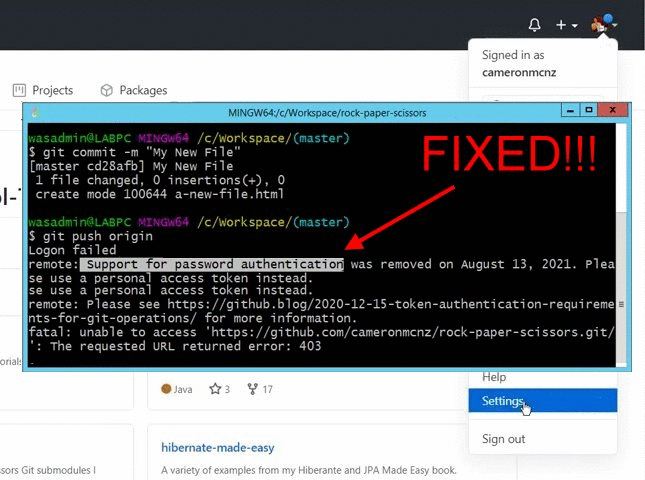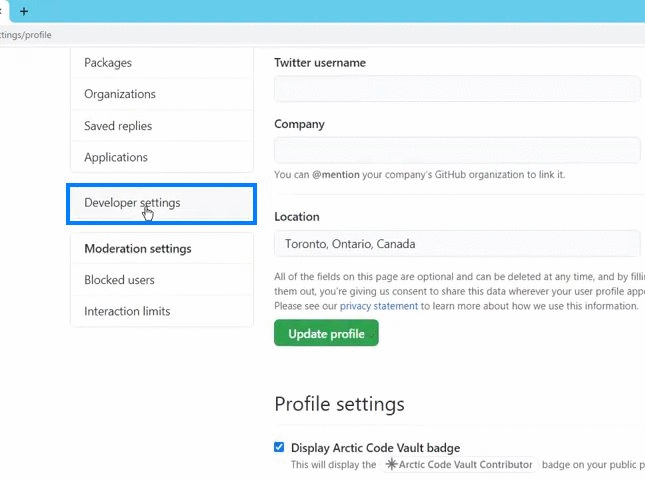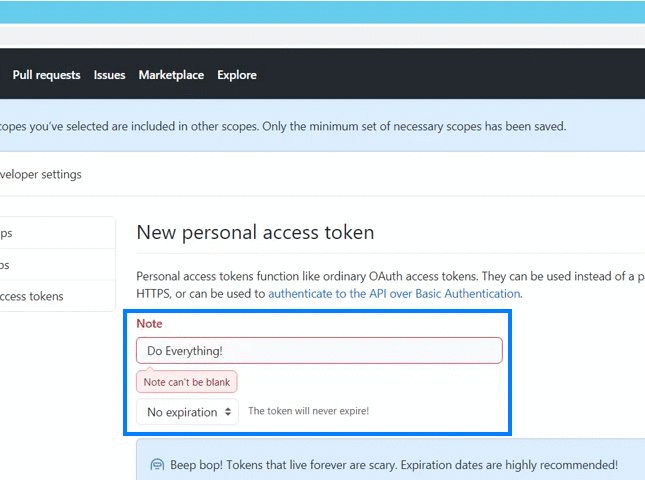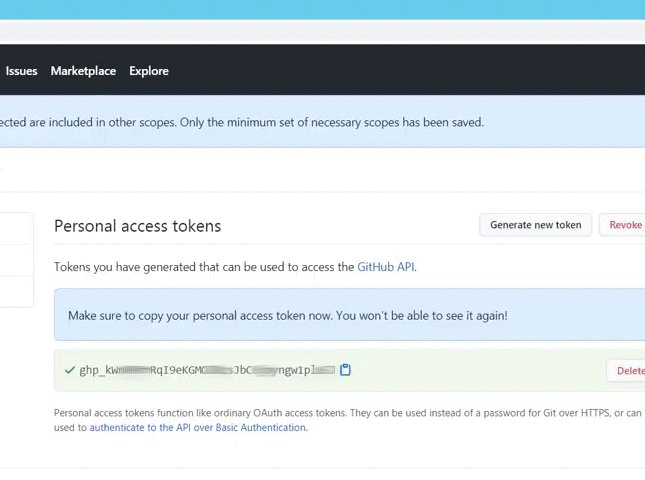
If you ask me, GitHub’s removal of support for password authentication on August 13, 2021 was a bit of an overstep. But fortunately, it’s not overly difficult to create and use a GitHub personal access token instead. Just generate the personal access token in GitHub, and provide the token whenever Git prompts for your password.
The link to create a GitHub Personal Access Token is found under ‘Developer Settings’ in the admin console.
To create a personal access token in GitHub, follow these steps:
If you try to push to GitHub, you are told you need a personal access token.
The GitHub personal access token replaces your password. Any operation like a Git push that requires credentials prompts you for your username and password.
For the username, simply provide your GitHub account name.
For the password, provide your GitHub personal access token.
The first time you perform a push to GitHub, you are prompted for your username and password. Simply provide your GitHub username and the access token and your files are uploaded to GitHub.
Use your GitHub personal access token as your password when you perform a git push to GitHub operation.
If you use Windows, your old credentials may be stored in the Windows Credentials Manager. Open this service, look for the web credential used by Git and delete it. Then perform a new push to GitHub.
The next time you perform a push with a GitHub personal access token, the new token will be stored by Windows. You won’t need to remember the value of the GitHub token on future Git push operations.
Microsoft’s Azure Advisor service offers recommendations based on five categories. Learn these categories and the roles they play.
Researchers with Palo Alto Networks took the stage at Black Hat to explain how configurations and system privileges in Kubernetes.
Источники информации:
- http://dev.to/gr2m/github-api-authentication-personal-access-tokens-53kd
- http://www.edgoad.com/2021/02/using-personal-access-tokens-with-git-and-github.html
- http://unetway.com/blog/sozdanie-tokena-personalnogo-dostupa-dla-komandnoj-stroki
- http://www.theserverside.com/blog/Coffee-Talk-Java-News-Stories-and-Opinions/How-to-create-a-GitHub-Personal-Access-Token-example