How to install addon blender
How to install addon blender
Addon Installation and Uninstallation
Guides and Info
Clone this wiki locally
These instructions will detail how to install or uninstall the FLIP Fluids addon for Blender 2.8+ or later. Instructions for Blender 2.79 can be found on this page: Addon Installation and Uninstallation (Blender 2.79).
Installing the Addon
Only one version of the addon should be installed at a time. If you are updating the addon to a new version, the previous version must be first uninstalled.
The easiest way to install the FLIP Fluids addon is to do so through directly through Blender:
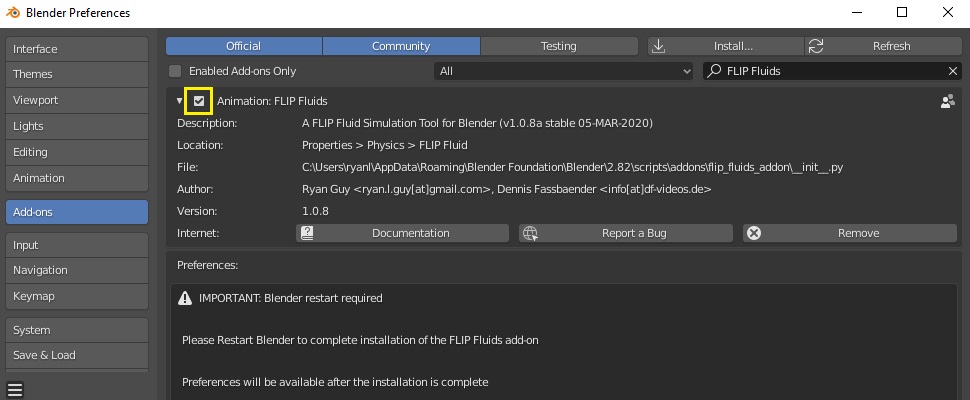
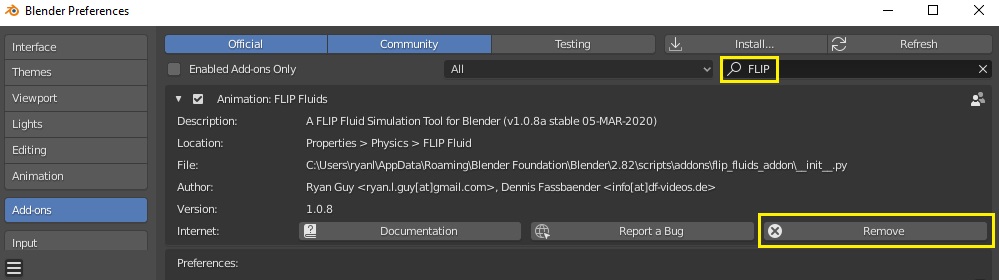
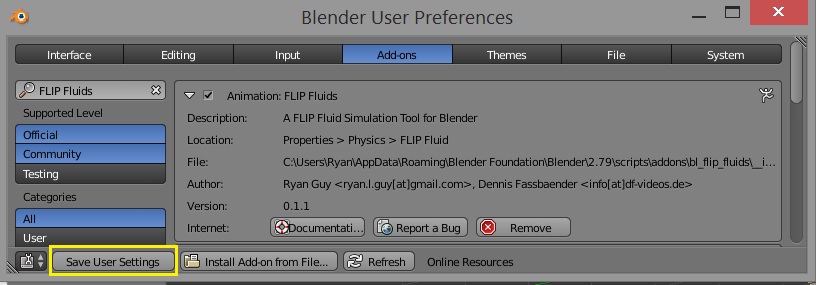
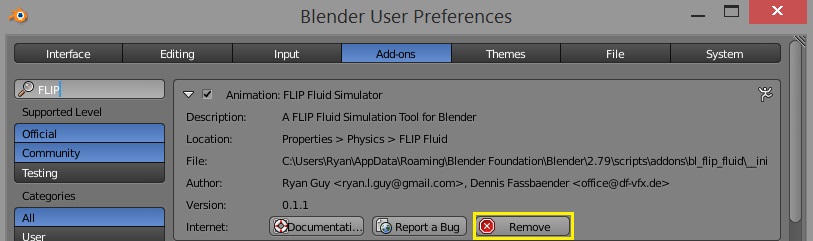
Uninstalling the Addon
Only one version of the addon should be installed at a time. If you are updating the addon to a new version, the previous version must be first uninstalled. The easiest way to uninstall the addon is to do so directly through Blender:
Note: If you are updating the addon to a new version, Blender should be restarted after uninstalling the previous version. This will ensure that all loaded scripts from the previous version are properly unloaded and do not cause any conflicts with the new version.
Updating the Addon
Before updating to a new version, you must first uninstall the previous version. The safest way to update to a new version is to:
See our Addon Installation Troubleshooting documentation for how to verify your FLIP Fluids installation file, verify your FLIP Fluids installation, and for how to manually install the FLIP Fluids addon.
Baking Error: AttributeError: ‘array.array’ object has no attribute ‘tostring’
If you are receiving this error message in Blender 2.93 or later, this will indicate that there is a compatibility error between your installed FLIP Fluids addon version and installed Blender version. You will need to update your FLIP Fluids addon version to at least v1.0.9b or later. FLIP Fluids version 1.0.9b adds compatibility support for Blender 2.93. FLIP Fluids version 1.2.0 adds compatibility support for Blender 3.0.
Baking Error: ‘The fluid engine version is not compatible with the addon version ‘
If you are receiving this error message (or a similar error) when trying to use the Bake operator, this may indicate that multiple versions of the FLIP Fluids addon are installed on your version of Blender and that a new installation was not able to overwrite an older file due to the previous version being in use.
The first thing to try is to restart Blender and test if the error still persists. If you are still getting an error message, uninstall and reinstall the addon. Make sure to follow the installation guide of restarting Blender before and after installation (See Updating the Addon).
Installation error: ‘RNA_Types’ object has no attribute ‘PHYSICS_PT_add’
This error is caused by a conflict with the Blend4Web addon. You will need to disable the Blend4Web addon to use the FLIP Fluids addon. This error has been reported to the Blend4Web developers here.
Installation error: ‘cannot import name MappingProxyType’
This error can be caused by placing the FLIP Fluids addon files in the incorrect location, such as directly in the scripts/addons directory instead of in the correct scripts/addons/flip_fluids_addon subfolder. To fix this error, delete the file scripts/addons/types.py which is causing a conflict with Blender’s script files.
Uninstallation error: ‘[WinError 5] Access is Denied’
This error means that the fluid engine is in use and Blender is unable to remove it. Simply restart Blender and try again.
Addon Installation and Uninstallation (Blender 2.79)
Guides and Info
Clone this wiki locally
These instructions will detail how to install or uninstall the the FLIP Fluids addon for Blender 2.79. Instructions for Blender 2.8 can be found on this page: Addon Installation and Uninstallation (Blender 2.8)
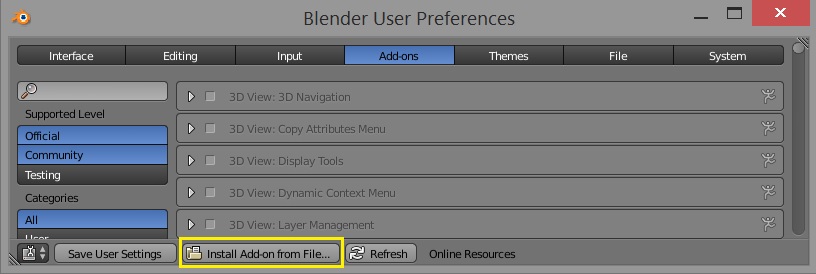
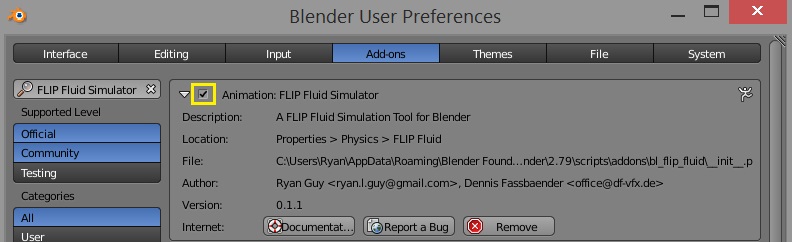
Installing the Addon
Only one version of the addon should be installed at a time. If you are updating the addon to a new version, the previous version must be first uninstalled.
The easiest way to install the FLIP Fluids addon is to do so through directly through Blender:
Uninstalling the Addon
Only one version of the addon should be installed at a time. If you are updating the addon to a new version, the previous version must be first uninstalled. The easiest way to uninstall the addon is to do do directly through Blender:
Note: If you are updating the addon to a new version, Blender should be restarted after uninstalling the previous version. This will ensure that all loaded scripts from the previous version are properly unloaded and do not cause any conflicts with the new version.
Updating the Addon
Before updating to a new version, you must first uninstall the previous version. The safest way to update to a new version is to:
Installation error: ‘RNA_Types’ object has no attribute ‘PHYSICS_PT_add’
This error is caused by a conflict with the Blend4Web addon. You will need to disable the Blend4Web addon to use the FLIP Fluids addon. This error has been reported to the Blend4Web developers here.
Installation error: ‘cannot import name MappingProxyType’
This error can be caused by placing the FLIP Fluids addon files in the incorrect location, such as directly in the scripts/addons directory instead of in the correct scripts/addons/flip_fluids_addon subfolder. To fix this error, delete the file scripts/addons/types.py which is causing a conflict with Blender’s script files.
Uninstallation error: ‘[WinError 5] Access is Denied’
This error means that the fluid engine is in use and Blender is unable to remove it. Simply restart Blender and try again.
Addon Tutorial¶
Introduction¶
Intended Audience¶
This tutorial is designed to help technical artists or developers learn to extend Blender. An understanding of the basics of Python is expected for those working through this tutorial.
Prerequisites¶
Before going through the tutorial you should.
Suggested reading before starting this tutorial.
To best troubleshoot any error message Python prints while writing scripts you run blender with from a terminal, see Use The Terminal.
Documentation Links¶
While going through the tutorial you may want to look into our reference documentation.
Addons¶
What is an Addon?В¶
An addon is simply a Python module with some additional requirements so Blender can display it in a list with useful information.
To give an example, here is the simplest possible addon.
This is a contrived example of an addon that serves to illustrate the point that the base requirements of an addon are simple.
So an addon is just a way to encapsulate a Python module in a way a user can easily utilize.
Running this script within the text editor won’t print anything, to see the output it must be installed through the user preferences. Messages will be printed when enabling and disabling.
Your First Addon¶
The simplest possible addon above was useful as an example but not much else. This next addon is simple but shows how to integrate a script into Blender using an Operator which is the typical way to define a tool accessed from menus, buttons and keyboard shortcuts.
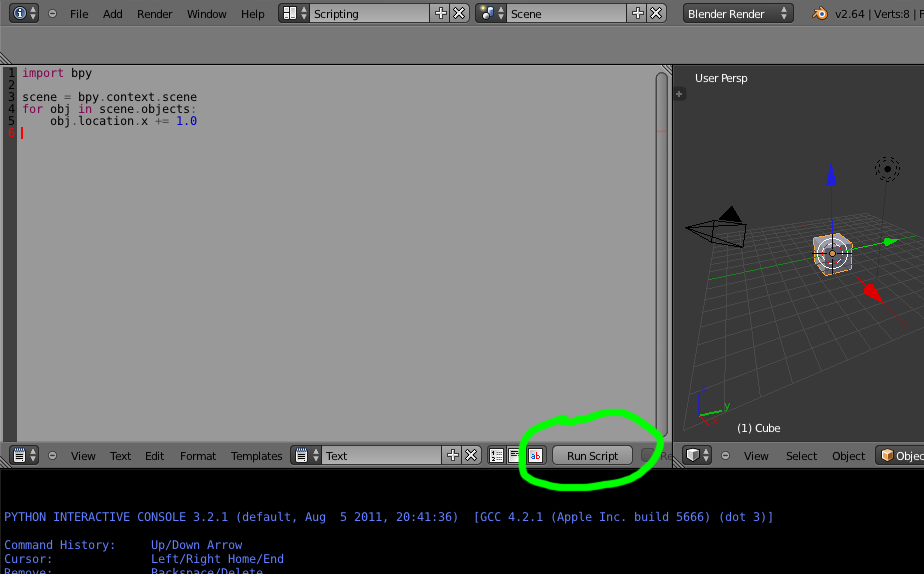
For the first example we’ll make a script that simply moves all objects in a scene.
Write The Script¶
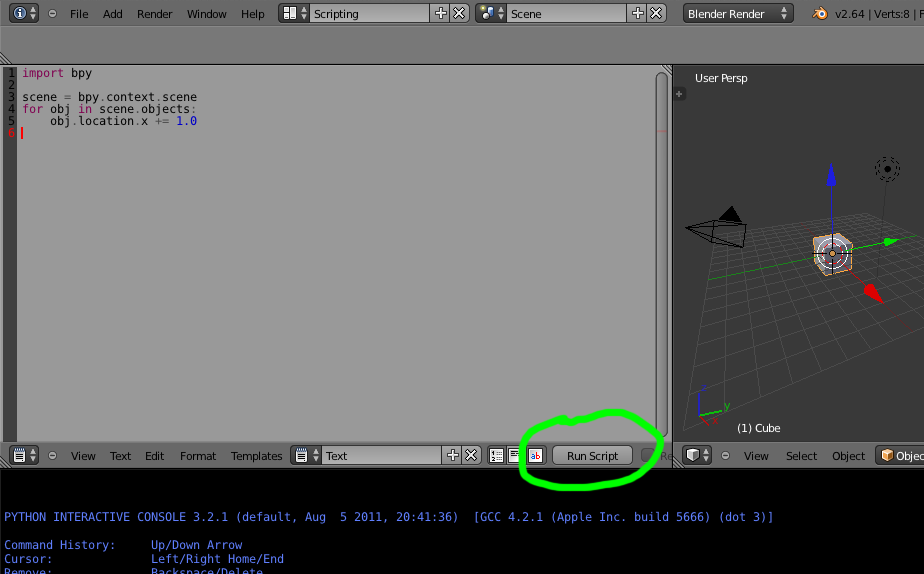
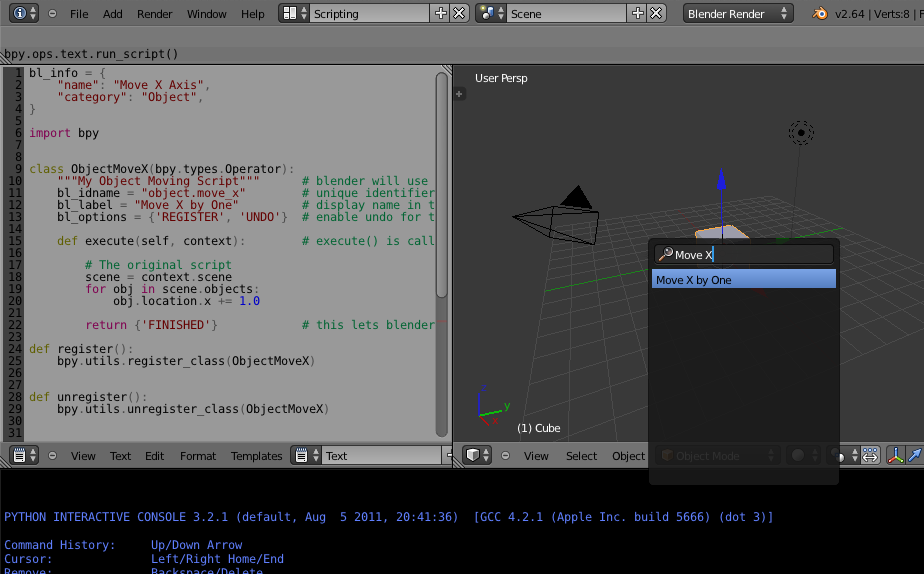
Add the following script to the text editor in Blender.
Click the Run Script button, all objects in the active scene are moved by 1.0 Blender unit. Next we’ll make this script into an addon.
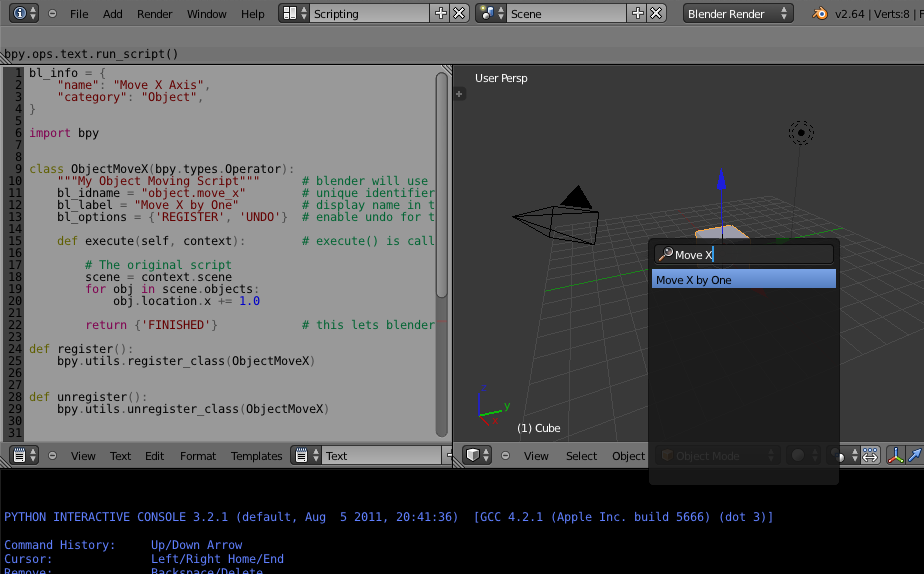
Write the Addon (Simple)В¶
This addon takes the body of the script above, and adds them to an operator’s execute() function.
bl_info is split across multiple lines, this is just a style convention used to more easily add items.
To test the script you can copy and paste this into Blender text editor and run it, this will execute the script directly and call register immediately.
However running the script wont move any objects, for this you need to execute the newly registered operator.
The objects should move as before.
Install The Addon¶
Once you have your addon within in Blender’s text editor, you will want to be able to install it so it can be enabled in the user preferences to load on startup.
Even though the addon above is a test, lets go through the steps anyway so you know how to do it for later.
Once the file is on disk, you can install it as you would for an addon downloaded online.
Now the addon will be listed and you can enable it by pressing the check-box, if you want it to be enabled on restart, press Save as Default.
The destination of the addon depends on your Blender configuration. When installing an addon the source and destination path are printed in the console. You can also find addon path locations by running this in the Python console.
More is written on this topic here: Directory Layout
Your Second Addon¶
Write The Script¶
As before, first we will start with a script, develop it, then convert into an addon.
Now try copy this script into Blender and run it on the default cube. Make sure you click to move the 3D cursor before running as the duplicate will appear at the cursor’s location.
Next, we’re going to do this in a loop, to make an array of objects between the active object and the cursor.
Try run this script with with the active object and the cursor spaced apart to see the result.
For now we’ll focus on making this script an addon, but its good to know that this 3D math module is available and can help you with more advanced functionality later on.
Write the Addon¶
The first step is to convert the script as-is into an addon.
Everything here has been covered in the previous steps, you may want to try run the addon still and consider what could be done to make it more useful.
Both these additions are explained next, with the final script afterwards.
Operator Property¶
There are a variety of property types that are used for tool settings, common property types include: int, float, vector, color, boolean and string.
These properties are handled differently to typical Python class attributes because Blender needs to be display them in the interface, store their settings in key-maps and keep settings for re-use.
While this is handled in a fairly Pythonic way, be mindful that you are in fact defining tool settings that are loaded into Blender and accessed by other parts of Blender, outside of Python.
This document doesn’t go into details about using other property types, however the link above includes examples of more advanced property usage.
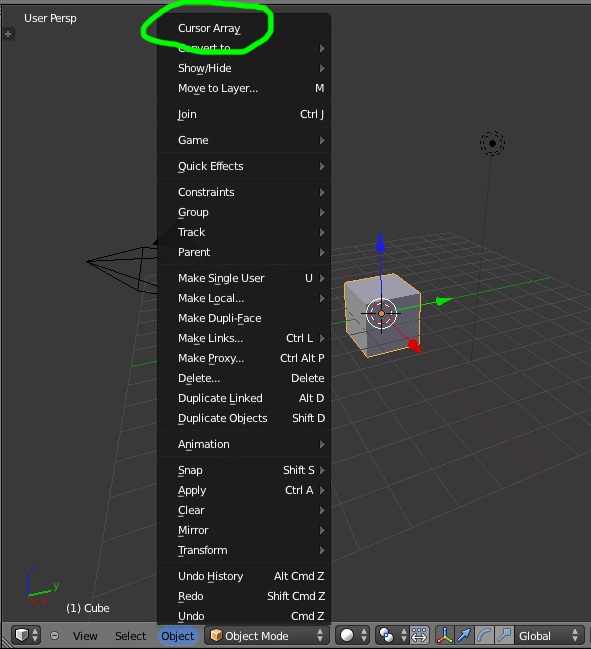
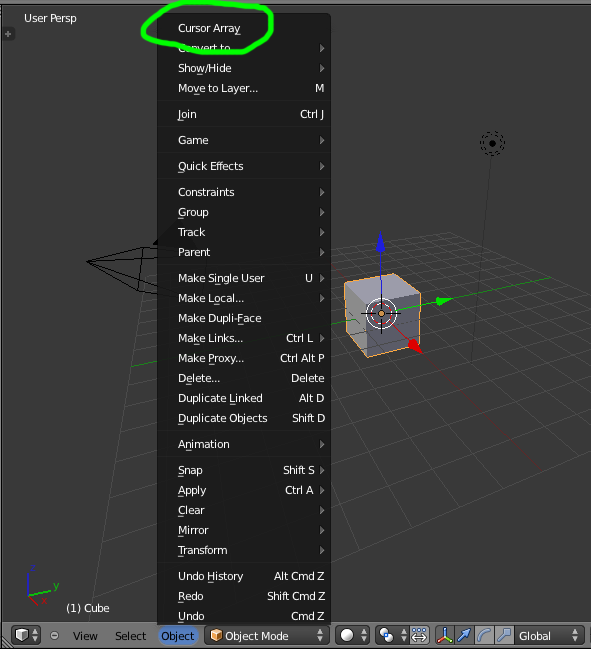
Menu Item¶
Addons can add to the user interface of existing panels, headers and menus defined in Python.
For this example we’ll add to an existing menu.
To find the identifier of a menu you can hover your mouse over the menu item and the identifier is displayed.
The method used for adding a menu item is to append a draw function into an existing class.
For docs on extending menus see: Menu(bpy_struct).
Keymap¶
In Blender addons have their own key-maps so as not to interfere with Blenders built in key-maps.
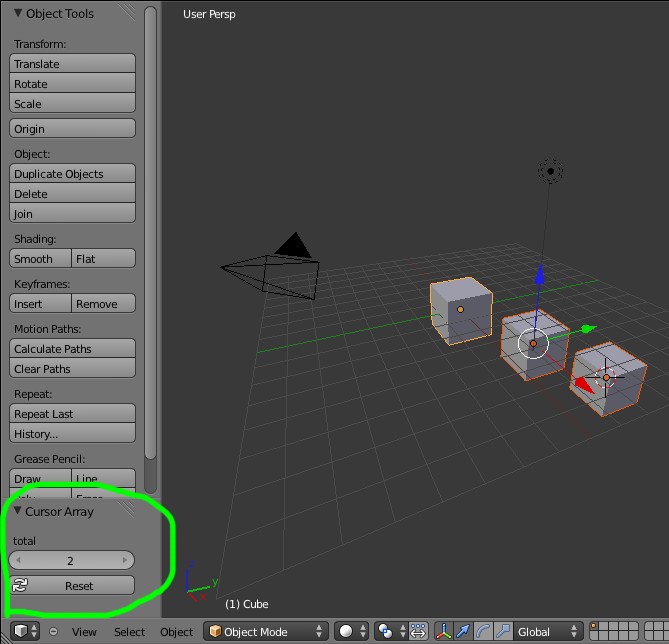
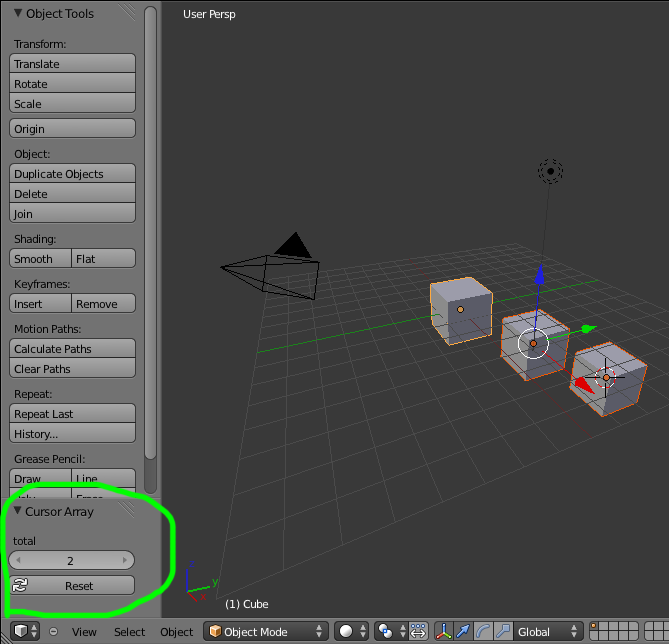
Notice how the key-map item can have a different total setting then the default set by the operator, this allows you to have multiple keys accessing the same operator with different settings.
While Ctrl-Shift-Space isn’t a default Blender key shortcut, its hard to make sure addons won’t overwrite each others keymaps, At least take care when assigning keys that they don’t conflict with important functionality within Blender.
Bringing it all together¶
Run the script (or save it and add it through the Preferences like before) and it will appear in the menu.
After selecting it from the menu, you can choose how many instance of the cube you want created.
Directly executing the script multiple times will add the menu each time too. While not useful behavior, theres nothing to worry about since addons won’t register them selves multiple times when enabled through the user preferences.
Conclusions¶
Addons can encapsulate certain functionality neatly for writing tools to improve your work-flow or for writing utilities for others to use.
While there are limits to what Python can do within Blender, there is certainly a lot that can be achieved without having to dive into Blender’s C/C++ code.
The example given in the tutorial is limited, but shows the Blender API used for common tasks that you can expand on to write your own tools.
Further Reading¶
Blender comes commented templates which are accessible from the text editor header, if you have specific areas you want to see example code for, this is a good place to start.
Here are some sites you might like to check on after completing this tutorial.
Addon Tutorial¶
Introduction¶
Intended Audience¶
This tutorial is designed to help technical artists or developers learn to extend Blender. An understanding of the basics of Python is expected for those working through this tutorial.
Prerequisites¶
Before going through the tutorial you should.
Suggested reading before starting this tutorial.
To best troubleshoot any error message Python prints while writing scripts you run blender with from a terminal, see Use The Terminal.
Documentation Links¶
While going through the tutorial you may want to look into our reference documentation.
Addons¶
What is an Addon?В¶
An addon is simply a Python module with some additional requirements so Blender can display it in a list with useful information.
To give an example, here is the simplest possible addon.
This is a contrived example of an addon that serves to illustrate the point that the base requirements of an addon are simple.
So an addon is just a way to encapsulate a Python module in a way a user can easily utilize.
Running this script within the text editor won’t print anything, to see the output it must be installed through the user preferences. Messages will be printed when enabling and disabling.
Your First Addon¶
The simplest possible addon above was useful as an example but not much else. This next addon is simple but shows how to integrate a script into Blender using an Operator which is the typical way to define a tool accessed from menus, buttons and keyboard shortcuts.
For the first example we’ll make a script that simply moves all objects in a scene.
Write The Script¶
Add the following script to the text editor in Blender.
Click the Run Script button, all objects in the active scene are moved by 1.0 Blender unit. Next we’ll make this script into an addon.
Write the Addon (Simple)В¶
This addon takes the body of the script above, and adds them to an operator’s execute() function.
bl_info is split across multiple lines, this is just a style convention used to more easily add items.
To test the script you can copy and paste this into Blender text editor and run it, this will execute the script directly and call register immediately.
However running the script wont move any objects, for this you need to execute the newly registered operator.
The objects should move as before.
Install The Addon¶
Once you have your addon within in Blender’s text editor, you will want to be able to install it so it can be enabled in the user preferences to load on startup.
Even though the addon above is a test, lets go through the steps anyway so you know how to do it for later.
Once the file is on disk, you can install it as you would for an addon downloaded online.
Now the addon will be listed and you can enable it by pressing the check-box, if you want it to be enabled on restart, press Save as Default.
The destination of the addon depends on your Blender configuration. When installing an addon the source and destination path are printed in the console. You can also find addon path locations by running this in the Python console.
More is written on this topic here: Directory Layout
Your Second Addon¶
Write The Script¶
As before, first we will start with a script, develop it, then convert into an addon.
Now try copy this script into Blender and run it on the default cube. Make sure you click to move the 3D cursor before running as the duplicate will appear at the cursor’s location.
Next, we’re going to do this in a loop, to make an array of objects between the active object and the cursor.
Try run this script with with the active object and the cursor spaced apart to see the result.
For now we’ll focus on making this script an addon, but its good to know that this 3D math module is available and can help you with more advanced functionality later on.
Write the Addon¶
The first step is to convert the script as-is into an addon.
Everything here has been covered in the previous steps, you may want to try run the addon still and consider what could be done to make it more useful.
Both these additions are explained next, with the final script afterwards.
Operator Property¶
There are a variety of property types that are used for tool settings, common property types include: int, float, vector, color, boolean and string.
These properties are handled differently to typical Python class attributes because Blender needs to be display them in the interface, store their settings in key-maps and keep settings for re-use.
While this is handled in a fairly Pythonic way, be mindful that you are in fact defining tool settings that are loaded into Blender and accessed by other parts of Blender, outside of Python.
This document doesn’t go into details about using other property types, however the link above includes examples of more advanced property usage.
Menu Item¶
Addons can add to the user interface of existing panels, headers and menus defined in Python.
For this example we’ll add to an existing menu.
To find the identifier of a menu you can hover your mouse over the menu item and the identifier is displayed.
The method used for adding a menu item is to append a draw function into an existing class.
For docs on extending menus see: Menu(bpy_struct).
Keymap¶
In Blender addons have their own key-maps so as not to interfere with Blenders built in key-maps.
Notice how the key-map item can have a different total setting then the default set by the operator, this allows you to have multiple keys accessing the same operator with different settings.
While Ctrl-Shift-Space isn’t a default Blender key shortcut, its hard to make sure addons won’t overwrite each others keymaps, At least take care when assigning keys that they don’t conflict with important functionality within Blender.
Bringing it all together¶
Run the script (or save it and add it through the Preferences like before) and it will appear in the menu.
After selecting it from the menu, you can choose how many instance of the cube you want created.
Directly executing the script multiple times will add the menu each time too. While not useful behavior, theres nothing to worry about since addons won’t register them selves multiple times when enabled through the user preferences.
Conclusions¶
Addons can encapsulate certain functionality neatly for writing tools to improve your work-flow or for writing utilities for others to use.
While there are limits to what Python can do within Blender, there is certainly a lot that can be achieved without having to dive into Blender’s C/C++ code.
The example given in the tutorial is limited, but shows the Blender API used for common tasks that you can expand on to write your own tools.
Further Reading¶
Blender comes commented templates which are accessible from the text editor header, if you have specific areas you want to see example code for, this is a good place to start.
Here are some sites you might like to check on after completing this tutorial.
Addon Tutorial¶
Introduction¶
Intended Audience¶
This tutorial is designed to help technical artists or developers learn to extend Blender. An understanding of the basics of Python is expected for those working through this tutorial.
Prerequisites¶
Before going through the tutorial you should.
Suggested reading before starting this tutorial.
To best troubleshoot any error message Python prints while writing scripts you run blender with from a terminal, see Use The Terminal.
Documentation Links¶
While going through the tutorial you may want to look into our reference documentation.
Addons¶
What is an Addon?В¶
An addon is simply a Python module with some additional requirements so Blender can display it in a list with useful information.
To give an example, here is the simplest possible addon.
This is a contrived example of an addon that serves to illustrate the point that the base requirements of an addon are simple.
So an addon is just a way to encapsulate a Python module in a way a user can easily utilize.
Running this script within the text editor won’t print anything, to see the output it must be installed through the user preferences. Messages will be printed when enabling and disabling.
Your First Addon¶
The simplest possible addon above was useful as an example but not much else. This next addon is simple but shows how to integrate a script into Blender using an Operator which is the typical way to define a tool accessed from menus, buttons and keyboard shortcuts.
For the first example we’ll make a script that simply moves all objects in a scene.
Write The Script¶
Add the following script to the text editor in Blender.
Click the Run Script button, all objects in the active scene are moved by 1.0 Blender unit. Next we’ll make this script into an addon.
Write the Addon (Simple)В¶
This addon takes the body of the script above, and adds them to an operator’s execute() function.
bl_info is split across multiple lines, this is just a style convention used to more easily add items.
To test the script you can copy and paste this into Blender text editor and run it, this will execute the script directly and call register immediately.
However running the script wont move any objects, for this you need to execute the newly registered operator.
The objects should move as before.
Install The Addon¶
Once you have your addon within in Blender’s text editor, you will want to be able to install it so it can be enabled in the user preferences to load on startup.
Even though the addon above is a test, lets go through the steps anyway so you know how to do it for later.
Once the file is on disk, you can install it as you would for an addon downloaded online.
Now the addon will be listed and you can enable it by pressing the check-box, if you want it to be enabled on restart, press Save as Default.
The destination of the addon depends on your Blender configuration. When installing an addon the source and destination path are printed in the console. You can also find addon path locations by running this in the Python console.
More is written on this topic here: Directory Layout
Your Second Addon¶
Write The Script¶
As before, first we will start with a script, develop it, then convert into an addon.
Now try copy this script into Blender and run it on the default cube. Make sure you click to move the 3D cursor before running as the duplicate will appear at the cursor’s location.
Next, we’re going to do this in a loop, to make an array of objects between the active object and the cursor.
Try run this script with with the active object and the cursor spaced apart to see the result.
For now we’ll focus on making this script an addon, but its good to know that this 3D math module is available and can help you with more advanced functionality later on.
Write the Addon¶
The first step is to convert the script as-is into an addon.
Everything here has been covered in the previous steps, you may want to try run the addon still and consider what could be done to make it more useful.
Both these additions are explained next, with the final script afterwards.
Operator Property¶
There are a variety of property types that are used for tool settings, common property types include: int, float, vector, color, boolean and string.
These properties are handled differently to typical Python class attributes because Blender needs to be display them in the interface, store their settings in key-maps and keep settings for re-use.
While this is handled in a fairly Pythonic way, be mindful that you are in fact defining tool settings that are loaded into Blender and accessed by other parts of Blender, outside of Python.
This document doesn’t go into details about using other property types, however the link above includes examples of more advanced property usage.
Menu Item¶
Addons can add to the user interface of existing panels, headers and menus defined in Python.
For this example we’ll add to an existing menu.
To find the identifier of a menu you can hover your mouse over the menu item and the identifier is displayed.
The method used for adding a menu item is to append a draw function into an existing class.
For docs on extending menus see: Menu(bpy_struct).
Keymap¶
In Blender addons have their own key-maps so as not to interfere with Blenders built in key-maps.
Notice how the key-map item can have a different total setting then the default set by the operator, this allows you to have multiple keys accessing the same operator with different settings.
While Ctrl-Shift-Space isn’t a default Blender key shortcut, its hard to make sure addons won’t overwrite each others keymaps, At least take care when assigning keys that they don’t conflict with important functionality within Blender.
Bringing it all together¶
Run the script (or save it and add it through the Preferences like before) and it will appear in the menu.
After selecting it from the menu, you can choose how many instance of the cube you want created.
Directly executing the script multiple times will add the menu each time too. While not useful behavior, theres nothing to worry about since addons won’t register them selves multiple times when enabled through the user preferences.
Conclusions¶
Addons can encapsulate certain functionality neatly for writing tools to improve your work-flow or for writing utilities for others to use.
While there are limits to what Python can do within Blender, there is certainly a lot that can be achieved without having to dive into Blender’s C/C++ code.
The example given in the tutorial is limited, but shows the Blender API used for common tasks that you can expand on to write your own tools.
Further Reading¶
Blender comes commented templates which are accessible from the text editor header, if you have specific areas you want to see example code for, this is a good place to start.
Here are some sites you might like to check on after completing this tutorial.
Источники информации:
- http://github.com/rlguy/Blender-FLIP-Fluids/wiki/Addon-Installation-and-Uninstallation-(Blender-2.79)
- http://docs.blender.org/api/blender_python_api_2_69_1/info_tutorial_addon.html
- http://docs.blender.org/api/blender_python_api_2_74_0/info_tutorial_addon.html
- http://docs.blender.org/api/blender_python_api_2_71_6/info_tutorial_addon.html