How to remove user ubuntu
How to remove user ubuntu
How to Delete User on Ubuntu
Follow any of the approaches you find easier.
Deleting User Using Graphical Interface
As a beginner of Ubuntu you will find this approach a way easier. Follow the steps below to remove user using GUI on Ubuntu System:
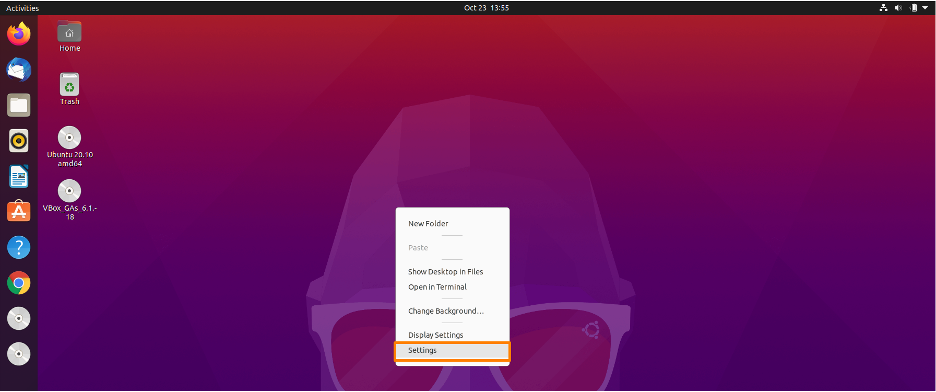
Step 1: Open setting
Firstly you need to open the Settings by opening “Activities” and typing setting in search bar and click on Settings icon:
Or you can left click on the desktop screen of Ubuntu a drop-down list will appear, click on Settings option.
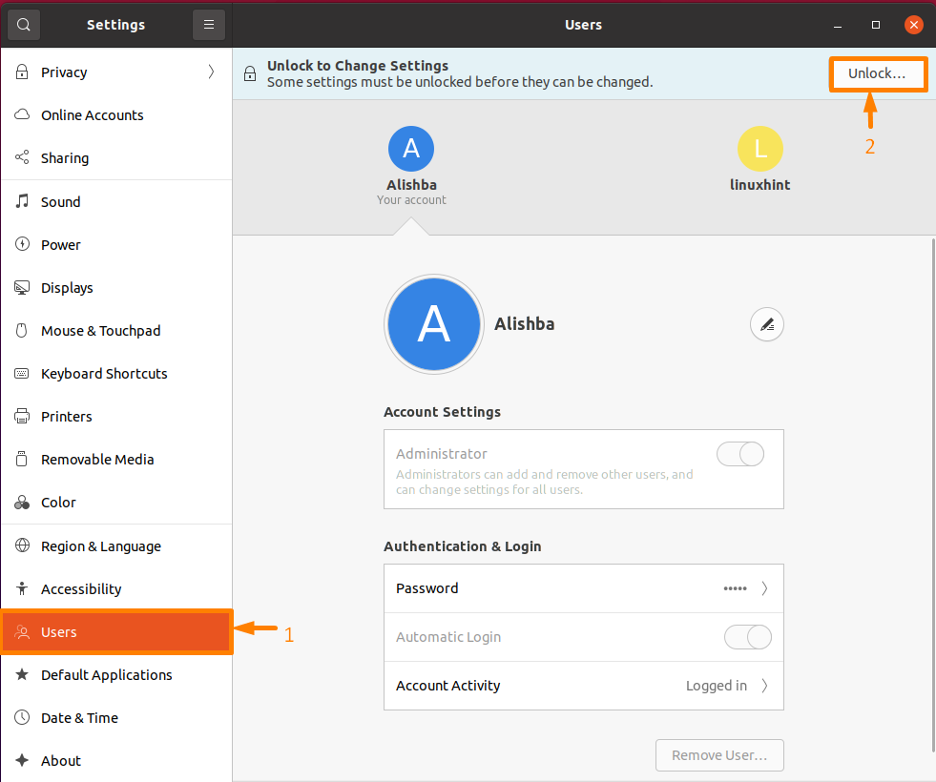
Step 2: Open Users setting
After the setting window will appear click on “Users” from list on left side, then on “Unlock…”:
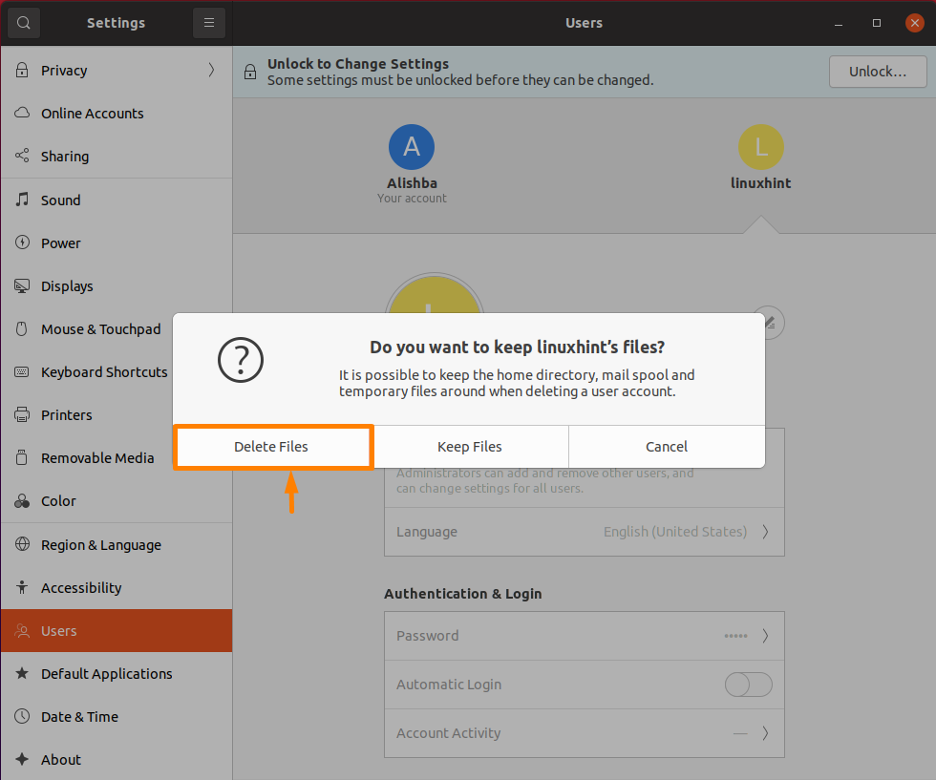
Step 3: Remove User Account
In the Users setting, the system users will be shown on the screen.Then, at the bottom of the page, click the “Remove User…” button next to the user you wish to delete. Below I am removing “linuxhint” user from my system:
Now a dialogue box will appear asking you to select an option. To remove all files of the user you want to delete then choose Delete Files option, but if you want to store the files of the user for later use then choose Keep Files option.
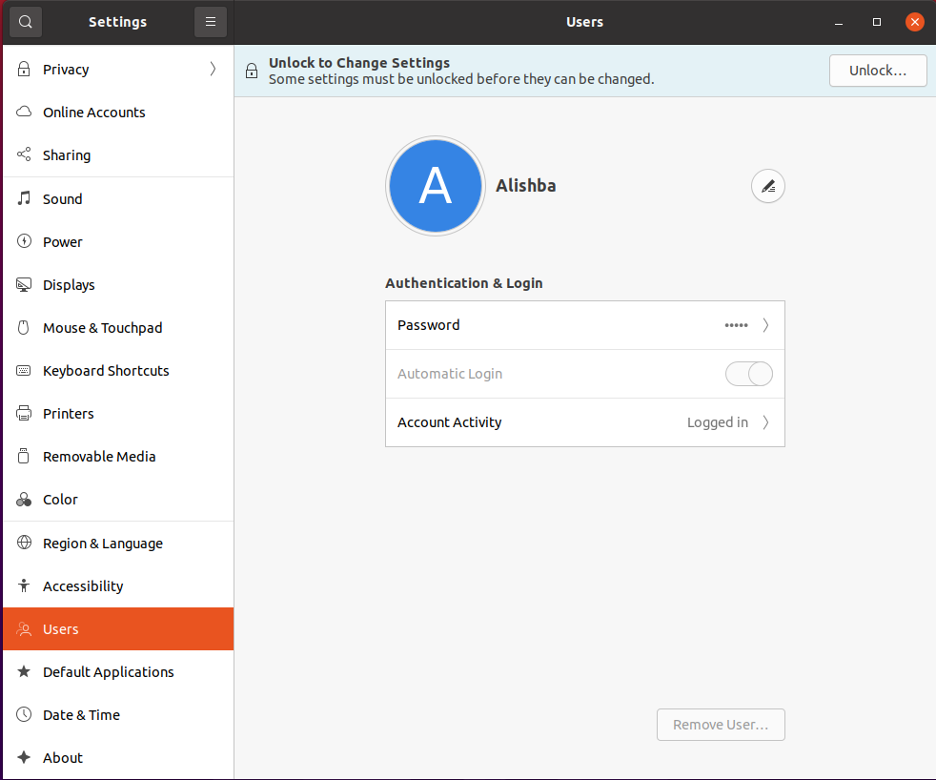
And user will be removed from list of users as shown below:
Deleting User using Command Line
If you are a Command Line user this method is for you. You can also remove the user by writing commands on the terminal.
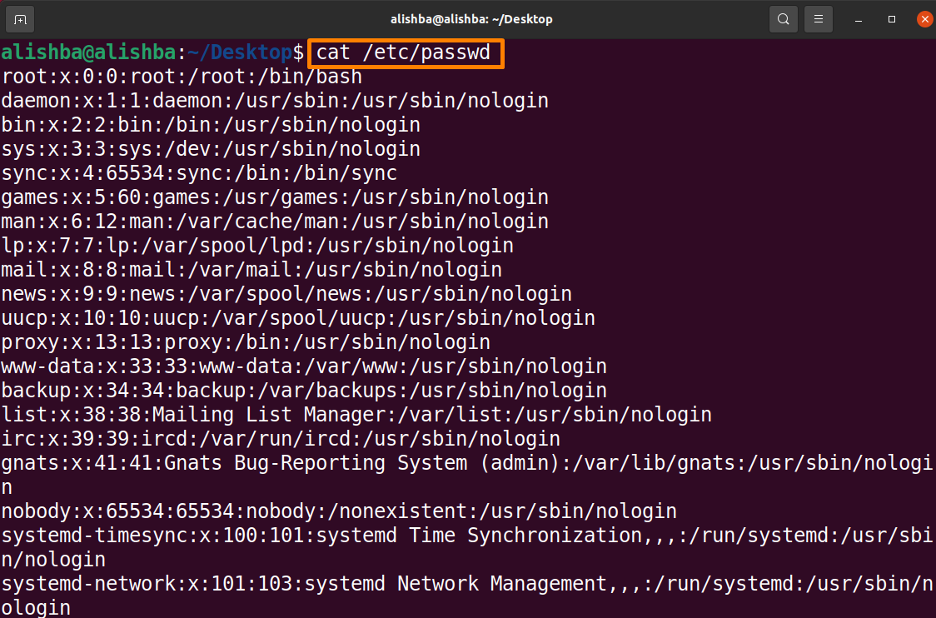
Step 1: List users
First check all the users registered on your system, the users are recorded in /etc/passwd, with the user account name as the first column.To see a list of existing user accounts, use the cat command, as seen below:
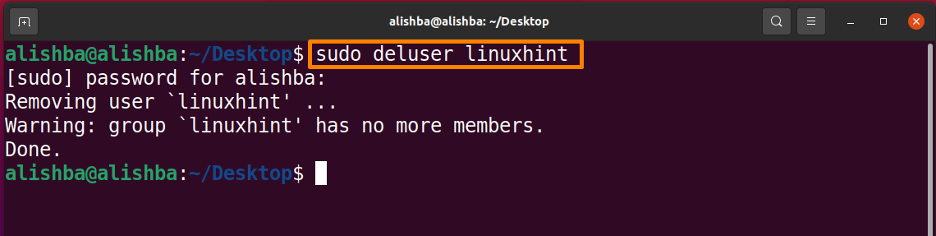
Step 2: Remove user
The “deluser” command is used for deleting or removing a user account from Ubuntu. The deluser command should be given the user account name. We also need capabilities to delete user accounts, which we can get by logging in as root or executing the sudo command as a regular user.
Below mentioned is the command to delete “linuxhint” user from my system:
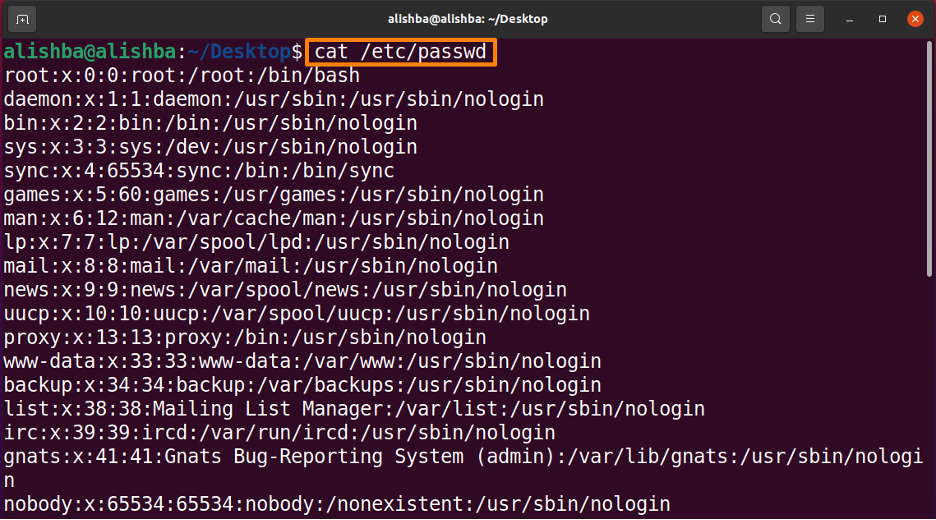
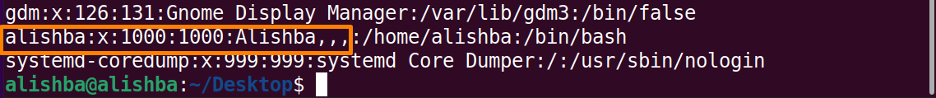
Step 3 : Check User
Now check whether the user is deleted by below mentioned command:
From above shown results we can check that “linuxhint” user no longer exists.
Conclusion
Ubuntu is an open source multi-user Linux distribution which provides several functionalities.It lets you add and remove users at any moment. In this Article, two approaches to delete the user from Ubuntu system are discussed; first is by GUI method and second is by Command line method using “deluser” command. To successfully delete the user, you can use any of the methods outlined in this article.
About the author
Alishba Iftikhar
I am currently an undergraduate student in my 1st year. I am an internee author with Linuxhint and loved learning the art of technical content writing from senior authors. I am looking forward to opting my career as a full time Linux writer after I graduate.
How to Add and Delete Users on Ubuntu 20.04
Introduction
Adding and removing users on a Linux system is one of the most important system administration tasks to familiarize yourself with. When you create a new system, you are often only given access to the root account by default.
While running as the root user gives you complete control over a system and its users, it is also dangerous and possibly destructive. For common system administration tasks, it’s a better idea to add an unprivileged user and carry out those tasks without root privileges. You can also create additional unprivileged accounts for any other users you may have on your system. Each user on a system should have their own separate account.
Prerequisites
To complete this tutorial, you will need access to a server running Ubuntu 20.04. Ensure that you have root access to the server and firewall enabled. To set this up, follow our Initial Server Setup Guide for Ubuntu 20.04.
Adding a User
If you are signed in as the root user, you can create a new user at any time by running the following:
If you are signed in as a non-root user who has been given sudo privileges, you can add a new user with the following command:
Either way, you will be required to respond to a series of questions:
Your new user is now ready for use and can be logged into with the password that you entered.
If you need your new user to have administrative privileges, continue on to the next section.
Granting a User Sudo Privileges
Adding the New User to the Sudo Group
By default, sudo on Ubuntu 20.04 systems is configured to extend full privileges to any user in the sudo group.
You can view what groups your new user is in with the groups command:
By default, a new user is only in their own group because adduser creates this in addition to the user profile. A user and its own group share the same name. In order to add the user to a new group, you can use the usermod command:
Specifying Explicit User Privileges in /etc/sudoers
As an alternative to putting your user in the sudo group, you can use the visudo command, which opens a configuration file called /etc/sudoers in the system’s default editor, and explicitly specify privileges on a per-user basis.
Using visudo is the only recommended way to make changes to /etc/sudoers because it locks the file against multiple simultaneous edits and performs a validation check on its contents before overwriting the file. This helps to prevent a situation where you misconfigure sudo and cannot fix the problem because you have lost sudo privileges.
If you are currently signed in as root, run the following:
If you are signed in as a non-root user with sudo privileges, run the same command with the sudo prefix:
Traditionally, visudo opened /etc/sudoers in the vi editor, which can be confusing for inexperienced users. By default on new Ubuntu installations, visudo will use the nano text editor, which provides a more convenient and accessible text editing experience. Use the arrow keys to move the cursor, and search for the line that reads like the following:
Below this line, add the following highlighted line. Be sure to change newuser to the name of the user profile that you would like to grant sudo privileges:
Testing Your User’s Sudo Privileges
Now your new user is able to execute commands with administrative privileges.
When signed in as the new user, you can execute commands as your regular user by typing commands as normal:
You can execute the same command with administrative privileges by typing sudo ahead of the command:
When doing this, you will be prompted to enter the password of the regular user account you are signed in as.
Deleting a User
In the event that you no longer need a user, it’s best to delete the old account.
You can delete the user itself, without deleting any of their files, by running the following command as root:
If you are signed in as another non-root user with sudo privileges, you would use the following:
If, instead, you want to delete the user’s home directory when the user is deleted, you can issue the following command as root:
If you’re running this as a non-root user with sudo privileges, you would run the same command with the sudo prefix:
If you previously configured sudo privileges for the user you deleted, you may want to remove the relevant line again:
Or use the following command if you are a non-root user with sudo privileges:
This will prevent a new user created with the same name from being accidentally given sudo privileges.
Conclusion
You should now have a fairly good handle on how to add and remove users from your Ubuntu 20.04 system. Effective user management will allow you to separate users and give them only the access that they are required to do their job.
Want to learn more? Join the DigitalOcean Community!
Join our DigitalOcean community of over a million developers for free! Get help and share knowledge in our Questions & Answers section, find tutorials and tools that will help you grow as a developer and scale your project or business, and subscribe to topics of interest.
How To Delete/Remove User Account In Ubuntu?
Adding and removing user accounts is a daily task for a Linux system administrator. Ubuntu is one of the most popular distributions used in the Enterprise environment where the delete or removing a user account is a daily task too. Removing or deleting a user account in Ubuntu requires administrative privileges which are generally provided by the root user. A user account can be deleted in different ways and with different options in Ubuntu. In this tutorial, we examine how to delete a user account by deleting its home directory, removing permissions, etc.
List User Accounts
Before deleting or removing a Ubuntu user account we can list currently existing accounts. The users are stored in the /etc/passwd where the first column is the user account name. We can list existing user accounts with the cat command like below.
Remove/Delete User Account with deluser Command
The official command to delete or remove the user account from the Ubuntu is the deluser command. The user account name should be provided to the deluser command. Also, we require privileges to delete a user account which can be provided by logging in root user or by using the sudo command as a regular user.
Remove/Delete User Account with deluser Removing User Home Directory
Remove/Delete User with userdel Command
The userdel command can be also used to remove existing user.
Remove/Delete User Account with GUI
The user management is provided via the Settings tool in Ubuntu. First, we open the Settings tool which can be opened in different ways like clicking dash and then typing settings which is listed below.
In the Settings navigate to the Users left pane and click the Unlock button in order to authenticate as sudo user to get the required privileges to delete the account.
Provide the current user password to get privileges.
In the following step we select the user we want to delete from the list of users. In this case, we select the user named ahmet to delete it and click to the Remove User. button in the right-left corner.
We asked if we want to delete the user’s files or if we want to keep them. This is the same operation as deleting the user’s home directory. In this example we Delete Files for the user ahmet.
Verify User Account Has Been Deleted From Ubuntu
We can verify if the user has been deleted successfully or check if a specific user account exists in Ubuntu by using the grep command. Just provide the user name to the grep command to filter passwd file like below. In the following example, we check if the user ahmet deleted successfully and if exists in the “/etc/passwd” file.
Temporarily Disable User Account
Deleting a user in Ubuntu removes the account and its home folder completely where they can not be recovered in a regular way. But if we want to revert them back later but do prevent access for a specific time period we can disable the account. The usermod command can be used to disable an account in Ubuntu.
Alternatively, we can specify the disable period where after the specified data the user account is enabled automatically. In the following example, we disable the account to the 2021-12-01. After 2021-12-01 the account is enabled automatically.
How to Remove (Delete) a User on Ubuntu 16.04
Pre-flight Check
Delete A User
Step 1: Remove the User
Insert the username you want to delete by placing it after the userdel command. In our example, I’ll be deleting our user, Tom.
If the above code produces the message below, don’t be alarmed, it is not an error, but rather /home/tom existed but /var/mail/tom did not.
userdel: tom mail spool (/var/mail/tom) not found
Step 2: Remove Root Privileges
By removing Tom’s username from our Linux system we are halfway complete, but we still need to remove their root privileges.
Navigate to the following section:
## Allow root to run any commands anywhere
root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
tom ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
## User privilege specification
root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
tom ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
With either result, remove access for your user by deleting the corresponding entry:
tom ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
Save and exit this file by typing :wq and press the enter key.
To add a user, see our frequently used article,В How to Add a User and Grant Root Privileges on Ubuntu 16.04. Are you using a different Ubuntu version? We’ve got you covered, check out our Knowledge Base to find your version.
Related Articles:
About the Author: Echo Diaz
Throughout Echo’s four year stint as a technical support specialist, her passion for breaking down complex concepts had to lead to a career in professional writing. As a former top tier support specialist, she added a distinctive element to her written work that spoke to customer feedback and concerns. Echo occasionally pops her head out from behind her computer to watch her dog energetically run around the yard and unabashedly shovels money into buying tickets to see her favorite musical artists.
Join our mailing list to receive news, tips, strategies, and inspiration you need to grow your business
How to Add and Delete Users on Ubuntu 16.04
Introduction
One of the most basic tasks that you should know how to do on a fresh Linux server is add and remove users. When you create a new system, you are often (such as on DigitalOcean Droplets) only given the root account by default.
While running as the root user gives you a lot of power and flexibility, it is also dangerous and can be destructive. It is almost always a better idea to add an additional, unprivileged user to do common tasks. You also should create additional accounts for any other users you may have on your system. Each user should have a different account.
How To Add a User
If you are signed in as the root user, you can create a new user at any time by typing:
If you are signed in as a non-root user who has been given sudo privileges, as demonstrated in the initial server setup guide, you can add a new user by typing:
Either way, you will be asked a series of questions. The procedure will be:
Your new user is now ready for use! You can now log in using the password you set up.
Note: Continue if you need your new user to have access to administrative functionality.
How To Grant a User Sudo Privileges
Add the New User to the Sudo Group
By default, sudo on Ubuntu 16.04 systems is configured to extend full privileges to any user in the sudo group.
You can see what groups your new user is in with the groups command:
By default, a new user is only in their own group, which is created at the time of account creation, and shares a name with the user. In order to add the user to a new group, we can use the usermod command:
Test Your User’s Sudo Privileges
Now, your new user is able to execute commands with administrative privileges.
When signed in as the new user, you can execute commands as your regular user by typing commands as normal:
You can execute the same command with administrative privileges by typing sudo ahead of the command:
You will be prompted to enter the password of the regular user account you are signed in as.
Specifying Explicit User Privileges in /etc/sudoers
As an alternative to putting your user in the sudo group, you can use the visudo command, which opens a configuration file called /etc/sudoers in the system’s default editor, and explicitly specify privileges on a per-user basis.
If you are currently signed in as root, type:
If you are signed in using a non-root user with sudo privileges, type:
Below this line, copy the format you see here, changing only the word “root” to reference the new user that you would like to give sudo privileges to:
You should add a new line like this for each user that should be given full sudo privileges. When you are finished, you can save and close the file by hitting Ctrl-X, followed by Y, and then Enter to confirm.
How To Delete a User
In the event that you no longer need a user, it is best to delete the old account.
You can delete the user itself, without deleting any of their files, by typing this as root:
If you are signed in as another non-root user with sudo privileges, you could instead type:
If, instead, you want to delete the user’s home directory when the user is deleted, you can issue the following command as root:
If you’re running this as a non-root user with sudo privileges, you would instead type:
If you had previously configured sudo privileges for the user you deleted, you may want to remove the relevant line again by typing:
Or use this if you are a non-root user with sudo privileges:
This will prevent a new user created with the same name from being accidentally given sudo privileges.
Conclusion
You should now have a fairly good handle on how to add and remove users from your Ubuntu 16.04 system. Effective user management will allow you to separate users and give them only the access that they are required to do their job.
Want to learn more? Join the DigitalOcean Community!
Join our DigitalOcean community of over a million developers for free! Get help and share knowledge in our Questions & Answers section, find tutorials and tools that will help you grow as a developer and scale your project or business, and subscribe to topics of interest.
Источники информации:
- http://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-add-and-delete-users-on-ubuntu-20-04
- http://linuxtect.com/how-to-delete-remove-user-account-in-ubuntu/
- http://www.liquidweb.com/kb/remove-delete-user-ubuntu-16-04/
- http://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-add-and-delete-users-on-ubuntu-16-04