How to render wireframe in blender
How to render wireframe in blender
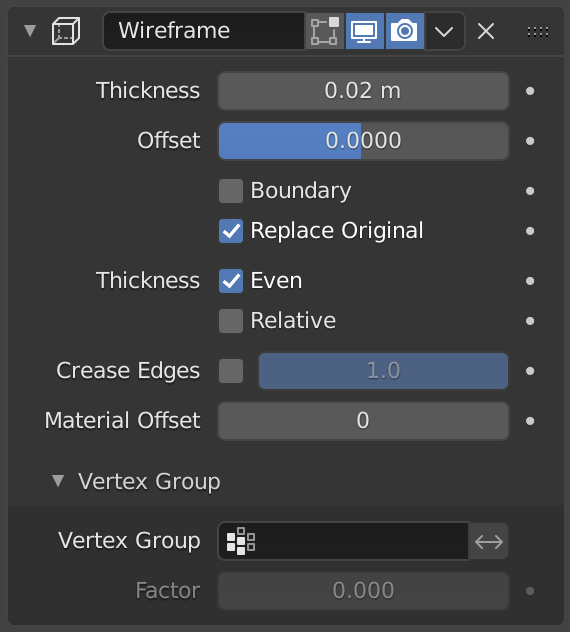
Wireframe ModifierпѓЃ
The Wireframe modifier transforms a mesh into a wireframe by iterating over its faces, collecting all edges and turning those edges into four-sided polygons. Be aware of the fact that your mesh needs to have faces to be wireframed. You can define the thickness, the material and several other parameters of the generated wireframe dynamically via the given modifier options.
OptionsпѓЃ
The Wireframe modifier. пѓЃ
The depth or size of the wireframes.
A value between (-1 to 1) to change whether the wireframes are generated inside or outside of the original mesh. Set to zero, Offset will center the wireframes around the original edges.
Creates wireframes on mesh island boundaries.
If this option is enabled, the original mesh is replaced by the generated wireframe. If not, the wireframe is generated on top of it.
Maintain thickness by adjusting for sharp corners. Sometimes improves quality but also increases computation time.
Determines the edge thickness by the length of the edge. Longer edges will be thicker.
This option is intended for usage with the Subdivision modifier. Enable this option to crease edges on their junctions and prevent large curved intersections.
Define how much crease (0 to 1, nothing to full) the junctions should receive.
Uses the chosen material index as the material for the wireframe; this is applied as an offset from the first material.
Wireframe thickness is an approximation. While Even Thickness should yield good results in many cases, skinny faces can cause ugly spikes. In this case you can either reduce the extreme angles in the geometry or disable the Even Thickness option.
Vertex GroupпѓЃ
The weights of the selected vertex group are multiplied onto the Thickness, so vertices with lower weights will be less thick. The vertices which are not part of the vertex group will be used as if their weight was zero.
Reverses the vertex group weights, so that the used weight is one minus the actual weight.
How much the vertex weights are taken into account.
If the final thickness of a vertex is zero, it will still generate a wireframe. Therefore creating duplicate geometry, which sometimes needs extra care.
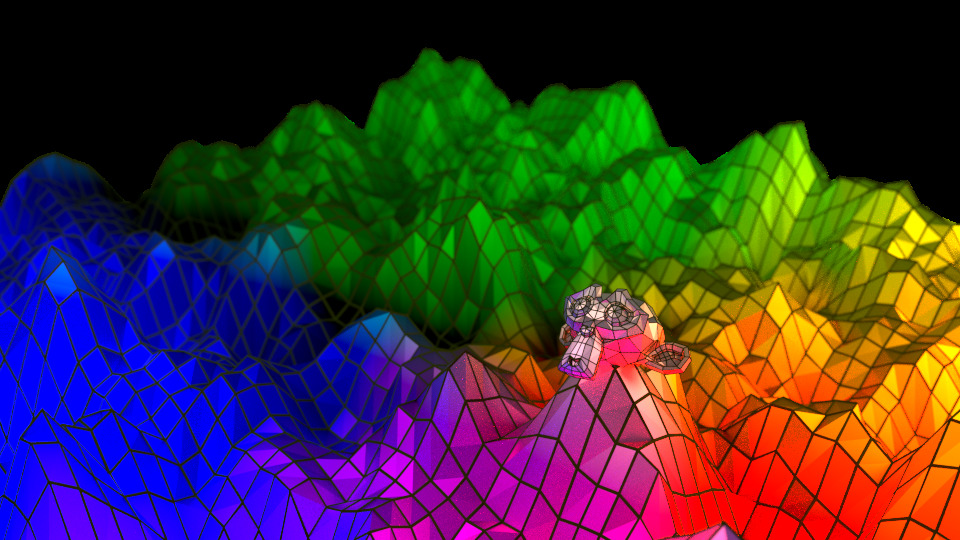
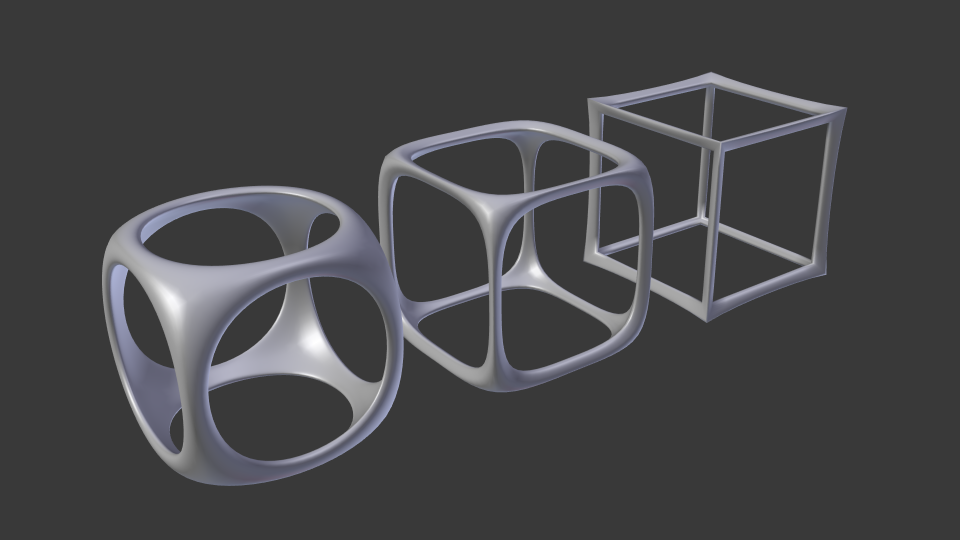
ExamplesпѓЃ
Wireframes on a displaced plane. пѓЃ
In this example, the wireframes carry a second (dark) material while the displaced plane uses its original one.
Vertex group weighting. пѓЃ
The weights of the vertex group gradually change from 0 to 1.
Wireframe and Subdivision Surface modifier. пѓЃ
Cube with enabled Crease Edges option. The Crease Weight is set to 0, 0.5 and 1.
© Copyright : This page is licensed under a CC-BY-SA 4.0 Int. License. Last updated on 08/15/2022.
How to render an object as a transparent wireframe?
I’m a psychology student (and 3D design noob) who’s been tasked with designing items for a test of spatial ability like this example.
I’ve been playing around with Blender, and I’ve gotten this far.
So the shapes I want are there, but I’m having trouble getting out rendered on white with black outlines.
I tried changing the World Horizon Color to white, which fixes the background, but the cube object renders solid. Any ideas on how to get it outlined like in the example?
P.S. That «LS» in the example is meant to be a window. Any suggestions on how to accomplish that would also be wonderful; I haven’t even attempted it yet.
4 Answers 4
One way you could do this is by using freestyle:
Create a transparent material and assign it to your objects:
Enable freestyle in Render settings:
In Render layers, set the line visibility to QI range and set the end to 1:
Think of the QI range like a sort of depth index; faces directly visible to the camera are 0, faces behind those faces are 1, faces behind those faces are 2, etc.
By only rendering lines on faces between 0 and 1 (inclusive), you can get a result like in your example image.
Or you could use wireframe materials:
Using blender internal you can set the material type to wire and it will only show the wireframe of the object.
For cycles there is a wireframe node that you can input into a mix node to define transparent areas but it will show a triangulated wireframe.
An option that is available in both renders is the wireframe modifier. This modifier was added in 2.70 and gives you control over how thick the wireframe will appear.
There are several ways to do this.
First: Using the Cycles render engine, this is now extremely easy. You can use the node setup below, with which you can control how opaque the faces are, and the color of the edges.
Another easy way to do this, is to use the Wirefame modifier.
This will alter the mesh to show a mesh along the edges of the base mesh, and will not render any faces. This works in viewport, BI and Cycles. Notice that you may need to get a more recent version of Blender depending on your current build.
Another option would be to make your item from modeled wires, and use that, instead of a texture.
The way to do this is to first create a «wire» from which to construct the wireframes. In the illustration below, I created a cylinder with 8 vertices, and unclosed ends (numbered «1» in the screentshot:
A material (black in this case) was assigned to the «wire», and it was duplicated, rotated, and the length of the cylinder was changed the length to create a 3D representation of the original image. Analyzing the blend file from which the screenshot was created,
it will be seen that the «wireframe» will show up in a render, because the wires are meshes, and not blender edges.
Want to master Blender? Click here! and get our E-Book
I needed a reliable way to render wireframes and came across freestyle rendering. I realized that freestyle was a lot of fun and had multiple uses. Everything from cartoons, to blueprints and wireframe rendering, can be made with freestyle.
What is freestyle rendering and How to use it in Blender? Freestyle rendering is an NPR(non-photo-realistic) render engine that adds a layer of lines above your render based on the geometry in your scene. In the render settings, check the checkbox on the freestyle section to enable it. In the view layer tab, you will find all the related settings to customize freestyle to your needs.
In the rest of this article, we will dive deeper into freestyle and how we can use it to do some common rendering effects like wire frame rendering and cartoon styles.
What is freestyle rendering?
Freestyle rendering is a Non-Photorealistic-Render(NPR) engine that was added to Blender in version 2.67. With it, we can create a line layer above our render based on the geometry we created.
What this means is that we can create a lot of different kinds of art that would not be possible without it. For instance, it can be used to make cartoons in different styles. We can also do more technical renders like blueprint renders and wire frame renders if we want to showcase how our original 3D renders were modeled.
If you want to create cartoon style renders but find freestyle to be a bit too complex, I would recommend to check out toonkit. It is an add-on that adds some shader nodes to Cycles as well as lamp, and world settings. Much easier to set up and work with. It also renders almost real time.
You can find it here:
How does freestyle rendering work?
Freestyle rendering is enabled in the render settings of either Eevee or Cycles. Both renderers are supported but they differ slightly in features.
Freestyle is enabled for the entire scene. But it can then be controlled on a view layer level. The scenes «global settings» for freestyle are in the render settings, then we have some freestyle settings that are related to a view layer.
When freestyle is enabled, each view layer has two additional layers of settings. After the «global settings» that are in effect for the entire view layer, there is the «Freestyle Line set» settings and the «Freestyle line styles».
Let’s start with line sets. We can have multiple line sets. The basic idea is that they will determine where a set of lines will be drawn. For example, we can have one line set that is selecting the silhouette of our objects. Another line set could be the internal lines of objects and the third set of lines could be any object that is behind one or more other objects.
There is also an option to mark any edge to be detected by freestyle manually if we want full and ultimate control.
The next layer is the line style. The line style will determine how a freestyle edge will be drawn, or how a line will look. Each line set can have a line style attached.
So if you can see the pattern, we first had some global settings. Then we had one or more line sets that will actually be a kind of selection of edges. Then the line style will give us the power to tell Blender what that line should look like.
How can we set up freestyle rendering?
We established three levels of settings for freestyle. What I like to call the «global settings» followed by line sets and line styles. Now let’s dive into a more practical example.
Here is a low poly scene that I made to test this. We have some basic geometry. Then there are some reshaped cubes, water with quite a bit of movement and waves as well as some cloth made with a cloth simulator. We also have some flat planes for the vegetation.
The scene is rendered in Eevee with some post-processing effects like bloom and depth of field.
Let’s get exploring. In the properties panel and under the render tab, check freestyle. We have two settings here. Generally, I never touch these.
Line thickness mode will use the line thickness setting when set to absolute. When set to relative, the line thickness is dependent on the resolution of the image. 480 pixels in height will correspond to 1pixel line thickness. Double that to 960pixels and the line thickness will be 2pixels.
The line thickness can be adjusted on the line style level instead.
Go to the view layer tab and you will find three sections related to freestyle.
The freestyle section has some overarching settings. I seldom touch these settings. But we will talk briefly about them. The control mode is a switch between using the parameters set here in the interface or to use a python script file to make the freestyle settings. We will stick to parameter editor.
Let’s jump down to the edge detection options. The Crease angle determines the degree at which a crease is considered a crease. This becomes important when we dive into edge types. Edge types are a big deal when it comes to selecting edges with a line set.
If face smoothness is ticked the faces that belong to the same smoothing group will not get a line even if the crease angle says that it would.
Culling will ignore any edge that can’t be seen from the camera, even if it is within the frame.
Ticking the advanced options and using these settings can help if we don’t get smooth lines on curved surfaces.
Freestyle Line sets
So far we mostly covered concepts and some lesser used settings. But this is where we start to set up freestyle for real.
We can have multiple line sets, each «selecting» a different set of edges. We then apply a single line style to each line set.
We have 5 different selection modes, we can have 1 or more of them enabled at once and it is the combination that creates the final selection. When multiple selection modes are used, the most restricted will apply.
Image border is really only a performance setting and will mostly be on. So in reality we only have 4.
Visibility
Visibility determines what edges will be rendered as freestyle by visibility. Set this to visible and freestyle will use the edges that we can see from the camera.
Hidden will use the lines that are not visible from the camera, but is hidden behind some other object or geometry.
QI Range lets us set a range from how many layers of geometry should be between the camera and the first object that gets rendered and how many layers after the first rendered lines that will be considered for freestyle drawing.
Edge types
Edge types is where we do 90% of our line set settings. It allows us to more dynamically select edges based on some criteria.
Before we look at the different types we have inclusive and exclusive, this just dictates if the freestyle lines should be drawn on the marked edges or on everything else.
The «logical or/logical and» can be a bit hard to understand at first, so I will try to explain it simply. With «logical or» we say that the edge need to be at least one of the selected criteria below to be marked. For instance, it has to be «Silhouette OR Border OR Contour». With «logical and» we say that the edge has to be «Silhouette AND Border AND Contour». This means that «logical and» will remove any edges from the selection that does not comply to all the edge types that we select.
These are the edge types:
You have probably noticed that there is both a checkbox and an «X» for each of them. The checkbox tells Blender that it should be «included in the calculation» if you will. The «X» gives the edge type a «NOT» in the calculation. This is confusing, yes I know. Let me try to explain.
We are dealing with Boolean operations here, and it gets a bit confusing to know what edge is actually being drawn. We will look at two example.
Let’s say that we are set to inclusive and «logical or». We also have Silhouette, Crease and border selected. That would give us this formula:
An edge will be marked if an edge is:
Let’s now say that we press the «X» on Border. Then it looks like this:
This formula will still draw an edge if «it is not» a border. Pressing the «X» may then actually still add more lines to the line set. It just means that lines that «are not» borders will be selected.
If you use «logical and» it may look like this if border is set to «X»:
We can’t have both «OR» and «AND» in our Boolean math. We need to go to python scripting for that.
Let’s leave the math for now and look a bit more at what the different edge types actually mark.
To help you see this a bit better I made an info graphic showing how each setting looks on our test image. You will notice how edge mark and Material Boundary is left out. I want to cover these separately.
Other than the edge type settings I use the default settings to show how these different edge types work.
Click on the image to open in new window and click it again to enlarge.
With edge mark we can mark an edge to be drawn as freestyle. This is very handy when we want ultimate control over what edges gets drawn. To mark an edge follow these steps:
Edge marking can be very useful for wire frame renders, where we need to show how our geometry was built. For instance, I use this when I sell stock 3D models to show that the wire frame is of good quality.
Edge marks is not useful when we want to draw the silhouette of an object that does not have an edge. This is most prominent on round objects where we may not have an edge right at the silhouette line.
Left for last is the material boundary setting. It is simple, it draws the freestyle line where there are two different materials of either side of the edge. I was just not smart enough to include an object with more than one material in the render I did for the info graphic.
Face marks
Facemark is something that I never use, and I imagine few others do as well thanks to where it is in the interface. It is similar to edge mark, but instead of marking an edge we mark a face and the edges holding up that face are being marked.
To mark a face do the following:
In the freestyle line set options we can choose to include or exclude the marked faces. If we exclude it, the unmarked faces will be drawn.
We also have the «one face» and «both faces» option. This determines if both faces on either side of an edge need to be marked in order for the edge to be drawn, or if it is enough if one face is marked.
Collection
Collections are interesting. It allows us to select a group of objects that will be rendered with the given freestyle line set, or be excluded. To use it, select it in the line set options and the interface will expand. Select the collection that you want to include or exclude.
As an example, let’s say that we have a background that we don’t want to render freestyle lines for, then we can exclude it by placing it in its own collection and using these settings.
We can also do the opposite and only include the foreground in a collection and use that.
Freestyle line styles
Let’s now take a look at what we can do when we combine line sets and line styles. Since Line styles really can be tweaked into the extreme with a huge range of possibilities we will walk through a few examples instead of going over the settings.
These are the examples we will go through.
Cartoon style
We will start with the cartoon style. I made a short animation of how it turned out that you can watch here.
A little background. I altered the scene that I showed earlier and that I also used in the info graphic above. I used Eevee as the render engine with the toonshader by Paul Caggegi.
The crosshatches on the ground is not freestyle rendering. It is a combination of the toon shader and a cross-hatch texture that I got from this link.
Freestyle line thickness is set to “absolute” and 2 pixels. The line set is set to “visibility” and “edge type”. The edge types then use “Inclusive” and “Logical OR” and these are the edge types used:
Now for the line style. I started with the default settings and tweaked only the thickness settings. For the base thickness I set 2. Then I added two modifiers. One “distance from camera” and “along stroke” below that and started setting up the «distance from camera» modifier.
By looking at the grid floor in my scene I estimated the furthest distance on the island from the camera. Not taking the ocean into account I came up with 40 meters for the max range. Then I changed the «min value» to 0.5.
I left all other settings as their default. However, I realized that the value max and value min that determines the thickness based on the distance actually makes the furthest lines thicker and closer lines thinner by default. I meant to have it reversed but did not realize this until it was too late. However, I think it turned out alright anyway since the cross-hatched lines would not be affected anyway it now just looks like there is some variation in the line thickness. Something to keep in mind though.
If you want a more dynamic flow between the lines’ appearance based on camera distance, you can change the modifier from linear to curve and you will be able to adjust the thickness however you like.
Next, I set up the “along stroke” modifier. This modifier allows us to set a dynamic line thickness based on a curve. Change the modifier from linear to curve. The curve can then be used to set the thickness from one end to the other.
For me I set both ends to 0 and the middle, close to 1. This set up makes every line taper of and the lines gets a more sketchy look.
These two thickness modifiers combined is a very common setup for cartoon styles and I think it demonstrates some basics of how to get started with a cartoon look in Eevee together with a toon shader that is simple to work with.
Wireframe render
We will now move over and take a look at wire frame renders. For this I have switched to cycles and setup a material override with a clay like material. This is because material override is not currently available in Eevee.
To set up wire frame rendering I have used a thinner line width of 0.5px in the freestyle render settings.
For the line set. I am now only using “Visibility” and “edge types” with “edge types” only set to “Edge Mark”. Then I have gone into edit mode and marked all edges except for the ground, ocean and the plants’ particle system.
In line style I set the thickness to 1 and change the base color to white in the color settings.
You can see that on the cloth, not all edges are drawn. This is because of “visibility” turned on. Freestyle does not detect all those edges as visible.
If I remove “Visibility” however we get a result that looks like this.
A quite messy net of spaghetti if you ask me. However, this could be further tweaked by using the “distance from camera” in the thickness section as well as in the alpha section. But this has already been covered in the cartoon style above, so I opted not to go further on this route.
If you are interested in more specific settings and what they do, as well as more descriptions of each modifier in each of the different sections of the line styles, I recommend to check out the blender manual.
Freestyle is not limited to these kind of simple lines, we can dive much deeper into more sketchy and painterly looks. We have not touched on the geometry or texture sections in this brief overview, but you may now be a little bit more hungry to explore those sections on your own.
How to reuse line styles?
Click the blend file to open it and find the «FreestyleLineStyle» folder. Inside it you will see the names of your line styles available in the file. Click «Append from library».
Go to your line style settings in the properties panel and view layer tab. Find the freestyle line style section and press the pen icon to open the list of line styles. Select your linestyle by name.
How to use freestyle in the compositor with Cycles and Eevee
In many cases when working with freestyle we need to combine it with other tools to create a full effect. This can be toon shaders, compositing nodes and dabbling with multiple scenes and view layers.
Update: In Blender 2.83 there is now a pass for freestyle. This means that we can go to the view layer tab and find the «freestyle» section. In there, there is a checkbox labeled «as render pass»». Check this to have Blender render freestyle on a separate pass that we can control in the compositor instead of combining it with the combined pass.
To use freestyle with the compositor it is essential to get the freestyle lines rendered on its own layer with an alpha background. This is currently only supported in cycles. We will look at how this is done. We will also be going over a workaround that enables us to use freestyle lines in Eevee as well.
If our scene is made in Eevee, and we want to render a pass of freestyle lines above it with an alpha background that we can use in the compositor. We can do so by using multiple scenes. It is not as complicated as it first sounds.
Start by turning off freestyle rendering under the render tab in the properties panel. In the top right corner of the interface we have two dropdowns. One for scenes and one for render layers.
Press the icon next to the right of the scene drop-down and select “linked copy”. This will create a linked copy of our scene. However, the render settings are not linked between the two scenes. This enables us to set the linked copy to render with cycles.
In your new scene. Find the render tab in the properties panel again and switch the render engine to cycles. Then go to the “film section” and check “transparency”. Also enable “freestyle”.
Next we will need to set up filters in order to render the freestyle lines without the geometry or background. Go to the view layer tab and find the “filter” section. Deselect all except freestyle.
If you have not yet setup your freestyle line sets and line styles, do so now.
Then render the scene. You should get a transparent image with only the freestyle lines visible.
Next switch back to the Eevee scene. Make sure that you disabled freestyle in the render settings so that you don’t get freestyle lines burned into the image. We will use the Cycles freestyle layer to composite on top of our Eevee render.
When the render is done, go to the compositing workspace and tick the “use nodes” checkbox in the header. A render layer node and composite node should appear. If not use “shift+a” and add them in.
This is one of the simples possible combinations of a freestyle line render and an Eeevee scene. From here we can use any tool available in the compositor to manipulatea each layer by itself or the combination.
If we want the same kind of setup, but we have a Cycles scene that we want a separate render layer with the freestyle lines above we can use a similar method. In this case though, we don’t need a separate scene. Instead, we use a separate render layer.
In the compositor you select the correct render layer instead of the scene in the render layer node and that is the only difference.
If you want to learn more about how you can organize your scene, this article can help you to understand the outliner and collections.
How can we export freestyle lines as SVG?
Freestyle can be converted to SVG and exported to be used in another application. It can also be imported into Blender again to work at it as a grease pencil object.
To export we need to enable the «Freestyle SVG Exporter» add-on. It comes with Blender by default.
You can select if you want to export from a full animation or just a frame. There are also some other output settings that can be useful, like how corners are treated and if we want to fill with the material color.
The SVG files will be exported to the output folder after the frame has been rendered. The output folder can be set in the output tab under the output section. This is the general output folder for animations and sometimes baked data in Blender.
Related questions
What other alternatives are there to freestyle?
Through google summer of code there is an ongoing project called LANPR that will most likely replace freestyle in the future. It is basically freestyle as a real time render engine.
How to render an object with both a base mesh wireframe and subdivision surface wireframe?
This is done with a texture, but is there another way?
2 Answers 2
I found a way to do it only in the Blender Internal render engine.
I add a subdivision surface modifier to the object. Then I add a new wireframe material and make it shadeless. Then I add a new material and assign it to the object. As long as the wireframe material is on top of the other materials, it will be shown in the render. Then in edit mode I hit E and then Mark freestyle edge. Then I click on Freestyle in the Render panel to enable freestyle and in the Render Layers panel I click only on Edge mark.
There are actually several ways of rendering wireframes in Cycles, and you can layer them to create the different thickness/color.
Wireframe modifier:
This method actually creates a 3D wireframe with the wireframe modifier and assigns it a separate material.
Then in the materials tab add a new material for the wireframe.
Wireframe node:
This method simply affects the shading, it does not modify the geometry of the object. Then downside is that it uses the tris of the geometry, not just the edges that you see in edit mode.
To do this just take whatever node setup you are using for your material and mix in whatever node setup you want for the wireframe based on an input > wireframe node.
Freestyle
As of Blender 2.72 Freestyle NPR is now available in Cycles. This allows much more control of the settings for the wireframe, such as only applying the wireframe to certain edges. It looks like you already know your way around Freestyle so I won’t go into too much detail here as there a a lot of settings.

In this render I only applied the freestyle edges to the basic Suzanne mesh and then added a subsurf modifier.
Then go to the render layers tab and setup the Freestyle edges. Unfortunately I don’t have space to go through all the settings here. But all I did was select only edge mark under edge types in the Freestyle line set rollout.
How to get solid render with wireframes and no shading
Basically, use object mode and check «wire» and «display edges». Then I adjust materials until I can get it as white as possible. Unfortunately, I still get some shading.
And to top it off, I’m a total Blender noob. I slog through it once a month to get wire frame images for a regular blog feature.
1 Answer 1
There are quite a few ways to accomplish this.
OpenGL
See this answer for details on setting up the wireframe.
Note that the Hidden Wire draw option can be useful for culling the wires on the back of the model without setting the color of the model to match the background.
See this answer for details on making the models in the viewport shadeless.
Pros: Very fast. Usually no artifacts or missing lines. Works with optimal (curved) wireframes.
Cons: Total hack, requires setting theme colors to adjust the color of the wire and background. No control over line width.
Blender Internal
See these two answers for setting up the wireframe materials.
To make the base material shadeless, enable Shadeless in material settings > Shading:
To make it automatically match the background color, enable Mask Transparency in the base material and set the alpha to 0:
Cons: Can have issues with the Z offset causing missing lines or visible lines which should be occluded. Limited control over line styled/width.
Cycles
To get wireframes directly in cycles, see this question and the wireframe node.
To make a shadeless material in cycles, see this answer.
Pros: It’s cycles
Cons: Perfect non-triangulated wireframes are not currently possible. There is a workaround with UV coordinates, however this results in line sizes relative to polygon size.
Wireframe modifier
The wireframe modifier generates actual mesh geometry representing the wireframe of the input mesh. Since the output is just a mesh, it works with both BI and Cycles.
See this answer for details on setting it up (answer is for cycles, but the process is identical for BI).
For shadeless renders, see the previous sections in this answer regarding BI and Cycles for descriptions of their respective methods of creating shadeless shaders.
Pros: Just works
Cons: Generates geometry; line thickness is defined in 3D space.
Freestyle
Freestyle is a line rendering engine which supports drawing over both BI and Cycles renders.
Pros: Lots of control over line style etc.
Cons: Sometimes edges have gaps/other artifacts. Can be resource hungry.
Источники информации:
- http://blender.stackexchange.com/questions/14932/how-to-render-an-object-as-a-transparent-wireframe
- http://artisticrender.com/a-guide-to-blender-freestyle-rendering-with-eevee-and-cycles/
- http://blender.stackexchange.com/questions/10999/how-to-render-an-object-with-both-a-base-mesh-wireframe-and-subdivision-surface
- http://blender.stackexchange.com/questions/36701/how-to-get-solid-render-with-wireframes-and-no-shading