Psycopg2 how to install
Psycopg2 how to install
psycopg2 2.9.3
pip install psycopg2 Copy PIP instructions
Released: Dec 29, 2021
Navigation
Project links
Statistics
View statistics for this project via Libraries.io, or by using our public dataset on Google BigQuery
License: GNU Library or Lesser General Public License (LGPL) (LGPL with exceptions)
Requires: Python >=3.6
Maintainers
Classifiers
Project description
Psycopg is the most popular PostgreSQL database adapter for the Python programming language. Its main features are the complete implementation of the Python DB API 2.0 specification and the thread safety (several threads can share the same connection). It was designed for heavily multi-threaded applications that create and destroy lots of cursors and make a large number of concurrent “INSERT”s or “UPDATE”s.
Psycopg 2 is mostly implemented in C as a libpq wrapper, resulting in being both efficient and secure. It features client-side and server-side cursors, asynchronous communication and notifications, “COPY TO/COPY FROM” support. Many Python types are supported out-of-the-box and adapted to matching PostgreSQL data types; adaptation can be extended and customized thanks to a flexible objects adaptation system.
Psycopg 2 is both Unicode and Python 3 friendly.
Documentation
Documentation is included in the doc directory and is available online.
For any other resource (source code repository, bug tracker, mailing list) please check the project homepage.
Installation
Building Psycopg requires a few prerequisites (a C compiler, some development packages): please check the install and the faq documents in the doc dir or online for the details.
If prerequisites are met, you can install psycopg like any other Python package, using pip to download it from PyPI:
or using setup.py if you have downloaded the source package locally:
You can also obtain a stand-alone package, not requiring a compiler or external libraries, by installing the psycopg2-binary package from PyPI:
The binary package is a practical choice for development and testing but in production it is advised to use the package built from sources.
Psycopg 2.9.3 documentation
Psycopg is a PostgreSQL adapter for the Python programming language. It is a wrapper for the libpq, the official PostgreSQL client library.
Quick Install¶
For most operating systems, the quickest way to install Psycopg is using the wheel package available on PyPI:
You may then import the psycopg2 package, as usual:
psycopg vs psycopg-binary¶
The psycopg2-binary package is meant for beginners to start playing with Python and PostgreSQL without the need to meet the build requirements.
If you are the maintainer of a published package depending on psycopg2 you shouldn’t use psycopg2-binary as a module dependency. For production use you are advised to use the source distribution.
The psycopg2 wheel package comes packaged, among the others, with its own libssl binary. This may create conflicts with other extension modules binding with libssl as well, for instance with the Python ssl module: in some cases, under concurrency, the interaction between the two libraries may result in a segfault. In case of doubts you are advised to use a package built from source.
Change in binary packages between Psycopg 2.7 and 2.8¶
In version 2.7.x, pip install psycopg2 would have tried to install automatically the binary package of Psycopg. Because of concurrency problems binary packages have displayed, psycopg2-binary has become a separate package, and from 2.8 it has become the only way to install the binary package.
which can be specified in your requirements.txt files too, e.g. use:
Prerequisites¶
The current psycopg2 implementation supports:
Python versions from 3.6 to 3.10
PostgreSQL server versions from 7.4 to 14
PostgreSQL client library version from 9.1
Build prerequisites¶
The build prerequisites are to be met in order to install Psycopg from source code, from a source distribution package, GitHub or from PyPI.
Psycopg is a C wrapper around the libpq PostgreSQL client library. To install it from sources you will need:
The Python header files. They are usually installed in a package such as python-dev or python3-dev. A message such as error: Python.h: No such file or directory is an indication that the Python headers are missing.
The libpq header files. They are usually installed in a package such as libpq-dev. If you get an error: libpq-fe.h: No such file or directory you are missing them.
Once everything is in place it’s just a matter of running the standard:
or, from the directory containing the source code:
Runtime requirements¶
Unless you compile psycopg2 as a static library, or you install it from a self-contained wheel package, it will need the libpq library at runtime (usually distributed in a libpq.so or libpq.dll file). psycopg2 relies on the host OS to find the library if the library is installed in a standard location there is usually no problem; if the library is in a non-standard location you will have to tell Psycopg how to find it, which is OS-dependent (for instance setting a suitable LD_LIBRARY_PATH on Linux).
Whatever version of libpq psycopg2 is compiled with, it will be possible to connect to PostgreSQL servers of any supported version: just install the most recent libpq version or the most practical, without trying to match it to the version of the PostgreSQL server you will have to connect to.
Non-standard builds¶
If you have less standard requirements such as:
then take a look at the setup.cfg file.
Some of the options available in setup.cfg are also available as command line arguments of the build_ext sub-command. For instance you can specify an alternate pg_config location using:
Creating a debug build¶
In case of problems, Psycopg can be configured to emit detailed debug messages, which can be very useful for diagnostics and to report a bug. In order to create a debug package:
Edit the setup.cfg file adding the PSYCOPG_DEBUG flag to the define option.
Set the PSYCOPG_DEBUG environment variable:
Run your program (making sure that the psycopg2 package imported is the one you just compiled and not e.g. the system one): you will have a copious stream of informations printed on stderr.
Non-standard Python Implementation¶
The psycopg2 package is the current mature implementation of the adapter: it is a C extension and as such it is only compatible with CPython. If you want to use Psycopg on a different Python implementation (PyPy, Jython, IronPython) there is a couple of alternative:
a Ctypes port, but it is not as mature as the C implementation yet and it is not as feature-complete;
a CFFI port which is currently more used and reported more efficient on PyPy, but please be careful of its version numbers because they are not aligned to the official psycopg2 ones and some features may differ.
Running the test suite¶
Once psycopg2 is installed you can run the test suite to verify it is working correctly. From the source directory, you can run:
The tests run against a database called psycopg2_test on UNIX socket and the standard port. You can configure a different database to run the test by setting the environment variables:
The database should already exist before running the tests.
If you still have problems¶
Try the following. In order:
Google for psycopg2 your error message. Especially useful the week after the release of a new OS X version.
If you think that you have discovered a bug, test failure or missing feature please raise a ticket in the bug tracker.
psycopg/psycopg2
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.rst
Psycopg is the most popular PostgreSQL database adapter for the Python programming language. Its main features are the complete implementation of the Python DB API 2.0 specification and the thread safety (several threads can share the same connection). It was designed for heavily multi-threaded applications that create and destroy lots of cursors and make a large number of concurrent «INSERT»s or «UPDATE»s.
Psycopg 2 is mostly implemented in C as a libpq wrapper, resulting in being both efficient and secure. It features client-side and server-side cursors, asynchronous communication and notifications, «COPY TO/COPY FROM» support. Many Python types are supported out-of-the-box and adapted to matching PostgreSQL data types; adaptation can be extended and customized thanks to a flexible objects adaptation system.
Psycopg 2 is both Unicode and Python 3 friendly.
Documentation is included in the doc directory and is available online.
For any other resource (source code repository, bug tracker, mailing list) please check the project homepage.
Building Psycopg requires a few prerequisites (a C compiler, some development packages): please check the install and the faq documents in the doc dir or online for the details.
If prerequisites are met, you can install psycopg like any other Python package, using pip to download it from PyPI:
or using setup.py if you have downloaded the source package locally:
You can also obtain a stand-alone package, not requiring a compiler or external libraries, by installing the psycopg2-binary package from PyPI:
The binary package is a practical choice for development and testing but in production it is advised to use the package built from sources.
| Linux/OSX: | |
|---|---|
| Windows: |
About
PostgreSQL database adapter for the Python programming language
Psycopg2 how to install
Copy raw contents
Psycopg is a PostgreSQL adapter for the Python programming language. It is a wrapper for the libpq, the official PostgreSQL client library.
For most operating systems, the quickest way to install Psycopg is using the wheel package available on PyPI:
You may then import the psycopg2 package, as usual:
psycopg vs psycopg-binary
The psycopg2-binary package is meant for beginners to start playing with Python and PostgreSQL without the need to meet the build requirements.
Change in binary packages between Psycopg 2.7 and 2.8
In version 2.7.x, :command:`pip install psycopg2` would have tried to install automatically the binary package of Psycopg. Because of concurrency problems binary packages have displayed, psycopg2-binary has become a separate package, and from 2.8 it has become the only way to install the binary package.
which can be specified in your :file:`requirements.txt` files too, e.g. use:
The build prerequisites are to be met in order to install Psycopg from source code, from a source distribution package, GitHub or from PyPI.
Psycopg is a C wrapper around the libpq PostgreSQL client library. To install it from sources you will need:
The Python header files. They are usually installed in a package such as python-dev or python3-dev. A message such as error: Python.h: No such file or directory is an indication that the Python headers are missing.
The libpq header files. They are usually installed in a package such as libpq-dev. If you get an error: libpq-fe.h: No such file or directory you are missing them.
Once everything is in place it’s just a matter of running the standard:
or, from the directory containing the source code:
If you have less standard requirements such as:
then take a look at the setup.cfg file.
Some of the options available in setup.cfg are also available as command line arguments of the build_ext sub-command. For instance you can specify an alternate :program:`pg_config` location using:
Creating a debug build
In case of problems, Psycopg can be configured to emit detailed debug messages, which can be very useful for diagnostics and to report a bug. In order to create a debug package:
Non-standard Python Implementation
The psycopg2 package is the current mature implementation of the adapter: it is a C extension and as such it is only compatible with CPython. If you want to use Psycopg on a different Python implementation (PyPy, Jython, IronPython) there is a couple of alternative:
Running the test suite
The tests run against a database called psycopg2_test on UNIX socket and the standard port. You can configure a different database to run the test by setting the environment variables:
The database should already exist before running the tests.
If you still have problems
Try the following. In order:
How to Install Psycopg2 in Windows
Introduction
In this article we talk in detail about how to install psycopg2 in Windows. Included are the command line commands and code you’ll need to do it yourself.
Prerequisites
Before we can install psycopg2 on windows operating system we must make certain prerequisites
Make sure to install and set up Python3 on your local device because Python2 is already deprecated and losses its support.
Basic knowledge on using Python and PostgreSQL database.
Install and setup the Python 3 in Windows 10
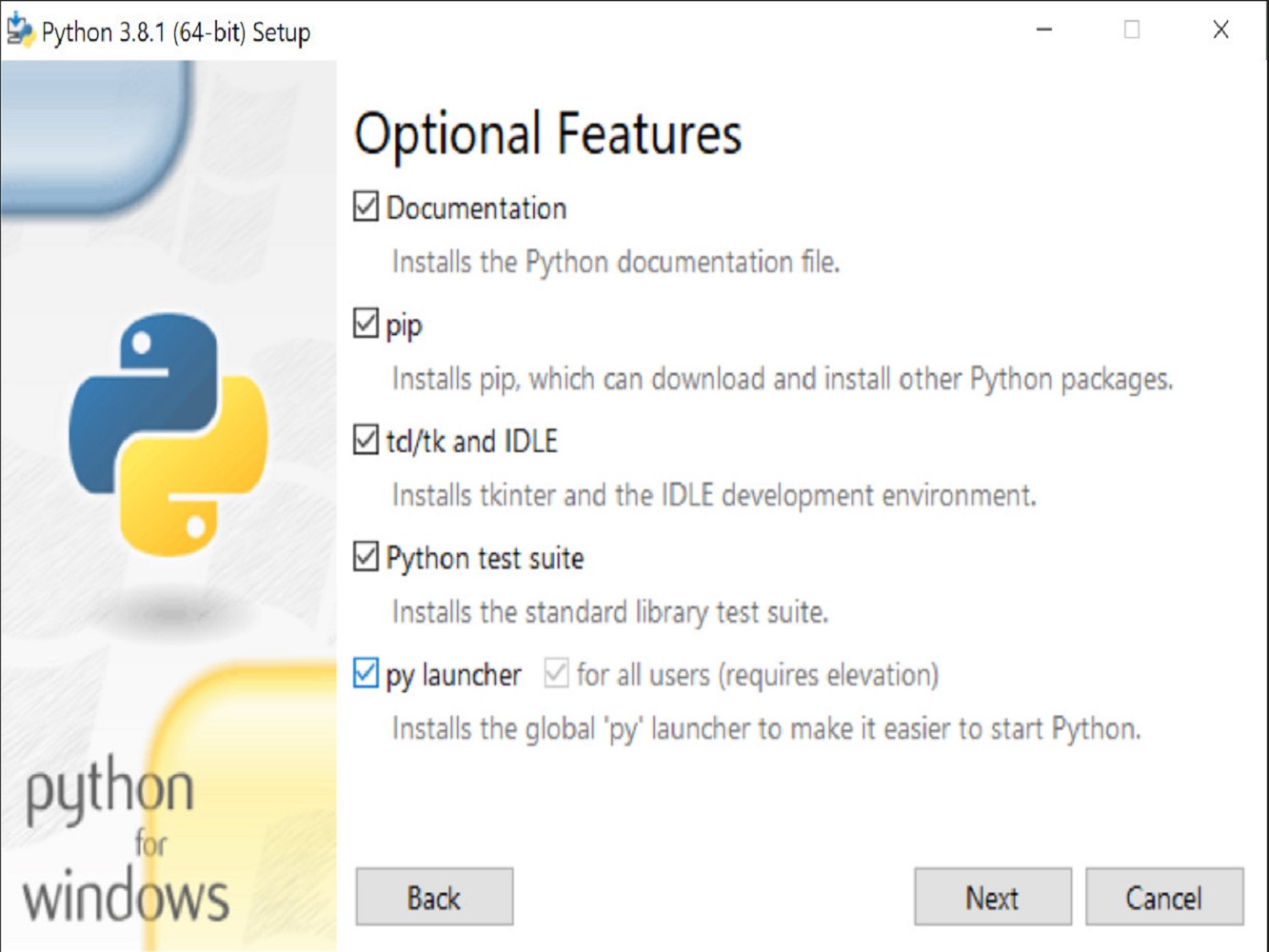
To install Python using the interactive EXE installer make sure to download it first and include the path. Also check the py launcher and pip checkboxes as well.
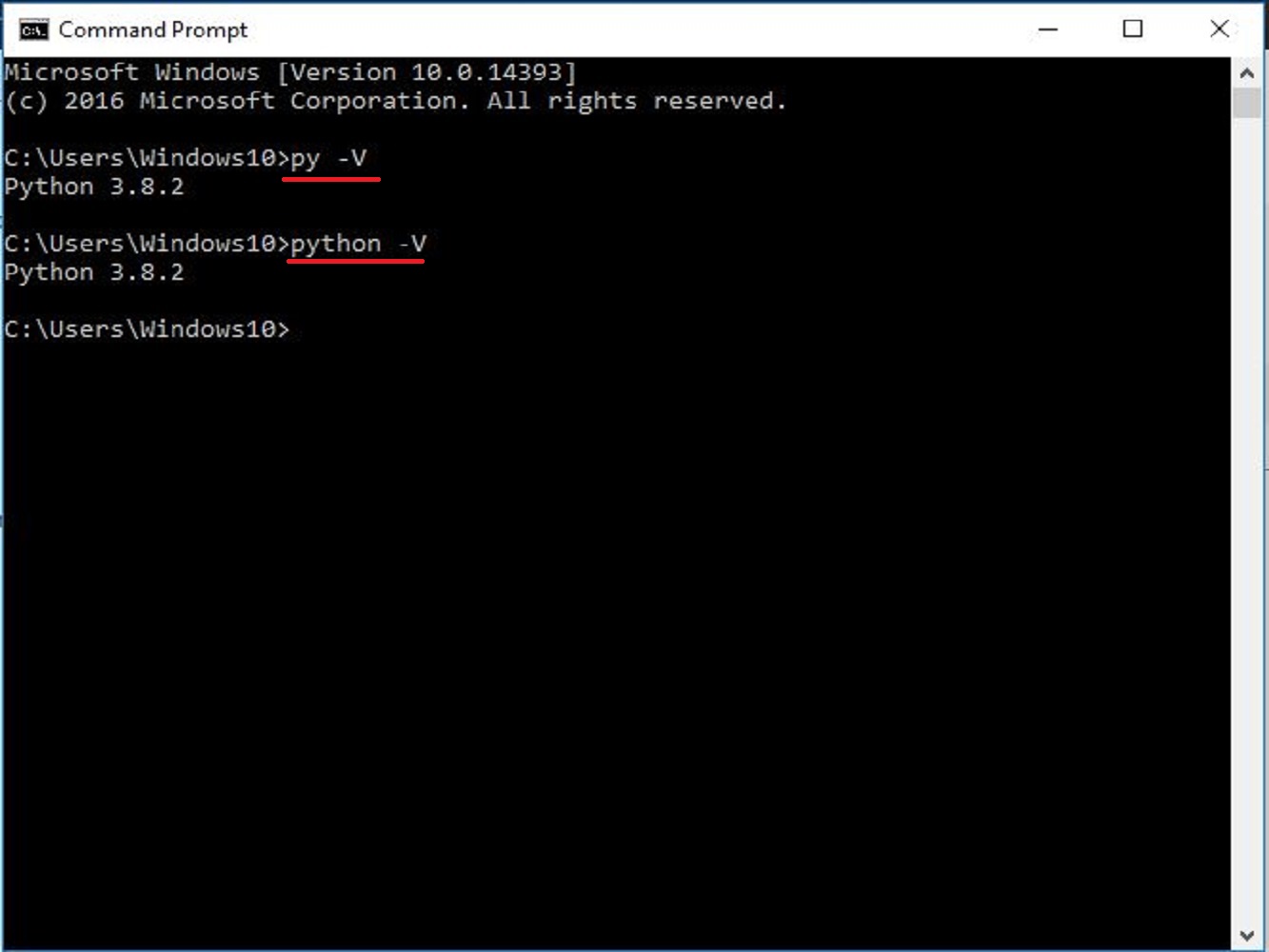
After it’s done installing, open the command prompt window terminal to verify if the Python3 is properly installed and working on your device :
The command above will return the Python version number.
Set the paths for python3 and pip3
To prevent an error when starting up python in your command prompt window, setup the PATH variable location of the Python so that the system will recognize it.
Create a Python virtual environment on Windows 10
Now go inside the Scripts directory and execute the activate.bat file to enter inside the virtual environment:
Upgrade pip3 using the py command
Execute the command py in your command prompt window to open the and enter into the interactive interpreter for Python 3. Just press the button CTRL + Z and then RETURN to exit the interface.
To check and verify the version of the PIP3 in your device, use the command below :
It should return something like this : pip 20.0.2 from C:\Path\To\AppData\Roaming\Python\Python38\site-packages\pip (python 3.8) because of the upgrade flag that we have used earlier.
Install the psycopg2 module in Windows 10
Now that we have our virtual environment setup and ready, install the psycopg2 module to create a simple connection in the PostgreSQL database cluster.
Make sure to upgrade the pip command to avoid error when installing a package module from python in a virtual environment.
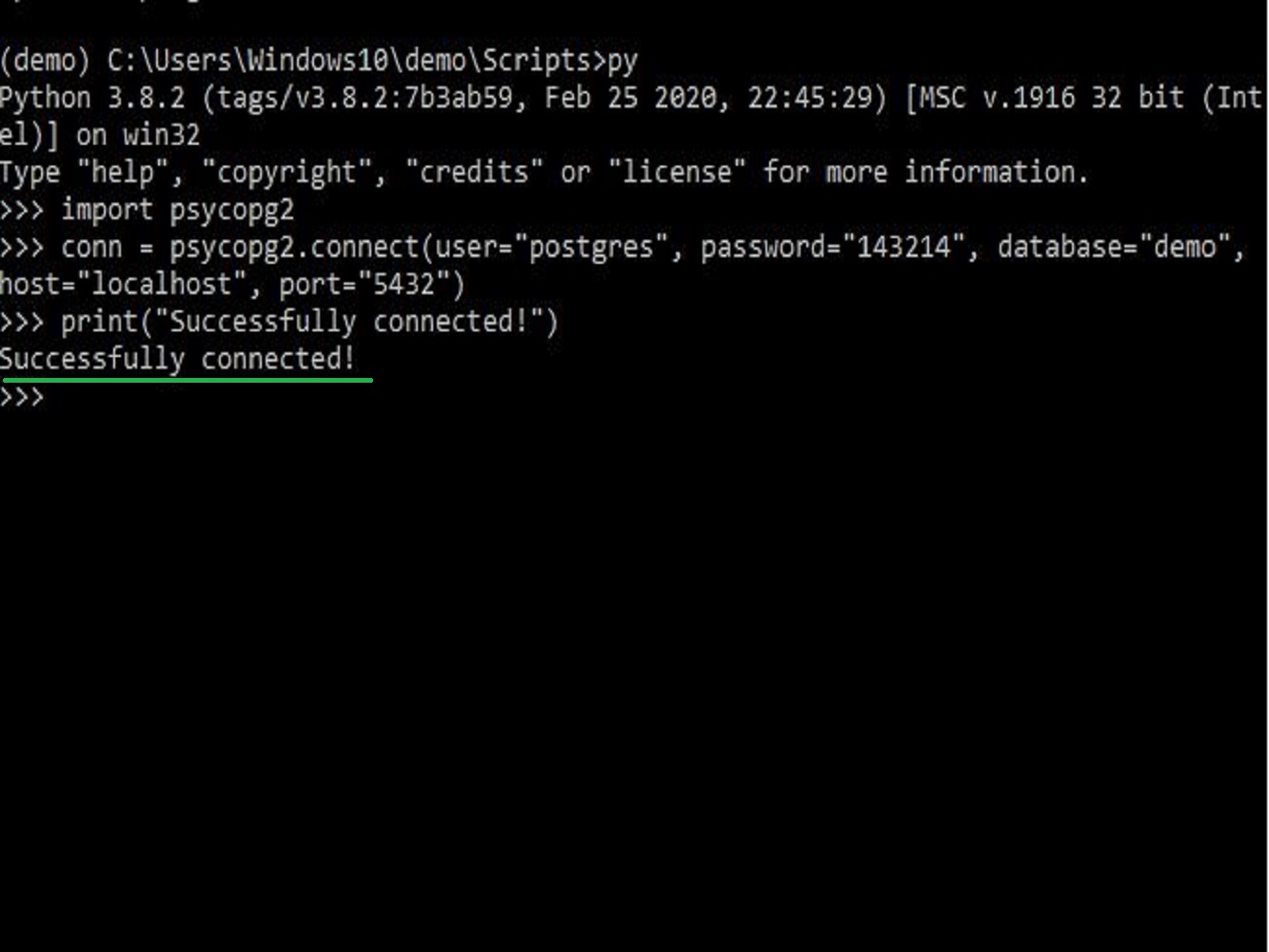
Create a Python script that connects into PostgreSQL database
On your command prompt window, use the command py or python to enter the Python interface.
And now we will try to use the cursor command to perform any PostgreSQL database queries and operations using the Python script.
Then, print the version of the PostgreSQL installed in your device.
Let’s take a look at the output:
Create table using the cursor command
Next is to insert some record of rows inside the table.
Then create a commit function and display that the record is successfully inserted.
And use the SELECT statement to verify the records of row inserted.
The result is the following:
Conclusion
In this article we have covered how to install psycopg2 in Windows. Below is a recap of the code we used in this tutorial in case you’d like to use or repurpose it.
Just the code
cursor = conn. cursor ( )
cursor. execute ( «CREATE TABLE py_tbl(id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, str_col VARCHAR(50),int_col INT);» )
print ( «Table successfully created!» )
cursor. execute ( «INSERT INTO py_tbl(str_col, int_col) VALUES(‘Hello World!’, 110);» )
cursor. execute ( «INSERT INTO py_tbl(str_col, int_col) VALUES(‘Welcome to ObjectRocket!’, 120);» )
cursor. execute ( «INSERT INTO py_tbl(str_col, int_col) VALUES(‘Greetings!’, 130);» )
conn. commit ( )
print ( «Records Successfully Inserted!)»
conn. close ( )
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.