How to install conda
How to install conda
How to Install conda in Windows?
Anaconda is open-source software that contains Jupyter, spyder, etc that is used for large data processing, data analytics, heavy scientific computing.
Conda is a package and environment management system that is available across Windows, Linux, and MacOS, similar to PIP. It helps in the installation of packages and dependencies associated with a specific language like python, C++, Java, Scala, etc. Conda is also an environment manager and helps to switch between different environments with just a few commands.
Installing Conda on Windows:
Follow the below steps to install conda on windows:
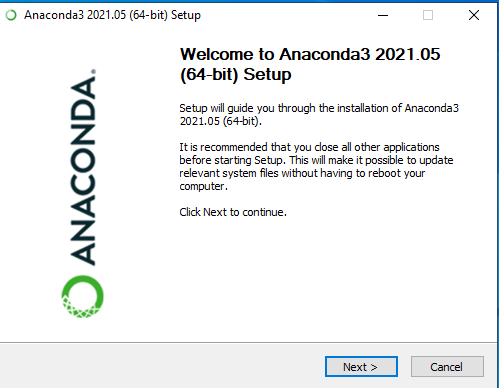
Step 1: Visit this website and download the Anaconda installer.
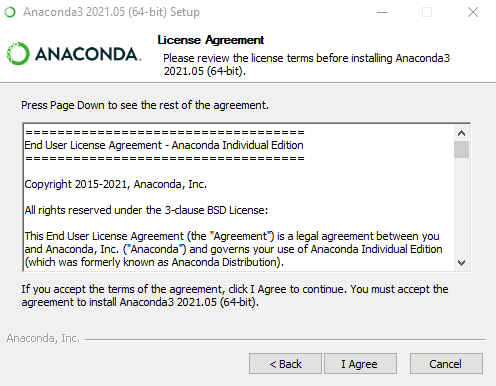
Step 3: Agree to the terms and conditions.
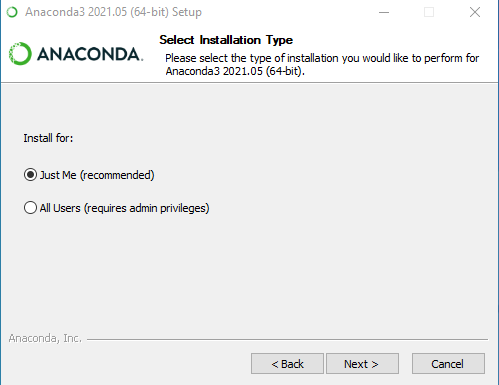
Step 4: Select the installation type.
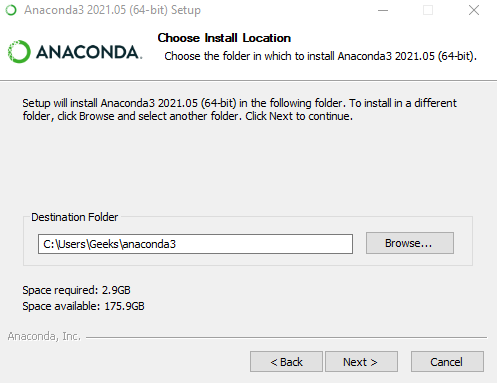
Step 5: Choose the installation location.
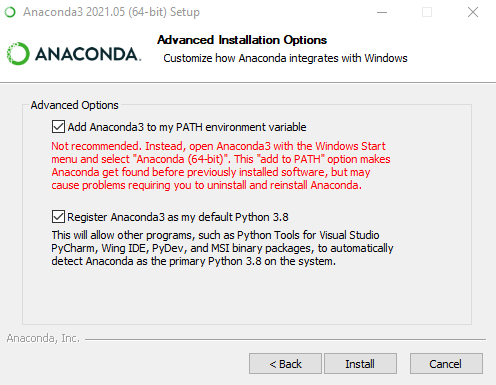
Step 6: Now check the checkbox to add Anaconda to your environment Path and click Install.
This will start the installation.
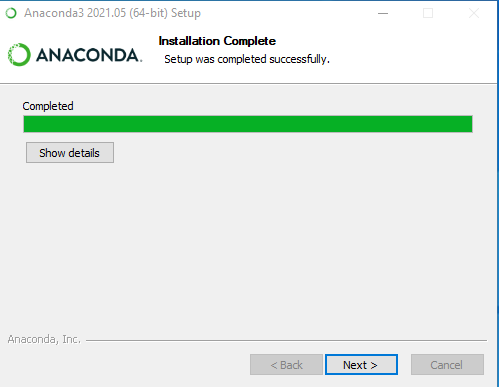
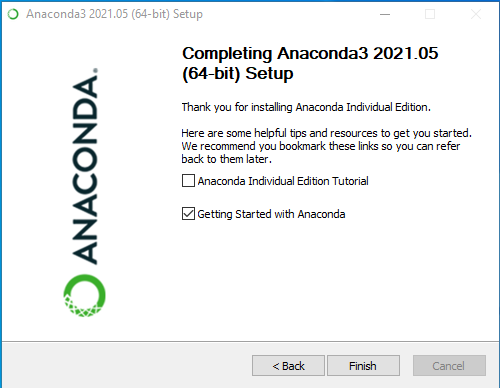
Step 7: After the installation is complete you’ll get the following message, here click on Next.
Step 8: You’ll get the following screen once the installation is ready to be used. Here click on Finish.
Verifying the installation:
Now open up the Anaconda Power Shell prompt and use the below command to check the conda version:
If conda is installed successfully, you will get a message as shown below:
Installing with condaпѓЃ
To install conda packages, in the terminal or an Anaconda Prompt, run:
During the install process, files are extracted into the specified environment, defaulting to the current environment if none is specified. Installing the files of a conda package into an environment can be thought of as changing the directory to an environment, and then downloading and extracting the artifact and its dependencies—all with the single conda install [packagename] command.
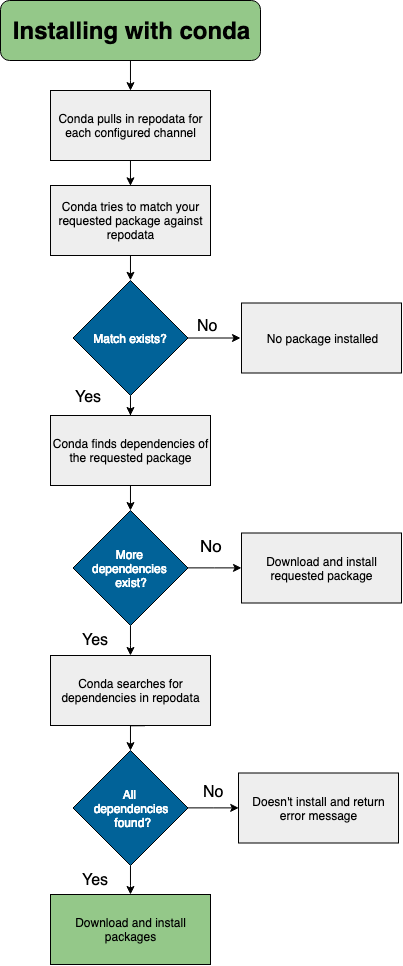
When you conda install a package that exists in a channel and has no dependencies, conda:
Looks at your configured channels (in priority).
Reaches out to the repodata associated with your channels/platform.
Parses repodata to search for the package.
Once the package is found, conda pulls it down and installs.
Conda update versus conda installпѓЃ
conda update is used to update to the latest compatible version. conda install can be used to install any version.
If Python 2.7.0 is currently installed, and the latest version of Python 2 is 2.7.5, then conda update python installs Python 2.7.5. It does not install Python 3.
If Python 3.7.0 is currently installed, and the latest version of Python is 3.9.0, then conda install python=3 installs Python 3.9.0.
Conda uses the same rules for other packages. conda update always installs the highest version with the same major version number, whereas conda install always installs the highest version.
Installing conda packages offlineпѓЃ
To install conda packages offline, run: conda install /path-to-package/package-filename.tar.bz2/
If you prefer, you can create a /tar/ archive file containing many conda packages and install them all with one command: conda install /packages-path/packages-filename.tar
If an installed package does not work, it may be missing dependencies that need to be resolved manually.
Installing packages directly from the file does not resolve dependencies.
Installing conda packages with a specific build numberпѓЃ
For example, if you want to install llvmlite 0.31.0dev0 on Python 3.7.8, you would enter:
Installing with condaпѓЃ
To install conda packages, in the terminal or an Anaconda Prompt, run:
During the install process, files are extracted into the specified environment, defaulting to the current environment if none is specified. Installing the files of a conda package into an environment can be thought of as changing the directory to an environment, and then downloading and extracting the artifact and its dependencies—all with the single conda install [packagename] command.
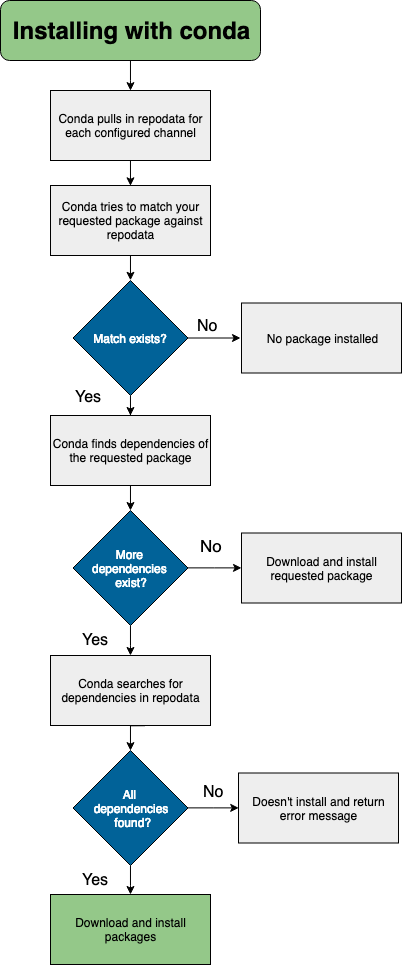
When you conda install a package that exists in a channel and has no dependencies, conda:
Looks at your configured channels (in priority).
Reaches out to the repodata associated with your channels/platform.
Parses repodata to search for the package.
Once the package is found, conda pulls it down and installs.
Conda update versus conda installпѓЃ
conda update is used to update to the latest compatible version. conda install can be used to install any version.
If Python 2.7.0 is currently installed, and the latest version of Python 2 is 2.7.5, then conda update python installs Python 2.7.5. It does not install Python 3.
If Python 3.7.0 is currently installed, and the latest version of Python is 3.9.0, then conda install python=3 installs Python 3.9.0.
Conda uses the same rules for other packages. conda update always installs the highest version with the same major version number, whereas conda install always installs the highest version.
Installing conda packages offlineпѓЃ
To install conda packages offline, run: conda install /path-to-package/package-filename.tar.bz2/
If you prefer, you can create a /tar/ archive file containing many conda packages and install them all with one command: conda install /packages-path/packages-filename.tar
If an installed package does not work, it may be missing dependencies that need to be resolved manually.
Installing packages directly from the file does not resolve dependencies.
Installing conda packages with a specific build numberпѓЃ
For example, if you want to install llvmlite 0.31.0dev0 on Python 3.7.8, you would enter:
Getting started with condaпѓЃ
Conda is a powerful package manager and environment manager that you use with command line commands at the Anaconda Prompt for Windows, or in a terminal window for macOS or Linux.
This 20-minute guide to getting started with conda lets you try out the major features of conda. You should understand how conda works when you finish this guide.
SEE ALSO: Getting started with Anaconda Navigator, a graphical user interface that lets you use conda in a web-like interface without having to enter manual commands. Compare the Getting started guides for each to see which program you prefer.
Before you startпѓЃ
You should have already installed Anaconda.
ContentsпѓЃ
Starting conda on Windows, macOS, or Linux. 2 MINUTES
TOTAL TIME: 20 MINUTES
Starting condaпѓЃ
Windows
From the Start menu, search for and open «Anaconda Prompt.»
On Windows, all commands below are typed into the Anaconda Prompt window.
MacOS
Open Launchpad, then click the terminal icon.
On macOS, all commands below are typed into the terminal window.
Linux
Open a terminal window.
On Linux, all commands below are typed into the terminal window.
Managing condaпѓЃ
Verify that conda is installed and running on your system by typing:
Conda displays the number of the version that you have installed. You do not need to navigate to the Anaconda directory.
EXAMPLE: conda 4.7.12
If you get an error message, make sure you closed and re-opened the terminal window after installing, or do it now. Then verify that you are logged into the same user account that you used to install Anaconda or Miniconda.
Update conda to the current version. Type the following:
Conda compares versions and then displays what is available to install.
If a newer version of conda is available, type y to update:
We recommend that you always keep conda updated to the latest version.
Managing environmentsпѓЃ
Conda allows you to create separate environments containing files, packages, and their dependencies that will not interact with other environments.
Create a new environment and install a package in it.
We will name the environment snowflakes and install the package BioPython. At the Anaconda Prompt or in your terminal window, type the following:
Conda checks to see what additional packages («dependencies») BioPython will need, and asks if you want to proceed:
Type «y» and press Enter to proceed.
To use, or «activate» the new environment, type the following:
Windows: conda activate snowflakes
macOS and Linux: conda activate snowflakes
conda activate only works on conda 4.6 and later versions.
For conda versions prior to 4.6, type:
Windows: activate snowflakes
macOS and Linux: source activate snowflakes
Now that you are in your snowflakes environment, any conda commands you type will go to that environment until you deactivate it.
To see a list of all your environments, type:
A list of environments appears, similar to the following:
The active environment is the one with an asterisk (*).
Change your current environment back to the default (base): conda activate
For versions prior to conda 4.6, use:
macOS, Linux: source activate
Managing PythonпѓЃ
When you create a new environment, conda installs the same Python version you used when you downloaded and installed Anaconda. If you want to use a different version of Python, for example Python 3.5, simply create a new environment and specify the version of Python that you want.
Create a new environment named «snakes» that contains Python 3.9:
When conda asks if you want to proceed, type «y» and press Enter.
Activate the new environment:
Windows: conda activate snakes
macOS and Linux: conda activate snakes
conda activate only works on conda 4.6 and later versions.
For conda versions prior to 4.6, type:
Windows: activate snakes
macOS and Linux: source activate snakes
Verify that the snakes environment has been added and is active:
Conda displays the list of all environments with an asterisk (*) after the name of the active environment:
The active environment is also displayed in front of your prompt in (parentheses) or [brackets] like this:
Verify which version of Python is in your current environment:
Deactivate the snakes environment and return to base environment: conda activate
For versions prior to conda 4.6, use:
macOS, Linux: source activate
Managing packagesпѓЃ
In this section, you check which packages you have installed, check which are available and look for a specific package and install it.
Check to see if a package you have not installed named «beautifulsoup4» is available from the Anaconda repository (must be connected to the Internet):
Conda displays a list of all packages with that name on the Anaconda repository, so we know it is available.
Install this package into the current environment:
Check to see if the newly installed program is in this environment:
InstallationпѓЃ
We recommend you install Anaconda for the local user, which does not require administrator permissions and is the most robust type of installation. You can also install Anaconda system wide, which does require administrator permissions.
For information on using our graphical installers for Windows or macOS, see the instructions for installing Anaconda.
System requirementsпѓЃ
32- or 64-bit computer.
For Miniconda—400 MB disk space.
For Anaconda—Minimum 3 GB disk space to download and install.
Windows, macOS, or Linux.
For Windows: Windows 8.1 or newer for Python 3.9, or Windows Vista or newer for Python 3.8.
You do not need administrative or root permissions to install Anaconda if you select a user-writable install location.
Regular installationпѓЃ
Follow the instructions for your operating system:
Installing in silent modeпѓЃ
You can use silent installation of Miniconda or Anaconda for deployment or testing or building services such as Travis CI and AppVeyor.
Follow the silent-mode instructions for your operating system:
Installing conda on a system that has other Python installations or packagesпѓЃ
You do not need to uninstall other Python installations or packages in order to use conda. Even if you already have a system Python, another Python installation from a source such as the macOS Homebrew package manager and globally installed packages from pip such as pandas and NumPy, you do not need to uninstall, remove, or change any of them before using conda.
Install Anaconda or Miniconda normally, and let the installer add the conda installation of Python to your PATH environment variable. There is no need to set the PYTHONPATH environment variable.
To see if the conda installation of Python is in your PATH variable:
To see which Python installation is currently set as the default:
Источники информации:
- http://docs.conda.io/projects/conda/en/latest/user-guide/concepts/installing-with-conda.html
- http://conda.io/projects/conda/en/latest/user-guide/concepts/installing-with-conda.html
- http://conda.io/projects/conda/en/latest/user-guide/getting-started.html
- http://conda.io/projects/conda/en/latest/user-guide/install/index.html