How to install nvidia drivers on ubuntu
How to install nvidia drivers on ubuntu
How to Install Nvidia Drivers on Ubuntu 20.04
Home » SysAdmin » How to Install Nvidia Drivers on Ubuntu 20.04
Nvidia GPUs (graphics processing units) have exceptional parallel computing potential, much higher than that of CPUs. That is why GPUs are becoming the main choice for high-performance workloads.
Aside from gaming, Nvidia GPUs are also used for 3D rendering, mining, visualization, machine learning, AI, and in data centers. For example, phoenixNAP GPU dedicated servers use Nvidia Tesla GPUs.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install the latest proprietary Nvidia drivers on Ubuntu 20.04.
Note: Learn why and how GPUs are used for machine learning and AI in our article on GPU Machine Learning.
Install Nvidia Driver Using GUI
Ubuntu comes with open-source Nouveau drivers for Nvidia GPUs out of the box. The Nouveau driver does not harness the GPU’s full power and sometimes performs worse or even causes system instability. Nvidia proprietary drivers are much more reliable and stable.
The first way to install Nvidia drivers is by using the GUI Software & Updates app.
Step 1: Open Software and Updates From the App Menu
1. Open the Applications menu and type “software and updates.”
2. Select the Software and Updates app.
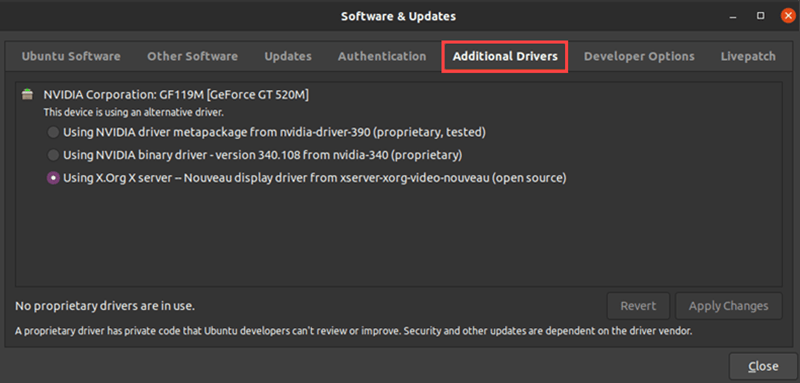
Step 2: Click the Additional Drivers Tab
Wait for the app to download a list of additional drivers available for your GPU.
The driver installed on your machine is selected by default. It is usually an open-source Nouveau display driver.
Step 3: Choose a Driver
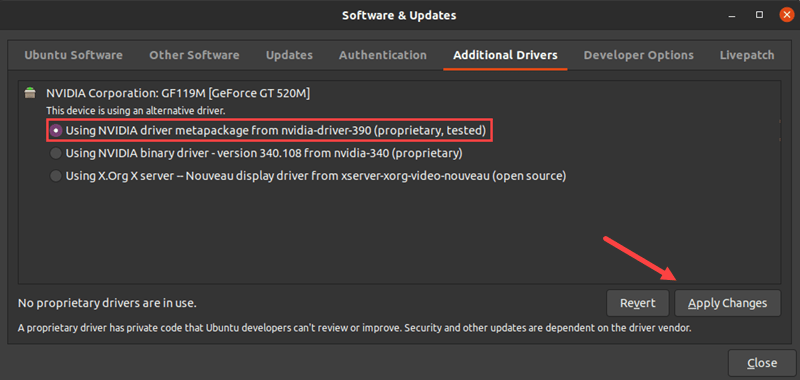
1. From the list, select the latest Nvidia driver labeled proprietary, tested. This is the latest stable driver published by Nvidia for your GPU.
2. Click Apply Changes.
3. Enter your password and wait for the installation to finish.
Step 4: Restart
Restart the machine for the changes to take effect.
Install Nvidia Driver via Command Line
The second way to install Nvidia drivers is by using the terminal.
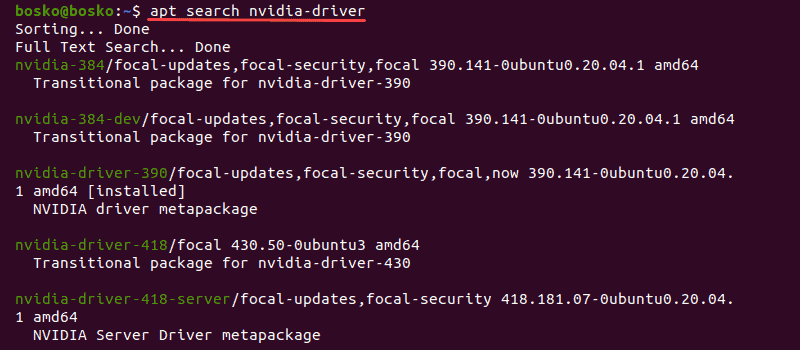
Step 1: Search for Nvidia Drivers
1. Open the terminal by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T or search for “terminal” in the Applications menu.
2. Run the following command:
The output shows a list of available drivers for your GPU.
Step 2: Update the System Package Repository
Before installing the driver, make sure to update the package repository. Run the following commands:
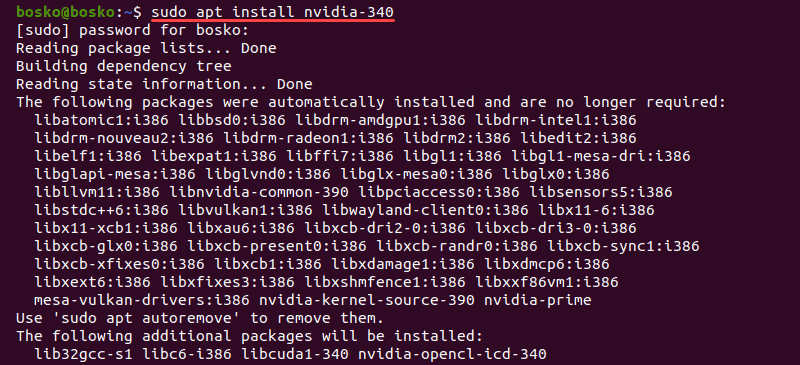
Step 3: Install the Right Driver for Your GPU
1. Choose a driver to install from the list of available GPU drivers. The best fit is the latest tested proprietary version.
2. The syntax for installing the driver is:
For this tutorial, we installed nvidia-driver-340, the latest tested proprietary driver for this GPU.
Step 4: Reboot
Reboot your machine with the following command:
Install Nvidia Beta Drivers via PPA Repository
The PPA repository allows developers to distribute software that is not available in the official Ubuntu repositories. This means that you can install the latest beta drivers, however, at the risk of an unstable system.
To install the latest Nvidia drivers via the PPA repository, follow these steps:
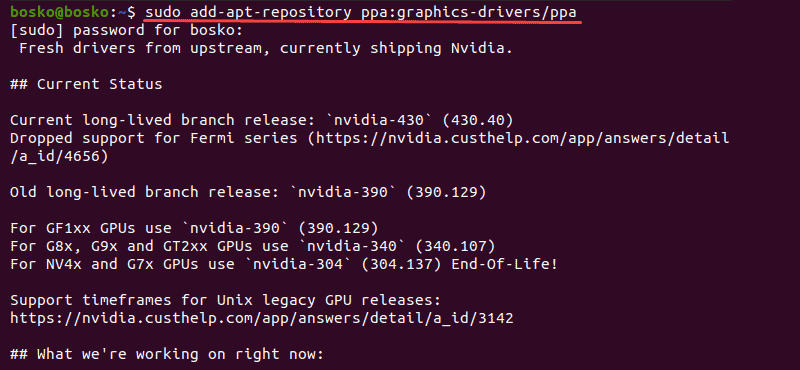
Step 1: Add PPA GPU Drivers Repository to the System
1. Add the graphics drivers repository to the system with the following command:
2. Enter your password and hit Enter when asked if you want to add the repository.
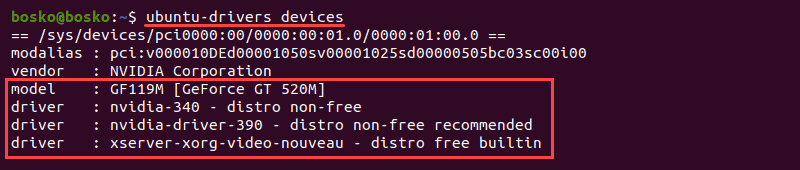
Step 2: Identify GPU Model and Available Drivers
To verify which GPU model you are using and to see a list of available drivers, run the following command:
The output shows your GPU model as well as any available drivers for that specific GPU.
Step 3: Install Nvidia Driver
1. To install a specific driver, use the following syntax:
For example, we installed the nvidia-340 driver version.
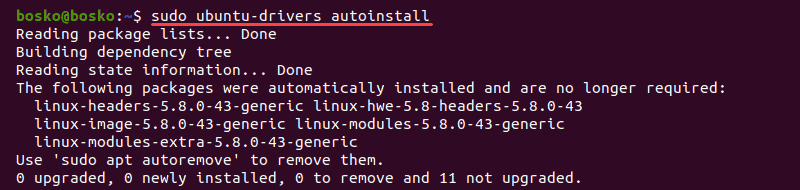
2. Alternatively, install the recommended driver automatically by running:
In this example, no changes were made as the recommended driver is already installed.
Step 4: Restart the System
Reboot the machine for the changes to take effect.
How to Uninstall Nvidia Driver
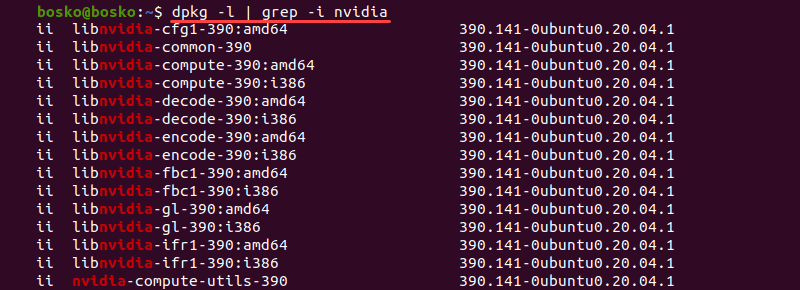
Step 1: See Installed Packages
To check which Nvidia packages are installed on the system, run the following command:
The output returns a list of all Nvidia packages on the system.
Note: The ubuntu-desktop package could also be purged because it is a dependency of the nvidia-common package, so you may need to reinstall it if it gets removed.
Step 2: Purge Nvidia Packages
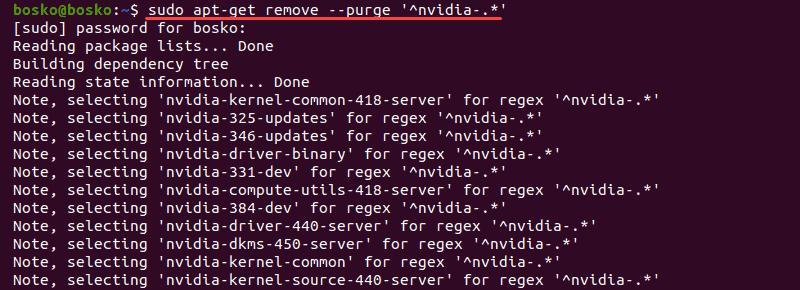
1. Run the following command:
The command purges every Nvidia package from the system.
2. If the ubuntu-desktop package is removed, reinstall it with the following command:
Step 4: Reboot the System
Note: Check out our other Nvidia installation guides:
You now know how to install proprietary Nvidia drivers on your system using the GUI app, official Ubuntu repository, or the PPA repository if you want the beta versions.
You also know how to uninstall Nvidia drivers if you want to go back to using the open-source Nouveau driver.
How to Install Nvidia Driver on Ubuntu 20.04
As Linux getting more user friendly, game developers are adding more support thanks to Steam. The performance of graphics processing units (GPUs) mainly depends on drivers. Ubuntu by default use open source video driver Nouveau which has limited support and features when compared with proprietary Nvidia drivers.
The proprietary Nvidia driver is essential to Ubuntu users looking to play games. However, if you are a basic user, there is no need to have this driver installed, as the open-source one works just fine.
In this tutorial, we are going to learn different ways to install Nvidia drivers on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
Check hardware Information of GPU
Before installing Nvidia drivers on Ubuntu, ensure that you have Nvidia GPU in your system. There are lots of commands available to get Linux hardware details.
To confirm this, simply run the following hwinfo command.
You can check which card is being used by the prime-select command:
The lshw command can display hardware and driver details of the currently used Nvidia card.
The lspci command is another option to get the GPU hardware details.
If you have installed inxi tool, run the following command.
Install Nvidia drivers using from GUI
Lets first check how to install Nvidia driver from the graphical user interface. On the main menu, type «software update manager» and click on it to open.
On the software updater pop-up, click on the ‘Settings & Livepatch‘ button as shown.
This will launch the ‘Software and Updates‘ window as shown below:
Then wait for the download to complete from the internet and click on the close button.
Reboot your computer for the changes to take effect. Run the following to reboot your PC.
Install Nvidia driver from the command line (CLI)
Then, run the following commands to check the list of driver devices available for the Nvidia card from the default Ubuntu repository.
After the Nvidia diver has been installed, we have to reboot the computer in order to allow Nvidia prime (which is the technology) to switch in between the Intel Graphics and the Nvidia Graphics card.
Verify using nvidia-smi
The nvidia-smi command line is a utility that is used for providing monitor and management capabilities for each and every devices i.e Nvidia Tesla, GRID, Quadro, and GeForce from Fermi and other higher architect families. Open the Terminal application and run the following command to see the Graphics Processing Unit and the process that is using the Nvidia GPU.
Configure the Nvidia Graphics driver
The Nvidia settings command starts a Graphics User Interface(GUI) tool for configuration of Nvidia Graphics driver. This enables you to have a glance at all the GPU information and configure external monitors that are connected to your system.
Run the command below to launch the ‘Nvidia and Server Settings‘ window.
How to uninstall the proprietary Nvidia driver
From open forums, I have noticed many users end up issues with removing Nvidia drivers and reinstalling. Let me share the steps I have followed to successfully uninstall the Nvidia driver and switch to the nouveau driver.
Step 1: Run the following command to confirm Nvidia drivers are installed in your system.
Step 2: Run the following commands to uninstall the proprietary Nvidia driver.
Note that, the use of purge command will remove Nvidia diver together with all configurations that will be made. Run the flowing command to reinstall the Ubuntu desktop package.
Step 3: Run these commands to switch back to the nouveau driver.
Step 3: Remove the Xorg configuration file
Run the rm command to remove the Xorg configuration file
Step 4: After that, reboot your system.
Uninstall Nvidia Driver through GUI
Uninstalling the Nvidia driver using a GUI is quite easy. First, locate the ‘software & Updates’ app then click on it to open. Once it has opened, select on the Additional Drivers tab.
Once Nvidia driver is uninstalled, a message will display saying, «No proprietary drivers are in use» Now close the Software & Updates application and then reboot your computer.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have covered two ways that you can use to install Nvidia drivers on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
With that said, Nvidia is bringing Vulkan which is intended to offer higher performance and more balanced CPU/GPU usage driver to Linux, a replacement for OpenGL.
In recent years Redhat developers are adding extra code to Nouveau improve opensource code to make it much better, let’s hope the near future we could use it for the modern game.
From Ubuntu 19.10, proprietary Nvidia drivers are available on install media (ie in ISO), which will bring a better fresh install experience for ubuntu users.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment.
Ubuntu Documentation
This page shows how to install the NVIDIA drivers from the command line, using either the ubuntu-drivers tool (recommended), or apt.
We package two types of NVIDIA drivers:
The recommended way (ubuntu-drivers tool)
The ubuntu-drivers tool relies on the same logic as the «Additional Drivers» graphical tool, and allow more flexibility on desktops and on servers.
The ubuntu-drivers tool is recommended if your computer uses Secureboot, since it always tries to install signed drivers which are known to work with Secureboot.
Check the available drivers for your hardware
You should see a list such as the following:
Installing the drivers for generic use (e.g. desktop and gaming)
You can either rely on automatic detection, which will install the driver that is considered the best match for your hardware:
Or you can tell the ubuntu-drivers tool which driver you would like installed. If this is the case, you will have to use the driver version (such as «460») that you saw when you used the «ubuntu-drivers list» command.
Let’s assume we want to install the 460 driver:
Installing the drivers on servers and/or for computing purposes
You can either rely on automatic detection, which will install the driver that is considered the best match for your hardware:
Let’s assume we want to install the 460-server driver (listed as «nvidia-driver-460-server»):
You will also want to install the following additional components:
Using apt
[ To be continued ]
NvidiaDriversInstallation (последним исправлял пользователь albertomilone 2021-07-29 12:35:32)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details
You can contribute to this wiki, see Wiki Guide for details
Ubuntu Documentation
The purpose of this page is to detail the necessary work to install the official NVIDIA Linux driver from www.nvidia.com. Note that this will not fix resolution problems, for that you need to see the FixVideoResolutionHowto.
When using manually installed NVIDIA binary drivers you will need to redo some of the following steps every time packages related to mesa or linux-image are updated (see the Kernel and Mesa Updates section for details). Attempts to revert to the Ubuntu provided NVIDIA binary drivers may prove troublesome and upgrades to the next Ubuntu release (e.g. from Ubuntu 7.04 to 7.10) may fail unless the manual install is correctly uninstalled first.
Complete Manual Install
Obtaining Needed Software
Before you begin, it is strongly advised that your already have Xorg working acceptably with the ‘nv’ drivers included.
First, make sure that your /etc/X11/xorg.conf is backed up.
Next, download the right drivers for your platform from the driver download page or the NVIDIA Unix Driver portal and save them to your home directory.
Open a terminal, and run the following command:
If you receive the «Unable to locate package» error, run the command:
It should then look something like this:
Or you can use simply run this:
This next step is optional. Most people will not need it, and it takes a fair amount of bandwidth and diskspace. It installs the Linux kernel source. If later steps fail, consider this a last resort.
The above command might print an error similar to the following:
In such case you could try following
The following command will then probably need adjustment also.
Disable Conflicting Software
Using Synaptic or apt-get, uninstall nvidia-glx, nvidia-glx-legacy, nvidia-glx-new and nvidia-settings if they are installed.
Open or create the /etc/default/linux-restricted-modules-common file with an editor, in Ubuntu use
and in Kubuntu use
and find the line:
replace it with:
Note: In Ubuntu 7.04 the nvidia_new is explicitly required in addition to nv on the DISABLED_MODULES line. See this launchpad bug about lrm-manager failing to disable the nvidia_new module when nv is specified alone. Additionally you may need to manually remove the hidden /lib/linux-restricted-modules/.nvidia_new_installed file.
Warning: Be wary of uninstalling nvidia-kernel-common or packages starting with the name linux-restricted-modules. Doing so will cause all restricted drivers to be uninstalled which may result in other hardware (e.g. certain wireless cards) or other software (e.g. VMware) failing to work after a reboot/kernel update. If you revert to use Jockey, reinstalling DKMS is needed to get all relevant drivers to be available by Jockey.
Prepare Configuration Files
The next step is to edit your xorg.conf file. This may not be needed in Hardy Heron and newer, but check anyway, esp. if you have upgraded from older versions of Ubuntu.
Find the section Module and comment out DRI using the # symbol, such as in the following example.
Now find the section Device, and change the Driver from nv (or vesa, fb, etc) to nvidia, as in the following example, and then save it.
Now that your Xorg.conf is saved, we need to shutdown the X11 server so that we can install the new drivers. To do this, save your work and press ctrl-alt-f1, and log in. Then run the following command to shutdown X11. Make sure your work is saved, Gnome/KDE is going to shutdown too.
For Ubuntu 11.04 or lower:
For Ubuntu 11.10 or higher:
Install the Driver
First navigate from the tty to the directory where you saved the install file (I will use /path/to/installer), then set executable permissions on it:
You can start the install script with the following command:
The installer will now walk you through the steps required. Assuming success, you can now restart your X11 server using:
For Ubuntu 11.04 or lower:
For Ubuntu 11.10 or higher:
Configure
You can now change settings for your video setup. In Ubuntu, go to Applications->System Tools->NVIDIA X Server Settings (or sometimes System->Administration->NVIDIA X Server Settings depending on the driver and/or install method). Alternatively, use the terminal:
For setting up dual head, see NvidiaMultiMonitors.
Load driver on boot
The X server will start in low-resolution if the nvidia driver is not loaded on boot, so
Kernel and Mesa Updates
Every time a new kernel comes out you will probably have to manually rebuild the NVIDIA binary driver kernel module. This can be done by booting to the new kernel and then running:
on the previously downloaded NVIDIA installer file.
Uninstalling the Driver
Sometimes it is necessary to uninstall the driver, like before a version upgrade of Ubuntu or if the installation fails or is no longer needed. For a manual install, you can remove the driver using the installer file:
You will probably be asked to reboot the computer.
It didn’t work! (Troubleshooting)
If the installer fails, go through the following checklist
Was Xorg already properly configured for the nv driver?
You may need to remove the file /lib/linux-restricted-modules/.nvidia_new_installed
Did you remove the nvidia-glx/nvidia-glx-legacy/nvidia-glx-new and nvidia-settings packages?
Did you read the log found in /var/log/nvidia-installer-log for errors that can guide you?
Did you check the NVIDIA Linux Forums for any current ‘known issues’ with the latest drivers?
Installation with Envy/EnvyNG
According to Envy’s website, EnvyNG does not support Ubuntu 10.04 and newer, it is recommended to use Jockey instead.
After installing, EnvyNG can be found from Applications->System Tools->EnvyNG in Ubuntu. You will want make sure you select NVIDIA drivers, not ATI:
Navigate there and click Apply, and the program will do the rest. You can then configure your card as described under the complete manual install section above.
Uninstalling the Driver
Free alternative
There is Nouveau: an open source driver with acceleration for NVIDIA cards. Currently (2008), there is 2D-support, and a very limited 3D support for extremely lucky developers. See http://nouveau.freedesktop.org/wiki/. Users that have installed the proprietary driver can help the development of Nouveau by sending information about their cards, see http://nouveau.freedesktop.org/wiki/REnouveauDumps.
See Also
Here are some other resources of interest:
NvidiaManual (последним исправлял пользователь gnaservicesinc 2015-05-30 01:32:49)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details
You can contribute to this wiki, see Wiki Guide for details
Установка драйвера Nvidia в Ubuntu 20.04
Если в вашем компьютере установлена видеокарта от компании Nvidia, лучше использовать официальные закрытые драйвера. Несмотря на то что за несколько последних лет качество стандартных драйверов стало в разы лучше, они практически не уступают проприетарным по производительности, вы не сможете использовать такие технологии, как Vulkan, CUDA и другие без проприетарного драйвера Nvidia.
Первое и самое заметное это, конечно, производительность, проприетарные драйвера от производителя разработаны с учетом различных технических тонкостей аппаратного обеспечения, что позволяет использовать возможности видеокарты по максимуму. К тому же поддерживается намного больше режимов работы карты и управление оборотами кулера, для правильного охлаждения.
В этой инструкции будет рассмотрена установка драйверов Nvidia в Ubuntu 20.04 из официального сайта и с помощью репозитория. Хотя статья ориентирована в первую очередь на Ubuntu 20.04, все ниже перечисленные действия будут прекрасно работать и в других редакциях и версиях этой операционной системы. Важно заметить, что данный способ работает на системах, в которых используется только одна видеокарта Nvidia, если нужно установить драйвер Nvidia в Ubuntu для гибридной графики, например, Nvidia и Intel, используйте Bamblebee.
Установка драйверов Nvidia
1. Узнаем необходимую версию драйвера
Первым делом нужно узнать номер модели вашей видеокарты, для того чтобы выбрать совместимую версию драйвера. Дело в том, что в новых версиях драйверов была отключена поддержка старых видеокарт, если у вас современная видеокарта, то беспокоится нет о чем, но проверить все же стоит.
Чтобы узнать номер модели используйте команду lspci:
Как вы видите, в этом примере видеокарта Nvidia GeForce GTX 780. Дальше откройте страницу загрузки драйверов Nvidia и заполните данные вашей видеокарты:
Теперь мы знаем какой драйвер, нужен, уже на этом этапе можно скачать установочный пакет и переходить к установке, но мы поступим по-другому. Дальше будет рассмотрена установка драйвера Nvidia в Ubuntu 20.04 из репозитория PPA.
2. Установка драйвера из официальных репозиториев
В Ubuntu 20.04 для управления драйверами оборудования используется утилита ubuntu-drivers. Конечно, мы можем как и раньше использовать apt, но я думаю, что так намного удобнее. Давайте посмотрим какую версию драйвера посоветует нам установить утилита:
Программа предлагает версию 470. Однако не всегда самая свежая версия доступа по умолчанию. Если вас устраивает эта версия, ее можно установить командой:
sudo ubuntu-drivers autoinstall
Также можно установить эту же версию с помощью apt:
sudo apt install nvidia-driver-470
Но если вы хотите самую новую версию, в данном случае 495, то надо использовать PPA.
2. Установка из PPA репозитория
Репозиторий graphics-drivers содержит самые последние версии драйверов nvidia. Его мы и будем использовать для установки. Для добавления graphics-drivers в систему, выполните команды
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:graphics-drivers/ppa
Теперь PPA репозиторий добавлен и списки пакетов обновлены, можно переходить к установке. Запустите еще раз утилиту ubuntu-drivers:
sudo apt search nvidia-driver
Для установки версии 495 используйте команду apt:
sudo apt install nvidia-driver-495
После завершения установки перезагрузите компьютер.
3. Установка драйверов Nvidia с помощью GUI
Если не хотите пользоваться консолью, можете включить драйвер с помощью утилиты Программы и обновления. Откройте главное меню Gnome и наберите в поиске Программы:
Запустите утилиту и перейдите на вкладку Драйверы:
Утилита видит те же самые драйвера из репозиториев, что и ubuntu-drivers. Просто выберите нужную версию драйвера и нажмите кнопку Применить изменения.
После завершения установки обязательно перезагрузите компьютер. В меню появиться ярлык утилиты Nvidia Settings, с помощью нее вы можете посмотреть характеристики видеокарты, а также настроить кое-какие параметры.
4. Установка из официального сайта
Это самый сложный вариант установки, поэтому если вы новичок, вам лучше использовать репозитории. Сначала загрузите официальный бинарный файл с драйвер со страницы на шаге 1. Там есть кнопка Загрузить сейчас. После её нажатия должно открыться ещё одно окно, в котором необходимо снова нажать Загрузить сейчас:
В итоге, в вашей папке загрузок должен появится такой файл:
/Загрузки | grep NVIDIA
Теперь необходимо добавить поддержку архитектуры i386 и установить библиотеку libc6 чтобы не получить проблем во время установки:
Устанавливать драйвер можно только из консоли. Если в момент установки будет запущен графический сервер, то ничего хорошего из этого не получится, вы просто не сможете потом загрузится в систему. Поэтому переключитесь во второй терминал сочетанием клавиш Ctrl+Alt+F2 и введите там свой логин и пароль. Затем выполните такую команду для остановки графического сервера:
sudo systemctl stop display-manager
Теперь можно переходить к установке. Запустите установочный скрипт командой:
Затем вам нужно будет принять лицензию и дождаться завершения установки. После чего можно перезагрузить компьютер такой командой:
Если установка nvidia ubuntu 18.04 прошла успешно, вы загрузитесь уже с новым драйвером.
Проверка правильности установки
После того как установка драйвера Ubuntu завершится, необходимо проверить правильно ли он установлен и настроен. Для этого выполните команду lspci и посмотрите какой модуль ядра используется для видеокарты, обратите внимание на сточку kernel driver in use:
Далее проверим поддержку аппаратного ускорения утилитой glxinfo:
glxinfo | grep OpenGL | grep renderer
Утилита настройки Nvidia
Вместе с драйверами в системе устанавливается графическая утилита настройки Nvidia X Server Settings, которую можно запустить из меню, или из консоли выполнив:
Эта утилита позволяет посмотреть информацию о видеокарте, подключенном мониторе, а также настроить различные параметры. Например, расширение монитора, или совместное использование двух мониторов. Настройка видеокарты nvidia ubuntu с помощью этой утилиты не так уж сложно.
Удаление драйверов Nvidia
Если во время установки что-то пошло не так попробуйте удалить драйвер Nvidia Ubuntu в режиме восстановления. Для открытия этого режима в меню загрузчика Grub выберите Дополнительные параметры Ubuntu, а затем пункт recovery mode или режим восстановления.
Перемонтируем файловую систему для записи:
Удаляем все пакеты nvidia:
apt-get purge nvidia*
Дополнительно
Для просмотра информации о драйвере используйте утилиты lsmod, modprobe или modinfo:
lsmod | grep nvidia
Выводы
Вот и все, установка драйвера Nvidia в Ubuntu 20.04 завершена. Теперь вы можете играть игры или использовать сложные эффекты в своей системе. Но будьте осторожны, теперь нельзя обновлять ядро выше поддерживаемой драйвером версии, потому что иначе система не загрузится. Если у вас остались вопросы, пишите в комментариях!