How to install yum
How to install yum
Question: How To Install Yum In Linux?
What is yum command in Linux?
YUM (Yellowdog Updater Modified) is an open source command-line as well as graphical based package management tool for RPM (RedHat Package Manager) based Linux systems.
It allows users and system administrator to easily install, update, remove or search software packages on a systems.
What is a yum repository?
YUM Repositories are warehouses of Linux software (RPM package files). RPM package file is a Red Hat Package Manager file and enables quick and easy software installation on Red Hat/CentOS Linux. YUM Repositories can hold RPM package files locally (local disk) or remotely (FTP, HTTP or HTTPS).
How do I enable yum repository?
For using yum to enable.disable repos you need to install config-manager attribute for that using yum-utils. Before enabling repository to make sure that all repository is in a stable state. When a system is registered using a subscription manager a file name redhat.repo is created, it is a special yum repository.
Can I use yum on Ubuntu?
Ubuntu uses apt not yum which is what Red Hat uses. You may be able to install it, or build it yourself, but it has limited usefulness in Ubuntu because Ubuntu is a Debian-based distro and uses APT. Yum is for use on Fedora and Red Hat Linux, much as Zypper is for use on OpenSUSE.
Can I install yum on Ubuntu?
3 Answers. You don’t. yum is the package management tool on RHEL-derived distributions and Fedora, Ubuntu uses apt instead. Repo is just a place from where you can install or fetch the package or tarball so no matter what you use in whatever system you’re using.
What is apt get Linux?
What does yum clean all do?
yum clean. During its normal use yum creates a cache of metadata and packages. This cache can take up a lot of space. The yum clean command allows you to clean up these files. All the files yum clean will act on are normally stored in /var/cache/yum.
What is the difference between Yum and RPM?
The major differences between YUM and RPM are that yum knows how to resolve dependencies and can source these additional packages when doing its work. Both tools can perform an install, and RPM will even allow you to install multiple versions simultaneously, but YUM will tell you that that package is already installed.
What yum install does?
How do I install a repository?
Method 1: Install Exodus on Kodi with the Lazy repository
How do I register redhat?
Step 1: Register and Active Red Hat Subscription
What is Linux repository?
A Linux repository is a storage location from which your system retrieves and installs OS updates and applications. Each repository is a collection of software hosted on a remote server and intended to be used for installing and updating software packages on Linux systems. Repositories contain thousands of programs.
Does Debian use yum?
On Debian-derived systems, dpkg handles individual package files. If a package has unmet dependencies, gdebi can often be used to retrieve them from official repositories. On CentOS and Fedora systems, yum and dnf are used to install individual files, and will also handle needed dependencies.
How do I get yum on Ubuntu?
How to Install RPM Packages On Ubuntu
What is the difference between yum and apt get?
Installing is basically the same, you do ‘yum install package’ or ‘apt-get install package’ you get the same result. Yum automatically refreshes the list of packages, whilst with apt-get you must execute a command ‘apt-get update’ to get the fresh packages. Another difference is upgrading all the packages.
How do I install packages in Ubuntu?
Can I install RPM on Ubuntu?
Install an RPM Package on Ubuntu Linux. Installing software on Ubuntu usually entails using Synaptic or by using an apt-get command from the terminal. This doesn’t always mean that an rpm will work on your system, though. You will need to install some prerequisite software packages in order to install alien, however.
Does Ubuntu use RPM or Deb?
Ubuntu 11.10 and other Debian based distributions work best with DEB files. Usually TAR.GZ files contain the source code of the program, so you would have to compile the program yourself. RPM files are mainly used in Fedora/Red Hat based distributions. Though it is possible to convert RPM packages to DEB ones.
How use apt get Linux?
How does sudo apt get install work?
The apt-get install command is usually to be prepended by sudo, which essentially means that you need to run the command with elevated privileges as root or superuser. This is a security requirement, as apt-get install affects the system files (beyond your personal home directory) while installing packages.
How do I install a package in Linux?
To install a new package, complete the following steps:
What does yum mean in Linux?
Yellowdog Updater, Modified
Can yum install RPM?
What is RPM and Yum in Linux?
The Red Hat Package Manager or RPM is the default package manager for Linux distributions that use packages with the same name. YUM stands for Yellowdog Updater Modified and is a front end for Linux distributions that utilize the RPM package format.
How do I install httpd?
Install Apache and PHP on CentOS 6
What Linux distro uses Yum?
RPM-based
How do I download a package using yum?
Use “yum groupinfo” to identify packages within a specific group. If only the package name is specified, the latest available package is downloaded (such as sshd).
Downloadonly plugin for yum
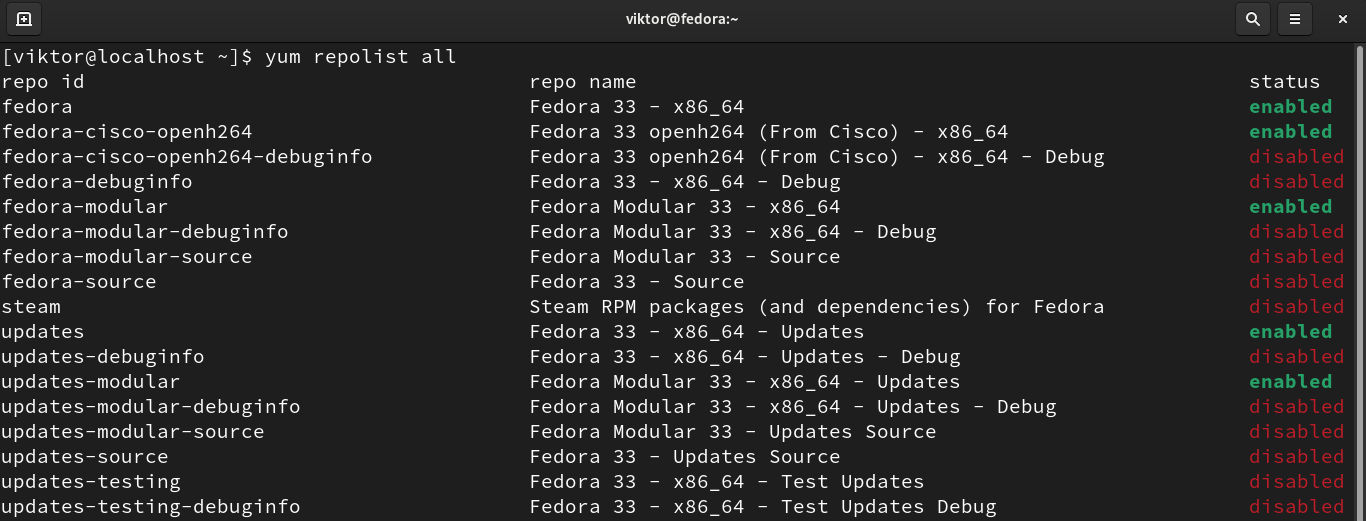
What is Repolist in Linux?
A “repolist” is a “repository list” — literally a list of URLs of websites that have indexed collections of Linux software. The various Linux package manager applications have a repolist (configuration file) with a list of repositories to check for software.
How do I run an RPM in Linux?
There are five basic modes for RPM command
What is Repodata in Linux?
A Linux software package is nothing but a compressed archive of files,consisting of a particular product information,program files,icons,libraries etc. which enables the functioning of that software package. RPM is the default package installation tool used in Red Hat Linux. RPM stands for Red Hat Package Manager.
Установка и использование менеджера пакетов YUM
Данная статья применима к:
Данное решение по умолчанию не входит в состав Astra Linux и не относится к компонентам ОС, на которые распространяется действие ТП.
Любые манипуляции с пакетной базой, не соответствующей текущему дистрибутиву, могут привести к проблемам с зависимостями и, в некоторых случаях, к неработоспособности ОС. См. также Использование стороннего программного обеспечения в аттестованных информационных системах, функционирующих под управлением ОС Astra Linux Special Edition
Подготовка к установке
Перед установкой менеджера пакетов YUM с необходимыми зависимостями в Astra Linux Special Edition следует добавить в качестве источника пакетов репозиторий ОС Debian Buster.
Открыть для редактирования файл /etc/apt/sources.list :
Добавить в открытый файл строку :
Установка
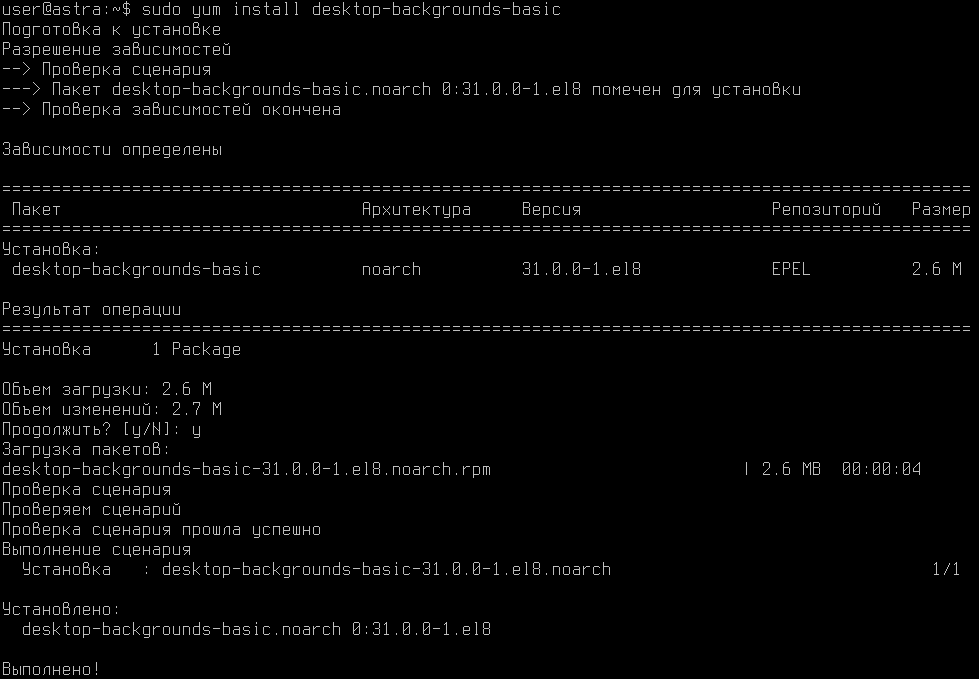
Для установки менеджера пакетов YUM выполнить команду:
После установки удалить или закомментировать символом # строку, добавленную в /etc/apt/sources.list :
Выполнить обновление списков источников пакетов командой:
Автоматическая установка
Открыть терминал ( ) и перейти в каталог, содержащий загруженный сценарий, например:
Использование YUM
Добавление репозиториев
Для добавления информации об источниках пакетов RPM открыть для редактирования файл /etc/yum/yum.conf :
внести информацию о репозитории в формате:
– уникальное имя для каждого репозитория, состоящее из одного слова;
– строка, описывающая добавляемый репозиторий;
Выполнить обновление списка источников пакетов RPM командой:
$ sudo yum update
EPEL | 4.7 kB 00:00:00
EPEL/primary_db | 3.5 MB 00:00:05
Подготовка к обновлению
Пакетов, отмеченных для обновления, нет.
Просмотреть список доступных в системе репозиториев можно командой:
Установка пакета
Для установки пакета RPM с помощью менеджера пакетов YUM необходимо в терминале выполнить команду:
Удаление пакета
Для удаления RPM-пакета из системы с помощью менеджера пакетов YUM необходимо в терминале выполнить команду:
How to Setup and Use YUM on Fedora?
A Linux distro can be described as a collection of inter-dependent packages on top of the Linux kernel. Together, they offer an amazing experience. To keep the packages in order, a package manager is a must-have for every distro.
In the case of Fedora, YUM and DNF are two package managers. In this guide, we’ll check out how to set up and use YUM on Fedora.
YUM on Fedora
YUM is the primary package manager for Fedora that can query info about packages, fetch packages from repos, install/uninstall packages with automatic dependency solution, and update the entire system. YUM can also work with additional repos or package sources. To extend the functionality, YUM also supports many plugins.
YUM can perform the same tasks as RPM but in a more efficient and simpler manner. It also simplifies configuring your own repositories and RPM packages.
In the modern-day, YUM is being replaced by DNF, a modern-day package manager. It’s because YUM has some inherent issues like poor performance, high memory consumption, poor documentation, etc. However, it’s still worth learning YUM because Fedora, CentOS, and RHEL still support YUM as a valid package manager.
Installing YUM on Fedora
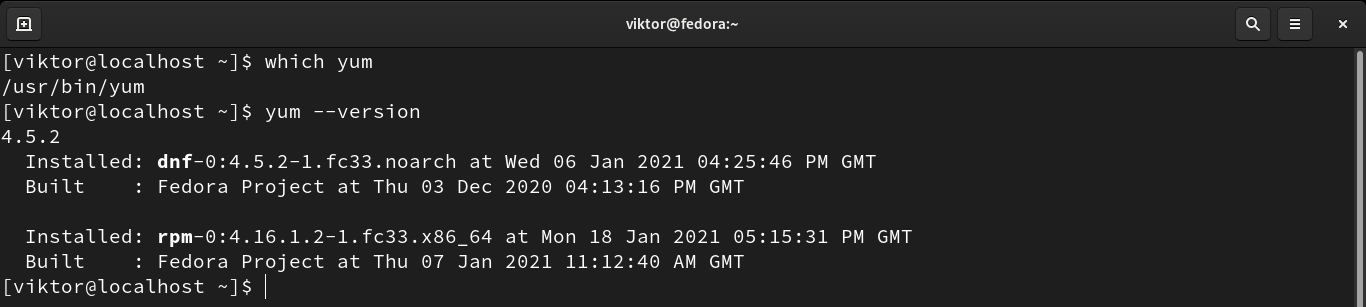
As one of the default package managers, YUM should come pre-installed with Fedora. Run the following commands to verify if YUM is installed:
If YUM isn’t installed, then the following command will install YUM right away.
Using YUM
It’s time to learn how to use YUM– a full-fledged package manager with tons of features. This section demonstrates some of its most common and important commands.
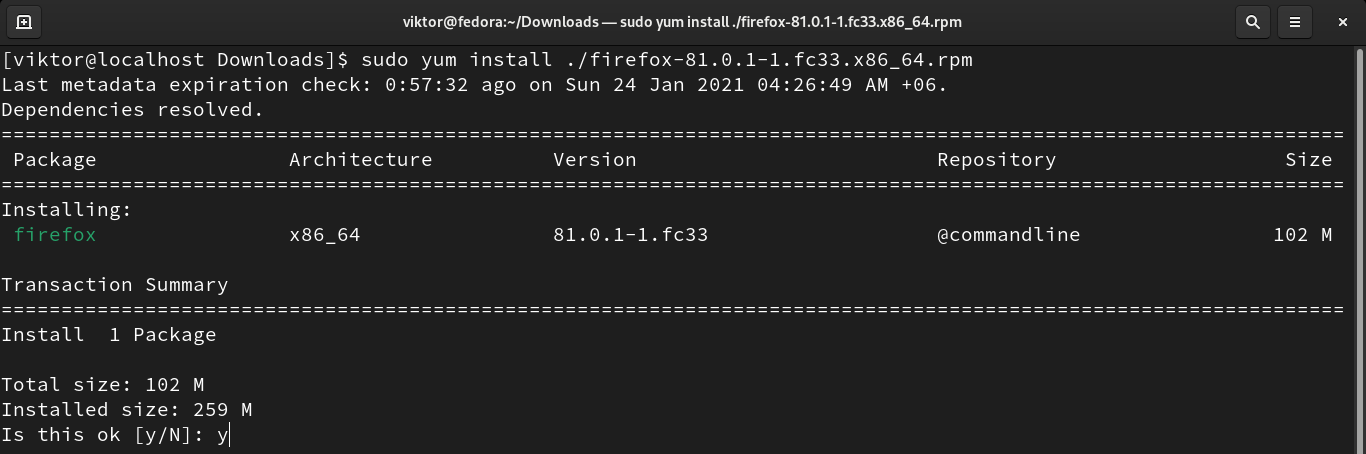
Installing a package
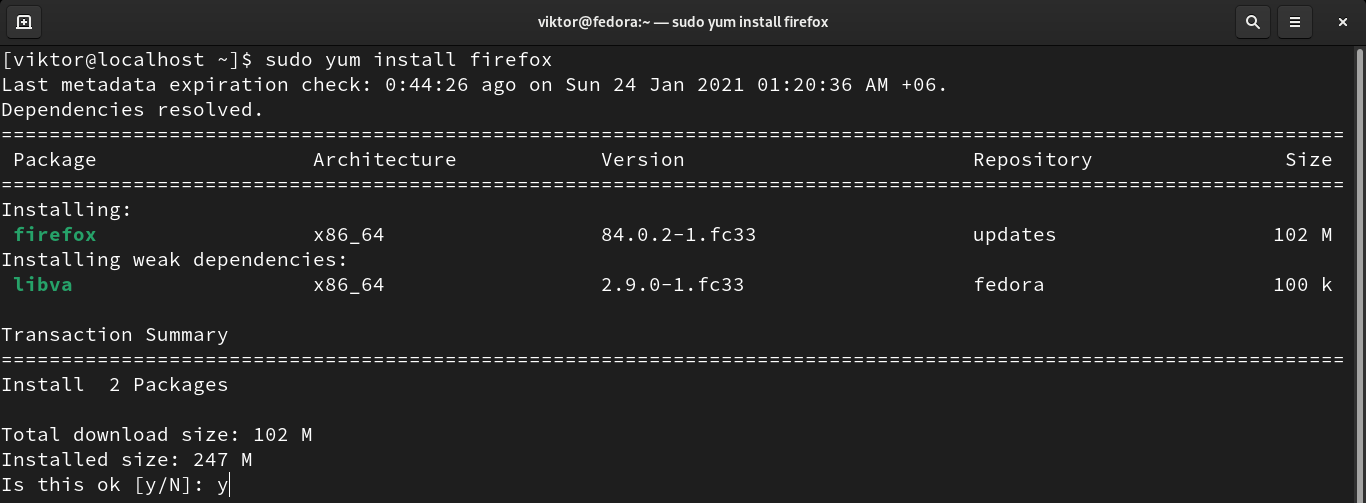
To install a package, YUM requires the package name. Assuming you have the package name, run the following command to install it. YUM will automatically resolve and install all the necessary dependencies.
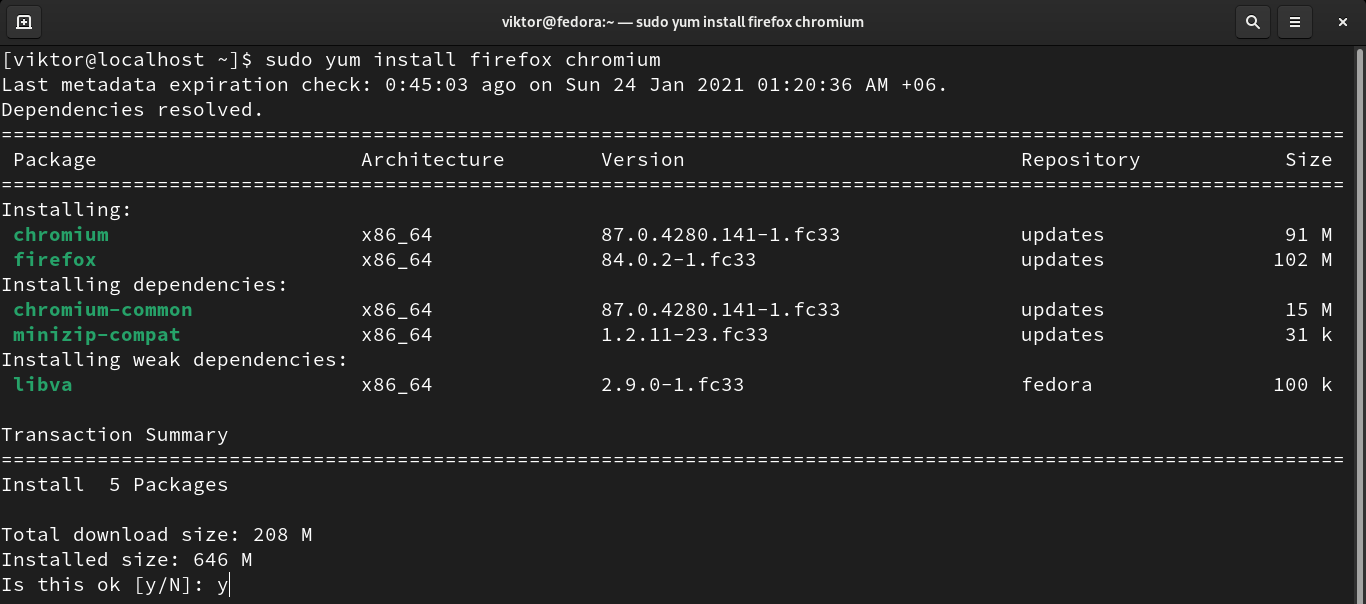
If there needs to install multiple packages, then just place all the package names separated by space.
When installing any package, YUM will ask for confirmation. If you want YUM to install the packages without asking any permission, then use the “-y” flag.
Install an RPM package
Various packages are directly available as RPM packages. While the default method of installing an RPM package is using the RPM tool, it’s recommended to use YUM to do so. If installed using YUM, the RPM package will be installed with all its dependencies (if available).
If there are multiple packages, then mention those as well.
It’s also possible to install an RPM package that’s available through a direct link. In the following example, YUM will download and install the RPM Fusion repo.
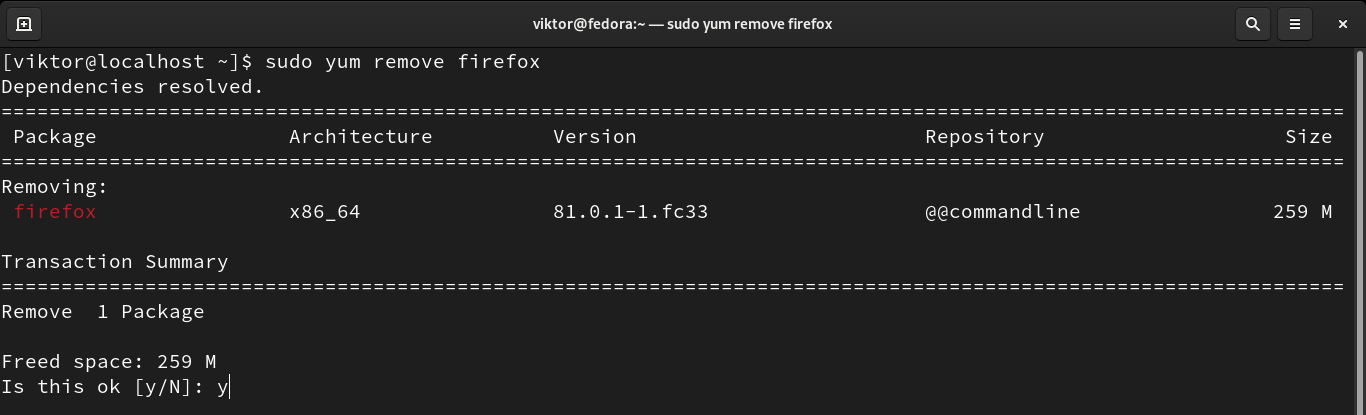
Removing a package
When a package is no longer needed, keeping it installed is redundant. To remove an unwanted package, use the following command structure:
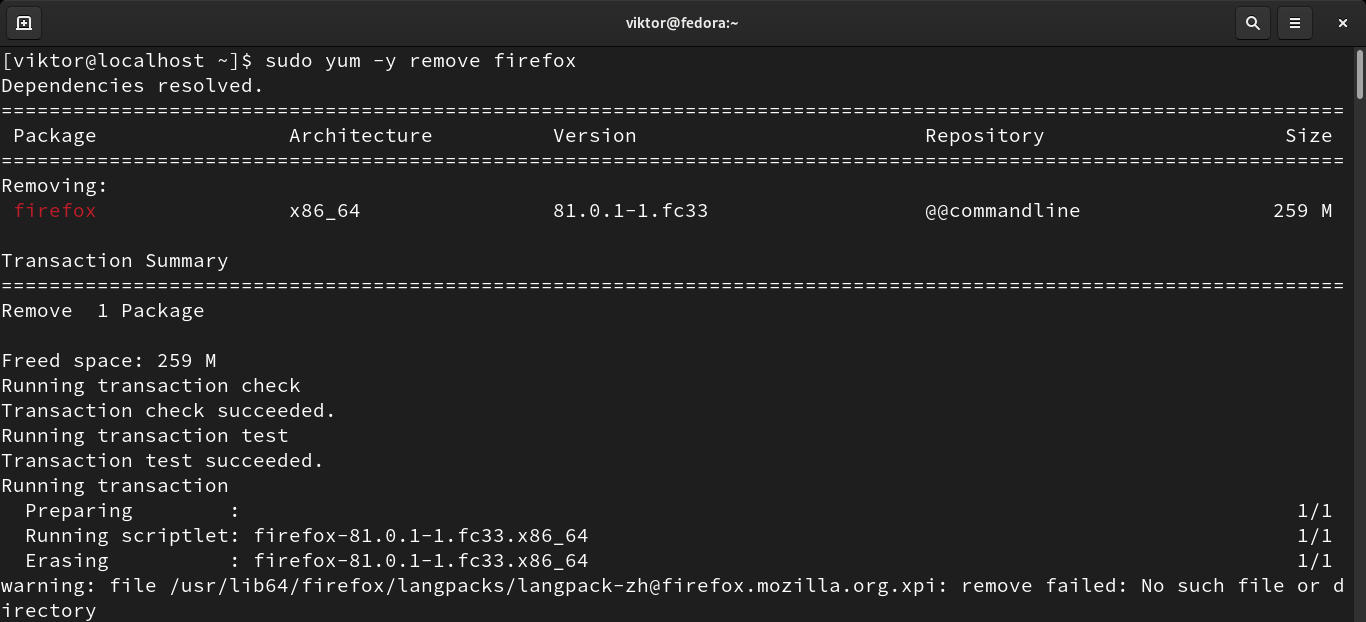
YUM will ask for permission to perform the action. If you want YUM to not ask for permission, use the “-y” flag.
Same as installing multiple packages, YUM can also remove multiple packages.
Searching a package
In many situations, the exact package name for a certain app is hard to keep track of. In such situations, the built-in searching feature of YUM comes really handy.
To search for a certain package name with a search term, use the following command structure:
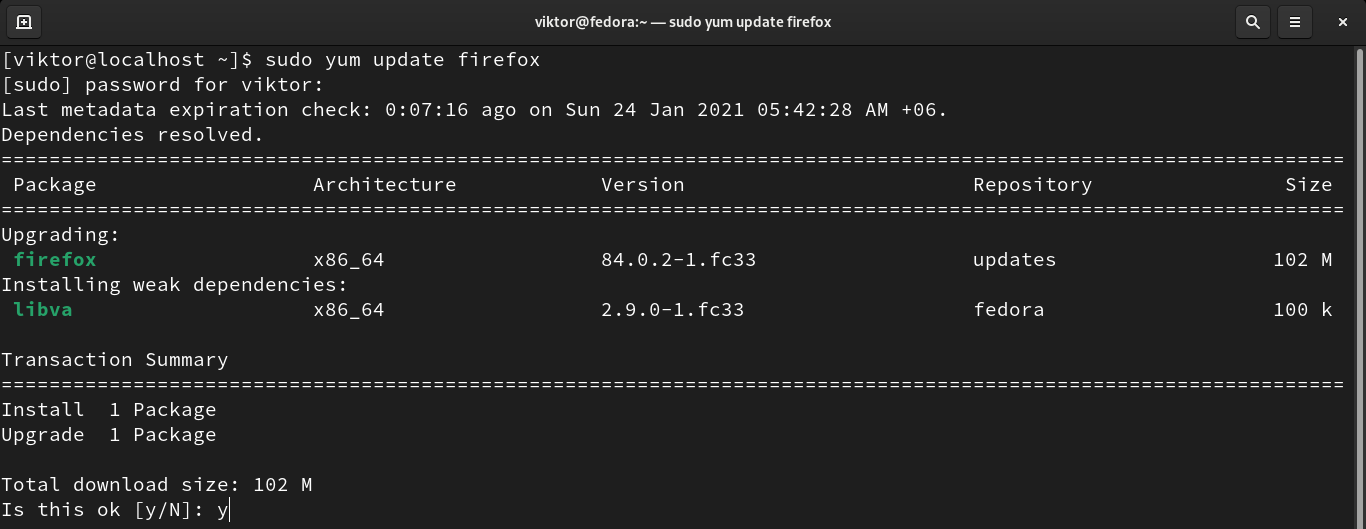
Updating a package
If there’s an update available for a certain package, it’s possible to individually update the package. By default, YUM will download and install the latest version of the package with dependencies.
Updating system
Instead of updating individual packages, it’s more efficient to let YUM update the entire system. YUM will check and download all the available updates and install them accordingly.
First, check if there’s any update available.
If there’s any update available, the following command will install all of them:
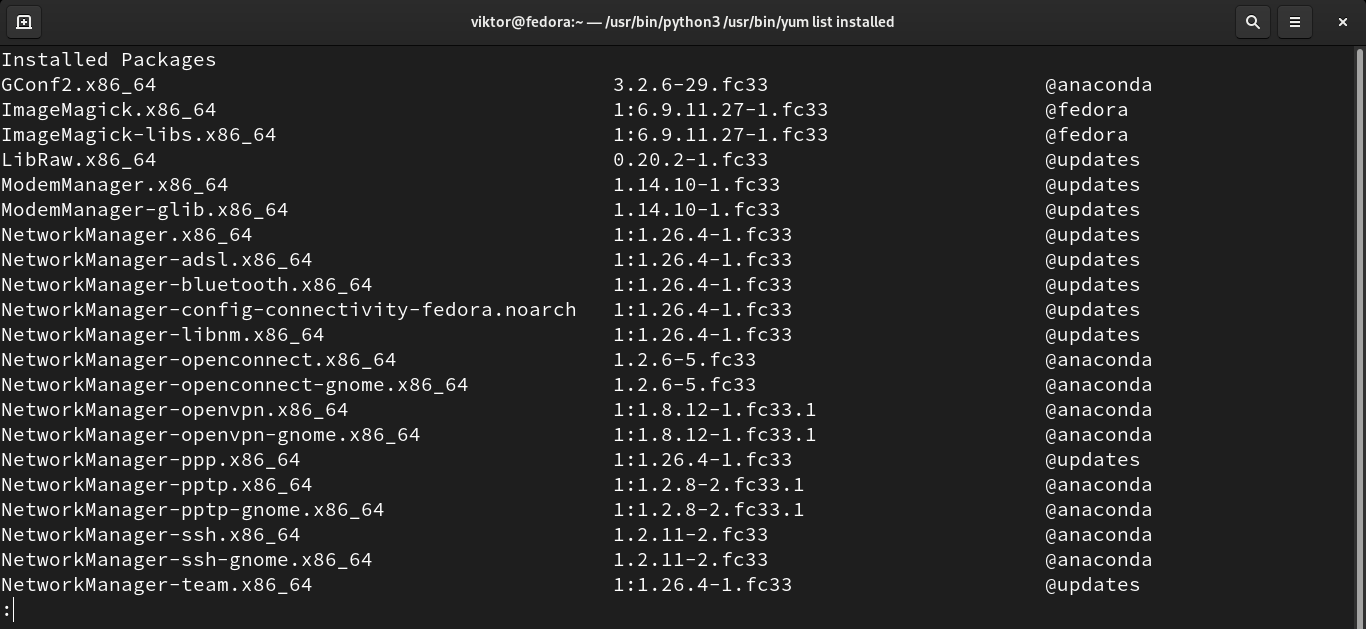
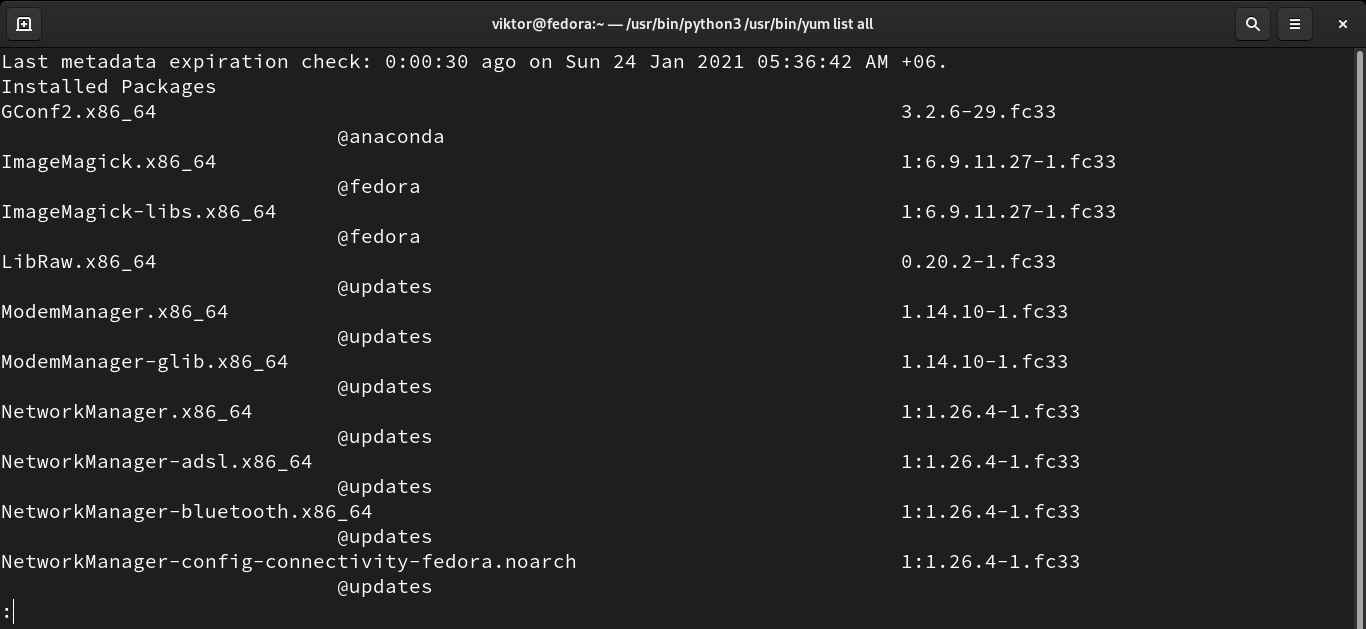
List packages
Using the “list” function, YUM can print all the list of packages, installed or available. This function can also search for an available package with a specific name.
To list all the installed packages, run the following command. The output will be huge, so we’ll be piping the output to “less” for easier browsing.
To list all the matching packages with a specific search term, use the following command:
To list all the packages (installed and available), run the following command:
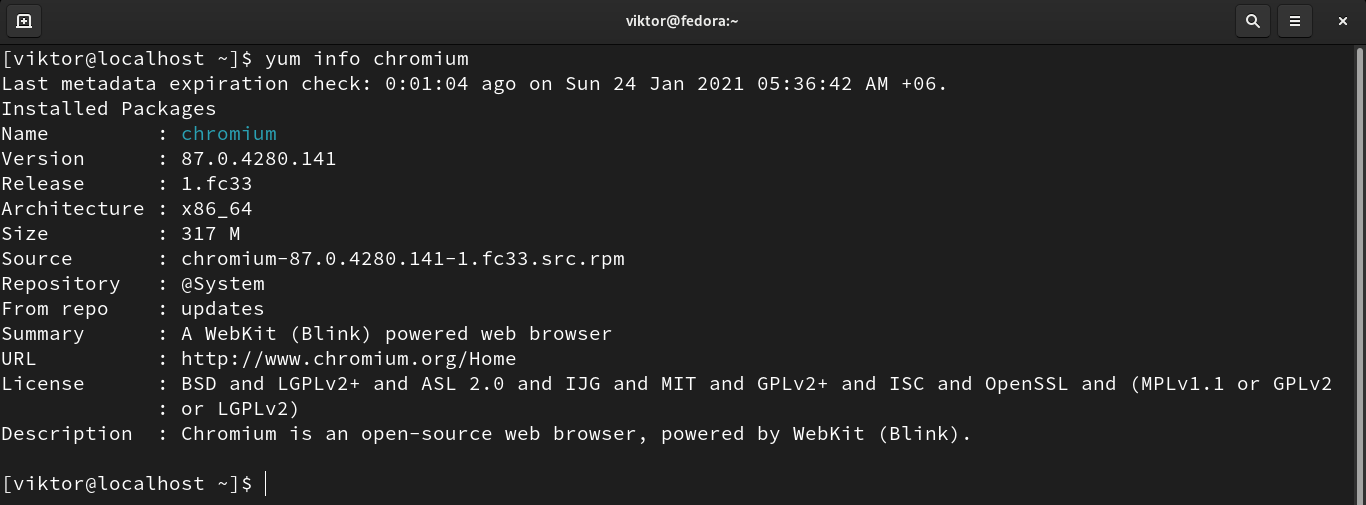
Information about a package
Before installation, YUM can show detailed info about a package, and it can be helpful in various situations. To check info about a package, run the following YUM command:
Group packages
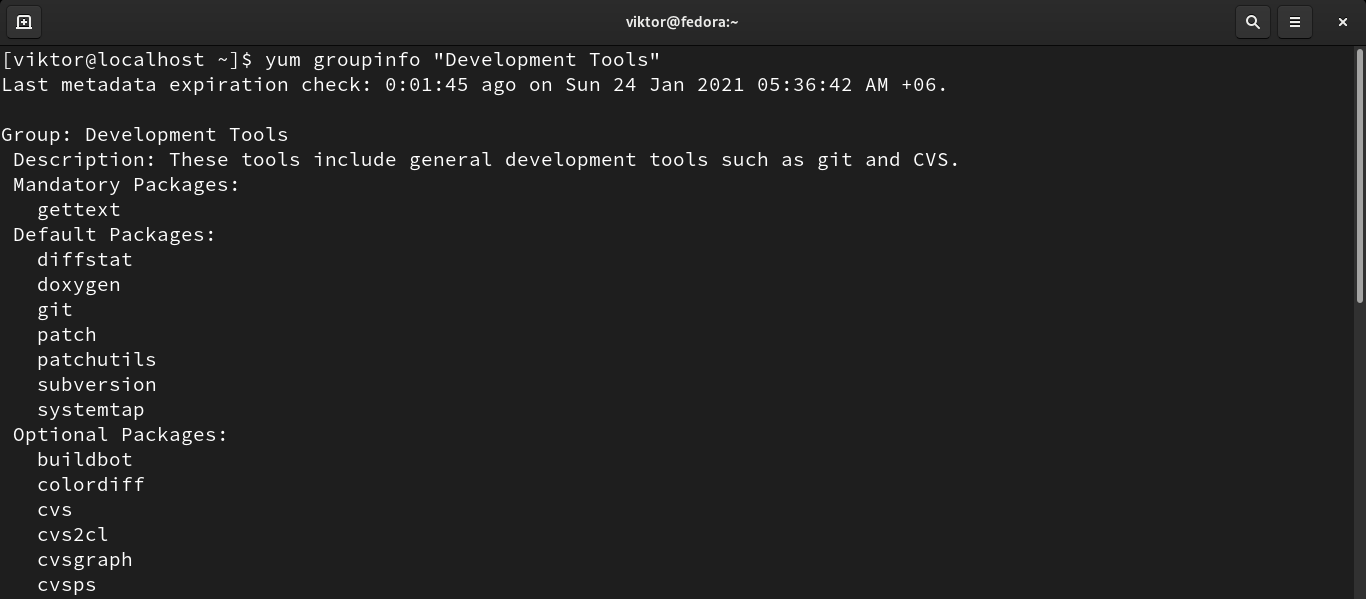
In Linux, a group is a bundle of a number of packages. A group will generally contain packages that are related to each other. For example, the group “Java Development” contains all the necessary tools for developing programs in the Java programming language.
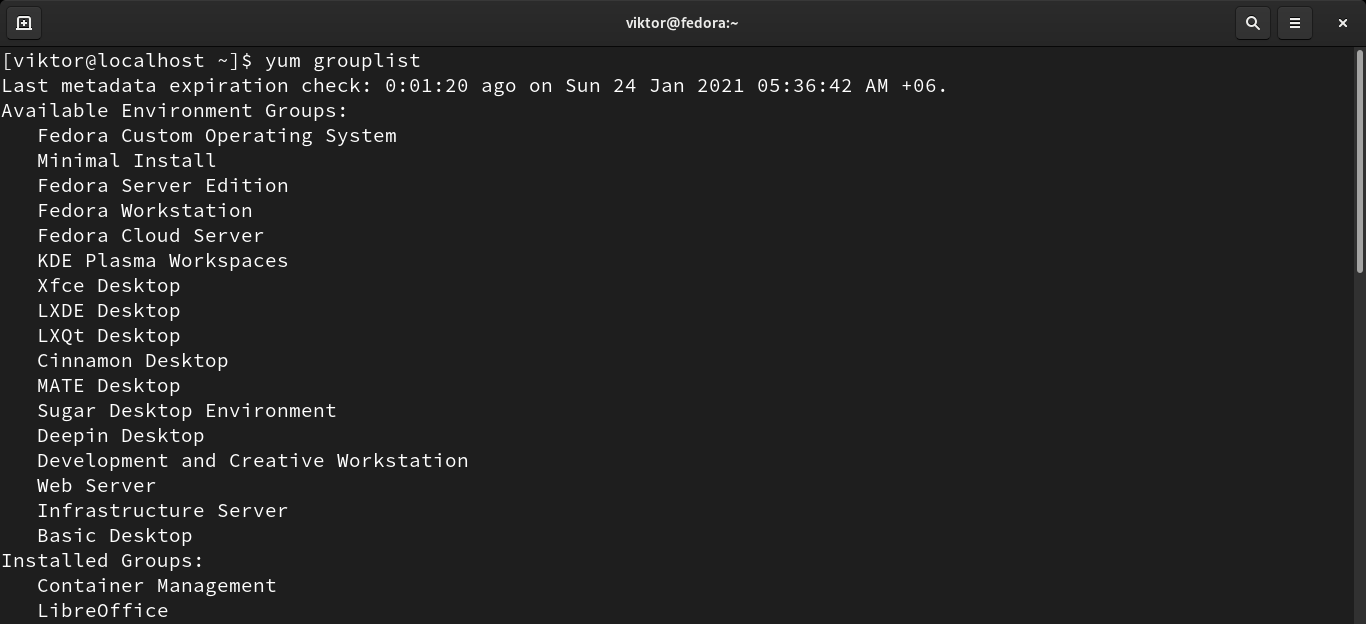
The following command will list all the available groups.
To check the information about a group, run the following command:
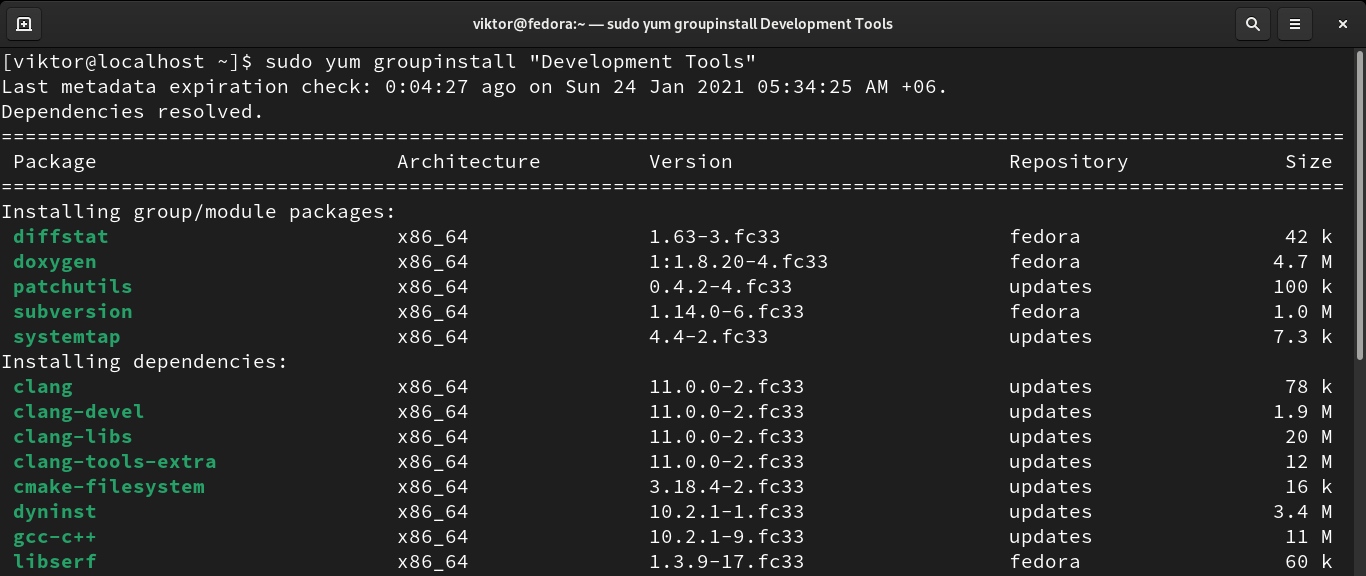
To install a group, run the following command:
If a group is to be updated, run the following command:
To uninstall a group, run the following command:
Repositories
YUM repositories are the primary sources for downloading and installing packages. Fedora comes with the Fedora repos by default. However, it’s possible to add/remove additional repositories.
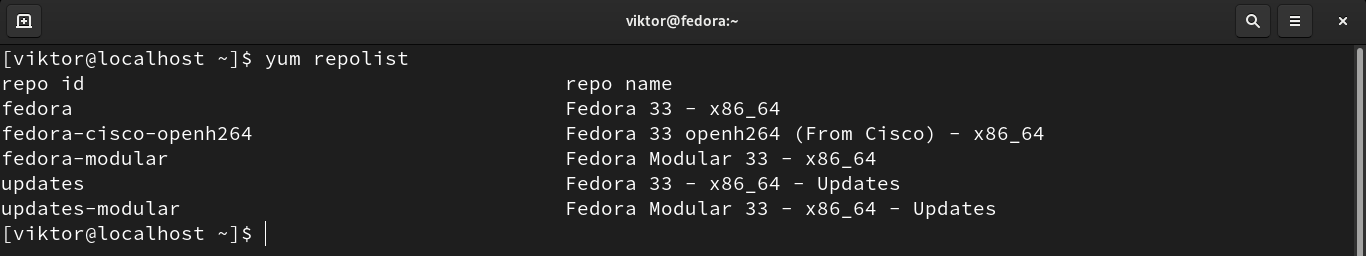
First, check out all the currently active repositories.
If there are some disabled repos, those won’t show on this list. To list all the repositories, run the following command:
To install a specific package from a specific repo, use the flag “–enablerepo”. It works on both enabled or disabled repo.
Cleaning up YUM
YUM generates all the repo package data in the “/var/cache/yum” location; each repo with its own sub-directory. While the cache is important for YUM to provide the fastest possible performance, a corrupted cache may be a problem, and cleaning it up will solve the issue.
Now, perform a system update. YUM will automatically generate the caches again.
Final thoughts
YUM is a powerful package manager. This guide demonstrates some of the most common usages of YUM. For quick help, check out the YUM help page.
For in-depth information about YUM, the man page is quite useful.
Installation and Configuration of Yum in Red Hat Linux 8
Yellowdog Updater Modifier sums as YUM and this is a PMT (Package Management Tool) for the RedHat Package Manager. YUM has been used for quite a long time. But, now in RHEL 8, we have a modest version of “yum” called “dnf” stands for Dandified YUM. Although both the commands work fine in Redhat 8 Linux but dnf is much faster, as some of the bugs have been removed.
Installing Yum to RHEL 8
Step 1: First move to the given location in RHEL 8 Linux CD or if you are using any virtual software then attach the iso or image file to the virtual machine and move to the location or folder below.
Step 2: Now open the terminal in the same folder where your rpm is present, and run the command given below.
Step 3: Here search for yum and you must get an rpm package, copy the name of the package.
Step 4: Now Type “yum” on the terminal and hit enter, if you see the output as bellow then yum has been installed.
Yum Can be Configured in 2 Ways
1. Manually
2. Using External Software/Program
Manually Configuration
Step 1: Go to
yum repository directory
Step 2: Create a repository file
Step 3: Type the code and Save. Before this, you must check your BaseOS CD-ROM name and replace it by RHEL-8-0-0-BaseOs-x86_64 and do the rest of it the same.
Using External Software
We can use external software or programs to configure yum for us. Two of these programs are epel and fusion. These create some repository files as we created manually and then add the baseurl for different software and programs for the respective version of Linux.
installing fusion program
Configuring yum using external programs is the most suitable and used method in the community, as it has reduced the headache of dependencies( explained below).
Why we really need YUM, DNF, APT-GET, and these kinds of software or programs?
Let us take an example to understand this. Suppose a wedding is there and you are the person who has to organize everything in the marriage. There are lots of tasks like:
So all the work has to be done by you and only you, from invitation to decoration. If you want to send an invitation card then the first contact with the printing press and decide the color, shape, and all that, these things are called dependencies. To complete a task there is some more task to be done first. But what if, you hire someone to do this job. Then you just have to give the orders and the work will be done in no time, without worry.
Similarly, yum, dnf and apt-get are hired software that does the work for the user, from installation to uninstalling the program and many more. This program has reduced the work of solving dependencies. Like if you want to install any software then these programs will install the most suitable software available according to your architecture. This is the big and short reason for the requirement of these kinds of programs.
Quick Answer: How To Install Yum On Linux?
What is yum command in Linux?
YUM (Yellowdog Updater Modified) is an open source command-line as well as graphical based package management tool for RPM (RedHat Package Manager) based Linux systems.
It allows users and system administrator to easily install, update, remove or search software packages on a systems.
How do I enable yum repository?
For using yum to enable.disable repos you need to install config-manager attribute for that using yum-utils. Before enabling repository to make sure that all repository is in a stable state. When a system is registered using a subscription manager a file name redhat.repo is created, it is a special yum repository.
Can I install yum on Ubuntu?
3 Answers. You don’t. yum is the package management tool on RHEL-derived distributions and Fedora, Ubuntu uses apt instead. Repo is just a place from where you can install or fetch the package or tarball so no matter what you use in whatever system you’re using.
How do I download a package using yum?
Use “yum groupinfo” to identify packages within a specific group. If only the package name is specified, the latest available package is downloaded (such as sshd).
Downloadonly plugin for yum
What is Linux yum repository?
YUM Repositories are warehouses of Linux software (RPM package files). RPM package file is a Red Hat Package Manager file and enables quick and easy software installation on Red Hat/CentOS Linux. YUM Repositories hold a number of RPM package files and enable download and installation of new software on our VPS.
What is apt get Linux?
How do I enable repos with Yum Config Manager enable repo?
To enable all repositories run “yum-config-manager –enable \*”. –disable Disable the specified repos (automatically saves). To disable all repositories run “yum-config-manager –disable \*”. –add-repo=ADDREPO Add (and enable) the repo from the specified file or url.
How do I register redhat?
Step 1: Register and Active Red Hat Subscription
How do I install a repository?
Method 1: Install Exodus on Kodi with the Lazy repository
How do I install packages in Ubuntu?
Can I install RPM on Ubuntu?
Install an RPM Package on Ubuntu Linux. Installing software on Ubuntu usually entails using Synaptic or by using an apt-get command from the terminal. This doesn’t always mean that an rpm will work on your system, though. You will need to install some prerequisite software packages in order to install alien, however.
Does Debian use yum?
On Debian-derived systems, dpkg handles individual package files. If a package has unmet dependencies, gdebi can often be used to retrieve them from official repositories. On CentOS and Fedora systems, yum and dnf are used to install individual files, and will also handle needed dependencies.
What is difference between RPM and Yum?
The major differences between YUM and RPM are that yum knows how to resolve dependencies and can source these additional packages when doing its work. Both tools can perform an install, and RPM will even allow you to install multiple versions simultaneously, but YUM will tell you that that package is already installed.
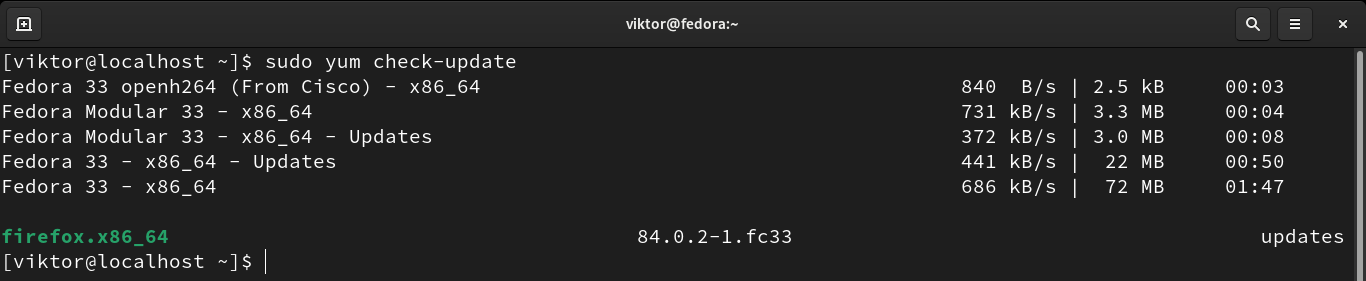
How do I check for yum updates?
To check for any updates available for your installed packages, use YUM package manager with the check-update subcommand; this helps you to see all package updates from all repositories if any are available. Loaded plugins: changelog, fastestmirror base. 3.6 kB 00:00:00 epel/x86_64/metalink.
Can I use yum on Ubuntu?
Ubuntu uses apt not yum which is what Red Hat uses. You may be able to install it, or build it yourself, but it has limited usefulness in Ubuntu because Ubuntu is a Debian-based distro and uses APT. Yum is for use on Fedora and Red Hat Linux, much as Zypper is for use on OpenSUSE.
How do I install software on Linux?
3 Command Line Tools to Install Local Debian (.DEB) Packages
What Linux distro uses Yum?
RPM-based
What is Yum and RPM in Linux?
The Red Hat Package Manager or RPM is the default package manager for Linux distributions that use packages with the same name. YUM stands for Yellowdog Updater Modified and is a front end for Linux distributions that utilize the RPM package format.
How use apt get Linux?
How does sudo apt get install work?
The apt-get install command is usually to be prepended by sudo, which essentially means that you need to run the command with elevated privileges as root or superuser. This is a security requirement, as apt-get install affects the system files (beyond your personal home directory) while installing packages.
How do I install an apt in Linux?
You can open the Terminal either through the system Dash or the Ctrl+alt+T shortcut.
Is Red Hat Linux free?
Members of the Red Hat Developer Program can now get a no-cost Red Hat Enterprise Linux license. It’s always been easy to get started with Linux development. Sure, Fedora, Red Hat’s community Linux, and CentOS, Red Hat’s free server Linux, can help, but it’s not the same thing.
Can I use Redhat without subscription?
3 Answers. Yes, you have to have an active RHEL subscription to download packages from RHEL’s repositories. If your machine has never been subscribed, or the subscription is expired, you will not be able to use any of the repositories provided by RHEL.
What is Rhn in Linux?
Red Hat Network (abbreviated to RHN) is a family of systems-management services operated by Red Hat. RHN makes updates, patches, and bug fixes of packages included within Red Hat Linux and Red Hat Enterprise Linux available to subscribers.