How to install zabbix
How to install zabbix
How to Install Zabbix on RHEL/CentOS and Debian/Ubuntu – Part 1
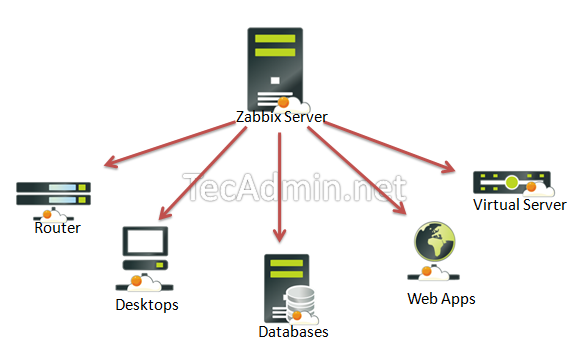
Zabbix is an Open Source, high-level enterprise software designed to monitor and keep track of networks, servers, and applications in real-time. Build in a server-client model, Zabbix can collect different types of data that are used to create historical graphics and output performance or load trends of the monitored targets.
The server has the ability to check standard networking services (HTTP, FTP, SMTP, IMAP, etc) without the need to install extra software on the monitored hosts.
However, in order to gather data and create statistics about local services or other specific system resources that run on remote instances, such as CPU, disks, internal system process, RAM, etc, you need to install and configure a Zabbix agent.
Following are the 4-article series about the Zabbix Monitoring application:
This tutorial will focus on how to install the latest version of the Zabbix Server on Debian/Ubuntu and RHEL/CentOS /Fedora/Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux with MySQL/MariaDB backend database to store collected data, PHP and Apache Web Server as the mainly web interface.
Important: The given Zabbix instructions also work on all Debian derivatives and RedHat-based distros like RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux.
Step 1: Install Apache Web Server and PHP
1. First, update the software packages and then install Apache Web Server alongside PHP and its extensions in order to provide the web-backed functionality for Zabbix Server by issuing the following command.
2. Next, you need to tune the PHP interpreter and adjust some values in order to run Zabbix Server. So, open Apache php.ini configuration file for editing by issuing the following command:
Now, search with CTRL+C and replace the following PHP values as it follows:
Replace the date.timezone variable according to your server’s geographical location. A list of PHP-supported Timezones can be found here http://php.net/manual/en/timezones.php.
3. After updating the PHP configuration file, restart Apache daemon to reflect changes by issuing the following command.
Step 2: Install MariaDB Database and Library
4. On the next step install the MariaDB database and MySQL development library from binary packages. As MariaDB installs on your system you will be asked to set a password for the database root user during installation (Only on Debian). Choose a strong password, repeat it and wait for the installation to finish.

5. When the installation of Mariadb finishes, start and secure the database by issuing mysql_secure_installation command with system root privileges ( answer with yes for removing anonymous users, disable root login remotely, remove test database and access to it and apply all changes).
Use the below screenshot as a guide.
6. The next requirement for Zabbix is setting up an RDBMS database. Log in to your LAMP stack database component (MySQL or MariaDB) and create a Zabbix database and the credentials required to manage the database, by issuing the following commands.
Make sure you replace the database name, user, and password to match your own settings.
Step 3: Install Zabbix Server
7. Now, start to install the Zabbix server and Zabbix PHP frontend application by adding the official Zabbix repositories to your system package manager by issuing the following commands with root privileges.
Install Zabbix on Debian
Install Zabbix on Ubuntu
Install Zabbix on RHEL-based Distros
If you want to download and compile an older version, please visit Zabbix official Sourceforge repositories.
8. On the next step, restart the Apache HTTP server in order to apply the Zabbix configuration file installed for Apache.
Step 4: Configure Zabbix Server and Agent
9. Before configuring the server, first, import Zabbix’s initial database schema to the MySQL database. Import the schema against the database created for the Zabbix application, by issuing the below command.
10. On the next step, set up the Zabbix server by opening the main configuration file for editing with the following command.
In zabbix_server.conf file search and modify the following lines as presented in the below excerpt. Update the variables to reflect your own database settings.
11. Finally, save and close the Zabbix server configuration file by pressing Ctrl+o and Ctrl+x file and restarting the Zabbix daemon to apply changes by issuing the below command.
12. Next, configure the Zabbix Agent configuration file by updating the following lines. First, open the file for editing.
Zabbix agent configuration file excerpt:
13. Save and close the Zabbix agent configuration file and restart Zabbix Agent to reflect changes by issuing the following command.
Step 5: Install and Configure Zabbix Frontend Interface
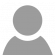
15. Now it’s time to install the Zabbix Server Frontend web interface. In order to accomplish this step open a browser and navigate to your server IP Address using HTTP or HTTPS protocol and the welcome screen should appear. Hit the Next button to move forward.
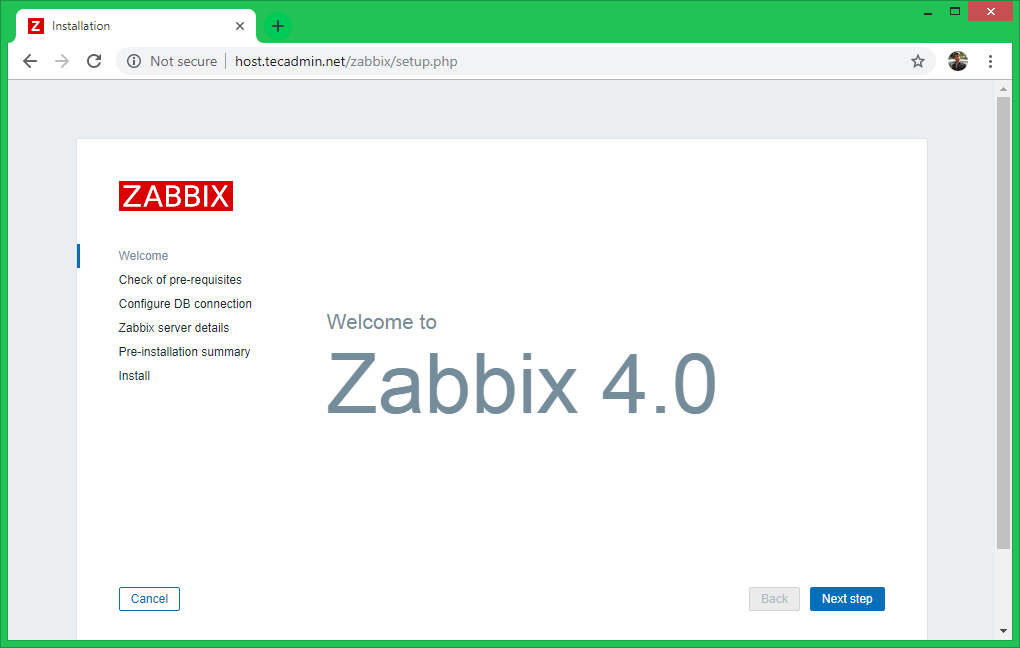
On the first welcome screen, just hit the Next step button to move to the new step of the installation process.

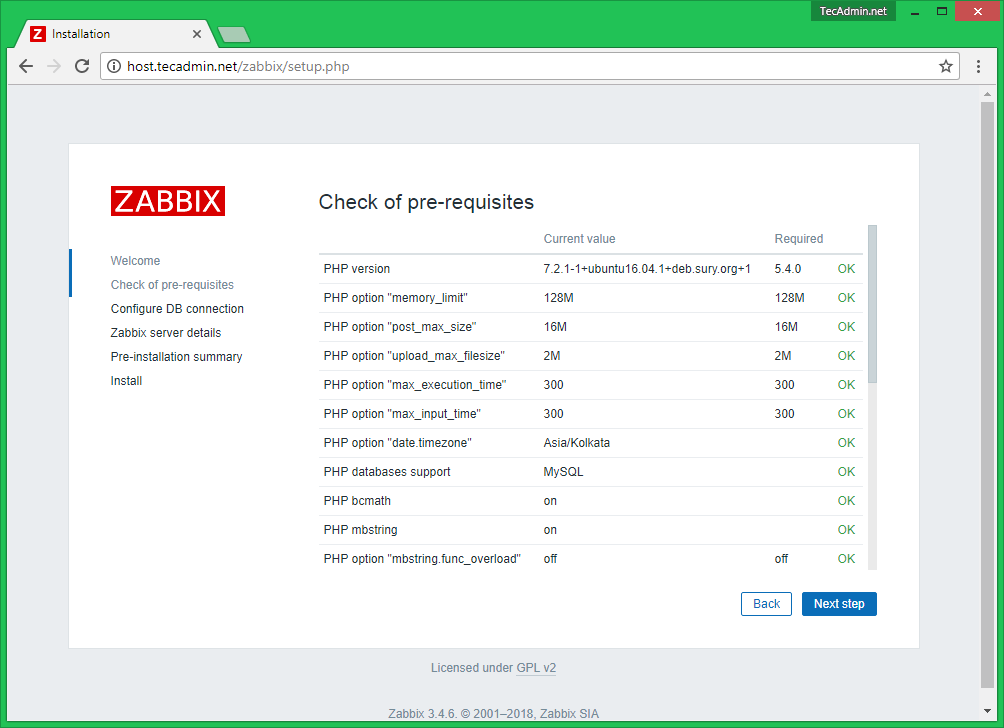
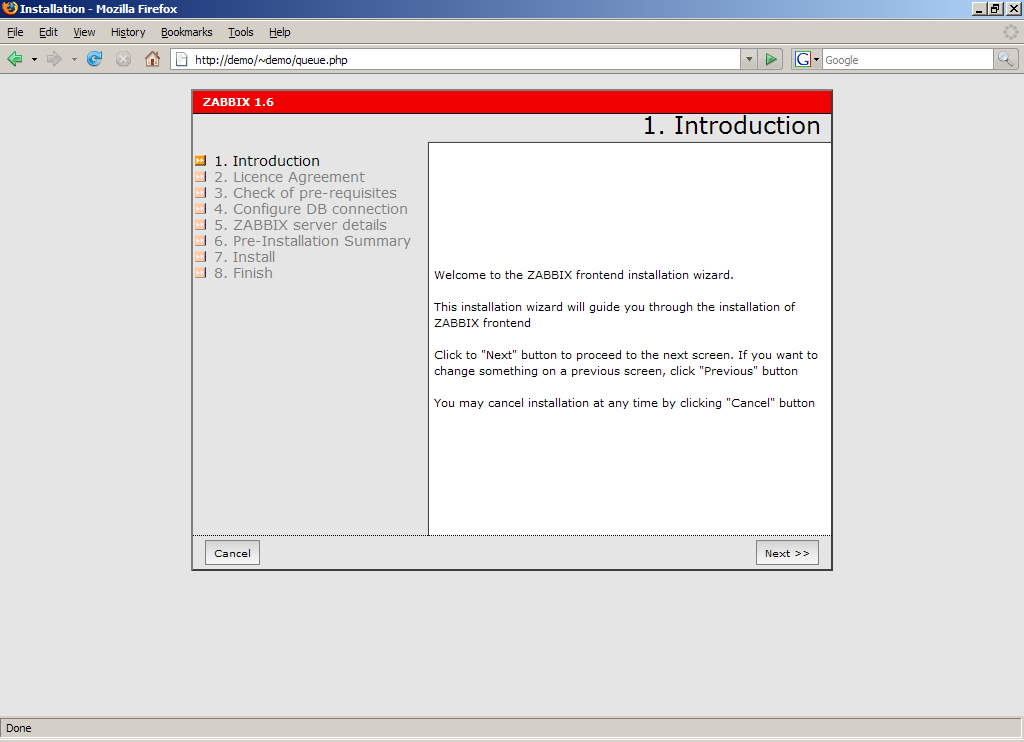
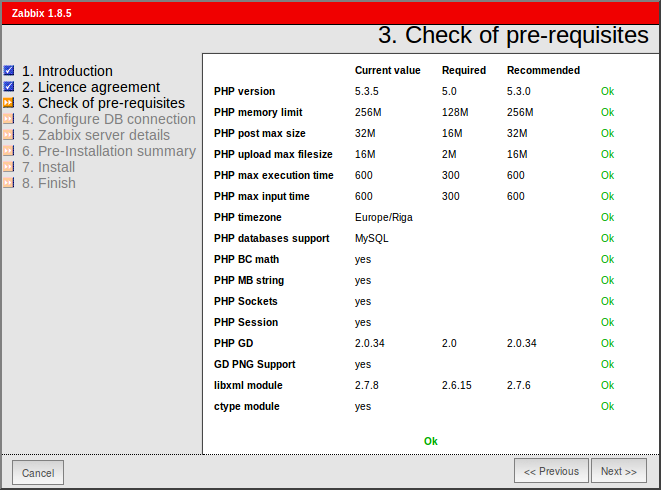
16. After a series of checks, if all pre-requires values are satisfied, hit the Next button to proceed further.

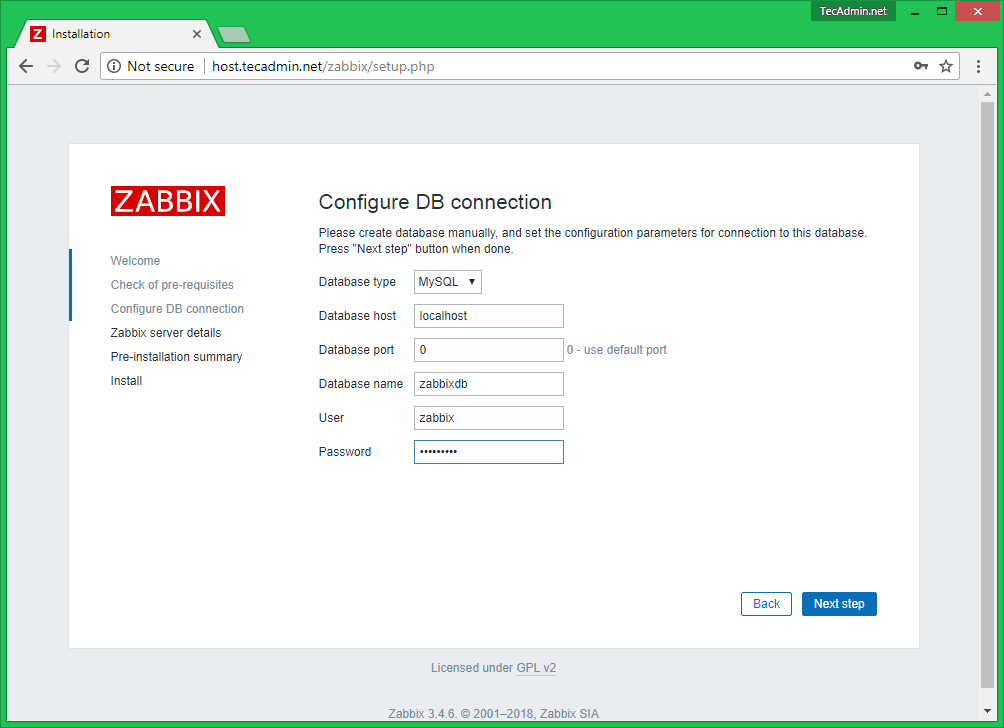
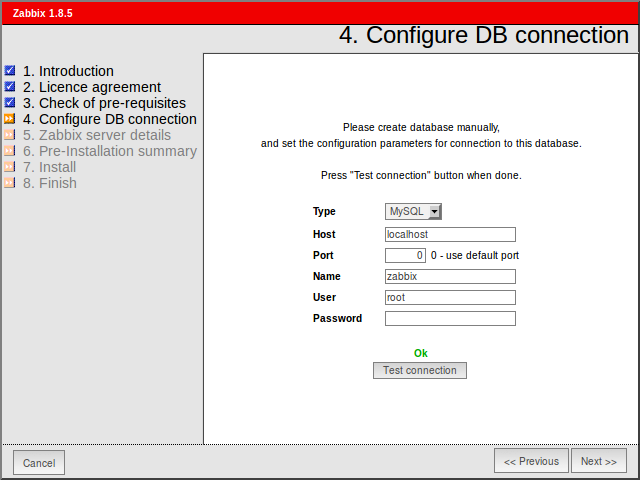
17. On the next step provide the settings for the MySQL database, hit the Test connection button to test MySQL connectivity, and move to the step by pressing the Next button.

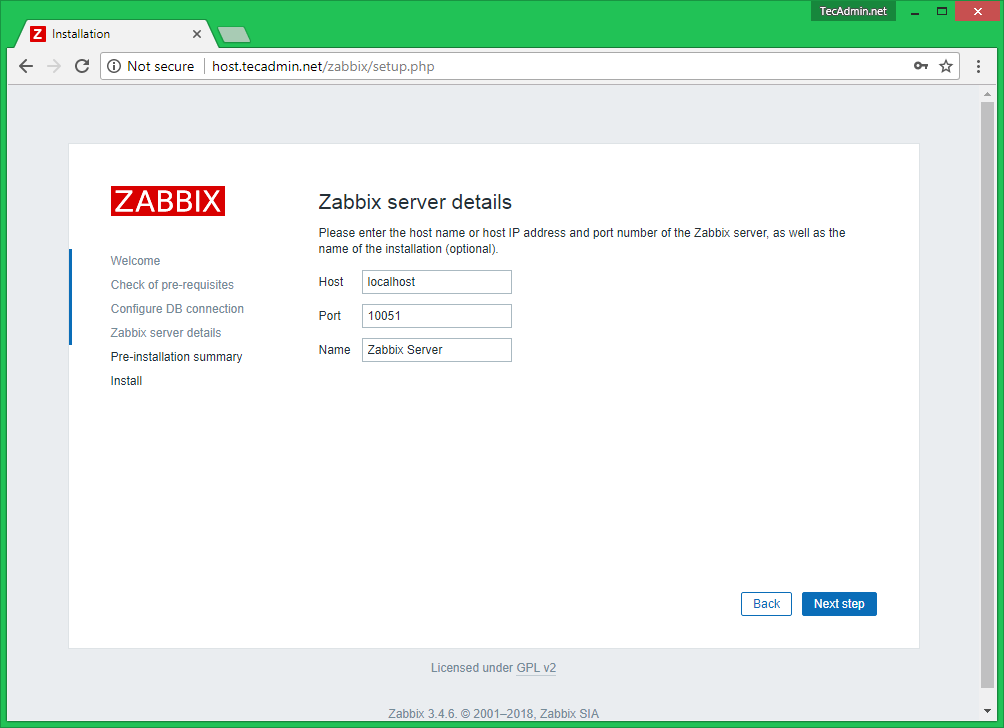
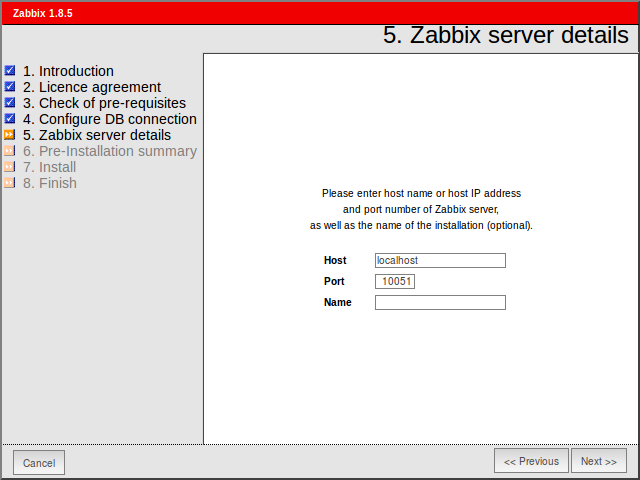
18. Next, supply the Host (or IP Address) and the Port of the Zabbix server (use the host localhost and the port 10051 because Zabbix server is configured to run on the same host as the Zabbix frontend web interface in this tutorial) and a Name for Zabbix frontend installation. When you’re done hit Next to continue.

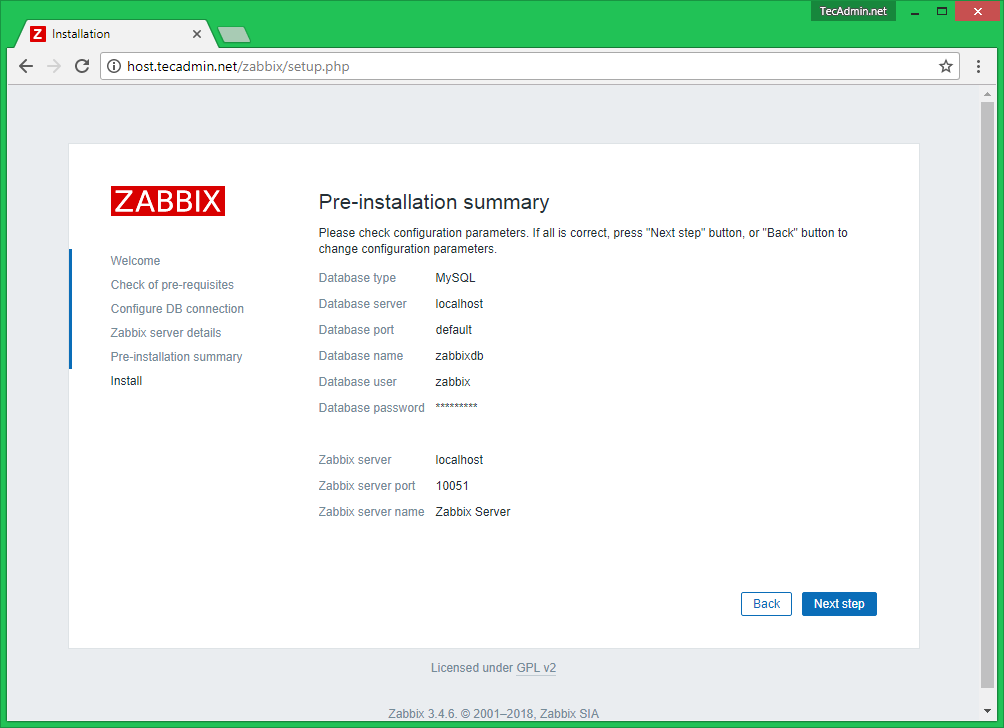
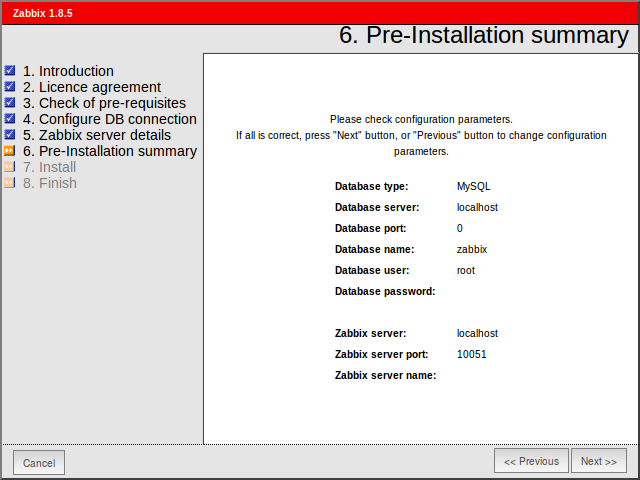
19. Next, check all the configurations parameters.

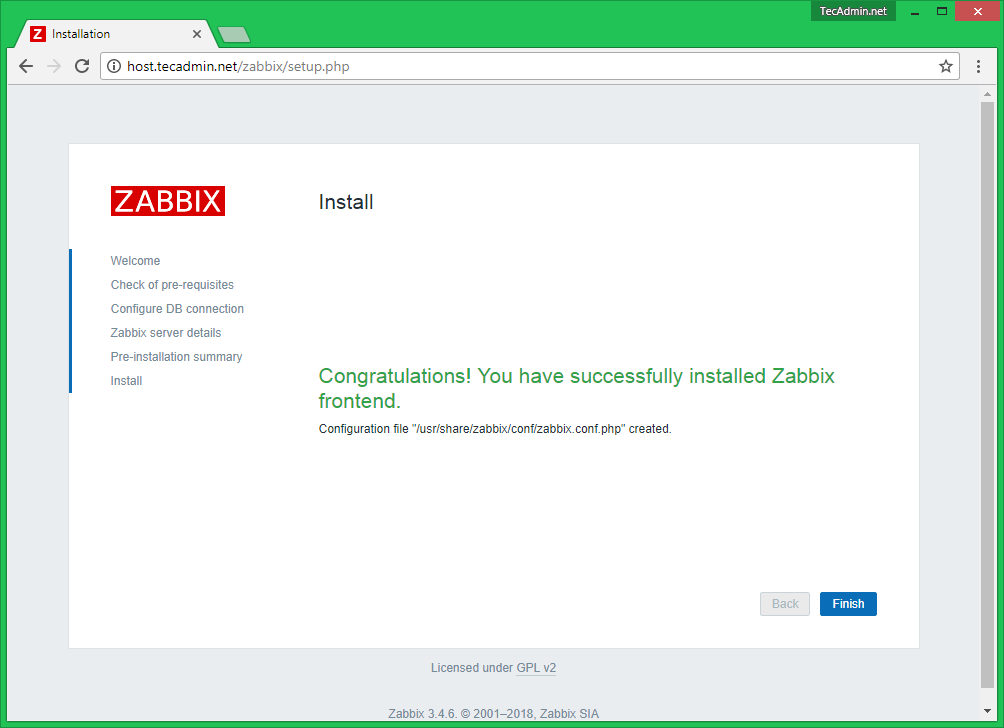
20. After the installation process completes, a congratulations message will appear in your browser. Hit on the Finish button to exit the Zabbix frontend installer.

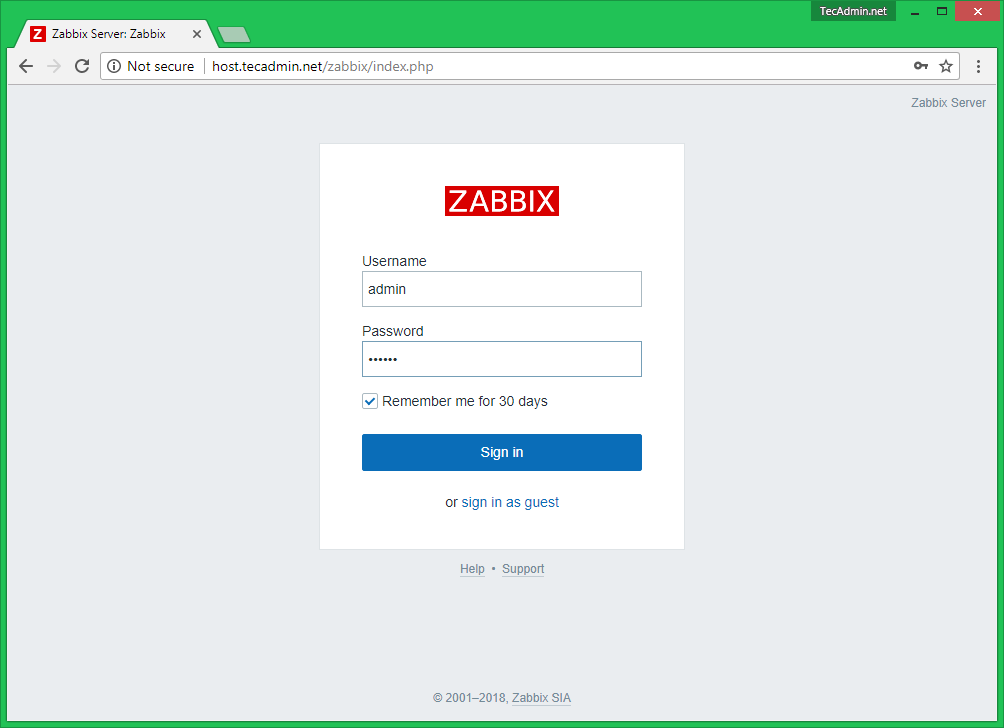
21. Finally, navigate to your server IP address or domain name by appending /zabbix URL address and log in to the Zabbix web admin panel with the default credentials presented below.
22. After you’ve logged in to the Zabbix admin panel, you can start to configure Zabbix and add new network resources to be monitored by the Zabbix server.


That’ll! The next series concerning the Zabbix monitoring system will discuss how to set up the server further using the web interface and how to install and configure Zabbix agents on different Linux distributions or even Windows systems.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
How to Install Zabbix Server 4.0 on Ubuntu 18.04 & 16.04 LTS
Zabbix is an open source software for networks and application monitoring. Zabbix provides agents to monitor remote hosts as well as Zabbix includes support for monitoring via SNMP, TCP and ICMP checks. Click here to know more about zabbix.
This article will help you to step by step install Zabbix on Ubuntu 18.04 & 16.04 LTS systems. If you are using CentOS, RHEL or Fedora then Click here to install Zabbix on CentOS, RHEL or Fedora
Step 1 – Install Apache, MySQL and PHP
You must have a LAMP environment on your server to use Zabbix. If you already have LAMP configured, just skip this step, else install Apache, MySQL, and PHP using the following commands.
Update timezone in php configuration file /etc/php/ PHP_VERSION /apache2/php.ini. Like below:
Step 2 – Enable Required Apt Repository
Before installing Zabbix first configure Zabbix package repository in your system using following commands. Use commands as per your operating system.
Step 3 – Install Zabbix Server
After adding Zabbix apt repository in your system use following command to install Zabbix server. Here zabbix-server-mysql package includes Zabbix server with MySQL support. The zabbix-frontend-php package provides and web interface is written in PHP for the Zabbix server management
Step 4 – Create Database Schema
Now create a database schema for your Zabbix server. Login to your MySQL server using administrative privileges and use the following queries to create MySQL database and user for the Zabbix server.
Also, load the Zabbix database schema to the database created above.
Step 5 – Edit Zabbix Configuration File
Edit Zabbix server configuration file /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.conf in your favorite text editor and update the following database configurations. This will be used by Zabbix server to connect to the database.
Step 6 – Restart Apache and Zabbix
Zabbix creates its own apache configuration file /etc/zabbix/apache.conf and make a link to Apache configuration directory. Let’s use the following command to restart Apache service.
After starting the Zabbix service, let’s go to Zabbix web installer and finish the installation.
Step 7 – Complete Zabbix Web Installer Wizzard
Zabbix web installer can be accessed on /zabbix subdirectory URL on your servers IP or domain. For example, host.tecadmin.net is pointed to my Zabbix server. Now access the Zabbix using the following URL. You must change FQDN as per your setup.
and follow the steps as per given screenshots below.
Zabbix Setup Welcome Screen
This is the welcome screen of Zabbix web installer. Go forward by click on next button.
Check for pre-requisities
Check if your system has all required packages, if everything is ok click next.
Configure DB Connection
Enter database details created in Step #4 and click next to continue.
Zabbix Server Details
This is the host and port of running Zabbix server. As your Zabbix server is running on the same host, so keep the values unchanged. You can give a name for your instance.
Pre-Installation Summary
In this step will show the summary you have entered previous steps, so simply click next.
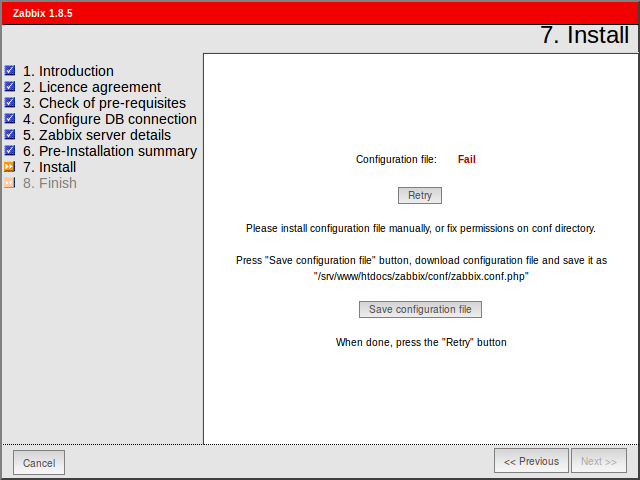
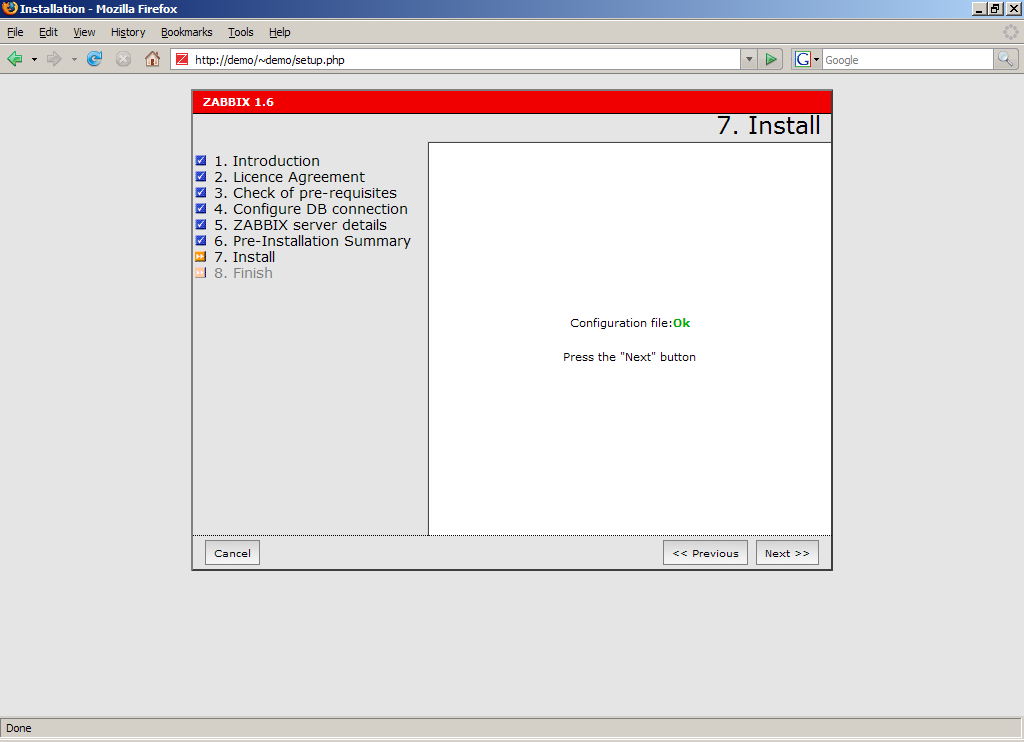
Install Zabbix
If everything goes correctly, You will see a successful installation message on this page. This will also show you a message for the created configuration file.
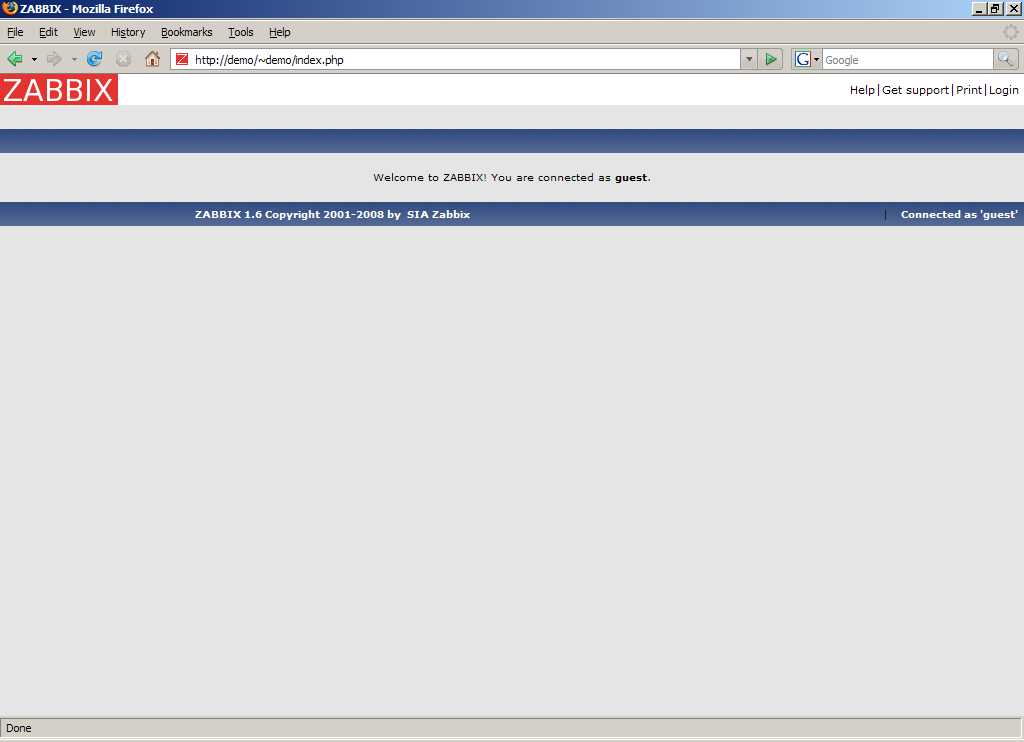
Zabbix Login Screen
Login to Zabbix using default credentials.
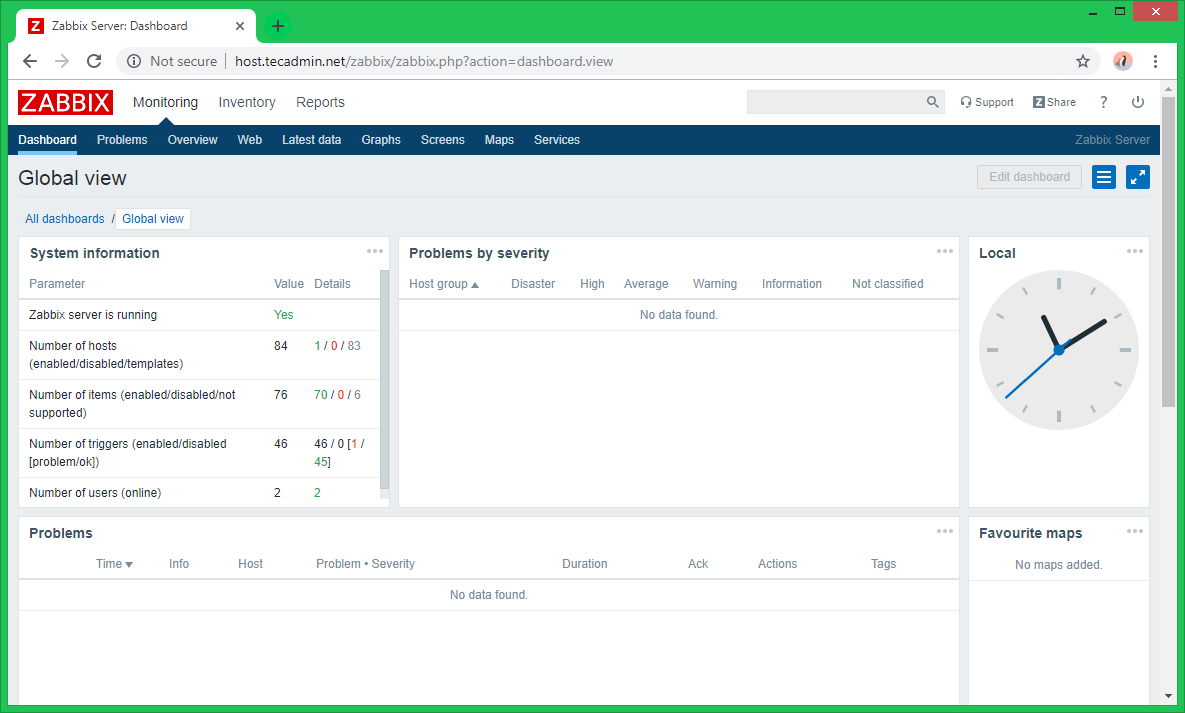
After successful login, You will get Zabbix dashboard like below.
Congratulation! Your Zabbix setup has been completed. Read our next article to Install Zabbix Agent and Add Host in Zabbix Server.
Related Posts
Setup Selenium with Python and Chrome on Ubuntu & Debian
How to Setup Squid Proxy Server on Ubuntu and Debian
How to Install Latest Node.js on Ubuntu
Setting Up Environment Variables on Ubuntu
How to Install Apache Maven on Ubuntu 22.04
Change Screen Resolution of An Ubuntu VM in Hyper-V
41 Comments
i am facing the issue
zabbix server is not running the information displayed may not be current
thank you very much friend
thank you abaout yout attention sir.
Please, can you help wit this error message. I tried to install zabbix 3.4 Everything went successful till when I login to the broswer.
I got the error below:
——————————————————————————–
Cannot connect to the database.
Details
The frontend does not match Zabbix database.
———————————————————————
I created the database manually but the error is still the same as above.
Amigo, como configuro para cambiar la URL desde la IP a un dominio dentro de zabbix? Actualmente tengo problemas el localhost o la ip me levanta mediante LYNX pero dentro en mi ordenador apunto al servidor donde se encuentra zabbix con su IP sin habilitarlo con pto solo xxx.xxxx.xxxx.xxx/zabbix y tarda en conectar hasta que no me levanta el frontend, servicios activos zabbixS, zabbixA,httpd,php. Pero quiero probar intentando cambiar la ip por el dominio. si mi host es el admlog01 como lo adiciono en el archivo etc/hostname
I just ran through this, had problems with my install. On Ubuntu 18.04 fresh install you need to install nmap (apt install nmap)
Hello sir. Thanks for sharing this post. I did step by step until item 7. When I try to run setup from http://zabbix.caruso.com.ar/zabbix, even I tried http://zabbix.caruso.com.ar/zabbix/setup.php, it doesnt’ show the page, I just see the following. Any help?
// VAR TYPE OPTIONAL FLAGS VALIDATION EXCEPTION
$fields = [
‘type’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, null, IN(‘”‘.ZBX_DB_MYSQL.’”,”‘.ZBX_DB_POSTGRESQL.’”,”‘.ZBX_DB_ORACLE.’”,”‘.ZBX_DB_DB2.’”‘), null],
‘server’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, null, null, null],
‘port’ => [T_ZBX_INT, O_OPT, null, BETWEEN(0, 65535), null, _(‘Database port’)],
‘database’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, null, NOT_EMPTY, null, _(‘Database name’)],
‘user’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, null, null, null],
‘password’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, null, null, null],
‘schema’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, null, null, null],
‘zbx_server’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, null, null, null],
‘zbx_server_name’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, null, null, null],
‘zbx_server_port’ => [T_ZBX_INT, O_OPT, null, BETWEEN(0, 65535), null, _(‘Port’)],
// actions
‘save_config’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, P_SYS, null, null],
‘retry’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, P_SYS, null, null],
‘cancel’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, P_SYS, null, null],
‘finish’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, P_SYS, null, null],
‘next’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, P_SYS, null, null],
‘back’ => [T_ZBX_STR, O_OPT, P_SYS, null, null],
];
CSession::start();
CSession::setValue(‘check_fields_result’, check_fields($fields, false));
if (!CSession::keyExists(‘step’)) <
CSession::setValue(‘step’, 0);
>
It looks you need to install libapache2-mod-php package on your system.
Documentation
Sidebar
Table of Contents
3 Installation from sources
You can get the very latest version of Zabbix by compiling it from the sources.
A step-by-step tutorial for installing Zabbix from the sources is provided here.
1 Installing Zabbix daemons
1 Download the source archive
Go to the Zabbix download page and download the source archive. Once downloaded, extract the sources, by running:
Enter the correct Zabbix version in the command. It must match the name of the downloaded archive.
2 Create user account
For all of the Zabbix daemon processes, an unprivileged user is required. If a Zabbix daemon is started from an unprivileged user account, it will run as that user.
However, if a daemon is started from a ‘root’ account, it will switch to a ‘zabbix’ user account, which must be present. To create such a user account (in its own group, «zabbix»),
on a RedHat-based system, run:
on a Debian-based system, run:
On RedHat-based systems, run:
On Debian-based systems, run:
A separate user account is not required for Zabbix frontend installation.
If Zabbix server and agent are run on the same machine it is recommended to use a different user for running the server than for running the agent. Otherwise, if both are run as the same user, the agent can access the server configuration file and any Admin level user in Zabbix can quite easily retrieve, for example, the database password.
3 Create Zabbix database
For Zabbix server and proxy daemons, as well as Zabbix frontend, a database is required. It is not needed to run Zabbix agent.
SQL scripts are provided for creating database schema and inserting the dataset. Zabbix proxy database needs only the schema while Zabbix server database requires also the dataset on top of the schema.
Having created a Zabbix database, proceed to the following steps of compiling Zabbix.
4 Configure the sources
When configuring the sources for a Zabbix server or proxy, you must specify the database type to be used. Only one database type can be compiled with a server or proxy process at a time.
To see all of the supported configuration options, inside the extracted Zabbix source directory run:
To configure the sources for a Zabbix server and agent, you may run something like:
To configure the sources for a Zabbix server (with PostgreSQL etc.), you may run:
To configure the sources for a Zabbix proxy (with SQLite etc.), you may run:
To configure the sources for a Zabbix agent, you may run:
or, for Zabbix agent 2:
A configured Go environment with a currently supported Go version is required for building Zabbix agent 2. See golang.org for installation instructions.
Notes on compilation options:
While config.log has a more detailed description:
5 Make and install everything
If installing from Zabbix Git repository, it is required to run first:
This step should be run as a user with sufficient permissions (commonly ‘root’, or by using sudo ).
Running make install will by default install the daemon binaries (zabbix_server, zabbix_agentd, zabbix_proxy) in /usr/local/sbin and the client binaries (zabbix_get, zabbix_sender) in /usr/local/bin.
Run zabbix_agentd on all the monitored machines.
Make sure that your system allows allocation of 2MB of shared memory, otherwise the agent may not start and you will see «Cannot allocate shared memory for collector.» in the agent log file. This may happen on Solaris 8.
If you have installed Zabbix proxy, run zabbix_proxy.
2 Installing Zabbix web interface
Copying PHP files
Zabbix frontend is written in PHP, so to run it a PHP supported webserver is needed. Installation is done by simply copying the PHP files from the ui directory to the webserver HTML documents directory.
Common locations of HTML documents directories for Apache web servers include:
It is suggested to use a subdirectory instead of the HTML root. To create a subdirectory and copy Zabbix frontend files into it, execute the following commands, replacing the actual directory:
If planning to use any other language than English, see Installation of additional frontend languages for instructions.
Installing frontend
Please see Web interface installation page for information about Zabbix frontend installation wizard.
3 Installing Java gateway
It is required to install Java gateway only if you want to monitor JMX applications. Java gateway is lightweight and does not require a database.
To install from sources, first download and extract the source archive.
Proceed to setup for more details on configuring and running Java gateway.
4 Installing Zabbix web service
Installing Zabbix web service is only required if you want to use scheduled reports.
To install from sources, first download and extract the source archive.
A configured Go version 1.13+ environment is required for building Zabbix web service.
Run zabbix_web_service on the machine, where the web service is installed:
Proceed to setup for more details on configuring Scheduled reports generation.
Documentation
Sidebar
Table of Contents
4 Installation from Source
4.1 Software requirements
Building of Zabbix server or agents from sources requires additional software.
The following software is required to compile Zabbix (required versions):
One of the following database engines:
Usually provided as part of mysql-dev, postgresql-dev, sqlite3-dev packages.
NET-SNMP (or UCD-SNMP) library and header files. Required for SNMP support. Optional.
Iksemel library and header files. Required to enable Jabber messaging. Optional.
Libcurl library and header files. Required for WEB monitoring module. Optional.
C Compiler. GNU C compiler is the best choice for open platforms. Other (HP, IBM) C compilers may be used as well.
GNU Make. GNU Make is required to process Zabbix Makefiles.
4.2 Structure of Zabbix distribution
The directory contains sources for all Zabbix processes except frontends.
The directory contains Makefile and sources for zabbix_server.
The directory contains Makefile and sources for zabbix_agent and zabbix_agentd.
The directory contains Makefile and sources for zabbix_get.
The directory contains Makefile and sources for zabbix_sender.
The directory contains Zabbix include files.
The directory contains start-up scripts for different platforms.
The directory contains files of PHP frontend.
The directory contains SQL script for initial database creation.
Database creation schemas.
Data for initial database creation.
The directory contains upgrade procedures for different versions of Zabbix.
4.3 Zabbix Server
Step 1
Create the Zabbix superuser account
This is the user the server will run as. For production use you should create a dedicated unprivileged account (‘zabbix’ is commonly used). Running Zabbix as ‘root’,’bin’, or any other account with special rights is a security risk. Do not do it!
Zabbix server process (zabbix_server) is protected from being run under root account.
If Zabbix server and agent are run on the same machine it is recommended to use a different user for running the server than for running the agent. Otherwise, if both are run as the same user, the agent can access the server configuration file and any Admin level user in Zabbix can quite easily retrieve, for example, the database password.
Step 2
Extract Zabbix sources
Step 3
Create the Zabbix database
Zabbix comes with SQL scripts used to create the required database schema and also to insert a default configuration. There are separate scripts for IBM DB2, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL and SQLite.
For IBM DB2:
Zabbix frontend uses OFFSET and LIMIT clauses in SQL queries. For this to work, IBM DB2 server must have DB2_COMPATIBILITY_VECTOR variable be set to 3. Run the following command before starting the database server:
For MySQL:
For Oracle (we assume that user zabbix with password password exists and has permissions to create database objects in service ORCL):
Copy directory data/images somewhere on oracle server, e. g. /home/oracle:
Edit file data/images_oracle.sql and set images_dir variable to «/home/oracle/images»:
Proceed with importing data:
Zabbix requires UTF8 database character set. If database is not UTF8 it can be converted by running: ALTER DATABASE NATIONAL CHARACTER SET UTF8;
For PostgreSQL:
For SQLite:
Step 4
Configure and compile the source code for your system
The sources must be compiled for both the server (monitoring machine) as well as the clients (monitored machines). To configure the source for the server, you must specify which database will be used.
However, if you want to compile client binaries along with server binaries, run:
Step 5
Make and install everything
By default, make install will install all the files in /usr/local/sbin, /usr/local/lib etc. Make sure that you have enough permissions.
Note that the port numbers are official Zabbix ports registered in IANA.
Step 7
If you plan to use zabbix_agent instead of the recommended zabbix_agentd, the following line must be added:
Modify default settings in configuration files
Step 8
Create a location to hold configuration files:
Step 9
You need to configure this file for every host with zabbix_agentd installed. The file should contain the IP address of the Zabbix server. Connections from other hosts will be denied. You may take misc/conf/zabbix_agentd.conf as example.
Step 10
For small installations (up to ten monitored hosts), default parameters are sufficient. However, you should change default parameters to maximize performance of Zabbix. See section [Performance tuning] for more details. You may take misc/conf/zabbix_server.conf as example.
Step 11
Run server processes
Run zabbix_server on server side.
Step 12
Run zabbix_agentd where necessary.
4.4 Zabbix Proxy
Zabbix Proxy is a special process. It is not required to run Zabbix.
Step 1
Create the Zabbix superuser account
This is the user the Proxy will run as. For production use you should create a dedicated unprivileged account (‘zabbix’ is commonly used). Running Zabbix Proxy as ‘root’, ‘bin’, or any other account with special rights is a security risk. Do not do it!
Zabbix Proxy process (zabbix_proxy) is protected from being run under root account.
Step 2
Extract Zabbix sources
Step 3
For Oracle (we assume that user ‘zabbix’ with password ‘password’ exists and has permissions to create database objects):
Check file out.log for any error messages. Zabbix requires UTF8 database character set. If database is not UTF8 it can be converted by running: ALTER DATABASE NATIONAL CHARACTER SET UTF8;
The database will be automatically created if it does not exist.
Step 4
Configure and compile the source code for your system
The sources must be compiled to enable compilation of Zabbix Proxy process. To configure the source for the Proxy, you must specify which database will be used.
However, if you want to compile client binaries along with proxy binaries, run:
Step 5
Make and install everything
Step 6
The step is optional. However, it is recommended. On the client (monitored) machines, add the following lines to /etc/services:
Step 7
If you plan to use zabbix_agent instead of the recommended zabbix_agentd, the following line must be added:
Step 8
Create a location to hold configuration files:
For small installations (up to ten monitored hosts), default parameters are sufficient. However, you should change default parameters to maximize performance of Zabbix Proxy. Make sure you have correct Hostname and Server parameters set. You may take misc/conf/zabbix_proxy.conf as example.
Step 9
Run Proxy processes
4.5 Zabbix Agent
Step 1
Create the Zabbix account
This is the user the agent will run as. For production use you should create a dedicated unprivileged account (“zabbix” is commonly used). Zabbix agents have protection against running under root account.
Step 2
Extract Zabbix sources
Step 3
Configure and compile the source code for your system
The sources must be compiled for the client only.
To configure the source for the client:
Step 4
Copy created binaries from bin/ to /opt/zabbix/bin or any other directory. Other common directories are /usr/local/bin or /usr/local/zabbix/bin.
Step 5
The step is not real requirement. However, it is recommended.
On the client (monitored) machines, add the following lines to /etc/services:
Step 6
If you plan to use zabbix_agent instead of the recommended zabbix_agentd, the following line must be added:
Step 7
Create a location to hold configuration files:
Step 8
You need to configure this file for every host with zabbix_agentd installed. The file should contain IP address of Zabbix server. Connections from other hosts will be denied. You may take misc/conf/zabbix_agentd.conf as example.
Step 9
Run zabbix_agentd on all monitored machines
You should not run zabbix_agentd if you have chosen to use zabbix_agent!
Make sure that your system allows allocation of 2MB of shared memory, otherwise the agent may not start and you will see «Can’t allocate shared memory for collector.» in agent’s log file. This may happen on Solaris 8.
4.6 Zabbix WEB Interface
Step 0
Zabbix frontend is written in PHP, so to run it a PHP supported webserver is needed. Installation is done by simply copying the PHP files into the webserver HTML documents directory. It is suggested to use a subdirectory instead of HTML root.
Common locations of the HTML documents directory for Apache web server include:
To create a subdirectory and copy Zabbix frontend files into it, execute the following commands, replacing with the correct path in your case:
When upgrading you simply replace the content of /zabbix with the new files copied over from frontends/php, in this step.
Step 1
Point your browser to Zabbix URL.
Step 2
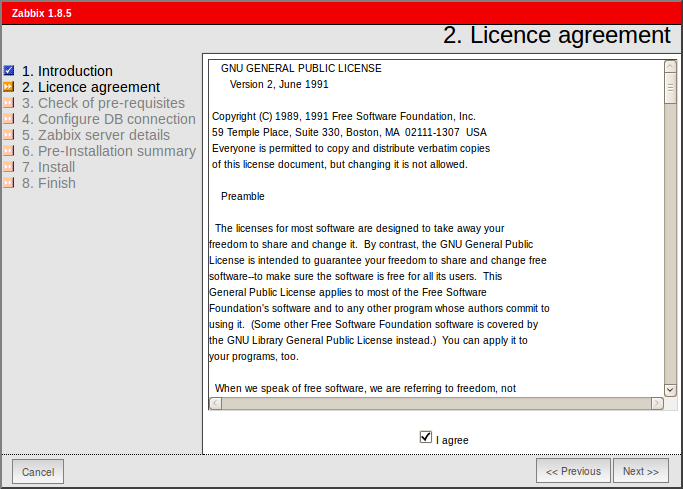
Read and accept GPL v2.
Step 3
Make sure that all software pre-requisites are met.
| Pre-requisite | Minimum value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PHP version | 5.0 | |
| PHP Memory limit | 8MB | In php.ini: memory_limit = 128M |
| PHP post max size | 8MB | In php.ini: post_max_size = 16M |
| PHP max execution time | 300 seconds | In php.ini: max_execution_time = 300 |
| PHP max input time | 300 seconds | In php.ini: max_input_time = 300 |
| PHP database support | One of: IBM DB2, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, SQLite | One of the following modules must be installed: ibm_db2, php-mysql, oci8, php-pgsql, php-sqlite3 |
| **PHP BC math ** | Any | Compiled in or separate module php-bcmath. |
| PHP multibyte support | Any | Compiled in or separate module php-mbstring. |
| GD Version | 2.0 or higher | Module php-gd. |
| Image formats | At least PNG | Module php-gd. |
Step 4
Configure database settings. Zabbix database must already be created.
Step 5
Enter Zabbix Server details.
Step 6
See summary of settings.
Step 7
Download configuration file and place it under conf/.
Step 8
Step 9
For distributed monitoring only!
If used in a distributed environment you have to run only once:
where Node ID is an unique Node identificator. For example:
This will convert database data for use with Node ID ‘1’ and also adds a local node.
Step 10
Zabbix frontend is ready! Default user name is Admin, password zabbix.
How To Install and Configure Zabbix to Securely Monitor Remote Servers on Ubuntu 20.04
The author selected the Computer History Museum to receive a donation as part of the Write for DOnations program.
Introduction
Zabbix is open-source monitoring software for networks and applications. It offers real-time monitoring of thousands of metrics collected from servers, virtual machines, network devices, and web applications. These metrics can help you determine the current health of your IT infrastructure and detect problems with hardware or software components before customers complain. Useful information is stored in a database so you can analyze data over time and improve the quality of provided services or plan upgrades of your equipment.
Zabbix uses several options for collecting metrics, including agentless monitoring of user services and client-server architecture. To collect server metrics, it uses a small agent on the monitored client to gather data and send it to the Zabbix server. Zabbix supports encrypted communication between the server and connected clients, so your data is protected while it travels over insecure networks.
The Zabbix server stores its data in a relational database powered by MySQL or PostgreSQL. You can also store historical data in NoSQL databases like Elasticsearch and TimescaleDB. Zabbix provides a web interface so you can view data and configure system settings.
In this tutorial, you will configure Zabbix on two Ubuntu 20.04 machines. One will be configured as the Zabbix server, and the other as a client that you’ll monitor. The Zabbix server will use a MySQL database to record monitoring data and use Nginx to serve the web interface.
Prerequisites
To follow this tutorial, you will need:
The server that will run the Zabbix server needs Nginx, MySQL, and PHP installed. Follow Steps 1–3 of our Ubuntu 20.04 LEMP Stack guide to configure those on your Zabbix server.
A registered domain name. This tutorial will use your_domain throughout. You can purchase a domain name from Namecheap, get one for free with Freenom, or use the domain registrar of your choice.
Both of the following DNS records set up for your Zabbix server. If you are using DigitalOcean, please see our DNS documentation for details on how to add them.
Additionally, because the Zabbix Server is used to access valuable information about your infrastructure that you would not want unauthorized users to access, it’s important that you keep your server secure by installing a TLS/SSL certificate. This is optional but strongly encouraged. If you would like to secure your server, follow the Let’s Encrypt on Ubuntu 20.04 guide after Step 3 of this tutorial.
Step 1 — Installing the Zabbix Server
First, you need to install Zabbix on the server where you installed MySQL, Nginx, and PHP. Log in to this machine as your non-root user:
Zabbix is available in Ubuntu’s package manager, but it’s outdated, so use the official Zabbix repository to install the latest stable version. Download and install the repository configuration package:
You will see the following output:
Update the package index so the new repository is included:
Then install the Zabbix server and web frontend with MySQL database support:
Also, install the Zabbix agent, which will let you collect data about the Zabbix server status itself.
Before you can use Zabbix, you have to set up a database to hold the data that the Zabbix server will collect from its agents. You can do this in the next step.
Step 2 — Configuring the MySQL Database for Zabbix
You need to create a new MySQL database and populate it with some basic information in order to make it suitable for Zabbix. You’ll also create a specific user for this database so Zabbix isn’t logging in to MySQL with the root account.
Log in to MySQL as the root user:
Create the Zabbix database with UTF-8 character support:
Then create a user that the Zabbix server will use, give it access to the new database, and set the password for the user:
That takes care of the user and the database. Exit out of the database console.
Next you have to import the initial schema and data. The Zabbix installation provided you with a file that sets this up.
Run the following command to set up the schema and import the data into the zabbix database. Use zcat since the data in the file is compressed:
Enter the password for the zabbix MySQL user that you configured when prompted.
This command may take a minute or two to execute. If you see the error ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user «zabbix«@’localhost’ (using password: YES) then make sure you used the right password for the zabbix user.
In order for the Zabbix server to use this database, you need to set the database password in the Zabbix server configuration file. Open the configuration file in your preferred text editor. This tutorial will use nano :
Look for the following section of the file:
These comments in the file explain how to connect to the database. You need to set the DBPassword value in the file to the password for your database user. Add this line after those comments to configure the database:
You’ve now configured the Zabbix server to connect to the database. Next, you will configure the Nginx web server to serve the Zabbix frontend.
Step 3 — Configuring Nginx for Zabbix
To configure Nginx automatically, install the automatic configuration package:
Next, you need to make changes to this file. Open the configuration file:
The file contains an automatically generated Nginx server block configuration. It contains two lines that determine the server name and what port it is listening on:
Uncomment the two lines, and replace example.com with your domain name. Your settings will look like this:
Save and close the file. Next, test to make sure that there are no syntax errors in any of your Nginx files and reload the configuration:
Now that Nginx is set up to serve the Zabbix frontend, you will make some modifications to your PHP setup in order for the Zabbix web interface to work properly.
Note: As mentioned in the Prerequisites section, it is recommended that you enable SSL/TLS on your server. If you would like to do this, follow our Ubuntu 20.04 Let’s Encrypt tutorial before you move on to Step 4 to obtain a free SSL certificate for Nginx. This process will automatically detect your Zabbix server block and configure it for HTTPS. After obtaining your SSL/TLS certificates, you can come back and complete this tutorial.
Step 4 — Configuring PHP for Zabbix
The Zabbix web interface is written in PHP and requires some special PHP server settings. The Zabbix installation process created a PHP-FPM configuration file that contains these settings. It is located in the directory /etc/zabbix and is loaded automatically by PHP-FPM. You need to make a small change to this file, so open it up with the following:
The file contains PHP settings that meet the necessary requirements for the Zabbix web interface. However, the timezone setting is commented out by default. To make sure that Zabbix uses the correct time, you need to set the appropriate timezone:
Uncomment the timezone line highlighted in the preceding code block and change it to your timezone. You can use this list of supported time zones to find the right one for you. Then save and close the file.
Now restart PHP-FPM to apply these new settings:
You can now start the Zabbix server:
Then check whether the Zabbix server is running properly:
You will see the following status:
Finally, enable the server to start at boot time:
The server is set up and connected to the database. Next, set up the web frontend.
Step 5 — Configuring Settings for the Zabbix Web Interface
The web interface lets you see reports and add hosts that you want to monitor, but it needs some initial setup before you can use it. Launch your browser and go to the address http:// zabbix_server_name or https:// zabbix_server_name if you set up Let’s Encrypt. On the first screen, you will see a welcome message. Click Next step to continue.
On the next screen, you will see the table that lists all of the prerequisites to run Zabbix.
All of the values in this table must be OK, so verify that they are. Be sure to scroll down and look at all of the prerequisites. Once you’ve verified that everything is ready to go, click Next step to proceed.
The next screen asks for database connection information.
You told the Zabbix server about your database, but the Zabbix web interface also needs access to the database to manage hosts and read data. Therefore enter the MySQL credentials you configured in Step 2. Click Next step to proceed.
On the next screen, you can leave the options at their default values.
The Name is optional; it is used in the web interface to distinguish one server from another in case you have several monitoring servers. Click Next step to proceed.
The next screen will show the pre-installation summary so you can confirm everything is correct.
Click Next step to proceed to the final screen.
Before you log in, set up the Zabbix agent on your second Ubuntu server.
Step 6 — Installing and Configuring the Zabbix Agent
Now you need to configure the agent software that will send monitoring data to the Zabbix server.
Log in to the second Ubuntu server:
Just like on the Zabbix server, run the following commands to install the repository configuration package:
Next, update the package index:
Then install the Zabbix agent:
While Zabbix supports certificate-based encryption, setting up a certificate authority is beyond the scope of this tutorial. But you can use pre-shared keys (PSK) to secure the connection between the server and agent.
First, generate a PSK:
Show the key by using cat so you can copy it somewhere:
The key will look something like this:
Save this for later; you will need it to configure the host.
Now edit the Zabbix agent settings to set up its secure connection to the Zabbix server. Open the agent configuration file in your text editor:
Each setting within this file is documented via informative comments throughout the file, but you only need to edit some of them.
First you have to edit the IP address of the Zabbix server. Find the following section:
Change the default value to the IP of your Zabbix server:
By default, Zabbix server connects to the agent. But for some checks (for example, monitoring the logs), a reverse connection is required. For correct operation, you need to specify the Zabbix server address and a unique host name.
Find the section that configures the active checks and change the default values:
Next, find the section that configures the secure connection to the Zabbix server and enable pre-shared key support. Find the TLSConnect section, which looks like this:
Then add this line to configure pre-shared key support:
Next, locate the TLSAccept section, which looks like this:
Configure incoming connections to support pre-shared keys by adding this line:
Next, find the TLSPSKIdentity section, which looks like this:
Choose a unique name to identify your pre-shared key by adding this line:
You’ll use this as the PSK ID when you add your host through the Zabbix web interface.
Then set the option that points to your previously created pre-shared key. Locate the TLSPSKFile option:
Add this line to point the Zabbix agent to your PSK file you created:
Save and close the file. Now you can restart the Zabbix agent and set it to start at boot time:
For good measure, check that the Zabbix agent is running properly:
You will see the following status, indicating the agent is running:
The agent will listen on port 10050 for connections from the server. Configure UFW to allow connections to this port:
Your agent is now ready to send data to the Zabbix server. But in order to use it, you have to link to it from the server’s web console. In the next step, you will complete the configuration.
Step 7 — Adding the New Host to the Zabbix Server
Installing an agent on a server you want to monitor is only half of the process. Each host you want to monitor needs to be registered on the Zabbix server, which you can do through the web interface.
Log in to the Zabbix Server web interface by navigating to the address http:// zabbix_server_name or https:// zabbix_server_name :
When you have logged in, click on Configuration and then Hosts in the left navigation bar. Then click the Create host button in the top right corner of the screen. This will open the host configuration page.
Adjust the Host name and IP address to reflect the host name and IP address of your second Ubuntu server, then add the host to a group. You can select an existing group, for example Linux servers, or create your own group. The host can be in multiple groups. To do this, enter the name of an existing or new group in the Groups field and select the desired value from the proposed list.
Before adding the group, click the Templates tab.
Type Template OS Linux by Zabbix agent in the Search field and then select it from the list to add this template to the host.
Finally, click the Add button at the bottom of the form to create the host.
You will see your new host in the list. Wait for a minute and reload the page to see green labels indicating that everything is working fine and the connection is encrypted.
If you have additional servers you need to monitor, log in to each host, install the Zabbix agent, generate a PSK, configure the agent, and add the host to the web interface following the same steps you followed to add your first host.
The Zabbix server is now monitoring your second Ubuntu server. Now, set up email notifications to be notified about problems.
Step 8 — Configuring Email Notifications
Zabbix automatically supports many types of notifications: email, OTRS, Slack, Telegram, SMS, etc. You can see the full list of integrations at the Zabbix website.
As an example, this tutorial will configure notifications for the Email media type.
Click on Administration, and then Media types in the left navigation bar. You will see the list of all media types. There are two preconfigured options for emails: for the plain text notification and for the HTML notifications. In this tutorial you will use plain text notification. Click on Email.
Adjust the SMTP options according to the settings provided by your email service. This tutorial uses Gmail’s SMTP capabilities to set up email notifications; if you would like more information about setting this up, see How To Use Google’s SMTP Server.
Note: If you use 2-Step Verification with Gmail, you need to generate an App Password for Zabbix. You’ll only have to enter an App password once during setup. You will find instructions on how to generate this password in the Google Help Center.
If you are using Gmail, type in smtp.gmail.com for the SMTP server field, 465 for the SMTP server port field, gmail.com for SMTP helo, and your email for SMTP email. Then choose SSL/TLS for Connection security and Username and password for Authentication. Enter your Gmail address as the Username, and the App Password you generated from your Google account as the Password.
On the Message templates tab you can see the list of predefined messages for various types of notifications. Finally, click the Update button at the bottom of the form to update the email parameters.
Now you can test sending notifications. To do this, click the Test underlined link in the corresponding line.
You will see a pop-up window. Enter your email address in the Send to field and click the Test button. You will see a message about the successful sending and you will receive a test message.
Close the pop-up by clicking the Cancel button.
Now, create a new user. Click on Administration, and then Users in the left navigation bar. You will see the list of users. Then click the Create user button in the top right corner of the screen. This will open the user configuration page:
Enter the new username in the Alias field and set up a new password. Next, add the user to the administrator’s group. Type Zabbix administrators in the Groups field and select it from the proposed list.
Once you’ve added the group, click the Media tab and click on the Add underlined link (not the Add button below it). You will see a pop-up window.
Select the Email option from the Type drop down. Enter your email address in the Send to field. You can leave the rest of the options at the default values. Click the Add button at the bottom to submit.
Now navigate to the Permissions tab. Select Zabbix Super Admin from the User type drop-down menu.
Finally, click the Add button at the bottom of the form to create the user.
Note: Using the default password is not safe. In order to change the password of the built-in user Admin click on the alias in the list of users. Then click Change password, enter a new password, and confirm the changes by clicking Update button.
Now you need to enable notifications. Click on the Configuration tab and then Actions in the left navigation bar. You will see a pre-configured action, which is responsible for sending notifications to all Zabbix administrators. You can review and change the settings by clicking on its name. For the purposes of this tutorial, use the default parameters. To enable the action, click on the red Disabled link in the Status column.
Now you are ready to receive alerts. In the next step, you will generate one to test your notification setup.
Step 9 — Generating a Test Alert
In this step, you will generate a test alert to ensure everything is connected. By default, Zabbix keeps track of the amount of free disk space on your server. It automatically detects all disk mounts and adds the corresponding checks. This discovery is executed every hour, so you need to wait a while for the notification to be triggered.
Create a temporary file that’s large enough to trigger Zabbix’s file system usage alert. To do this, log in to your second Ubuntu server if you’re not already connected:
Next, determine how much free space you have on the server. You can use the df command to find out:
In this case, the free space is 77G. Your free space may differ.
Use the fallocate command, which allows you to pre-allocate or de-allocate space to a file, to create a file that takes up more than 80% of the available disk space. This will be enough to trigger the alert:
After around an hour, Zabbix will trigger an alert about the amount of free disk space and will run the action you configured, sending the notification message. You can check your inbox for the message from the Zabbix server. You will see a message like:
You can also navigate to the Monitoring tab and then Dashboard to see the notification and its details.
Now that you know the alerts are working, delete the temporary file you created so you can reclaim your disk space:
After a minute Zabbix will send the recovery message and the alert will disappear from the main dashboard.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to set up a simple and secure monitoring solution that will help you monitor the state of your servers. It can now warn you of problems, and you have the opportunity to analyze the processes occurring in your IT infrastructure.
To learn more about setting up monitoring infrastructure, check out our Monitoring topic page.
Want to learn more? Join the DigitalOcean Community!
Join our DigitalOcean community of over a million developers for free! Get help and share knowledge in our Questions & Answers section, find tutorials and tools that will help you grow as a developer and scale your project or business, and subscribe to topics of interest.
Источники информации:
- http://tecadmin.net/install-zabbix-on-ubuntu/
- http://www.zabbix.com/documentation/current/en/manual/installation/install
- http://www.zabbix.com/documentation/1.8/en/manual/installation/installation_from_source
- http://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-install-and-configure-zabbix-to-securely-monitor-remote-servers-on-ubuntu-20-04