How to learn java
How to learn java
How To Learn Java (Step by Step Guide)
Table of Contents
Java is among the top programming languages of 2022. Java is a robust, statically typed, safe, class-based programming language that has been ruling the web for some time. Java is used in almost all domains like retail, finance, healthcare, logistics, etc. It is compatible and versatile and used for mobile, desktop, and web applications, games, web servers, application servers, database connection, client-side validations, and many more.
The product is free, and open-source adds to its popularity. Also, most graduates learn about C/C++ as part of their curriculum, so learning Java becomes easy and this blog post wil give you a detailed guidelines about how to learn java programming.
Why Should You Learn Java?
Before you know how to learn Java, you should be convinced about why you should learn it!
Learning Java has a lot of advantages when compared to other languages. You can perform any task in Java as there are rich libraries and plugins. Java is platform-independent at the source-code and binary levels, which means the code you compile once can be used anywhere. Since Java is object-oriented, the code is split into independent modules, making the code reusable and free from bugs.
Java has a lot of security features and cross-platform capabilities. It is also the right choice for data science and machine learning, of course, after Python and R. Many websites and web applications continue to be built on the Java platform, thus keeping the demand for Java developers and designers always on the higher side.
Because of its many advantages and unique features, Java was still the most preferred language even after its first release 25 years ago. By learning Java, you get to code in Core Java and move in the direction of becoming a JavaScript expert, a web application developer using J2EE and related web technologies, principal architect, designer, and so on. Most of the Android phones have their operating system written in Java, which is about 88% of the total global smartphone market.
If you learn Java, it also becomes easier for you to learn any other OOP based programming language in less time.
Prerequisites
To learn Java, you must have a little idea about computer science. Java can be your first programming language to learn, but you should first be familiar with the following computer science concepts:
OOP Concepts
Since Java is an Object-Oriented Programming language (OOP), you need to know about polymorphism, inheritance, abstraction, encapsulation, and other OOP concepts. Learn more about OOP concepts.
Data Structures and Algorithms
A data structure is an assembly of data values that are organized, managed, and stored in a particular format. It also defines relationships between data values so that the values can be easily manipulated.
Java uses a lot of collection objects to organize and store data in different ways. For example, a simple list can store some integers, or names of students, or complete set of information that define a person using objects:
This will give the output as [James, Shane, Abby].
Similarly, algorithms like Binary search, merge sort, bubble sort, etc., are widespread, and you should be familiar with them to know the internal workings of Java collections.
How to Set up the Environment
To set up Java in your machine, install JDK or Java Development Kit and JRE, i.e., Java Runtime Engine. You should have the required system memory space to install both. Both JDK and JRE can be downloaded from the Oracle website for any platform (Windows, macOS, Linux, etc.). It is simple to follow the instructions on the screen for installation; it is very straightforward. After installation, you have to set up the environment variables (PATH) on your machine. The path is nothing but the location where JDK and JRE have been installed (most likely C:\Program Files).
IDE (Integrated Development Environment)
Online Compiler
For your own reasons, if you do not want to install an IDE on your system, you can also use an online compiler. Tutorialspoint provides a relatively faster online Java compiler compared to other online compilers.
How to Learn Java
Java is easy to learn, and you don’t have to spend too much time learning the concepts. Once you get the foundations right, you can start practicing.
System.out.println(«Welcome to the Java World!»);
Run this program as a Java application, and the message will be displayed on the console.
Don’t worry about all the keywords used in the program. The point is that it takes just these many steps to make a Java project run! To understand these keywords and modifiers, read this short introduction to Java, and get started. You can take up the following excellent courses to further your practical learning experience:
Java Courses and Tutorials (Free and Paid)
1. Complete Java developer course: Udemy
This paid bestseller course from Udemy teaches core java skills, JavaEE, Spring framework, Android development, etc. The course focuses on Java 8 and 11 and also prepares you for the Oracle Java certification exam. It covers OOP concepts, collection, control flow statements, Generics, concurrency, network programming, and many more introductory and intermediate Java topics. It is reasonably priced, and you get discounts from time to time.
2. Object-Oriented Java Programming: Data Structures and Beyond: Coursera
This is a specialization of about 4-6 months’ worth of content covering Java OOP, data structures and advanced data structures (like graphs), performance tuning, and tips and opportunities for clearing Java interviews. This is an intermediate course and has real-world projects and lectures from Google. You can take up all or individual courses of the specialization. Coursera works on a monthly subscription basis, so one can take up any number of courses.
3. Learn Java: Codecademy
This course covers the fundamental OOP concepts and how they are used in Java to develop web applications. You will be doing a lot of practical projects on different levels. It is an introductory course which doesn’t require any prerequisites. You will learn about conditionals, control flow, Arrays, ArrayList, Strings, inheritance, etc. The code also covers debugging exceptions, compile-time, and run-time errors. Codecademy has both free and paid courses, this is a free one.
4. Pluralsight Java Course
Pluralsight offers a range of Java courses for different levels. Each course is about 3 hours. You can start with the basic course, i.e., working with classes and interfaces, then take up the intermediate courses, like Java design patterns, web fundamentals, persistence API, etc. Take up the Pluralsight subscription, or if this is your first course, you can try it for free.
5. LinkedIn
LinkedIn provides many short courses for learning Java. Few popular courses like Learning Java, Advanced Java Programming, and Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms in Java are some good courses to start with. These three courses together cover the basic and advanced concepts of Java. LinkedIn provides a monthly subscription option, and the first month is free for learners.
For a detailed description and information of the best Java courses visit here.
Java Official Documentation
To learn more about Java’s API and various utility methods, you should always look up the official API documentation page. You will also get to know the inheritance structure, interfaces, abstract classes, utility classes, and other OOP flavors through the API.
Projects
Most tutorials also give hands-on towards the end through projects. However, doing more projects without any external help will boost your confidence and increase your expertise level. Projects will help you master Java as quickly as possible.
Certifications
So, now you are done with learning Java through tutorials and have done some projects. You must be confident enough to take up certifications and add them to your resume. Certifications add a boost to your resume and give you an edge over other candidates with similar experience. Check out the Top Java certifications recommended by Java Developers.
Java Interview Questions
Now, it’s time to put all your knowledge together and prepare for the big day. It would be best if you were thorough with the practical and concept-based questions of Java. For example, the evaluator may ask you to write code for the Fibonacci series or ask you about the implementation for Hashmap! Learn about Garbage collection, collection (LinkedList, Map, Tree, etc.), exception handling, and threads, amongst other topics! These are important questions that are asked in every Java interview. Some crucial questions are:
Check out the complete list of 100+ top Java interview questions that will help you crack even that tough one!
Wrapping Up
We hope you enjoyed reading this guide to learning Java and it urges you to begin coding as soon as you read it. Try it out and let us know your feedback.
Ramya Shankar
A cheerful, full of life and vibrant person, I hold a lot of dreams that I want to fulfill on my own. My passion for writing started with small diary entries and travel blogs, after which I have moved on to writing well-researched technical content. I find it fascinating to blend thoughts and research and shape them into something beautiful through my writing. View all posts by the Author
Best Way to Learn Java
Table of Contents
Learning Java is easy and fun, no matter what background you have. With this comprehensive guide, you will have all the resources that will help you start your Java journey and master the essential concepts.
Java code runs on the Java Virtual Machine, which translates Java code into a language that the OS understands. All these features and more make Java one of the top programming languages of 2022.
Best way to learn Java
Well, there is no shortcut to learning anything, and the same is valid for Java. If you want to master the language (believe me, it is worth it), you have to set it up on your system and get practicing. Download and install JDK (Java Development Kit) and JRE (Java Runtime Environment) and also any IDE that you are comfortable with. Easy Eclipse works just fine for writing programs and building stand-alone applications.
Okay, before we get into the core concepts, here are a few things you should remember always –
Now that we have a positive mindset and zing to learn let us look at all the concepts we need to learn to write efficient code in Java –
Variables and data types
On a day to day basis, we come across different types of data. For example, the telephone number of your car driver is an integer, but his name is a string (array of characters). Same way, the price of petrol that he puts in your vehicle is a floating-point (decimal). Java handles a lot of data types –
One of the best practices in Java is to follow the right naming conventions. Variables (driverName, telephone. etc…) like the above and methods should start with a small case, and the following word begins with a capital letter – driverName. Same way, since a boolean data type returns true or false, it is a good practice to name the variables starting with is, are, has, etc.…
The advantage of storing data in variables is that we can use the variable anywhere in the code. The limit of using a variable is defined by its scope, which can be local, static, or global.
The data types char, int, float, boolean and double are called primitive types, and Java has corresponding objects for each of these. For example, int has Integer; boolean has Boolean, and so on. A string is an object.
So, what do we do with the data? We perform some operations on it!
Operations
For example, based on whether the driver is regular or not, we can give him some incentives or, based on the amount of petrol he fills, we can know how many kilometers he drives.
Conditions
Just like we saw above, the ‘if’ is a condition that tests for something to be accurate and returns results accordingly. It is usually combined with else if and else statements that can handle multiple situations.
Note that && means both the expressions have to be true for the if to be successful.
Functions
A lot of code that we write can be segregated into blocks of code so that many parts of the application can reuse it. Such blocks of the system are called as functions. For example, applying the grade can be a function based on the marks. The system, when divided into smaller functions, looks neat and is easy to understand. It is modular and reusable.
Function names in Java start with the small case, with the following words having the first letter as capital. For example, get grades(float marks) that return a char, isRegular(String driverName) that returns a boolean, and so on.
Okay, now comes the real power of Java.
Object-oriented programming
If you want to get into details of OOPS concepts, go through with the above-given video, which I have embedded in this article previously. Still, for this article, all you need to know is that in OOPS, everything is considered as an object. A pencil is an object, a car, plant, animal, and even a Driver is an object.
Continuing our driver example, let us say, the following attributes identify driver – driverName, joiningDate, isRegular, dateOfBirth, and avgCustomerRating.
Let us say a service provider like Uber, will have many such drivers. Each driver has all these attributes that will be differentiated with their unique values. That means, we can create a class ‘Driver’ with these attributes as the members of the course. Whenever we need to get or set a particular driver’s details, we will create an ‘object’ of the Driver class using the new operator.
When we create the class, we also create the ‘getter and setter’ methods for the members through which we can get individual values of the members. If we have to set the whole object, we can do using a constructor that we should define in the class.
Now, when we want to create an object, we can do so by just calling the new operator and this constructor as –
Data structures and looping
There are many data structures in Java-like arrays, lists, maps, trees, and so on. All these come under the Collection framework except Array, which is part of the java.util package. Learning about Collection will give you immense satisfaction about storing and retrieving data – which means half the battle won for you. Let us do a quick example with arrays. In my article, What is Java, I have used ArrayList to do similar kind of operations, do check that too.
//Set driver details for each driver or fetch it from database or user input
Let us say there are five drivers, and we want to set the salary based on some conditions for each of the drivers. We use a ‘for’ loop for this.
Note that we get each driver’s detail and then do some checks for each of the drivers. After that, we set a value. Here we have hardcoded the cost of Driver to 5, but in a real application, we will fetch that from a database or the console.
User inputs
Consider fetching the driver details from the user. For each driver, let us bring the further information using the for loop we just learned. First, let’s create the array. This time we will not fix the length. Let’s ask the user for it.
If you haven’t created our favorite Driver class, do that now using your IDE. These things are best learned when practiced. To create this class, let us first create a project on the IDE. Create a project of any name, for example, SampleProject. Then create a package named src (which means source code). Inside the package, create the class Driver with the members. With the click of a few buttons, generate getters and setters on the IDE.
Now write or create the constructor as we discussed earlier.
Now, let us create our Test Class, which will have the public static void primary (String args[]) method.
To get input from the user, the best way is to use the ‘Scanner’ method.
After this, we can get the inputs one by one using the next() method of the scanner. The first thing we get is the number of drivers for which information needs to be stored. Then, we create an array of the same length, loop through it, instantiate each object inside the loop, and set the values using constructor or setter methods.
Connecting to the database
For our java code to connect to the database, we need a JDBC driver (which is different from our car Driver). Different databases have different drivers; for example, for MySQL, the driver will be com.mysql.jdbc.Driver. Next, we need to connect to the URL (location) where the database is located. For accessing the database, we need a username and password too. After getting the connection, we can execute queries via code to get or set the necessary details.
For any simple or complex web application, you must know JDBC (Java Database Connectivity). Take up this nice tutorial explaining about JDBC connectivity. You will enjoy learning it all by yourself.
Handling files
File handling in Java is done using two classes FileWriter and FileReader. Java documentation describes all the methods and constructors that are provided with these classes, and they are pretty much straightforward. Earlier, FileInputStream and FileOutputStream were used, but the former two are preferable because they write stream of characters while the latter two are byte stream classes. Remember that with file handling, it is essential to catch exceptions like FileNotFoundException.
Exception handling
Java permits a lot of flexibility. But as a developer, we need to know what are the scenarios where our code can give incorrect results. One such case is the user not entering correct values. For example, if you have set driverName as a String, and the user introduces some numbers or random characters, we should be able to handle such cases and inform the user. These are generally done on the client-side using JavaScript, but JavaScript can be disabled. As developers, we need this validation done from our side too. Some standard exceptions are-: NullPointerException: when we are trying to do some operation on a null object.
NumberFormatException: when we try to convert a string into a number, and it is not valid.
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: when we try to access an element more than the size of the list
There are many such checked and unchecked exceptions in Java that you need to be aware of for robust code.
Garbage collection
While we always loathe when we think of garbage, Java GC is something that you will love to know about it. As a programmer, you don’t have to worry about how the garbage collector thread works. It just does its job quietly. However, if you are interested, it makes for a good read and is asked about in some core java interviews too. Read about Java garbage collection here.
Multithreading
To handle concurrency, Java supports multithreading and has efficient built-in methods. While many people find Threads to be a dreadful topic, it is not so in the case of Java. Threads do behave differently at times, but we all have mood swings at some point, don’t we? If handled delicately, threads are always in their best mood just like us.
For example, you are trying to book a cab. While you check out multiple options, a couple of more users try to seek the same cab from the same starting point.
Who gets the booking?
The first person to confirm and get the handle! If you make your booking fast, the ride is locked for you — the other riders than don’t see this particular cab. However, if you cancel the cab for some reason, the lock is released, and the cab is available for others. The same concept is with the threads. If one thread is changing a part of the code which others want to access, the others have to wait for their turn so that all the threads don’t work on the same data at the same time and corrupt it. Multithreading has made our life easy – think of online ticketing, banking transactions, and all secure transactions – if everyone had access to the same data at the same time, the world would be full of chaos!
I learned threads through this excellent brain friendly guide by Kathy Sierra. I don’t know if it’s their familiar way of explaining or the head first approach, the concept was planted so permanently in my mind that I could write a whole 2-page program within minutes during an interview. The interviewer (who was eventually my manager) was stunned and talked about it even days after I joined the company!
Creating web applications
Okay, so now we have come to the real thing! The whole point of learning Java is to create robust web applications that are interactive and fast. If you already have the IDE setup, all you need to do is install J2EE components into your IDE. Read this blog to understand how J2EE helps build scalable and robust web applications.
To build web applications, you will need to know the basics of servlets and JSP (Java Server Pages), which are easy to learn. There are many other frameworks like Spring, Struts, which give powerful web applications when combined with Java. Here is an excellent tutorial that covers all of them in a single course and with a practical (hands-on) approach.
Creating web services
Java web services are used to interact with the different layers of an MVC architecture. There are two ways for Java Web Service (JWS) application to communicate – SOAP and RESTful services. The communication is done through WSDL (Web Services Description Language). Read this extensive tutorial that covers all about SOAP and REST to get you started on Java web services.
Conclusion
In this blog, I have given you a lot of resources and links to various subtopics that you need to know to master Java. There are a lot of other OOPS concepts that Java uses – like boxing, unboxing, design patterns, generics, and so on that help you with better coding practices, but these are the concepts that will help you build a functional application. While you are at it, you should also make sure your understanding is correct by checking out if you can answer these Java Interview Questions! Here is also a nice paid tutorial that you can take up once you are done playing with the basics. Do check out our comprehensive list of Java books that will make learning Java, an enjoyable and thorough experience for you.
Ramya Shankar
A cheerful, full of life and vibrant person, I hold a lot of dreams that I want to fulfill on my own. My passion for writing started with small diary entries and travel blogs, after which I have moved on to writing well-researched technical content. I find it fascinating to blend thoughts and research and shape them into something beautiful through my writing. View all posts by the Author
How to start learning Java
The Java language
Low barrier to entry.
Learning Java is easier than most languages with a C-like syntax.
Object orientation.
Programs in Java are built based on objects and interactions between objects. This lets you enjoy all the advantages of OOP.
Portability.
Because an interpreter (the Java virtual machine) is used, programs can be run on various platforms and devices.
Platform independence
A Java program written for one platform is compiled into intermediate byte code that can be run on other platforms, because it is interpreted by a JVM for each specific platform.
Advanced multithreading.
Java tools let you control the execution of multiple threads, which means you can create multithreaded applications.
Security.
Because the JVM has built-in bytecode verification, and Java has no manual memory management, tracks stack overflows, and has various APIs that let you control security, you can create really safe applications in Java.
Fault tolerance.
The exception mechanism increases programs’ fault tolerance and reduces the number of errors, both at compile time and run time.
Interpretability.
The Java interpreter can execute Java bytecode on any machine that has a JVM and JRE.
Distributability.
Java has tools for creating distributed applications.
Performance.
A JIT (just-in-time) compiler provides high speed performance comparable to C and C++.
How to start programming in Java?
What do you need to program in Java?
First, you need to install software for developing and running programs — the Java Development Kit (JDK). After that, configure the JDK on your computer, download and install an integrated development environment (IDE), which is an environment for software development. The most popular IDE is IntelliJ IDEA. Alternatives are Eclipse, NetBeans, JCreator, and even an ordinary text editor.
How to Learn Java From Scratch with a Right Learning Plan?
Why learn Java?
High demand for Java developers. With thousands of Java programmers around the world, there is still demand for new programmers. This is because Java is everywhere: Android phones are increasing in numbers; many games are developed and maintained in Java; not to mention the extensive use of Java on enterprise-level server applications.
Platforms and devices variety. Java can run on a wide variety of devices like cell phones, laptops, PCs or gaming consoles. It also can function on almost any operating system e.g. Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, etc.
Strong community with huge learning resources. Java has a very powerful beginner-friendly community where members discuss the features and future of the language and share learning resources. There are countless courses and tutorials teaching Java from beginner to master levels.
Common Problems When Starting From Scratch
Imbalance Between Theory and Practice
Lack of Planning
Inattention to Errors And the Debugging Process
Studying Alone
Ways to Improve
The Course is 80% Practice. It has 1200 Practical Tasks that start from the very first lesson.
The course is distinctly structured. The CodeGym course contains 600 lessons. Each of them explains one topic so that the student can focus on that topic without being distracted.
IntellijIDEA integration. This offers you debugging tools while coding.
Strong Java community. With a large community of like-minded people, you won’t be alone. You’re always a few clicks away from the help you need when you are really stuck.
How to Become a Java Developer From Scratch?
Java Core. These are the core concepts that you need to master to develop meaningful programs. You need to understand what are objects, classes, methods, what data types are supported by Java, and what operations are valid on them. Moreover, how can your program execute certain code under some conditions (called if statements) and how to make it repeat certain tasks (called loop statements).
Java Syntax. This is Java’s spelling and grammar. It’s the set of rules that define what combination of keywords, symbols, and operators are right and acceptable as Java code.
Object-oriented Programming (OOP). It’s a programming model where programs are developed around the idea of “objects” rather than “functions” and these objects have attributes and behaviors. Once you learn it, you can start doing class abstractions or inheritance, or many other cool things.
Java Collections. This allows you to interact with individual objects as one unit (a collection).
Java Exceptions. Exceptions are events (errors) that arise when something goes wrong during the execution of the code. They’re very useful for debugging and making sure that the program runs smoothly against unexpected circumstances.
Input/Output Streams. Streams are how Java handles input and output operations, such as reading from or writing to a file.
Algorithms and Puzzles. Algorithms are a set of instructions on how to perform a specific task (e.g. sorting algorithms — step-by-step instructions on how to sort elements). They can be very useful to help you understand how computers work and how to approach certain problems in the most effective ways. In the same vein, puzzles can challenge you to think outside the box to find creative ways to solve problems.
Java Multithreading. This refers to making different parts of your code run concurrently to make the maximum use of the CPU.
Java Patterns. This concept is related to program design; how to write a program that makes use of well-developed programming patterns to save time and resources.
Unit Testing. This is an integral part of developing your program and an ongoing process. It entails making tests for different parts of your code; with the unit as the smallest testable part of your code.
Lambda Expressions. They were added in Java 8. They enable treating functions as a method argument or code as data.
10 Ways to Learn Java in just a Couple of Weeks
Java is not to be confused with JavaScript, it has been built as a Write once, run anywhere language – which in simple technical terms means that it can be run on pretty much any device that there is.
What is Java Programming Language?
We interact with Java on a daily basis, whether we acknowledge that fact or not, and on many occasions – a website might tell us that we need to install Java in order to browse it, this goes a lot for websites that are flash dependent and have some kind of flash components integrated within the core system.
Java is also one of those programs that you usually download straight away, after a purchase of a new computer – I’m not quite sure whether anyone ships Java as a default program within the operating system. Its history with security issues is not one of the most pleasant, but for the most part, it has made the language as mature as it is.
From laptops to datacenters, game consoles to scientific supercomputers, cell phones to the Internet, Java is everywhere!
as we can see with the above statistics, the Java programming language is very sought after, and there is definitely a big market for it.
Salary for Java Programmers
I’d love to briefly touch the subject of Java salaries, and how much you’re able to earn – within a reasonable amount of time – by becoming a full-time Java developer.
Programming Java for Beginners
I published this post a little while ago, and ever since then, I have received mixed feedback, mostly about the fact that people are saying it takes a lot longer than just a couple of weeks to learn this programming language. I’ve to say that I can’t disagree, and because of that – I’ve added this additional course that I suggest you take part in.
It does cost a little bit of money, but keep in mind that you’ll be getting access to a unique and separate community section in which you’ll find all 35,000 students who’ve taken part in this course. It contains over 10 hours of content, more than 100 lectures, and hundreds of discussions on the most problematic of topics.
You won’t find a better way to learn Java than by taking part in this course, the ultimate best alternative would be to learn in real-life from an expert, but that isn’t always that easy. I’d be more than happy to answer questions about this course.
1. Java Basics
It doesn’t really matter which programming language we’re going to learn, we will always begin with the basics, and Java is no exception. Thankfully, the official Oracle (company behind Java) website has a great introduction to Java, explaining what it is and showing you the basics of how it works.
You will also find that there a lot of resources for further learning, but most importantly – this page will help you get started with all the necessary tools and other stuff that’s required to begin learning Java.
2. Introduction to Programming in Java

This is another great resource, and not only because it is being presented by one of the top universities in the world, but you’re also bound to learn quality stuff from taking this tiny course. It will force you to read a ton of stuff, all of which is essential to the process of learning Java.
It has also been acclaimed as one of the most beginner friendly resources for learning Java, no matter how technical it might seem at first. It’s full of images, samples, preview code and documentation to get you going.
3. Learn Java Online
In recent years, interactive tutorials have become quite a thing, and so I feel obliged to include some links to what’s available on the web in this list. It’s worth knowing that you won’t learn a whole lot from this interactive tutorial (let us be honest), but I recommend it as a starting point for the first couple of chapters for any of the books you pick.
Plus, its always nice to be able to load some code and test it, without having to worry about launching your IDE to do it.
4. Learn Java the Hard Way
You can see (and work with) the first 16 chapters for free, online, the link is here. I think many people are going to love this one, it is friendly designed combined with friendly exercises, what more could you ask for.
5. Programming by Doing

This website is built by the same person that has published the above book I listed, this site is also the inspiration for that book. You’ll find a lot of challenges that do not require a lot of programming skills at first, but as you advance through the challenges they’ll get tougher and tougher.
I’ve always believed that the absolute best way of learning something is by doing it first, testing and then going at it once again. Just pick any of the tutorials or books in this list and you’ll be ready to go.
6. Java for Complete Beginners
Some people prefer to learn from the video content, that’s totally acceptable. Sometimes, when you’re busy and got a lot of things to do, it’s better to have access to videos that you can just repeat whenever, to grasp some of the essentials of a programming language, in this case, Java.
It’s a free Udemy (you’ll need an account to view it) course that has got well over 100,000 students enrolled, and is one of the most popular courses on the site. It’s led by John Purcell, a software engineer who has had many years of experience with Java.
You’ll get nearly 20 hours of content, with over 70 lectures in total. If you don’t know Udemy, then you will also get access to a very large support community (all those 100k students who have done/are doing this course), and there is an in-built support system for asking questions.
7. CodingBat
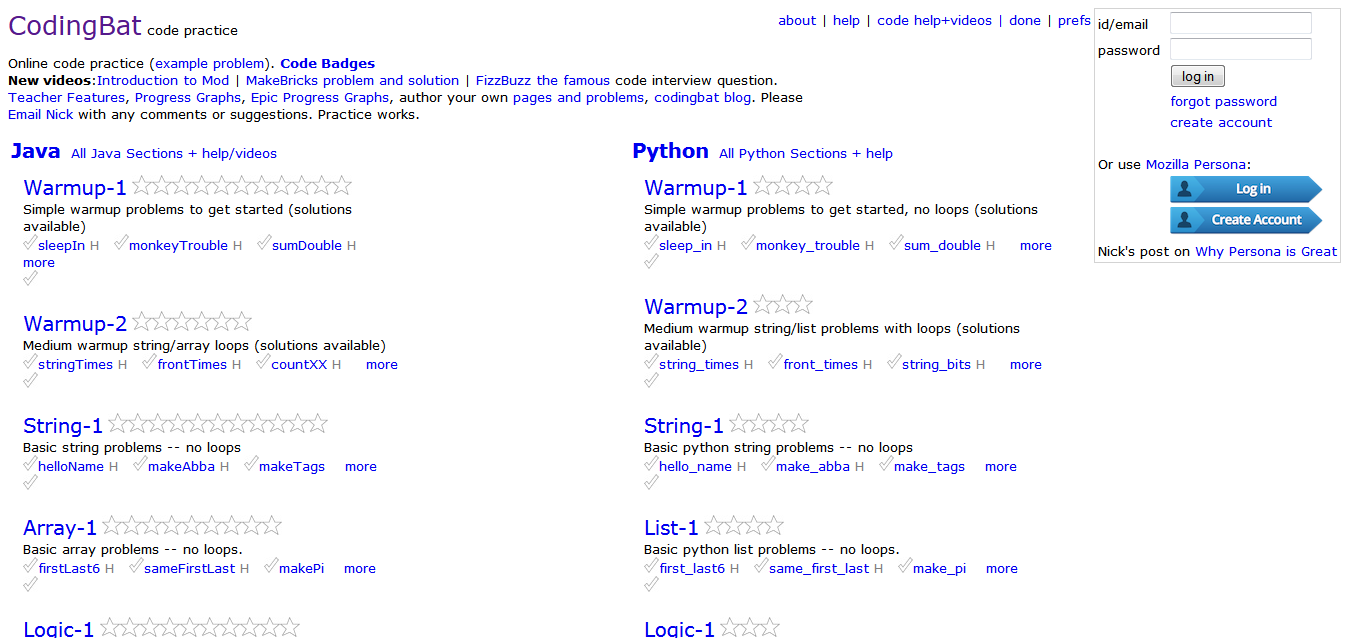
Don’t let the design fool you if anything – it will keep you distraction free. CodingBat (formerly JavaBat) is one of the best ways of learning Java for free, interactively within your browser. It’s the second site in our list that offers interactive education, I do have to say its also better than the previous site.
The issues that you might experience with CodingBat is that unlike sites like Codecademy, which explain everything from bottom to top, step-by-step, CodingBat is more of an do what you know and pick what you’re capable of. Just don’t confuse it for being unorganized, there are plenty of tutorials for each section and you’ll be learning rather quickly.
8. Java (Beginner) Programming Tutorials
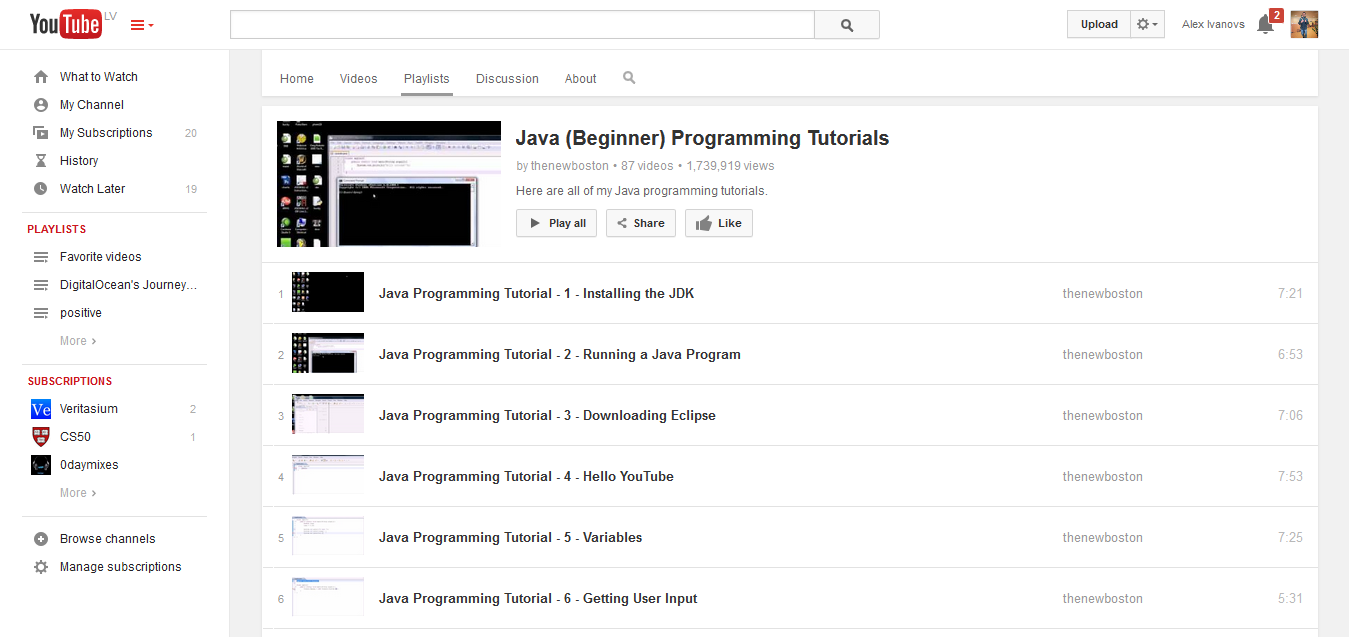
The New Boston is known for having great and comprehensive introduction videos for a lot of Java Programming Languages, and Java is no exception. You’ll find 80 step-by-step videos for learning Java and all that it has to offer, though I think its a little bit dated now. (Java 7)
Don’t count on what I said about it being dated, it’s still an incredibly useful resource for anyone who wants to begin to learn Java with determination, plus it doesn’t require of you to signup unlike Udemy does. The comments are quite insightful, for some of the videos.
9. Object-Oriented programming with Java
Another University course, it will take you roughly 6 weeks to complete it. Very beginner friendly, and everything can be done from within the browser. It also has one of the best gettings started tutorials on how to install Java and the necessary tools. In the course, you will learn all the basics of computer programming, algorithms and object-oriented programming using the Java programming language.
There is also part 2 available, which is another 6 weeks of programming. In total, you’ll be looking at 12-13 weeks of learning Java. By the end of it, you should know how to build your own apps, and how to think like a Java programmer. You’ll also be ready to advance to higher rankings, and explore the language much more in-depth.
10. Java Programming Exercises
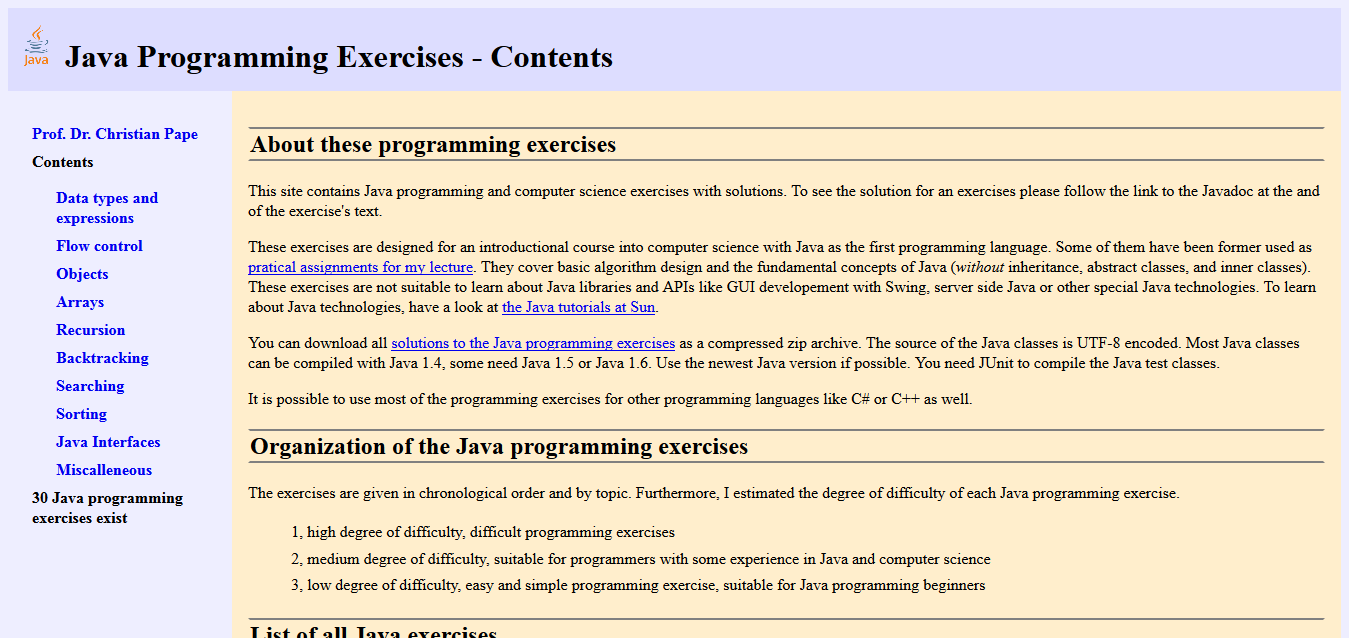
I’m wrapping this up by giving you another website for Java programming exercises, specifically designed for Java that also contains the answers to each of the puzzles. It’s so important to practice, especially when it comes to a language like Java – which at first is not at all easy to master.
In total there are thirty exercises for you to try, and instead of saying ‘It’s impossible’ – take a break and come back to it later, that’s usually when the answer arrives.
10 Ways to Learn Java
It might not be a transparent as my learn Python post was, I certainly blame the fact that it is not as easy of programming language to learn, and does require higher levels of attention to detail. It’s among the top programming languages to learn this year, and it has a great deal of community behind it.
By which I mean that it’s advised of you to join sites like StackOverflow, and Reddit – for finding answers to common questions, and learning more by asking questions yourself. Without asking questions, we’re just telling ourselves we can live without a solution when that is not entirely the case.
You can try out other online tutorials such as ‘Java for beginners Step-by-step handson guide to Java’ which is a great resource if you are a beginner.
I hope the resources, books, and website in this post will be of help for you, and whether you do become a professional Java developer or not, it would be nice of you to pass this on to your friends who’re looking to join the development community. Good luck!