Thin parts like thread that can be made into cloth
Thin parts like thread that can be made into cloth
fibre
Смотреть что такое «fibre» в других словарях:
fibre — [ fibr ] n. f. • 1372; lat. fibra 1 ♦ Anat. Formation élémentaire, végétale ou animale, d aspect filamenteux, se présentant généralement sous forme de faisceaux. Fibre conjonctive, musculaire, nerveuse. ⇒ nerf. Petite fibre. ⇒ fibrille. ♢ Cour.… … Encyclopédie Universelle
Fibre — zur Verwendung als Besatzmaterial für Bürsten Fibre (engl.=Faser) ist eine gelbe Naturfaser. Sie wird aus den Blattrippen hauptsächlich zweier Agavenarten gewonnen, die auf dem mexikanischen Hochplateau wachsen. Ursprünglich wurden die Blätter… … Deutsch Wikipedia
fibre — UK US /ˈfaɪbər/ noun UK (US fiber) ► [C or U] a thread like part made from plants or artificial material which can be made into products: »Natural fibres such as cotton tend to be cooler. »artificial/man made/synthetic fibre(s) »They use… … Financial and business terms
fibre — (US fiber) ► NOUN 1) a thread or filament from which a plant or animal tissue, mineral substance, or textile is formed. 2) a substance formed of fibres. 3) dietary material containing substances such as cellulose, that are resistant to the action … English terms dictionary
fibre — n. Same as
Fibre — [dt. (Glas )Faser], britische Schreibweise für Fiber … Universal-Lexikon
fibré — fibré, ée (fi bré, brée) adj. Synonyme de fibreux … Dictionnaire de la Langue Française d’Émile Littré
fibre — British English spelling of FIBER (Cf. fiber) (q.v.); for spelling, see RE (Cf. re) … Etymology dictionary
fibre — is the spelling in BrE and fiber in AmE … Modern English usage
fibre — FIBRE. s. f. On appelle ainsi Certains filaments deliez qui se trouvent dans toutes les parties charnuës ou membraneuses du corps de l animal, L alongement des fibres. le relaschement des fibres. l accourcissement des fibres. les fibres des… … Dictionnaire de l’Académie française
fibre — [fī′bər] n. Brit. sp. of FIBER … English World dictionary
fibre
1 fibre
2 fibre
3 fibre
4 fibre
5 fibre
glass fibre — стекловолокно, стеклянное волокно
fibre composite — волоконный композиционный материал, волокнит
6 fibre
7 fibre
8 fibre
волокно
Длинная узкая клетка или группа клеток, из которых в основном состоит древесина.
http://www.wood.ru/ru/slterm.html
Тематики
оптическое волокно
волокно
Оптический волновод ВОСП, выполненный в виде нити из диэлектрических материалов с покрытием.
[ ГОСТ 26599-85]
оптическое волокно
волокно
Оптический волновод из диэлектрического материала (обычно стекло, кварц или полимер) в форме тонкой нити.
[ http://www.lexikon.ru/dict/net/index.html]
волокно оптическое
Диэлектрический волновод для передачи информационных сигналов в диапазоне волн оптического излучения
[ОАО РАО «ЕЭС России» СТО 17330282.27.010.001-2008]
EN
optical fibre
filament-shaped waveguide made of dielectric materials for guiding optical waves
Source: 704-02-07 MOD, 731-02-01 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-35]
FR
fibre optique, f
guide d’ondes en forme de filament, composé de substances diélectriques et destiné à guider des ondes optiques
Source: 704-02-07 MOD, 731-02-01 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-35]
Тематики
3.4 волокно (fibre): Частица длиной более 100 мкм с соотношением длины к ширине не менее 10:1.
3.1.5 волокно (fibre): Частица вытянутой формы, длина которой превышает ширину в 10 или более раз (ИСО 14644-1, пункт 2.2.7).
2.66 волокно (fibre): Частица (2.102) вытянутой формы, длина которой превышает ширину в 10 или более раз.
[ИСО 14644-1:1999, статья 2.2.7], [ИСО 14644-5:2004, статья 3.1.5]
4.17 волокно (fibre): Частица вытянутой формы с минимальным отношением длины к толщине 3:1.
9 fibre
10 fibre
11 fibre
12 fibre
fibre composite — волоконный композиционный материал, волокнит
13 fibre
14 fibre
15 fibre
fibre diagram — диаграмма волокна; физер-диаграмма
16 fibre
fibre composite — волоконный композиционный материал, волокнит
17 fibre
fibre composite — волоконный композиционный материал, волокнит
18 fibre
19 fibre
20 fibre
См. также в других словарях:
fibre — [ fibr ] n. f. • 1372; lat. fibra 1 ♦ Anat. Formation élémentaire, végétale ou animale, d aspect filamenteux, se présentant généralement sous forme de faisceaux. Fibre conjonctive, musculaire, nerveuse. ⇒ nerf. Petite fibre. ⇒ fibrille. ♢ Cour.… … Encyclopédie Universelle
Fibre — zur Verwendung als Besatzmaterial für Bürsten Fibre (engl.=Faser) ist eine gelbe Naturfaser. Sie wird aus den Blattrippen hauptsächlich zweier Agavenarten gewonnen, die auf dem mexikanischen Hochplateau wachsen. Ursprünglich wurden die Blätter… … Deutsch Wikipedia
fibre — UK US /ˈfaɪbər/ noun UK (US fiber) ► [C or U] a thread like part made from plants or artificial material which can be made into products: »Natural fibres such as cotton tend to be cooler. »artificial/man made/synthetic fibre(s) »They use… … Financial and business terms
fibre — (US fiber) ► NOUN 1) a thread or filament from which a plant or animal tissue, mineral substance, or textile is formed. 2) a substance formed of fibres. 3) dietary material containing substances such as cellulose, that are resistant to the action … English terms dictionary
fibre — n. Same as
Fibre — [dt. (Glas )Faser], britische Schreibweise für Fiber … Universal-Lexikon
fibré — fibré, ée (fi bré, brée) adj. Synonyme de fibreux … Dictionnaire de la Langue Française d’Émile Littré
fibre — British English spelling of FIBER (Cf. fiber) (q.v.); for spelling, see RE (Cf. re) … Etymology dictionary
fibre — is the spelling in BrE and fiber in AmE … Modern English usage
fibre — FIBRE. s. f. On appelle ainsi Certains filaments deliez qui se trouvent dans toutes les parties charnuës ou membraneuses du corps de l animal, L alongement des fibres. le relaschement des fibres. l accourcissement des fibres. les fibres des… … Dictionnaire de l’Académie française
fibre — [fī′bər] n. Brit. sp. of FIBER … English World dictionary
fibre
moral fibre — моральная устойчивость
Смотреть что такое «fibre» в других словарях:
fibre — [ fibr ] n. f. • 1372; lat. fibra 1 ♦ Anat. Formation élémentaire, végétale ou animale, d aspect filamenteux, se présentant généralement sous forme de faisceaux. Fibre conjonctive, musculaire, nerveuse. ⇒ nerf. Petite fibre. ⇒ fibrille. ♢ Cour.… … Encyclopédie Universelle
Fibre — zur Verwendung als Besatzmaterial für Bürsten Fibre (engl.=Faser) ist eine gelbe Naturfaser. Sie wird aus den Blattrippen hauptsächlich zweier Agavenarten gewonnen, die auf dem mexikanischen Hochplateau wachsen. Ursprünglich wurden die Blätter… … Deutsch Wikipedia
fibre — UK US /ˈfaɪbər/ noun UK (US fiber) ► [C or U] a thread like part made from plants or artificial material which can be made into products: »Natural fibres such as cotton tend to be cooler. »artificial/man made/synthetic fibre(s) »They use… … Financial and business terms
fibre — (US fiber) ► NOUN 1) a thread or filament from which a plant or animal tissue, mineral substance, or textile is formed. 2) a substance formed of fibres. 3) dietary material containing substances such as cellulose, that are resistant to the action … English terms dictionary
fibre — n. Same as
Fibre — [dt. (Glas )Faser], britische Schreibweise für Fiber … Universal-Lexikon
fibré — fibré, ée (fi bré, brée) adj. Synonyme de fibreux … Dictionnaire de la Langue Française d’Émile Littré
fibre — British English spelling of FIBER (Cf. fiber) (q.v.); for spelling, see RE (Cf. re) … Etymology dictionary
fibre — is the spelling in BrE and fiber in AmE … Modern English usage
fibre — FIBRE. s. f. On appelle ainsi Certains filaments deliez qui se trouvent dans toutes les parties charnuës ou membraneuses du corps de l animal, L alongement des fibres. le relaschement des fibres. l accourcissement des fibres. les fibres des… … Dictionnaire de l’Académie française
fibre — [fī′bər] n. Brit. sp. of FIBER … English World dictionary
Textiles – текстильные изделия на английском языке
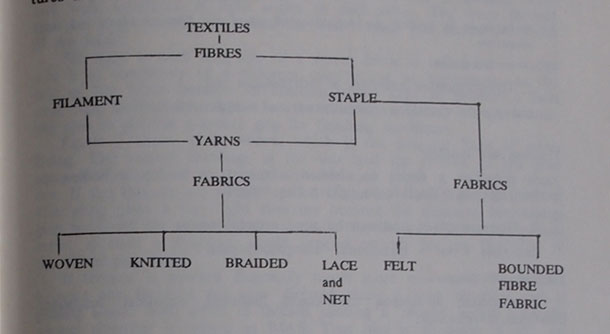
It is generally accepted that a textile is a fabric made from fibres. (Принято считать, что текстильное изделие – это ткань, сделанная из волокна.) But Figure 1 shows that the fibres may either be converted into yarn first and then the yarns put together to make fibres, or the fibres can be converted directly into a fabric. (Но на Рисунке 1 видно, что волокно может быть преобразовано сначала в пряжу, а потом из этой пряжи делают ткани, либо волокно может быть сразу преобразовано в ткань.)
Figure 1 (Рис.1.)
But not all fibres are suitable for textile purposes because a textile fibre must possess sufficient length, fineness, strength and flexibility to be suitable for manufacture into fabrics. (Не все волокна подходят для текстильных изделий, так как текстильное волокно должно иметь достаточную длину, высокое качество, прочность и эластичность, чтобы быть подходящим для изготовления тканей.)
The basic structural elements of all textiles (woven fabrics, knitted and bonded fabrics, braids, laces) are staples and filaments. (Основными структурными элементами всех текстильных материалов (тканей, трикотажных и нетканых полотен, тесьм, кружев) являются текстильные (элементарные) волокна и текстильные нити.) These two terms – staple and filament – represent the two basic forms of textile fibres. (Эти два термина – текстильное (элементарное) волокно и текстильная нить – являются двумя основными формами текстильных волокон.)
Staple is the name given to fibres of limited length used for manufacturing of yarn and textile products. (Текстильное волокно – это волокно ограниченной длины, употребляемое для изготовления пряжи и текстильных изделий.) An example of a natural staple fibre is cotton. (Пример натурального текстильного волокна – хлопок.)
Filament is the name given to a fibre of continuous length. (Текстильная нить – это нить ограниченной длины.) An example of a natural filament is silk. (Пример натуральной текстильной нити – шелк.)
All fibres fall into (Все волокна подразделяются на):
After cleaning and blending, the fibres are spun into yarn. (После чистки и смешивания волокна скручивают в пряжу.) Yarn can consist of either staple fibres, or of filaments put together. (Пряжа может состоять либо из текстильных волокон, либо из текстильных нитей, соединенных вместе.) This is then processed into fabric in a weaving mill or knitting mill. (Далее она преобразовывается в ткань на ткацкой или трикотажной фабрике.) The next stage, called finishing, includes various mechanical and chemical processes for (Следующая стадия, называемая отделкой, включает различные механические и химические процессы для):
The appearance of the fabric may also be improved by napping, shearing, pressing, brushing, and polishing. (Внешний вид ткани может также улучшаться ворсованием, стрижкой ткани, прессованием, очисткой и шлифовкой.)
After finishing, the woven material is ready for delivery to (После отделки тканый материал готов к доставке):
Various techniques and processes are used to produce fibres of different qualities (Для производства волокон разного качества используются различные методы и процессы):
Fibres
Techniques and processes
Qualities of fibres
Looking after your fabrics is important if you want to make them last. Care labels tell you about (Если хотите, чтобы ткань прослужила долго, за ней необходимо следить. Ярлыки на одежде расскажут вам следующее):
| Washing (стирка) |  | Indicates that normal (maximum) washing conditions may be used at the appropriate temperature; the number indicates the maximum temperature (Максимальная температура стирки) |
| Bleaching (отбеливание) |  | Means that chlorine bleach may be used (Разрешена стирка с отбеливателями, содержащими хлор) |
| Ironing (глажка) | 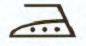 | Means that a hot iron may be used (Можно гладить) |
| Dry-cleaning (химчистка) |  | Indicates that the garment must be professionally cleaned (Указывает, что одежде необходима профессиональная чистка) |
| Tumble drying (сушка во вращающемся барабане) |  | Means that the garment may be tumble dried (Можно сушить во вращающемся барабане) |
А теперь предлагаем выполнить следующие задания.
When caring for your fabrics, remember that:
COTTON
is easy to care for. It is (a) ______ and dry-cleanable and has good colour retention.
LINEN
is twice as strong as cotton and hand-washable or (b) ______.
SILK
is (c) _____ or dry-cleanable, but has poor resistance to prolonged exposure to (d) ______.
NYLON
is easy to wash, resist (e) ______ and wrinkling, is fast (f) ______, but has poor resistance to continuous sunlight.
POLYESTER
is resistant to (g) ______; can be washed or dry-cleaned; is quick drying and wrinkle resistant; because of its low absorbency, (h) ______ removal can be a problem.
Однако мы не упомянули еще один вид тканей – «интеллектуальные ткани» (intelligent fabrics). Предлагаем вашему вниманию видео на эту тему:
It’s the fashion show season, and in parallel, Paris has been hosting the largest textile show in the world – “Premiere Vision”. Seven hundred and forty-two exhibitors from thirty countries presented their offerings for the “Autumn – Winter 2007-2008” seasons. And this year some special guests – so-called intelligent fabrics – textiles, for example, that have built-in protection against staining.
If we imagine normal cloth being flat, with nanotechnologies the cloth takes a form a little like mountain. The structure’s invisible, of course, and dirt can’t stick to a material like that. It runs off. So, here I’ll put a bit of ketchup on and I’ll take some water and there you see it’s a white cloth, and you can rinse off the dirt immediately.
Stain resistant materials, bacteria resistant materials, mosquito resistant materials, materials that can absorb smell or reduce perspiration. Materials that can measure your heart beat, or your breathing pattern. Textiles that are totally impermeable, textiles that are ultra absorbent, cosmetic textiles that moisten the skin, or apply perfume.
The world of intelligent textiles is expanding and a multitude of European research centres are part of it.
Here at Centexbel in Belgium, not far from Liege, scientists are dreaming of the next generation of intelligent or functional textiles. Prototype maker Martin Delgeder’s job is to transform these dreams into reality.
Here we have a pullover that’s entirely knitted. The keyboard is supple. It enables the user to send a range of different commands. It was conceived for handicapped people, to allow them, for example, with a given code to open a garage door, to switch on the television. We’ve also got undergarments that allow you to monitor different body functions: breathing, heartbeat and so on using electrodes that are in direct contact with the body. We can also insert fibre optics into carpet. They are integrated in the production process to make the carpet luminous. They can be used for emergency exit, for example, if there’s a power-cut, or just to create putty patterns within the carpet. We’ve also used fibre optics in knitting. This creates the possibility of luminous knitwear. It can be used for outdoor safety clothing, or it can be stuck on walls and ceilings for decorative effects.
The most complex of these prototypes is probably the textile keyboard which can also function as a simple calculator. Jean Leonard has spent two years working on it. The key, and the interaction of materials that do and don’t conduct electricity.
In addition to the conventional materials, which are electrical insulators we’ve used metallic fibres that do conduct electricity. The principle is that when you don’t apply pressure, there is no contact between two conducting layers. And when you apply pressure, you create a contact between the two layers. In addition to this, there’s a small micro electric component which has been miniaturized as much as possible, so that it disrupts the cloth as little as possible, because the goal is to preserve the characteristics of the textiles: suppleness and comfort.
Suppleness and comfort – those are watchwords for functional and intelligent clothing. Yvette Rogister is in charge of the microbiology lab at the centre. She unlocks the secrets of textiles using this giant microscope. Her research helps to build an understanding how fibres react to the presence of certain nanoparticles. For example, cosmetic nanoparticles that release perfumes into clothes.
There are microcapsules which contain a perfume that’s integrated within the fibres that make up the cloth. What we’ve been looking at here, is how uniformly the microcapsules are spread across the cloth. And also we wanted to have an idea of their dimensions. And then, after the material’s being used, we wanted to see how the microcapsules react, they are supposed to explode and release the perfume.
And in fact, what we’ve seen here is that they are indeed microcapsules that have exploded and thus released their perfume.
At the “Institut Francias du Textile et de l’habillement” outside Lyons intelligent textiles are tested for resistance against heat, flames, tearing, liquids. Engineers work on several Europe-wide projects and also invent their own textiles for the future. Once the concept has been established, the cloth is modeled to a chosen design; and added to a virtual collection of tomorrow’s fashion. The dreams to become a reality, you need a plasma machine like this. Here, in a vacuum, textiles are put in contact with different gases: oxygen, nitrogen, fluoride, or ammonia. In this way researcher Jack Makeone changes the textile properties. Fluorides, for example, make normally absorbent cotton impermeable, while nitrogen makes normally resistant materials absorbent. Nitrogen will separate off and try to impregnate itself in the textiles, so using nitrogen gas you can make a kind of water plasma which will attach itself to the surface. And when you put water next to this, there is a very strong affinity and that makes the material that absorbs very easily, which is good for cleaning materials or for absorbing sweat, or for sticky materials or for printable materials. On the other hand, fluoride gas makes cotton water-resistant, so when it rains, it’s impermeable, but still comfortable.
In these workshops a European programme to make threads of the future is being researched. Christophe Angelloz is developing polypropylene thread that resists high temperatures. The polypropylene is mixed with chemical microparticles whose composition is a commercial secret. The mixture is pummelled, melted, stretched and woven into yarn.
It’s all polypropylene, but by changing the manufacturing conditions like the extrusion temperature, the weaving speed, the stretching tension you can optimize the thread production.
Threads with like others made at the centre will now undergo testing to see if they might be useful in the creation of the new intelligent textiles of the future.
Если вы нашли ошибку, пожалуйста, выделите фрагмент текста и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Man Made Fibres vs Natural Fibres vs Synthetic Fibres
Many people are unaware that they have been wearing man made fibres for many decades, sometimes without knowing it – and many don’t know the difference between a natural fibre or synthetic fibre.
In fact, when I wrote this guide to the different types of fabric types, I talked a little about fibres and have since received many more questions!
So, in this article I’ll be explaining the difference between natural, synthetic and man-made fibres, the benefits of each type, and giving you a run down on the most common types to be found in your wardrobe today.
What Are The Key Differences Between The Three Fibre Types?
Let’s dig in deeper, starting with natural fiber which is the oldest type of fibre used in clothing.
What Are Natural Fibres?
Natural fibres are made from organic materials such as plants and animals. The raw material is processed and then spun and woven or knitted into fabrics.
The most well known type of natural fibre is cotton, which comes directly from the cotton boll. Other popular natural fibres include linen, which is made from the flax plant and silk which is made by silkworms who create a cocoon of silky thread to protect themselves with. Finally, there is wool which comes from sheep’s fleece and hair, which comes from a variety of animals.
Some natural fibres have been used by man since ancient times such as cotton, linen or silk but since the 20th century manmade and synthetic fibres such as nylon, polyester and modal have become more popular.
What Are The Benefits Of Natural Fibers?
Natural fibers have a number of benefits:
6 Popular Natural Fibres
There are of course many natural fibres used to create fabric for clothes, but the six most popular natural fibres are:
What Is Cashmere?
Cashmere fibre is a natural fibre obtained from the permed wool of cashmere goats and has been used for several hundred years. It is a more insulating wool than wool collected from sheep and it has a soft, silky feel.
It can be woven into light or heavy weight fabrics depending on what you want to achieve. Fabric made with cashmere is usually more expensive than wool fabrics.
What Is Cotton?
The most well known natural fibre is cotton which has been used for centuries to create clothes and other textiles.
It is the most popular natural fibre because it’s easy to grow. It can also be viewed as more environmentally friendly as cotton crops are often harvested with minimal use of pesticides or herbicides.
What Are The Benefits Of Cotton?
Cotton has a number of benefits:
What Is Hemp?
Hemp is a natural fibre, in existence for thousands of years and was very popular for clothing up until the 1920s – it is now seeing a surge in popularity due to its sustainability credentials.
Hemp is one of the strongest natural fibres and has natural antibacterial properties, and is found in both woven and knitted fabric form.
What Are The Benefits Of Hemp?
As well as being stronger than cotton, hemp is also more breathable, has great antibacterial and one of the more environmentally friendly fibres!
What Is Linen?
Linen is a natural fibre and originates from the flax plant. The raw material is processed into thread, which can then be woven into linen cloth. A special kind of weaving technique known as dobby creates the characteristic cross-hatch pattern on the fabric surface of linen.
Linen is a natural fibre that is super comfortable. It’s popularity increased in the 18th century when it became popular with the wealthy.
What Are The Benefits Of Linen?
Linen is very breathable – helping you stay cool in summer and warm in winter, which is great for people with sensitive skin as it doesn’t irritate it the way other materials can.
What Is Silk?
Silk is made from silkworm cocoons and was first used as a fabric in China during the Han dynasty.
What Are The Benefits Of Silk?
As silk is a natural fibre, the benefits are fairly obvious:
More sustainable options for silk include peace silk, which is made from the natural web of a wild silk moth, and organic silk which can be treated with natural pesticides.
Silkworms are not harmed when in the production of this type of silk because it comes from the natural web that they create to protect themselves in their cocoon. Once the silkworm has become a moth, it is able to leave it’s cocoon.
What Is Wool?
Wool is a natural fibre gathered from sheep. It’s widely recognised as being a natural and sustainable fibre that is great for the environment. Wool also has natural thermoregulatory properties which means it regulates temperature without needing to be washed every time you wear it – this makes it ideal for cold climates!
What Are The Benefits Of Wool?
It has some great benefits because it’s so natural – for example wool can absorb about 30% of its weight in moisture without feeling wet!
Can Natural Fibres Be Recycled?
The answer is yes. Recycling natural fibres like cotton and linen can be tricky, due to the high levels of contamination from man-made materials such as polyester or rayon, but it’s not impossible!
What Are Man Made Fibres?
Man made fibers (sometimes called semi-synthetic or regenerated fibres) are made from natural polymers. These include regenerated cellulose, which is a natural fibre made from wood or cotton pulp.
Although this type of fibre starts with a natural element, it is processed in a way that makes the resulting fibre more ‘synthetic’ than ‘natural’.
5 Common Man Made Fibres
There are many different types of man made fibre now, but the five most common used within garment making are:
What Is Acetate?
Acetate fabric is a cellulose acetate based natural fibre. It does not require the use of solvents during its production process, which makes it relatively environmentally friendly and sustainable.
It is popular with designers who love its natural, lustrous appearance which is similar to silk. Acetate can be slippery so it is often worn next to the skin in the form of lining.
As well as being prone to static electricity buildup acetate is quite prone to melting when near a heat source. For this reason, it is recommended that garments made with acetate are either hand washed or dry cleaned.
Acetate is most often used as a lining, trim, or interlining.
What Is Bamboo?
Bamboo fabric is a man-made fibre from a natural resource. Bamboo is an eco-friendly fabric and as it grows, so does the bamboo plant making it quite sustainable!
What Are The Benefits Of Bamboo?
There are several benefits to using bamboo fabric when making clothing:
Cupro
Cupro fabric – also known as Bemberg or ammonia silk – is made from cotton waste which is treated with ammonia, caustic soda and copper. Cupro is viewed as a vegan silk alternative as it does not contain any animal substances. This makes it the perfect material for vegans and vegetarians.
Benefits Of Cupro Fabric
What Is Modal?
Modal is a man made fibre coming from the beech wood and of rainforest trees and part of what is called a ‘closed loop’ process – this is where the chemicals used in the manufacturing process are reused.
Fabric created with modal is very soft while being strong, and is often used to create knit fabrics for knitwear garments.
What Are The Benefits Of Modal?
There are several benefits to using modal:
What Is Rayon?
Rayon – known as viscose in the UK – is another regenerated cellulose fibre made mostly from wood pulp materials. It’s made by breaking down natural material into a cellulose fiber form, then processing the resulting regenerated fibers to give them desired properties for different uses.
Rayon can be used in clothing fabrics because of its strength, drapability, easy care and wrinkle resistance. It is often described as a silk substitute or ‘artificial silk’!
It feels smooth to the touch and has a natural, cotton-like feel that’s cool in hot weather, making it perfect for warm climates. Rayon is also much lighter than other fabrics like wool or polyester which makes it easier to carry when travelling!
What Are The Benefits Of Rayon?
The benefits of using rayon fabric are:
Ok, that’s man made regenerated fibres covered, let’s now look at synthetic fibres!
What Are Synthetic Fibres?
The term synthetic fibre refers to a man-made fibre created from a non-naturally occurring resource – also referred to as synthetic polymers. Synthetic fibres are created in factories from chemicals and processed into fibres or threads which are then woven or knitted to make fabrics.
Because of the manufacturing process used to create synthetic materials, they are non-biodegradable creating a significant environmental impact.
5 Examples Of Synthetic Fibres
There are many fabrics made from synthetic fibres now, but the most commonly recognised are:
What Is Lycra?
Also known as elastane and spandex, lycra is an extremely elastic fibre invented in 1958. From the 1970s it became a very popular used in the manufacturing of athletic wear.
It is added to other fibres to create a stretchiness in the fabric – skinny denim jeans were only possible once the elastane was added in which allows the denim to cling to the shape of the legs.
A side effect of adding in this fibre is that it is very hard to recycle fabrics. We’re all familiar with the story of how 100% cotton denim used to be recycled and turned into American dollars. With the additional of lycra / elastane / spandex, this is no longer the case.
Lycra is used in swimwear, athletic wear and in other garment types too!
Extracting this stretch fibre from mixed blend fabrics – typically cotton or polyester – is extremely difficult and has had a huge environmental impact.
What Is Nylon?
Nylon is a man made fibre that was first developed in the 1930s. It is a durable fabric and can be made in many different weights, has good elasticity and does not wrinkle easily.
Nylon is commonly used to create stockings and tights, as well as net and mesh fabric types!
What Is Polyester?
Polyesters are made from natural gas and petroleum, so they’re not as sustainable as man-made regenerated fibres since the resources need to be constantly replenished.
Polyester is a synthetic fibre which has very good elasticity and can be made in many different weights. It does not wrinkle easily and it’s often used for making shirts, dresses, trousers, skirts and more.
Polyester blend fabrics are popular because they have the look of natural fibres but with the durability of polyester – poly cotton is one example of a polyester blend fabric and is used often in children’s school uniforms!
What Are The Benefits Of Polyester?
Polyesters are always man made, and are not at all sustainable, but they do have some benefits. They are:
While Polyester is essentially a plastic, and as such, not considered environmentally friendly, when it is recycled by melting down and respinning into new fibre, it has better sustainability credentials. This type of polyester is known as rPET.
What Is PVC?
With 40 million tonnes of PVC manufactured every year, it is a very commonly used synthetic fibre. But how is PVC used in clothing?
PVC has been used for clothing since the late 1960s. It has a high shine factor, and comes in very bold colours as well as black and white. The patent style of PVC makes it very popular with goth and punk subcultures as well as fetishwear enthusiasts.
PVC is also used for bags and clothing as it is made from several layers and can be quite structured too.
What Are The Pitfalls Of PVC
Because of the way PVC is constructed, it:
What Is PU?
Also known as polyurethane, PU is fully synthetic fibre. As a fabric, it is often referred to as a vegan leather because of the way it is constructed – two layers! – and it’s pliability.
PU fabric is also more breathable that PVC and has an upper layer that more closely resembles real leather.
When you see faux leather jackets and trousers, these are typically made from PU.
Final Thoughts On Different Fibre Types
Synthetic fibres are a byproduct of petroleum oil processing which is why they can be so difficult to recycle or reuse when disposed of in landfills, whereas natural fibers like cotton have been found to degrade much more quickly than man-made materials. Polyester for example is almost impossible to recycle due to the chemical reactions that take place during the manufacturing process.
Natural fibres are often more breathable and absorbent than synthetic fibers which make them better for those with sensitive skin or those prone to allergies, but they can be harder to care for.
Man-made fibers are are regenerated fibres that use natural cellulosic fibres.
There are of course benefits and drawbacks to each fibre type – not only in terms of cost and usage but also the sustainability of each, but it is worth noting that there isn’t really a best type of fibre – it’s up to you, the individual, to decide which is more important for your needs!
Eve Tokens (aka The Creative Curator) is a fashion designer, creative pattern cutter and sewing pattern designer.
Eve graduated with a 2:1 in Fashion Design from the University of The Creative Arts in the UK, has a BTEC diploma in Creative Pattern Cutting, a Foundation Degree in Art & Design from Wimbledon College of Art and gained extensive experience in the fashion industry by interning and freelancing for London based fashion brands – Hardy Amies, Roland Mouret, Peter Pilotto and others.
As well as running her own small sustainable fashion brand, Eve has more than 25 years experience sewing and making clothes for herself and family members.